LFS(Linux From Scratch)构建过程全记录(二):磁盘分区
写在前面
本文将会详细记录LFS中,构建分区,构建文件系统和挂载分区的全过程
准备新硬盘
为了更加符合“从零开始构建Linux”的要求,我在虚拟机中,新建了一个磁盘

我们将会在这个新磁盘上构建所需的分区和文件系统,并对其进行挂载
创建新磁盘后,我们启动虚拟机,输入sudo fdisk -l,查看当前虚拟机磁盘的情况
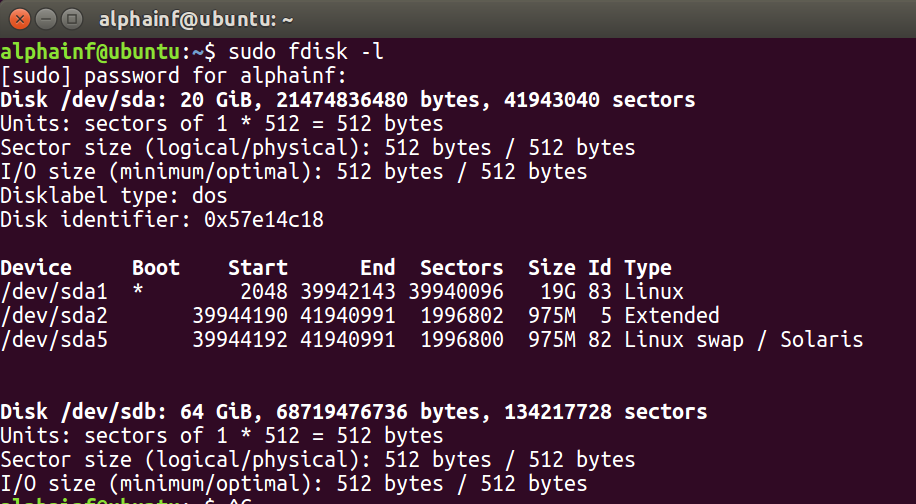
复制出来的信息如下所示:
1 alphainf@ubuntu:~$ sudo fdisk -l
2 [sudo] password for alphainf:
3 Disk /dev/sda: 20 GiB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
4 Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
5 Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
6 I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
7 Disklabel type: dos
8 Disk identifier: 0x57e14c18
9
10 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
11 /dev/sda1 * 2048 39942143 39940096 19G 83 Linux
12 /dev/sda2 39944190 41940991 1996802 975M 5 Extended
13 /dev/sda5 39944192 41940991 1996800 975M 82 Linux swap / Solaris
14
15
16 Disk /dev/sdb: 64 GiB, 68719476736 bytes, 134217728 sectors
17 Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
18 Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
19 I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
如上所示,有sda和sdb两个硬盘
其中sda所挂载的是当前系统,分了三个区,分别是Linux,Extended和Swap
sdb为我们刚创建的新硬盘,尚未进行分区
分区
根据书中的要求,我们至少需要完成三个分区的构造
分别为boot,根分区,交换分区
由于磁盘空间足够,boot和根分区我们都将分配20G,交换分区分配8G
构建boot分区的过程如下,注意,我输入的内容均在冒号的后面
比如Command (m for help): p中的p
alphainf@ubuntu:~$ sudo fdisk /dev/sdb Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.27.1).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command. Device does not contain a recognized partition table.
Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xd868f5e0. Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 64 GiB, 68719476736 bytes, 134217728 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xd868f5e0 Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-134217727, default 2048):
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-134217727, default 134217727): +20G Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 20 GiB. Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 64 GiB, 68719476736 bytes, 134217728 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xd868f5e0 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdb1 2048 41945087 41943040 20G 83 Linux
我们可以看到/dev/sdb1已经出现
我们可以通过同样的方法,构造出/dev/sdb2,也是20GB,/sdb2将作为根分区
接下来,我们构建/dev/sdb3,并将该分区的类型调整为交换分区
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (3,4, default 3):
First sector (83888128-134217727, default 83888128):
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (83888128-134217727, default 134217727): +8G Created a new partition 3 of type 'Linux' and of size 8 GiB. Command (m for help): t #注意这里,用于调整分区类型
Partition number (1-3, default 3):
Partition type (type L to list all types): 82 Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux swap / Solaris'. Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 64 GiB, 68719476736 bytes, 134217728 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xd868f5e0 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdb1 2048 41945087 41943040 20G 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 41945088 83888127 41943040 20G 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 83888128 100665343 16777216 8G 82 Linux swap / Solaris
我们可以通过以下指令实现
在完成上述设置后,记得输入w并回车,以保存对磁盘分区的修改
修改完成后将出山以下提示:
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
我们最后再输入sudo fdisk -l 确认分区情况
alphainf@ubuntu:~$ sudo fdisk -l
[sudo] password for alphainf:
