Self-Taught Learning to Deep Networks
In this section, we describe how you can fine-tune and further improve the learned features using labeled data. When you have a large amount of labeled training data, this can significantly improve your classifier's performance.
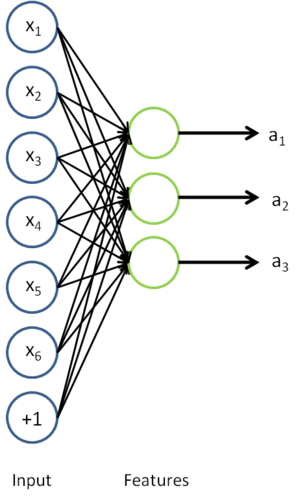
In self-taught learning, we first trained a sparse autoencoder on the unlabeled data. Then, given a new example
, we used the hidden layer to extract features
. This is illustrated in the following diagram:
We are interested in solving a classification task, where our goal is to predict labels
. We have a labeled training set
of
labeled examples. We showed previously that we can replace the original features
with features
computed by the sparse autoencoder (the "replacement" representation). This gives us a training set
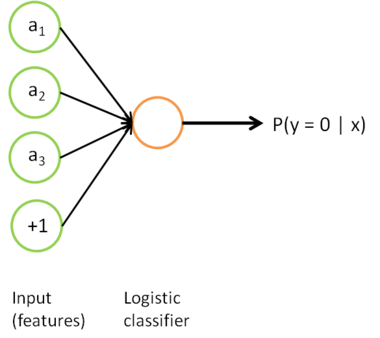
. Finally, we train a logistic classifier to map from the features
to the classification label
.
we can draw our logistic regression unit (shown in orange) as follows:
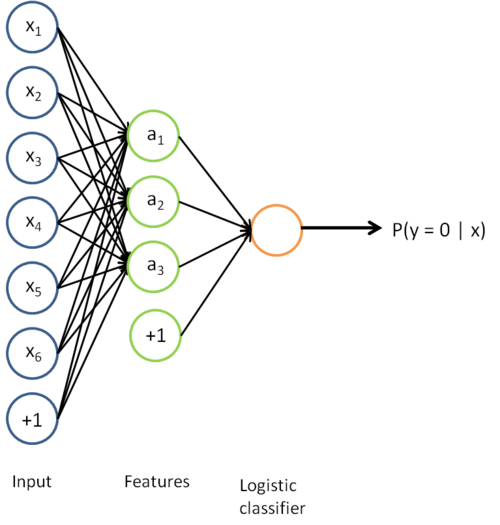
Now, consider the overall classifier (i.e., the input-output mapping) that we have learned using this method. In particular, let us examine the function that our classifier uses to map from from a new test example
to a new prediction p(y = 1 | x). We can draw a representation of this function by putting together the two pictures from above. In particular, the final classifier looks like this:
The parameters of this model were trained in two stages: The first layer of weights 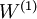 mapping from the input
mapping from the input 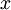 to the hidden unit activations
to the hidden unit activations 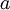 were trained as part of the sparse autoencoder training process. The second layer of weights
were trained as part of the sparse autoencoder training process. The second layer of weights 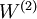 mapping from the activations
mapping from the activations 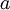 to the output
to the output 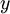 was trained using logistic regression (or softmax regression).
was trained using logistic regression (or softmax regression).
But the form of our overall/final classifier is clearly just a whole big neural network. So, having trained up an initial set of parameters for our model (training the first layer using an autoencoder, and the second layer via logistic/softmax regression), we can further modify all the parameters in our model to try to further reduce the training error. In particular, we can fine-tune the parameters, meaning perform gradient descent (or use L-BFGS) from the current setting of the parameters to try to reduce the training error on our labeled training set 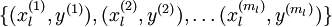 .
.
When fine-tuning is used, sometimes the original unsupervised feature learning steps (i.e., training the autoencoder and the logistic classifier) are called pre-training. The effect of fine-tuning is that the labeled data can be used to modify the weights W(1) as well, so that adjustments can be made to the features a extracted by the layer of hidden units.
if we are using fine-tuning usually we will do so with a network built using the replacement representation. (If you are not using fine-tuning however, then sometimes the concatenation representation can give much better performance.)
When should we use fine-tuning? It is typically used only if you have a large labeled training set; in this setting, fine-tuning can significantly improve the performance of your classifier. However, if you have a large unlabeled dataset (for unsupervised feature learning/pre-training) and only a relatively small labeled training set, then fine-tuning is significantly less likely to help.
