List的同步类比较
TL;NRs
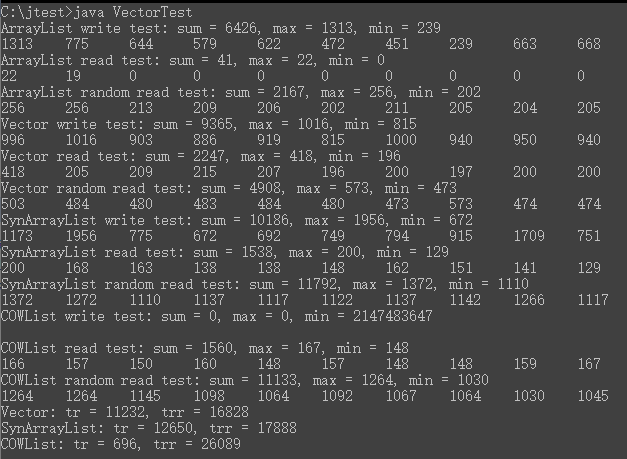
CopyOnWriteArrayList类在多线程顺序读取上有很大的优势,但在随机读取上反而有较大的劣势,且在写入方面性能极差。Vector类在顺序读取方面性能较差,但在随机读取方面有较大的优势,写入方面性能也还可以。
1,引言
java线程安全的List实现有以下三种:
new Vector<>()Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>())new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>()
通常认为使用了synchronized会导致运行变慢,那么在java针对synchronized进行一系列优化后,现在的情况如何呢?为了检验这一说法,写了一个验证程序进行验证。
2,验证代码
以ArrayList作为基础,分别测试4种List的顺序写入(0 ~ 1 << 24)、顺序读取和随机读取,各十轮。据此编写代码。代码太长了,所以放到最后
3,测试平台
垃圾笔记本,使用Intel酷睿i5 7200U
java版本为java 12,HotSpot虚拟机
4,测试结果
单位:毫秒
5,结果分析
ArrayList(A)、Vector(V)、Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>())(S)、以及CopyOnWriteArrayList(C)四种类型的结果分别如下
十轮写入,单位毫秒
| A | V | S | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总时间 | 6426 | 9365 | 10186 | inf |
| 最大时间 | 1313 | 1016 | 1096 | inf |
| 最小时间 | 239 | 815 | 672 | inf |
十轮单线程顺序读,单位毫秒
| A | V | S | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总时间 | 41 | 2247 | 1538 | 1560 |
| 最大时间 | 22 | 418 | 200 | 167 |
| 最小时间 | 0 | 196 | 129 | 148 |
十轮单线程随机读,单位毫秒
| A | V | S | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总时间 | 2167 | 4908 | 11792 | 11133 |
| 最大时间 | 256 | 573 | 1372 | 1264 |
| 最小时间 | 202 | 473 | 1110 | 1030 |
十线程顺序读,单位毫秒
| V | S | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总时间 | 11232 | 12650 | 696 |
十线程随机读,单位毫秒
| V | S | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总时间 | 16828 | 17888 | 26089 |
6,结论
单线程写入性能:A > V = S >>>> C
单线程顺序读取性能:A >> S = C > V
单线程随机读取性能:A > V > S = C
20线程顺序读取性能:C >> V > S
20线程随机读取性能:V > S >> C
COW顺序读取性能较好,随机读取性能较差,写入性能极差。
Vector随机读取性能较好,顺序读取性能和写入性能较差。
附录 测试代码
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class VectorTest {
private static final int CNT = 1 << 24;
private static final Random rand = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int writeRound = 10, readRound = 10, randomReadRound = 10;
int nRead = 20, nRandomRead = 20;
List<Integer> lsA = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> lsV = new Vector<>();
List<Integer> lsS = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
List<Integer> lsC = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
test(lsA, "ArrayList", writeRound, readRound, randomReadRound);
test(lsV, "Vector", writeRound, readRound, randomReadRound);
test(lsS, "SynArrayList", writeRound, readRound, randomReadRound);
lsC.addAll(lsA);
test(lsC, "COWList", 0, readRound, randomReadRound);
multiThreadTest(lsV, "Vector", nRead, nRandomRead);
multiThreadTest(lsS, "SynArrayList", nRead, nRandomRead);
multiThreadTest(lsC, "COWList", nRead, nRandomRead);
}
private static void test(List<Integer> list, String name, int writeRound, int readRound, int randomReadRound) {
int max = 0, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, sum = 0;
int[] w = new int[writeRound], r = new int[readRound], rr = new int[randomReadRound];
for (int i = 0; i < writeRound; i++) {
list.clear();
int v = w[i] = writeTest(list);
max = Math.max(max, v);
min = Math.min(min, v);
sum += v;
}
