list使用详解
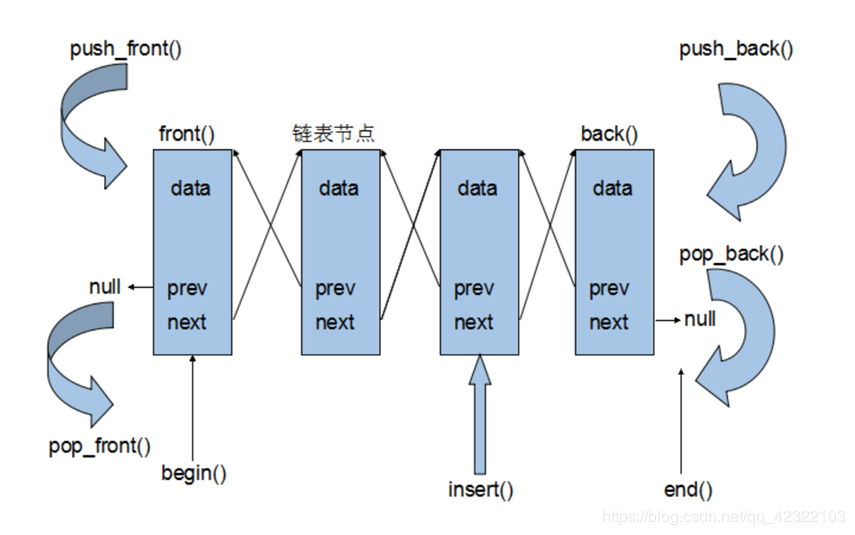
List双向链表
再谈链表
List链表的概念再度出现了,作为线性表的一员,C++的STL提供了快速进行构建的方法,为此,在前文的基础上通过STL进行直接使用,这对于程序设计中快速构建原型是相当有必要的,这里的STL链表是单链表的形式。
头文件
头文件:#include<list>
初始化
格式为:explicit list (const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
我们以int类型作为参数为例进行创建,其创建方法与vector无异
定义的代码如下:
list<int> l1; //创建一个空链表
list<int> l2(10); //创建一个链表其有10个空元素
list<int> l3(5,20); //创建一个链表其有5个元素内容为20
list<int> l4(l3.begin(),l3.end()); //创建一个链表其内容为l3的内容
list<int> l5(l4); //创建一个链表其内容为l4的内容
除此之外,还可以直接使用数组来初始化向量:
int n[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
list<int> a(n, n + 5); // 将数组n的前5个元素作为列表a的初值
迭代器
遍历代码举例(其方法和vector版本无异只是更加精简):
list<int> li;
for(list<int>::iterator it=li.begin();it!=li.end();it++){
cout<<*it<<' ';
}
基本操作
3.1 容量函数
- 容器大小:
lst.size(); - 容器最大容量:
lst.max_size(); - 更改容器大小:
lst.resize(); - 容器判空:
lst.empty();
#include <iostream>
#include <list> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<int> lst;
for (int i = 0; i<6; i++)
{
lst.push_back(i);
} cout << lst.size() << endl; // 输出:6
cout << lst.max_size() << endl; // 输出:357913941
lst.resize(0); // 更改元素大小
cout << lst.size() << endl; // 输出:0
if (lst.empty())
cout << "元素为空" << endl; // 输出:元素为空 return 0;
}
3.2 添加函数
- 头部添加元素:
lst.push_front(const T& x); - 末尾添加元素:
lst.push_back(const T& x); - 任意位置插入一个元素:
lst.insert(iterator it, const T& x); - 任意位置插入 n 个相同元素:
lst.insert(iterator it, int n, const T& x); - 插入另一个向量的 [forst,last] 间的数据:
lst.insert(iterator it, iterator first, iterator last);
#include <iostream>
#include <list> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<int> lst; // 头部增加元素
lst.push_front(4);
// 末尾添加元素
lst.push_back(5);
// 任意位置插入一个元素
list<int>::iterator it = lst.begin();
lst.insert(it, 2);
// 任意位置插入n个相同元素
lst.insert(lst.begin(), 3, 9);
// 插入另一个向量的[forst,last]间的数据
list<int> lst2(5, 8);
lst.insert(lst.begin(), lst2.begin(), ++lst2.begin()); // 遍历显示
for (it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " "; // 输出:8 9 9 9 2 4 5
cout << endl; return 0;
}
li.insert(li.begin(),10); //在链表最前端插入数据10
li.insert(li.begin(),5,20); //在链表最前端插入5个数据内容为20 list<int> k(2,50); //创建一个新的链表k,其拥有2个元素内容均为50
li.insert(li.begin(),li.begin(),li.end()); //在链表v最前端插入链表上K的全部内容
3.3 删除函数
- 头部删除元素:
lst.pop_front(); - 末尾删除元素:
lst.pop_back(); - 任意位置删除一个元素:
lst.erase(iterator it); - 删除 [first,last] 之间的元素:
lst.erase(iterator first, iterator last); - 清空所有元素:
lst.clear();
#include <iostream>
