《机器学习Python实现_10_02_集成学习_boosting_adaboost分类器实现》
一.简介
adaboost是一种boosting方法,它的要点包括如下两方面:
1.模型生成
每一个基分类器会基于上一轮分类器在训练集上的表现,对样本做权重调整,使得错分样本的权重增加,正确分类的样本权重降低,所以当前轮的训练更加关注于上一轮误分的样本;
2.模型组合
adaboost是采用的加权投票的方法
简单来说,adaboost算法涉及两种权重的计算:样本权重、分类器权重,接下来直接讲算法流程
二.算法流程
输入:训练集\(T=\{(x_1,y_1),(x_2,y_2),...,(x_N,y_N)\}\),其中\(x_i\in R^n,y_i\in\{+1,-1\},i=1,2,...,N\)
输出:最终分类器\(G(x)\)
(1)初始化训练数据的权重分布:
\]
(2)对\(m=1,2,...,M:\)
(2.1)使用具有权重分布\(D_m\)的训练数据集学习,得到基本分类器:\(G_m(x)\)
(2.2)计算\(G_m(x)\)在训练集上的分类误差率:\(e_m=\sum_{i=1}^NP(G_m(x_i)\neq y_i)=\sum_{i=1}^Nw_{mi}I(G_m(x_i)\neq y_i)\)
(2.3)计算\(G_m(x)\)的权重系数:\(\alpha_m=\frac{1}{2}ln\frac{1-e_m}{e_m}\)
(2.4)更新训练样本权重:
\]
这里\(Z_m\)是归一化因子
(3)基于基分类器,构建最终的分类器:
\]
简单来说大致流程如下:
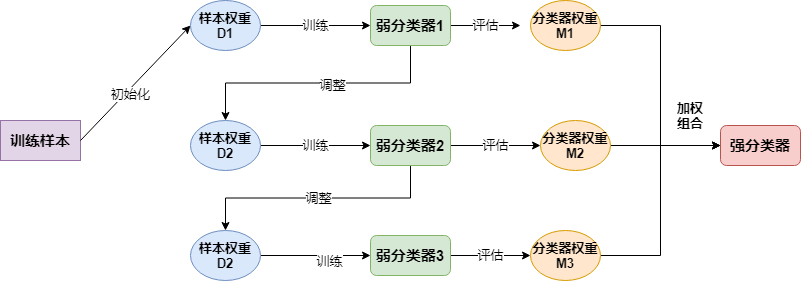
三.代码实现
import os
os.chdir('../')
from ml_models import utils
from ml_models.tree import CARTClassifier
import copy
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
"""
AdaBoost分类器的实现,封装到ml_models.ensemble
"""
class AdaBoostClassifier(object):
def __init__(self, base_estimator=None, n_estimators=10, learning_rate=1.0):
"""
:param base_estimator: 基分类器,允许异质;异质的情况下使用列表传入比如[estimator1,estimator2,...,estimator10],这时n_estimators会失效;
同质的情况,单个estimator会被copy成n_estimators份
:param n_estimators: 基分类器迭代数量
:param learning_rate: 学习率,降低后续基分类器的权重,避免过拟合
"""
self.base_estimator = base_estimator
self.n_estimators = n_estimators
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
if self.base_estimator is None:
# 默认使用决策树桩
self.base_estimator = CARTClassifier(max_depth=2)
# 同质分类器
if type(base_estimator) != list:
estimator = self.base_estimator
self.base_estimator = [copy.deepcopy(estimator) for _ in range(0, self.n_estimators)]
# 异质分类器
else:
self.n_estimators = len(self.base_estimator)
# 记录estimator权重
self.estimator_weights = []
def fit(self, x, y):
n_sample = x.shape[0]
sample_weights = np.asarray([1.0] * n_sample)
for index in range(0, self.n_estimators):
self.base_estimator[index].fit(x, y, sample_weight=sample_weights)
indicates = (self.base_estimator[index].predict(x) == y).astype(int)
# 计算误分率
error_rate = np.sum([sample_weights[j] * (1.0 - indicates[j]) for j in range(0, n_sample)]) / n_sample