System.out.printf("%s write test: sum = %d, max = %d, min = %d\n", name, sum, max, min);
for (int v : w) System.out.printf("%d\t", v);
System.out.println();
sum = max = 0;
min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < readRound; i++) {
int v = r[i] = readTest(list);
max = Math.max(max, v);
min = Math.min(min, v);
sum += v;
}
System.out.printf("%s read test: sum = %d, max = %d, min = %d\n", name, sum, max, min);
for (int v : r) System.out.printf("%d\t", v);
System.out.println();
sum = max = 0;
min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < randomReadRound; i++) {
int v = rr[i] = randomReadTest(list);
max = Math.max(max, v);
min = Math.min(min, v);
sum += v;
}
System.out.printf("%s random read test: sum = %d, max = %d, min = %d\n", name, sum, max, min);
for (int v : rr) System.out.printf("%d\t", v);
System.out.println();
}
private static int writeTest(List<Integer> list) {
long t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < CNT; i++) list.add(i);
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
return (int)(t1 - t0);
}
private static int readTest(List<Integer> list) {
long t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < CNT; i++) list.get(i);
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
return (int)(t1 - t0);
}
private static int randomReadTest(List<Integer> list) {
long t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < CNT; i++) list.get(rand.nextInt(CNT));
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
return (int)(t1 - t0);
}
private static List<Integer> ls;
private static long t2 = 0;
private static CountDownLatch cdl;
public static class ThreadRead extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < CNT; i++) ls.get(i);
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
t2 = Math.max(t1, t2);
cdl.countDown();
}
}
public static class ThreadRandomRead extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < CNT; i++) ls.get(rand.nextInt(CNT));
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
t2 = Math.max(t1, t2);
cdl.countDown();
}
}
private static void multiThreadTest(List<Integer> list, String name, int nRead, int nRandomRead) throws InterruptedException {
int tr = 0, trr = 0;
ls = list;
cdl = new CountDownLatch(nRead);
long t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < nRead; i++) {
new ThreadRead().start();
}
cdl.await();
tr = (int)(t2 - t0);
cdl = new CountDownLatch(nRandomRead);
t2 = 0;
t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < nRandomRead; i++) {
new ThreadRandomRead().start();
}
cdl.await();
trr = (int)(t2 - t0);
System.out.printf("%s: tr = %d, trr = %d\n", name, tr, trr);
}
}
List的同步类比较的更多相关文章
- Java中多线程同步类 CountDownLatch
在多线程开发中,常常遇到希望一组线程完成之后在执行之后的操作,java提供了一个多线程同步辅助类,可以完成此类需求: 类中常见的方法: 其中构造方法:CountDownLatch(int count) ...
- 16.同步类容器Collections.synchronized
voctor动态数组.同步类容器,底层实现基于:Collections.synchronized package demo5; import java.util.ArrayList; import j ...
- 15.同步类容器Vector
同步类容器1 1.线程都是安全的. 2.在某些场景下需要加锁来保护“复合操作” a.迭代:反复去访问元素.遍历完容器所有的元素 b.跳转:根据下标制定去访问查找元素 c.条件运算 3.复合操作在多线程 ...
