Tensorflow 循环神经网络 基本 RNN 和 LSTM 网络 拟合、预测sin曲线
时序预测一直是比较重要的研究问题,在统计学中我们有各种的模型来解决时间序列问题,但是最近几年比较火的深度学习中也有能解决时序预测问题的方法,另外在深度学习领域中时序预测算法可以解决自然语言问题等。
在网上找到了 tensorflow 中 RNN 和 LSTM 算法预测 sin 曲线的代码,效果不错。
LSTM:
#encoding:UTF-8 import random
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.rnn.python.ops import core_rnn
from tensorflow.contrib.rnn.python.ops import core_rnn_cell def build_data(n):
xs = []
ys = []
for i in range(0, 2000):
k = random.uniform(1, 50) x = [[np.sin(k + j)] for j in range(0, n)]
y = [np.sin(k + n)] # x[i] = sin(k + i) (i = 0, 1, ..., n-1)
# y[i] = sin(k + n)
xs.append(x)
ys.append(y) train_x = np.array(xs[0: 1500])
train_y = np.array(ys[0: 1500])
test_x = np.array(xs[1500:])
test_y = np.array(ys[1500:])
return (train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y) length = 10
time_step_size = length
vector_size = 1
batch_size = 10
test_size = 10 # build data
(train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y) = build_data(length)
print(train_x.shape, train_y.shape, test_x.shape, test_y.shape) X = tf.placeholder("float", [None, length, vector_size])
Y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 1]) # get lstm_size and output predicted value
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10, 1], stddev=0.01))
B = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1], stddev=0.01)) def seq_predict_model(X, w, b, time_step_size, vector_size):
# input X shape: [batch_size, time_step_size, vector_size]
# transpose X to [time_step_size, batch_size, vector_size]
X = tf.transpose(X, [1, 0, 2]) # reshape X to [time_step_size * batch_size, vector_size]
X = tf.reshape(X, [-1, vector_size]) # split X, array[time_step_size], shape: [batch_size, vector_size]
X = tf.split(X, time_step_size, 0) # LSTM model with state_size = 10
cell = core_rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=10,
forget_bias=1.0,
state_is_tuple=True)
outputs, _states = core_rnn.static_rnn(cell, X, dtype=tf.float32) # Linear activation
return tf.matmul(outputs[-1], w) + b, cell.state_size pred_y, _ = seq_predict_model(X, W, B, time_step_size, vector_size)
loss = tf.square(tf.subtract(Y, pred_y))
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss) with tf.Session() as sess:
tf.global_variables_initializer().run() # train
for i in range(50):
# train
for end in range(batch_size, len(train_x), batch_size):
begin = end - batch_size
x_value = train_x[begin: end]
y_value = train_y[begin: end]
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={X: x_value, Y: y_value}) # randomly select validation set from test set
test_indices = np.arange(len(test_x))
np.random.shuffle(test_indices)
test_indices = test_indices[0: test_size]
x_value = test_x[test_indices]
y_value = test_y[test_indices] # eval in validation set
val_loss = np.mean(sess.run(loss,
feed_dict={X: x_value, Y: y_value}))
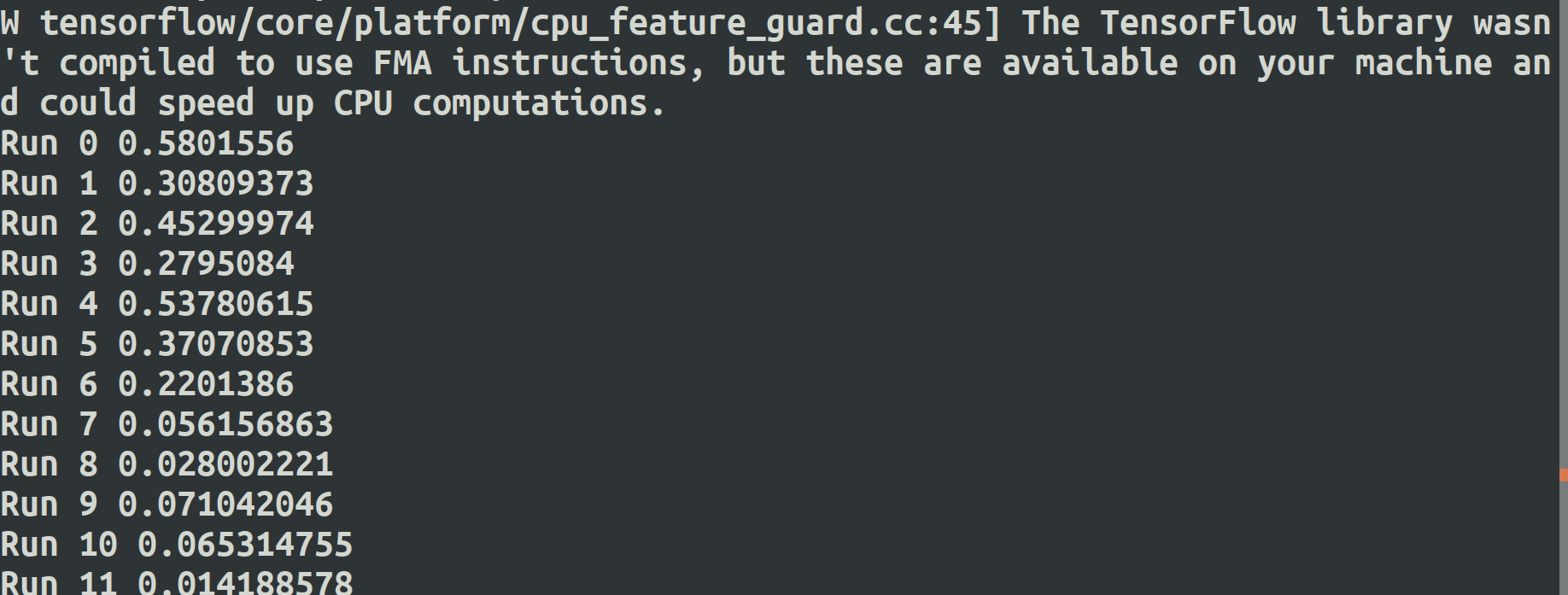
print('Run %s' % i, val_loss) for b in range(0, len(test_x), test_size):
x_value = test_x[b: b + test_size]
y_value = test_y[b: b + test_size]
pred = sess.run(pred_y, feed_dict={X: x_value})
for i in range(len(pred)):
print(pred[i], y_value[i], pred[i] - y_value[i])
RNN :