# 计算权重系数
alpha_rate = 1.0 / 2.0 * np.log((1 - error_rate) / (error_rate + 1e-7))
alpha_rate = min(10.0, alpha_rate)
self.estimator_weights.append(alpha_rate)
# 更新样本权重
for j in range(0, n_sample):
sample_weights[j] = sample_weights[j] * np.exp(-1.0 * alpha_rate * np.power(-1.0, 1 - indicates[j]))
sample_weights = sample_weights / np.sum(sample_weights) * n_sample
# 更新estimator权重
for i in range(0, self.n_estimators):
self.estimator_weights[i] *= np.power(self.learning_rate, i)
def predict_proba(self, x):
# TODO:并行优化
result = np.sum(
[self.base_estimator[j].predict_proba(x) * self.estimator_weights[j] for j in
range(0, self.n_estimators)],
axis=0)
return result / result.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
def predict(self, x):
return np.argmax(self.predict_proba(x), axis=1)
#造伪数据
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
data, target = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_classes=2, n_informative=1, n_redundant=0,
n_repeated=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, class_sep=.5,random_state=21)
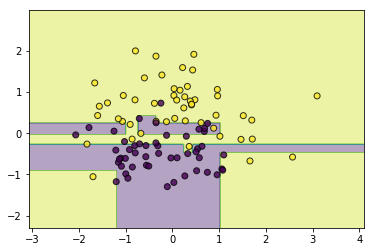
# 同质
classifier = AdaBoostClassifier(base_estimator=CARTClassifier(max_depth=2),n_estimators=10)
classifier.fit(data, target)
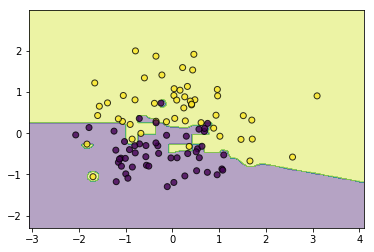
utils.plot_decision_function(data, target, classifier)
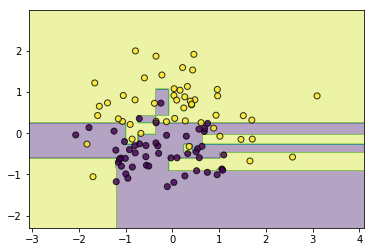
#异质
from ml_models.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from ml_models.svm import SVC
classifier = AdaBoostClassifier(base_estimator=[LogisticRegression(),SVC(kernel='rbf',C=5.0),CARTClassifier()])
classifier.fit(data, target)
utils.plot_decision_function(data, target, classifier)
# 权重衰减
classifier = AdaBoostClassifier(base_estimator=[LogisticRegression(),SVC(kernel='rbf',C=5.0),CARTClassifier()],learning_rate=0.5)
classifier.fit(data, target)
utils.plot_decision_function(data, target, classifier)
四.问题讨论
1.基本要求:弱可学习
注意有个基本要求,那就是\(e_m<0.5\),即分类器至少是弱可学习的,这样才能保证\(\alpha_m>0\),此时样本的权重调整(如下公式)才有意义,即正确分类的样本权重降低,错误分类的样本权重升高:
\frac{w_{mi}}{Z_m}e^{-\alpha_m}, & G_m(x_i)= y_i \\
\frac{w_{mi}}{Z_m}e^{\alpha_m} & G_m(x_i)\neq y_i
\end{matrix}\right.
\]
对于二分类问题,弱可学习其实是很容易保证的,对于\(e_m>0.5\)的情况,只需要对其预测取反,即可得到\(1-e_m<0.5\)的错误率
2.基分类器不支持样本权重怎么办?