Disk /dev/sda: 20 GiB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x57e14c18 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sda1 * 2048 39942143 39940096 19G 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 39944190 41940991 1996802 975M 5 Extended
/dev/sda5 39944192 41940991 1996800 975M 82 Linux swap / Solaris Disk /dev/sdb: 64 GiB, 68719476736 bytes, 134217728 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xd868f5e0 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdb1 2048 41945087 41943040 20G 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 41945088 83888127 41943040 20G 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 83888128 100665343 16777216 8G 82 Linux swap / Solaris
我们发现,sdb出现了分区,这是我们期望的状态
在分区上创建文件系统
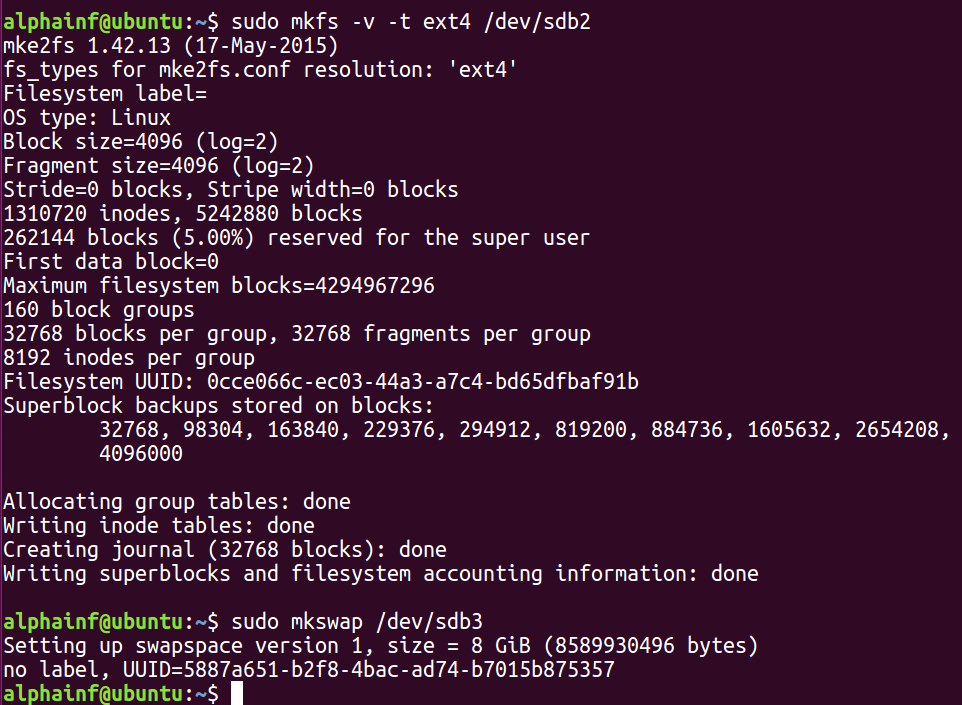
我们可以依次输入下列指令,实现文件系统的创建
sudo mkfs -v -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
sudo mkfs -v -t ext4 /dev/sdb2
sudo mkswap /dev/sdb3
以下是输入指令后的输出信息(以根目录的创建和交换分区创建的输出为例)
我们还可以打开文件夹,看到这两个刚生成的磁盘
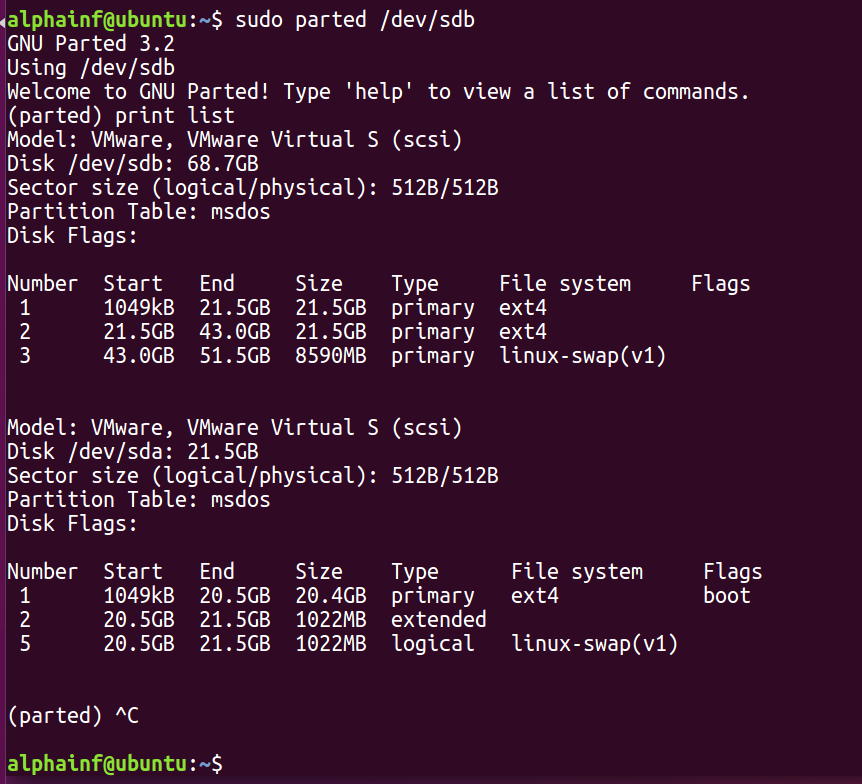
创建完成后,我们可以先输入sudo parted /dev/sdb ,再输入print list查看分区文件系统类型
设置$LFS环境变量
在接下来的配置中,为了方便设置,我们将多次使用LFS变量
设置LFS的代码如下:
export LFS=/mnt/lfs
我们可以使用echo $LFS进行确认
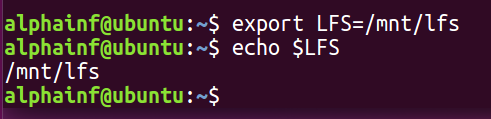
经确认,环境变量已正确设置
挂载分区
将分区/dev/sdb2挂载到/mnt/lfs中,代码如下:
sudo mkdir -pv $LFS
sudo mount -v -t ext4 /dev/sdb2 $LFS
设置交换分区代码如下
sudo /sbin/swapon -v /dev/sdb3
以上构建LFS分区的准备工作已完成
记得进行快照的保存,命名为STEP 2,并进行备注
LFS(Linux From Scratch)构建过程全记录(二):磁盘分区的更多相关文章
- LFS(Linux From Scratch)构建过程全记录(五):交叉工具链的构建
写在前面 本文将详细讲述如何构建工具链 前置知识 在LFS-BOOK中,我们需要学习一些关于"交叉编译"的内容,详见书本 安装Binutils-2.39 我们cd到sources文 ...
- LFS(Linux From Scratch)构建过程全记录(三):下载所需的软件包
写在前面 本文将记录构建LFS的过程中,下载软件包的全过程 准备下载的路径 注意请确保$LFS已经设置完毕 我们需要创建一个文件夹,地址为$LFS/sources,用于保存对应的源码 输入的指令如下: ...
- LFS(Linux From Scratch)构建过程全记录(一):准备工作
写在前面 本人修学了一门课,名曰<操作系统课程设计>,其任务为基于LFS以编译源代码的方式制作一个基本的Linux操作系统,并且编写在linux下的GUI软件. 本操作系统构建的全过程将分 ...
- LFS(Linux From Scratch)构建过程全记录(七):进入Chroot并构建临时工具
写在前面 本章将完成临时系统构建的最后缺失部分和各种包构建所需的工具. 解决了所有循环依赖关系后,就可以使用与主机操作系统完全隔离的"chroot"环境进行构建. 注意:接下来的指 ...
