MonolithFirst
As I hear stories about teams using a microservices architecture, I've noticed a common pattern.
- Almost all the successful microservice stories have started with a monolith that got too big and was broken up
- Almost all the cases where I've heard of a system that was built as a microservice system from scratch, it has ended up in serious trouble.
This pattern has led many of my colleagues to argue that you shouldn't start a new project with microservices, even if you're sure your application will be big enough to make it worthwhile..
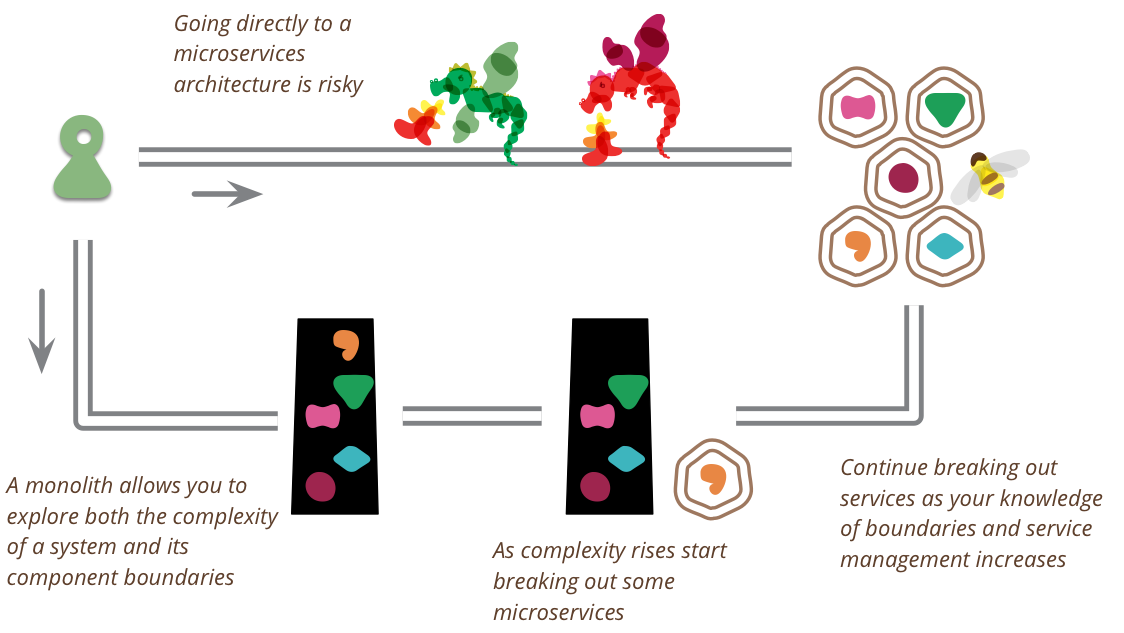
Microservices are a useful architecture, but even their advocates say that using them incurs a significant MicroservicePremium, which means they are only useful with more complex systems. This premium, essentially the cost of managing a suite of services, will slow down a team, favoring a monolith for simpler applications. This leads to a powerful argument for a monolith-first strategy, where you should build a new application as a monolith initially, even if you think it's likely that it will benefit from a microservices architecture later on.
The first reason for this is classic Yagni. When you begin a new application, how sure are you that it will be useful to your users? It may be hard to scale a poorly designed but successful software system, but that's still a better place to be than its inverse. As we're now recognizing, often the best way to find out if a software idea is useful is to build a simplistic version of it and see how well it works out. During this first phase you need to prioritize speed (and thus cycle time for feedback), so the premium of microservices is a drag you should do without.
The second issue with starting with microservices is that they only work well if you come up with good, stable boundaries between the services - which is essentially the task of drawing up the right set of BoundedContexts. Any refactoring of functionality between services is much harder than it is in a monolith. But even experienced architects working in familiar domains have great difficulty getting boundaries right at the beginning. By building a monolith first, you can figure out what the right boundaries are, before a microservices design brushes a layer of treacle over them. It also gives you time to develop the MicroservicePrerequisites you need for finer-grained services.