#include <list> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<int> lst;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
lst.push_back(i); // 头部删除元素
lst.pop_front();
// 末尾删除元素
lst.pop_back();
// 任意位置删除一个元素
list<int>::iterator it = lst.begin();
lst.erase(it);
// 删除[first,last]之间的元素
lst.erase(lst.begin(), ++lst.begin()); // 遍历显示
for (it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " "; // 输出:3 4 5 6
cout << endl; // 清空所有元素
lst.clear(); // 判断list是否为空
if (lst.empty())
cout << "元素为空" << endl; // 输出:元素为空 return 0;
}
li.erase(li.begin()); //删除第一个元素
li.erase(li.begin(),li.begin()+4); //删除前4个元素
3.4 访问函数
- 访问第一个元素:
lst.front(); - 访问最后一个元素:
lst.back();
#include <iostream>
#include <list> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<int> lst;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
lst.push_back(i); // 访问第一个元素
cout << lst.front() << endl; // 输出:0
// 访问最后一个元素
cout << lst.back() << endl; // 输出:5 return 0;
}
3.5 其他函数
- 多个元素赋值:
lst.assign(int nSize, const T& x); // 类似于初始化时用数组进行赋值 - 交换两个同类型容器的元素:
swap(list&, list&); 或 lst.swap(list&); - 合并两个列表的元素(默认升序排列):
lst.merge(); - 在任意位置拼接入另一个list:
lst.splice(iterator it, list&); - 删除容器中相邻的重复元素:
lst.unique();
#include <iostream>
#include <list> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// 多个元素赋值s
list<int> lst1;
lst1.assign(3, 1);
list<int> lst2;
lst2.assign(3, 2); // 交换两个容器的元素
// swap(lst1, lst2); // ok
lst1.swap(lst2);
// 遍历显示
cout << "交换后的lst1: ";
list<int>::iterator it;
for (it = lst1.begin(); it!=lst1.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " "; // 输出:2 2 2
cout << endl; // 遍历显示
cout << "交换后的lst2: ";
for (it = lst2.begin(); it != lst2.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " "; // 输出:1 1 1
cout << endl; list<int> lst3;
lst3.assign(3, 3);
list<int> lst4;
lst4.assign(3, 4);
// 合并两个列表的元素
lst4.merge(lst3); // 不是简单的拼接,而是会升序排列
cout << "合并后的lst4: ";
for (it = lst4.begin(); it != lst4.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " "; // 输出:3 3 3 4 4 4
cout << endl; list<int> lst5;
lst5.assign(3, 5);
list<int> lst6;
lst6.assign(3, 6);
// 在lst6的第2个元素处,拼接入lst5
lst6.splice(++lst6.begin(), lst5);
cout << "拼接后的lst6: ";
for (it = lst6.begin(); it != lst6.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " "; // 输出:6 5 5 5 6 6
cout << endl; // 删除容器中相邻的重复元素
list<int> lst7;
lst7.push_back(1);
lst7.push_back(1);
lst7.push_back(2);
lst7.push_back(2);
lst7.push_back(3);
lst7.push_back(2);
lst7.unique();
cout << "删除容器中相邻的重复元素后的lst7: ";
for (it = lst7.begin(); it != lst7.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " "; // 输出:1 2 3 2