Self-Taught Learning to Deep Networks的更多相关文章
- 【论文考古】联邦学习开山之作 Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data
B. McMahan, E. Moore, D. Ramage, S. Hampson, and B. A. y Arcas, "Communication-Efficient Learni ...
- Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data
郑重声明:原文参见标题,如有侵权,请联系作者,将会撤销发布! Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intell ...
- Deep Learning 8_深度学习UFLDL教程:Stacked Autocoders and Implement deep networks for digit classification_Exercise(斯坦福大学深度学习教程)
前言 1.理论知识:UFLDL教程.Deep learning:十六(deep networks) 2.实验环境:win7, matlab2015b,16G内存,2T硬盘 3.实验内容:Exercis ...
- (转)Understanding, generalisation, and transfer learning in deep neural networks
Understanding, generalisation, and transfer learning in deep neural networks FEBRUARY 27, 2017 Thi ...
- 论文笔记之:UNSUPERVISED REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS
UNSUPERVISED REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS ICLR 2 ...
- 深度学习材料:从感知机到深度网络A Deep Learning Tutorial: From Perceptrons to Deep Networks
In recent years, there’s been a resurgence in the field of Artificial Intelligence. It’s spread beyo ...
- This instability is a fundamental problem for gradient-based learning in deep neural networks. vanishing exploding gradient problem
The unstable gradient problem: The fundamental problem here isn't so much the vanishing gradient pro ...
- [译]深度神经网络的多任务学习概览(An Overview of Multi-task Learning in Deep Neural Networks)
译自:http://sebastianruder.com/multi-task/ 1. 前言 在机器学习中,我们通常关心优化某一特定指标,不管这个指标是一个标准值,还是企业KPI.为了达到这个目标,我 ...
- Learning Combinatorial Embedding Networks for Deep Graph Matching(基于图嵌入的深度图匹配)
1. 文献信息 题目: Learning Combinatorial Embedding Networks for Deep Graph Matching(基于图嵌入的深度图匹配) 作者:上海交通大学 ...
随机推荐
- Activity的启动模式和onNewIntent()
1:首先,在默认情况下,当您通过Intent启到一个Activity的时候,就算已经存在一个相同的正在运行的Activity,系统都会创建一个新的Activity实例并显示出来.为了不让Activit ...
- sql的系统关键字的概述
create proc proc_B as SELECT * FROM [ZkbTest].[dbo].[T_ZKB] exec sp_helptext proc_B select * from sy ...
- PostgreSQL Replication之第四章 设置异步复制(6)
4.6 有效的清理和恢复结束 最近几年, recovery.conf 已经变得越来越强大了.早在初期(在 PostgreSQL 9.0之前), 仅有 restore_command 和一些 recov ...
- vue中Object.defineProperty用法
function def (obj, key, val, enumerable) { Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { value: val, enumerable: ...
- Embedding Flash Fullscreen in the Browser Window
For Developers > Design Documents > Embedding Flash Fullscreen in the Browser Window Auth ...
- Linux安装多功能词典GoldenDict
Linux安装多功能词典GoldenDict 活腿肠 2017.08.01 20:52* 字数 671 阅读 1555评论 0喜欢 2 Goldendict 简介 GoldenDict是一种开源的辞典 ...
- Unity C# 设计模式(六)原型模式
定义:用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并通过拷贝这些原型来创建新的对象. 优点: 1.原型模式向客户隐藏了创建新实例的复杂性 2.原型模式允许动态增加或较少产品类. 3.原型模式简化了实例的创建结构,工 ...
- Java基础学习总结(21)——数组
一.数组的基本概念 数组可以看成是多个相同类型数据组合,对这些数据的统一管理. 数组变量属引用类型,数组也可以看成是对象,数组中的每个元素相当于该对象的成员变量. 数组的元素可以是任何数据类型,包括基 ...
- Spring-boot非Mock测试MVC,调试启动tomcat容器
平常我们在使用spring-boot去debug一个web应用时,通常会使用MockMvc. 如下配置: @RunWith(value = SpringRunner.class) @SpringBoo ...
- js阻止默认事件与js阻止事件冒泡
e.stopPropagation(); //阻止事件冒泡 功能:停止事件冒泡 function stopBubble(e) { // 如果提供了事件对象,则这是一个非IE浏览器 if ( e &am ...