import random import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.rnn.python.ops import core_rnn
from tensorflow.contrib.rnn.python.ops import core_rnn_cell def build_data(n):
xs = []
ys = []
for i in range(0, 2000):
k = random.uniform(1, 50) x = [[np.sin(k + j)] for j in range(0, n)]
y = [np.sin(k + n)] # x[i] = sin(k + i) (i = 0, 1, ..., n-1)
# y[i] = sin(k + n)
xs.append(x)
ys.append(y) train_x = np.array(xs[0: 1500])
train_y = np.array(ys[0: 1500])
test_x = np.array(xs[1500:])
test_y = np.array(ys[1500:])
return (train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y) length = 10
time_step_size = length
vector_size = 1
batch_size = 10
test_size = 10 # build data
(train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y) = build_data(length)
print(train_x.shape, train_y.shape, test_x.shape, test_y.shape) X = tf.placeholder("float", [None, length, vector_size])
Y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 1]) # get lstm_size and output predicted value
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10, 1], stddev=0.01))
B = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1], stddev=0.01)) def seq_predict_model(X, w, b, time_step_size, vector_size):
# input X shape: [batch_size, time_step_size, vector_size]
# transpose X to [time_step_size, batch_size, vector_size]
X = tf.transpose(X, [1, 0, 2])
# reshape X to [time_step_size * batch_size, vector_size]
X = tf.reshape(X, [-1, vector_size])
# split X, array[time_step_size], shape: [batch_size, vector_size]
X = tf.split(X, time_step_size, 0) cell = core_rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(num_units=10)
initial_state = tf.zeros([batch_size, cell.state_size])
outputs, _states = core_rnn.static_rnn(cell, X, initial_state=initial_state) # Linear activation
return tf.matmul(outputs[-1], w) + b, cell.state_size pred_y, _ = seq_predict_model(X, W, B, time_step_size, vector_size)
loss = tf.square(tf.subtract(Y, pred_y))
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss) with tf.Session() as sess:
tf.global_variables_initializer().run() # train
for i in range(50):
# train
for end in range(batch_size, len(train_x), batch_size):
begin = end - batch_size
x_value = train_x[begin: end]
y_value = train_y[begin: end]
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={X: x_value, Y: y_value}) # randomly select validation set from test set
test_indices = np.arange(len(test_x))
np.random.shuffle(test_indices)
test_indices = test_indices[0: test_size]
x_value = test_x[test_indices]
y_value = test_y[test_indices] # eval in validation set
val_loss = np.mean(sess.run(loss,
feed_dict={X: x_value, Y: y_value}))
print('Run %s' % i, val_loss) for b in range(0, len(test_x), test_size):
x_value = test_x[b: b + test_size]
y_value = test_y[b: b + test_size]
pred = sess.run(pred_y, feed_dict={X: x_value})
for i in range(len(pred)):
print(pred[i], y_value[i], pred[i] - y_value[i])

-------------------------------------------------------------------
Tensorflow 循环神经网络 基本 RNN 和 LSTM 网络 拟合、预测sin曲线的更多相关文章
- 深度学习项目——基于循环神经网络(RNN)的智能聊天机器人系统
基于循环神经网络(RNN)的智能聊天机器人系统 本设计研究智能聊天机器人技术,基于循环神经网络构建了一套智能聊天机器人系统,系统将由以下几个部分构成:制作问答聊天数据集.RNN神经网络搭建.seq2s ...