cout << endl; return 0;
}
排序sort()
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;s
int cmp(const int &a,const int &b){
//简单的自定义降序序列
return a>b;
}
int main(){
list<int> li; //创建一个空链表
for(int i=10;i>=6;i--){
li.push_back(i);
}
li.push_front(3);
li.push_back(20);
list<int> li2(li);
for(list<int>::iterator it=li.begin();it!=li.end();it++){
cout<<*it<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
//排序前3 10 9 8 7 6 20//
li.sort(); for(list<int>::iterator it=li.begin();it!=li.end();it++){
cout<<*it<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
//默认排序后 3 6 7 8 9 10 20//
li2.sort(cmp);
for(list<int>::iterator it=li2.begin();it!=li2.end();it++){
cout<<*it<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
//自定义排序后 20 10 9 8 7 6 3//
return 0;
}
迭代器与算法
1. 迭代器
- 开始迭代器指针:
lst.begin(); - 末尾迭代器指针:
lst.end();// 指向最后一个元素的下一个位置 - 指向常量的开始迭代器指针:
lst.cbegin();// 意思就是不能通过这个指针来修改所指的内容,但还是可以通过其他方式修改的,而且指针也是可以移动的。 - 指向常量的末尾迭代器指针:
lst.cend(); - 反向迭代器指针,指向最后一个元素:
lst.rbegin(); - 反向迭代器指针,指向第一个元素的前一个元素:
lst.rend();
#include <iostream>
#include <list> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<int> lst;
lst.push_back(1);
lst.push_back(2);
lst.push_back(3); cout << *(lst.begin()) << endl; // 输出:1
cout << *(--lst.end()) << endl; // 输出:3
cout << *(lst.cbegin()) << endl; // 输出:1
cout << *(--lst.cend()) << endl; // 输出:3
cout << *(lst.rbegin()) << endl; // 输出:3
cout << *(--lst.rend()) << endl; // 输出:1
cout << endl; return 0;
}
2. 算法
- 遍历元素
list<int>::iterator it;
for (it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++)
cout << *it << endl;
- 元素翻转
#include <algorithm>
reverse(lst.begin(), lst.end());
- 元素排序
#include <algorithm>
sort(lst.begin(), lst.end()); // 采用的是从小到大的排序 // 如果想从大到小排序,可以采用先排序后反转的方式,也可以采用下面方法:
// 自定义从大到小的比较器,用来改变排序方式
bool Comp(const int& a, const int& b)
{
return a > b;
} sort(lst.begin(), lst.end(), Comp);
总结
可以看到,list 与 vector、deque 的用法基本一致,除了以下几处不同:
- list 为双向迭代器,故不支持
it+=i; - list 不支持下标访问和at方法访问。
list使用详解的更多相关文章
- Linq之旅:Linq入门详解(Linq to Objects)
示例代码下载:Linq之旅:Linq入门详解(Linq to Objects) 本博文详细介绍 .NET 3.5 中引入的重要功能:Language Integrated Query(LINQ,语言集 ...
- 架构设计:远程调用服务架构设计及zookeeper技术详解(下篇)
一.下篇开头的废话 终于开写下篇了,这也是我写远程调用框架的第三篇文章,前两篇都被博客园作为[编辑推荐]的文章,很兴奋哦,嘿嘿~~~~,本人是个很臭美的人,一定得要截图为证: 今天是2014年的第一天 ...
- EntityFramework Core 1.1 Add、Attach、Update、Remove方法如何高效使用详解
前言 我比较喜欢安静,大概和我喜欢研究和琢磨技术原因相关吧,刚好到了元旦节,这几天可以好好学习下EF Core,同时在项目当中用到EF Core,借此机会给予比较深入的理解,这里我们只讲解和EF 6. ...