对于不能支持样本权重训练的基分类器,可以通过样本重采样来实现
五.训练误差分析
这一部分证明训练误差会随着基分类器的数量增加而指数下降,首先抛出第一个不等式关系:
\]
这里\(f(x)=\sum_{m=1}^M\alpha_mG_m(x),G(x)=sign(f(x)),Z_m\)与上面的定义一样,前半部分很好证明:如果\(G(x_i)\neq y_i\),则\(y_if(x_i)<0\),所以\(exp(-y_if(x_i))\geq 1=I(G(x_i)\neq y_i)\),而对于\(G(x_i)= y_i\)的情况,显然有\(exp(-y_if(x_i))\geq 0=I(G(x_i\neq y_i))\);
接下来证明后半部分,根据之前的推导,有如下的两点条件需要注意:
条件2:w_{mi}exp(-\alpha_my_iG_m(x_i))=Z_mw_{m+1,i},i=1,2,...,N,m=1,2,...,M
\]
所以:
=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^Nexp(-\sum_{m=1}^M\alpha_my_iG_m(x_i)))\\
=\sum_{i=1}^N \frac{1}{N}\prod_{m=1}^Mexp(-\alpha_my_iG_m(x_i))\\
=\sum_{i=1}^N w_{1i}\prod_{m=1}^Mexp(-\alpha_my_iG_m(x_i))(用到了条件1)\\
=\sum_{i=1}^N w_{1i}exp(-\alpha_1y_iG_1(x_i))\prod_{m=2}^Mexp(-\alpha_my_iG_m(x_i))\\
=\sum_{i=1}^N Z_1w_{2i}\prod_{m=2}^Mexp(-\alpha_my_iG_m(x_i))(用到了条件2)\\
=Z_1\sum_{i=1}^N w_{2i}\prod_{m=2}^Mexp(-\alpha_my_iG_m(x_i))\\
=Z_1Z_2\sum_{i=1}^N w_{3i}\prod_{m=3}^Mexp(-\alpha_my_iG_m(x_i))\\
=\cdots\\
=\prod_{m=1}^MZ_m
\]
接下来要抛出第二个关系式,对于二分类问题有如下不等式成立:
\]
这里:\(\gamma_m=\frac{1}{2}-e_m\),首先证明等式部分,由前面的算法部分,我们知道\(e_m=\sum_{i=1}^Nw_{mi}I(G_m(x_i)\neq y_i)\),所以:
=\sum_{y_i=G_m(x_i)}w_{mi}e^{-\alpha_m}+\sum_{y_i\neq G_m(x_i)}w_{mi}e^{\alpha_m}\\
=(1-e_m)e^{-\alpha_m}+e_me^{\alpha_m}\\
=2\sqrt{e_m(1-e_m)}\\
=\sqrt{1-4\gamma_m^2}
\]
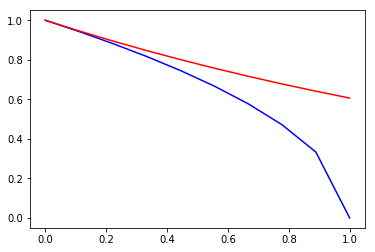
至于不等式部分,其实对于\(\forall 0\leq x\leq 1\),都有\(e^{-x/2}\geq \sqrt{1-x}\)恒成立(证明从略,直观理解如下图),将\(x\)替换为\(4\gamma_m^2\)即可得到上面的不等式,从而关系式2得到证明;
接下来简单做一个推论:一定能找到一个\(\gamma>0\),对所有\(\gamma_m\geq\gamma\)成立,则有如下关系:
\]
结合关系式1、2、3可以得出:
\]
即adaboost的误差上界会随着\(M\)的增加以指数速率下降
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=np.linspace(0,1,10)
plt.plot(x,np.sqrt(1-x),'b')
plt.plot(x,np.exp(-0.5*x),'r')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x21a6b0c1048>]
《机器学习Python实现_10_02_集成学习_boosting_adaboost分类器实现》的更多相关文章
- 简单物联网:外网访问内网路由器下树莓派Flask服务器
最近做一个小东西,大概过程就是想在教室,宿舍控制实验室的一些设备. 已经在树莓上搭了一个轻量的flask服务器,在实验室的路由器下,任何设备都是可以访问的:但是有一些限制条件,比如我想在宿舍控制我种花 ...