- LFS(Linux From Scratch)构建过程全记录(六):交叉编译临时工具
写在前面 本章将展示如何使用刚刚构建的跨工具链来交叉编译基本实用程序. M4安装 和前文一样,先进行解压,然后cd进入 注意:不需要构建build文件夹,直接输入以下配置文件 ./configure ...
- LFS(Linux From Scratch)构建过程全记录(四):最后的准备
写在前面 本章将进行一系列的环境配置 目录创建 在LFS中创建文件目录 我们可以用以下的指令来创建一些基础的目录,并进行连接 mkdir -pv $LFS/{etc,var} $LFS/usr/{bi ...
- 在CentOS6上配置MHA过程全记录
在CentOS6上配置MHA过程全记录 MHA(Master High Availability)是一款开源的MariaDB or MySQL高可用程序,为MariaDB or MySQL主从复制架构 ...
- 在CentOS7上通过RPM安装实现LAMP+phpMyAdmin过程全记录
在CentOS7上通过RPM安装实现LAMP+phpMyAdmin过程全记录 时间:2017年9月20日 一.软件环境: IP:192.168.1.71 Hostname:centos73-2.sur ...
- SAP S4HANA1610/Fiori安装过程全记录
经历各种坑,从硬件到文件,终于安装成功. 有需要安装或使用S4HANA(含Fiori)的同学可以参考. 安装文件分享给大家 链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1mi7LfIS 密码: ...
随机推荐
- jieba分词原理解析:用户词典如何优先于系统词典
目标 查看jieba分词组件源码,分析源码各个模块的功能,找到分词模块,实现能自定义分词字典,且优先级大于系统自带的字典等级,以医疗词语邻域词语为例. jieba分词地址:github地址:https ...
- Spring Data JPA系列5:让IDEA自动帮你写JPA实体定义代码
大家好,又见面了. 这是本系列的最后一篇文档啦,先来回顾下前面4篇: 在第1篇<Spring Data JPA系列1:JDBC.ORM.JPA.Spring Data JPA,傻傻分不清楚?给你 ...
- LVGL库入门教程 - 动画
动画可以说是 LVGL 中的特色之一,不过在使用动画前,请确保单片机具有足够的性能来维持足够的帧率. transition:过渡动画 当一个控件的状态发生改变时,可以让样式也发生变化以提醒用户.通过过 ...
- python小题目练习(八)
题目:电视剧的收视率排行榜 需求:实现如下图所示需求 代码展示: """Author:mllContent:电视剧的收视率排行榜Date:2020-11-16" ...
- Tapdata 携手精诚瑞宝,共拓 Real Time DaaS 蓝海市场
2021年10月22日,深圳钛铂数据有限公司「Tapdata」 与精诚瑞宝计算机系统有限公司「精诚瑞宝」战略合作签约仪式在深圳举行,Tapdata 创始人唐建法先生与精诚瑞宝副总经理余灿雄先生签署 ...
- 时空图神经网路:STGNNs
STGNNs:SPATIAL–TEMPORAL GRAPH NEURAL NETWORKS 许多实际应用中的图在图结构和图输入方面都是动态的.STGNNs在捕获图的动态性方面占有重要地位. 这类方法的 ...
- 【跟着大佬学JavaScript】之节流
前言 js的典型的场景 监听页面的scroll事件 拖拽事件 监听鼠标的 mousemove 事件 ... 这些事件会频繁触发会影响性能,如果使用节流,降低频次,保留了用户体验,又提升了执行速度,节省 ...
- docker安装Nessus
Nessus家庭版最大只支持扫描16个主机,但利用docker无限使用,当然虚拟机快照也可以. 关于网上其他的破解版,我是没有成功(显示成功了,其实是自慰版),所以才弄得这个镜像 提供两个镜像(不懂d ...
- Mybatis-Generator 自定义注释
继承DefaultCommentGenerator 或者CommentGenerator package com.zhianchen.mysqlremark.toword.config;import ...
- 聊聊 C++ 中的几种智能指针 (上)
一:背景 我们知道 C++ 是手工管理内存的分配和释放,对应的操作符就是 new/delete 和 new[] / delete[], 这给了程序员极大的自由度也给了我们极高的门槛,弄不好就得内存泄露 ...