- Java 字符串格式化详解
Java 字符串格式化详解 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 微博:厉圣杰 文中如有纰漏,欢迎大家留言指出. 在 Java 的 String 类中,可以使用 format() 方法 ...
- Android Notification 详解(一)——基本操作
Android Notification 详解(一)--基本操作 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 微博:厉圣杰 源码:AndroidDemo/Notification 文中如有纰 ...
- Android Notification 详解——基本操作
Android Notification 详解 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 前几天项目中有用到 Android 通知相关的内容,索性把 Android Notificatio ...
- Git初探--笔记整理和Git命令详解
几个重要的概念 首先先明确几个概念: WorkPlace : 工作区 Index: 暂存区 Repository: 本地仓库/版本库 Remote: 远程仓库 当在Remote(如Github)上面c ...
- Drawable实战解析:Android XML shape 标签使用详解(apk瘦身,减少内存好帮手)
Android XML shape 标签使用详解 一个android开发者肯定懂得使用 xml 定义一个 Drawable,比如定义一个 rect 或者 circle 作为一个 View 的背景. ...
- Node.js npm 详解
一.npm简介 安装npm请阅读我之前的文章Hello Node中npm安装那一部分,不过只介绍了linux平台,如果是其它平台,有前辈写了更加详细的介绍. npm的全称:Node Package M ...
- .NET应用和AEAI CAS集成详解
1 概述 数通畅联某综合SOA集成项目的统一身份认证工作,需要第三方系统配合进行单点登录的配置改造,在项目中有需要进行单点登录配置的.NET应用系统,本文专门记录.NET应用和AEAI CAS的集成过 ...
随机推荐
- Java-Dubbo学习及整合SpringBoot
Dubbo架构 Dubbo是Java的RPC框架,具有三大核心功能:面向接口的远程方法调用,智能容错和负载均衡,以及服务的自动注册和发现 Dubbo架构图: 节点角色说明: 节点 说明 Provide ...
- mybatis源码核心代码
/** * mybatis源码测试类 * @param args * @throws IOException * @see org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuratio ...
- JavaScript-DOM-节点简介与分类
简介 节点(node)是一个网络术语,它表示网络中的一个连接点.一个网络就是由一些节点构成的集合. 在DOM里,文档是由节点构成的集合,此时的节点是文档树上的树枝和树叶. 分类 DOM中包含许多不同类 ...
- E: Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock - open (11: Resource temporarily unavailable) E: Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/), is another process using it?
E: Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock - open (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)E: Unable to l ...
- 使用npm安装 Ant Design Vue 时报错—ant-design-vue@latest(sha1-qsf / gCIFcRYxyGmOKgx7TmHf1z4 =)seems to be corrupted.
安装 Ant Design Vue 时报错: npm install ant-design-vue --save ant-design-vue @ latest(sha1-qsf / gCIFcRYx ...
- 依赖注入@Autowired@Primary@Quelifier使用
@Autowired 注入声明的SpringBean对象,根据一定的规则首先按照注入的类型去查找,如果没有找到安装注入的名称去匹配你要注入的属性名称,如果都没有找到启动项目时抛出异常,@Autowir ...
- C#基础知识---is与as
一.is与as对比 is检查一个对象是否兼容于指定的类型,并返回一个Boolean值:true或者fasle. 注:is操作符永远不会抛出异常 经常按如下方法使用: ClassA { .... } O ...
- 怎样在Qt中建立使用动态链接库
参考网址: https://blog.csdn.net/q496713258/article/details/6990837 qt 的学习网址: http://c.biancheng.net/view ...
- Mybatis的分页工具
配置拦截器插件 特别注意,新版拦截器是 com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor. com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper 现在是一个特殊的 ...
- ArcGIS Engine中实现ArcMap的捕捉效果
注意要将捕捉相关接口的对象放在OnCreate方法中,这样在初始化就可以有捕捉效果,(捕捉对象赋值放在OnClick中出现第一次点击之前不能捕捉的BUG) 这里是直接在工具中实现的 ,可以按需求将捕捉 ...