- Java线程同步类容器和并发容器(四)
同步类容器都是线程安全的,在某些场景下,需要枷锁保护符合操作,最经典ConcurrentModifiicationException,原因是当容器迭代的过程中,被并发的修改了内容. for (Iter ...
- 同步类容器和并发类容器——ConcurrentMap、CopyOnWrite、Queue
一 同步类容器同步类容器都是线程安全的,但在某些场景中可能需要加锁来保证复合操作. 符合操作如:迭代(反复访问元素,遍历完容器中所有元素).跳转(根据指定的顺序找到当前元素的下一个元素).条件运算. ...
- Java多线程信号量同步类CountDownLatch与Semaphore
信号量同步是指在不同线程之间,通过传递同步信号量来协调线程执行的先后次序.CountDownLatch是基于时间维度的Semaphore则是基于信号维度的. 1:基于执行时间的同步类CountDown ...
- 同步类的基础AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS)
同步类的基础AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS) 我们之前介绍了很多同步类,比如ReentrantLock,Semaphore, CountDownLatch, Reentr ...
- 解读java同步类CountDownLatch
同步辅助类: CountDownLatch是一个同步辅助类,在jdk5中引入,它允许一个或多个线程等待其他线程操作完成之后才执行. 实现原理 : CountDownLatch是通过计数器的方式来实现, ...
- synchronized 线程同步-类级别锁定
1.demo 说明:代码中通过 printNum 方法传入参数判断 a.b 分别对 num 这个参数的值进行了修改. package demo1; import sun.applet.Main; pu ...
随机推荐
- ML第5周学习小结
本周收获 总结一下本周学习内容: 1.学习了<深入浅出Pandas>的第五章:Pandas高级操作的两个内容 数据迭代 函数应用 我的博客链接: pandas:数据迭代.函数应用 2.&l ...
- ClickHouse(01)什么是ClickHouse,ClickHouse适用于什么场景
ClickHouse的由来 ClickHouse是什么数据库?ClickHouse速度有多快?应用场景是怎么样的?ClickHouse是关系型数据库吗?ClickHouse目前是很火爆的一款面向OLA ...
- 深入C++03:面向对象
面向对象 类和对象.this指针 不用做太多笔记,都可以看初识C++的笔记: 记住:声明后面都要加":",比如声明方法和变量还有class结束的地方:而实现函数出来的地方是不需要加 ...
- c++ RMQ
关于 RMQ ,即 Range Maxnum (Minnum) Query .用于查询静态区间最大(最小)值, 思路基于动态规划 (DP) 思路 设 F[i][j] 为 [i,i+2j] 区间内的的最 ...
- Camunda如何适配国产数据库达梦
前言 camunda流程引擎官方支持的数据库有:MySQL .MariaDB .Oracle .DB2 .PostgreSQL .SQL Server.H2.对于其他类型的数据库如何支持,尤其是国产数 ...
- VMware 虚拟机安装CentOS镜像详细步骤
CentOS目前官网提供的下载版本有6.7.8,最新的版本为8,不过个人推荐CentOS 7 的版本,因为相比较于最新版本,版本7更加地稳定.而相比于版本6,版本7新增了很多的功能.CentOS 7 ...
- 解决Invalid bound statement (not found)的异常
今天在搭建框架的时候,报了一个Invalid bound statement (not found)的异常 经过分析,得出原因: 我的mybatis相关的dao和mapper.xml是通过逆向工程生成 ...
- C语言求100以内的和的4种方式
C语言的一个很经典的例子,帮助熟练运行几个循环的写法 * 方法一(do---while语句) #include main () { int i,sum=0; do { sum=sum+i; i++; ...
- 动画 ---Animejs 简单使用与源码解析
Anime是什么 Anime有什么用 Anime是作何做的 requireAnimationFrame() engine(){ // 处理让多个帧运动起来 play() step()} ani ...
- HashSet 添加/遍历元素源码分析
HashSet 类图 HashSet 简单说明 HashSet 实现了 Set 接口 HashSet 底层实际上是由 HashMap 实现的 public HashSet() { map = new ...