- 大话循环神经网络(RNN)
在上一篇文章中,介绍了 卷积神经网络(CNN)的算法原理,CNN在图像识别中有着强大.广泛的应用,但有一些场景用CNN却无法得到有效地解决,例如: 语音识别,要按顺序处理每一帧的声音信息,有些结果 ...
- Coursera Deep Learning笔记 序列模型(一)循环序列模型[RNN GRU LSTM]
参考1 参考2 参考3 1. 为什么选择序列模型 序列模型能够应用在许多领域,例如: 语音识别 音乐发生器 情感分类 DNA序列分析 机器翻译 视频动作识别 命名实体识别 这些序列模型都可以称作使用标 ...
- 【学习笔记】循环神经网络(RNN)
前言 多方寻找视频于博客.学习笔记,依然不能完全熟悉RNN,因此决定还是回到书本(<神经网络与深度学习>第六章),一点点把啃下来,因为这一章对于整个NLP学习十分重要,我想打好基础. 当然 ...
- TensorFlow(十一):递归神经网络(RNN与LSTM)
RNN RNN(Recurrent Neural Networks,循环神经网络)不仅会学习当前时刻的信息,也会依赖之前的序列信息.由于其特殊的网络模型结构解决了信息保存的问题.所以RNN对处理时间序 ...
- CNN(卷积神经网络)、RNN(循环神经网络)、DNN,LSTM
http://cs231n.github.io/neural-networks-1 https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.07285.pdf https://adeshpande3.g ...
- 深度学习之循环神经网络(RNN)
循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network,RNN)是一类具有短期记忆能力的神经网络,适合用于处理视频.语音.文本等与时序相关的问题.在循环神经网络中,神经元不但可以接收其他神经元 ...
- TensorFlow——循环神经网络基本结构
1.导入依赖包,初始化一些常量 import collections import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf TRAIN_DATA = "./d ...
- [深度学习]理解RNN, GRU, LSTM 网络
Recurrent Neural Networks(RNN) 人类并不是每时每刻都从一片空白的大脑开始他们的思考.在你阅读这篇文章时候,你都是基于自己已经拥有的对先前所见词的理解来推断当前词的真实含义 ...
随机推荐
- dt开发之-自定义函数获取分类名称
需要在api/extend.func.php 文件中加入的函数 获取分类名称 cat_name($catid) 传入分类id function cat_name($catid) { global $d ...
- 2019-2020-1 20199302《Linux内核原理与分析》第三周作业
云班课学习内容 一.C语言中嵌入汇编代码 1.内嵌汇编语法 (1)C语言中嵌入汇编代码的写法: asm( 汇编语句模板: 输出部分: 输入部分: 破坏描述部分): 说明:输出部分和输入部分对应着C语言 ...
- P4462 [CQOI2018]异或序列 莫队
题意:给定数列 \(a\) 和 \(k\) ,询问区间 \([l,r]\) 中有多少子区间满足异或和为 \(k\). 莫队.我们可以记录前缀异或值 \(a_i\),修改时,贡献为 \(c[a_i\bi ...
- 洛谷 P4408 [NOI2003] 逃学的小孩 题解
Analysis 题意虽然说先去谁家再去谁家,但是我们不需要管这个,因为AA.BB.CC三个点我们可以任意互相交换它们所代表的对象,所以题目要求的就是在一棵树上找到3个点AA.BB.CC令AB+BCA ...
- DW-ODS
ODS (操作数据存储) 编辑 讨论 操作数据存储ODS(Operational Data Store)是数据仓库体系结构中的一个可选部分,也被称为贴源层.ODS具备数据仓库的部分特征和OLTP系统的 ...
- greenplum 表在各个节点数据的分布情况
select gp_segment_id,count(*) from table_name group by gp_segment_id;
- learning java Math类
output: //取整,返回小于目标数的最大整数System.out.println(Math.floor(-1.2));// 取整,返回在于目标数的最大整数System.out.println(M ...
- 洛谷 P1855 榨取kkksc03 题解
P1855 榨取kkksc03 题目描述 洛谷2的团队功能是其他任何oj和工具难以达到的.借助洛谷强大的服务器资源,任何学校都可以在洛谷上零成本的搭建oj并高效率的完成训练计划. 为什么说是搭建oj呢 ...
- I9300 国行联通定制修复手记
同事拿来个I9300给我修,说是打不了电话,试了一下,打电话的时候会提示“网络未注册”,于是果断找了个国行的4.1.2五件套刷砖.5分钟后,刷机成功,开机拨号,依旧是这个问题,怎么回事呢?上百度一查, ...
- Class T泛型和通配符泛型的区别
平时看java源代码的时候,如果碰到泛型的话,我想? T K V E这些是经常出现的,但是有时想不起来代表什么意思,今天整理下: ? 表示不确定的java类型. T 表示java类型. K V 分别代 ...