- 利用ssh反向代理以及autossh实现从外网连接内网服务器
前言 最近遇到这样一个问题,我在实验室架设了一台服务器,给师弟或者小伙伴练习Linux用,然后平时在实验室这边直接连接是没有问题的,都是内网嘛.但是回到宿舍问题出来了,使用校园网的童鞋还是能连接上,使 ...
- 外网访问内网Docker容器
外网访问内网Docker容器 本地安装了Docker容器,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Docker容器? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Docker容器 ...
- 外网访问内网SpringBoot
外网访问内网SpringBoot 本地安装了SpringBoot,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地SpringBoot? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装Java 1 ...
- 外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB
外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB 本地安装了Elasticsearch,只能在局域网内访问其WEB,怎样从外网也能访问本地Elasticsearch? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Rails
外网访问内网Rails 本地安装了Rails,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Rails? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Rails 默认安装的Rails端口 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Memcached数据库
外网访问内网Memcached数据库 本地安装了Memcached数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Memcached数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网CouchDB数据库
外网访问内网CouchDB数据库 本地安装了CouchDB数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地CouchDB数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Cou ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网DB2数据库
外网访问内网DB2数据库 本地安装了DB2数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地DB2数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动DB2数据库 默认安装的DB2 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库
外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库 本地安装了OpenLDAP数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地OpenLDAP数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动 ...
随机推荐
- ProBuilder快速原型开发技术 ---不规则模型与材质
ProBuilder开发模型的强大之处,还在于可以按照要求精确定制不规则模型.克隆镜像模型.给模型着色以及添加材质等,下面笔者就这几方面进行讲解. 一:定制不规则模型 PB有一个专门定制不规则模型的功 ...
- HTML5基础入门一天学完
HTML 什么是HTML HTML:Hyper Text Markup Language(超文本编辑语言) HTML的发展史 HTML5优势 世界知名浏览器厂商对HTML5的支持 市场的需求 跨平台 ...
- C#关于个Base64,MD5,16进制的转换
1,待签名数据以UTF-8的格式转字节流,对字节流进行MD5算法得到的签名字节流,再转换为16进制字符串,即生成了数字签名. byte[] targetData = md5.ComputeHash(S ...
- 学员和教师管理优化用例点整理v2.0
更新记录: 更新内容 更新人 更新时间 新建 Young 2021.01.08 12:06 彭洋洋确认结果疑问 Young 2021.01.08 15:06 问题集锦 1. 购买成功页点击完成返回路径 ...
- SHA算法摘要处理
byte[] input="sha".getBytes();//待做消息摘要算法的原始信息,可以是任意字符串 MessageDigest sha=MessageDigest.get ...
- CSS网页的布局
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="U ...
- ELK(ElasticSearch+Logstash+Kibana)配置中的一些坑基于7.6版本
三个组件都是采用Docker镜像安装,过程简单不做赘述,直接使用Docker官方镜像运行容器即可,注意三个组件版本必须一致. 运行容器时最好将三个组件的核心配置文件与主机做映射,方便直接在主机修改不用 ...
- windows创建签名文件pfx
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/84847/how-do-i-create-a-self-signed-certificate-for-code-signing ...
- vue中常见的问题以及解决方法
有一些问题不限于 Vue,还适应于其他类型的 SPA 项目. 1. 页面权限控制和登陆验证 页面权限控制 页面权限控制是什么意思呢? 就是一个网站有不同的角色,比如管理员和普通用户,要求不同的角色能访 ...
- 【linux】系统编程-3-system-V IPC 信号量
目录 前言 5. 信号量 5.1 概念 5.2 工作原理 5.3 操作函数 5.3.1 semget() 5.3.2 semop() 5.3.3 semctl() 5.4 例程 参考: 前言 原文链接 ...