I've heard different ways to execute a monolith-first strategy. The logical way is to design a monolith carefully, paying attention to modularity within the software, both at the API boundaries and how the data is stored. Do this well, and it's a relatively simple matter to make the shift to microservices. However I'd feel much more comfortable with this approach if I'd heard a decent number of stories where it worked out that way. [1]
A more common approach is to start with a monolith and gradually peel off microservices at the edges. Such an approach can leave a substantial monolith at the heart of the microservices architecture, but with most new development occurring in the microservices while the monolith is relatively quiescent.
Another common approach is to just replace the monolith entirely. Few people look at this as an approach to be proud of, yet there are advantages to building a monolith as a SacrificialArchitecture. Don't be afraid of building a monolith that you will discard, particularly if a monolith can get you to market quickly.
Another route I've run into is to start with just a couple of coarse-grained services, larger than those you expect to end up with. Use these coarse-grained services to get used to working with multiple services, while enjoying the fact that such coarse granularity reduces the amount of inter-service refactoring you have to do. Then as boundaries stabilize, break down into finer-grained services. [2]
While the bulk of my contacts lean toward the monolith-first approach, it is by no means unanimous. The counter argument says that starting with microservices allows you to get used to the rhythm of developing in a microservice environment. It takes a lot, perhaps too much, discipline to build a monolith in a sufficiently modular way that it can be broken down into microservices easily. By starting with microservices you get everyone used to developing in separate small teams from the beginning, and having teams separated by service boundaries makes it much easier to scale up the development effort when you need to. This is especially viable for system replacements where you have a better chance of coming up with stable-enough boundaries early. Although the evidence is sparse, I feel that you shouldn't start with microservices unless you have reasonable experience of building a microservices system in the team.
I don't feel I have enough anecdotes yet to get a firm handle on how to decide whether to use a monolith-first strategy. These are early days in microservices, and there are relatively few anecdotes to learn from. So anybody's advice on these topics must be seen as tentative, however confidently they argue.
Further Reading
Sam Newman describes a case study of a team considering using microservices on a greenfield project.
Notes
1: You cannot assume that you can take an arbitrary system and break it into microservices. Most systems acquire too many dependencies between their modules, and thus can't be sensibly broken apart. I've heard of plenty of cases where an attempt to decompose a monolith has quickly ended up in a mess. I've also heard of a few cases where a gradual route to microservices has been successful - but these cases required a relatively good modular design to start with.
2: I suppose that strictly you should call this a "duolith", but I think the approach follows the essence of monolith-first strategy: start with coarse-granularity to gain knowledge and split later.
Acknowledgements
I stole much of this thinking from my coleagues: James Lewis, Sam Newman, Thiyagu Palanisamy, and Evan Bottcher. Stefan Tilkov's comments on an earlier draft played a pivotal role in clarifying my thoughts. Chad Currie created the lovely glyphy dragons. Steven Lowe, Patrick Kua, Jean Robert D'amore, Chelsea Komlo, Ashok Subramanian, Dan Siwiec, Prasanna Pendse, Kief Morris, Chris Ford, and Florian Sellmayr discussed drafts on our internal mailing list.
https://www.martinfowler.com/bliki/MonolithFirst.html
MonolithFirst的更多相关文章
- 【译文】用Spring Cloud和Docker搭建微服务平台
by Kenny Bastani Sunday, July 12, 2015 转自:http://www.kennybastani.com/2015/07/spring-cloud-docker-mi ...
- How Microservices are Transforming Python Development
https://blog.appdynamics.com/engineering/how-microservices-are-transforming-python-development/ Summ ...
- Atitit s2018.2 s2 doc list on home ntpc.docx \Atiitt uke制度体系 法律 法规 规章 条例 国王诏书.docx \Atiitt 手写文字识别 讯飞科大 语音云.docx \Atitit 代码托管与虚拟主机.docx \Atitit 企业文化 每日心灵 鸡汤 值班 发布.docx \Atitit 几大研发体系对比 Stage-Gat
Atitit s2018.2 s2 doc list on home ntpc.docx \Atiitt uke制度体系 法律 法规 规章 条例 国王诏书.docx \Atiitt 手写文字识别 ...
- Spring Cloud和Docker搭建微服务平台
用Spring Cloud和Docker搭建微服务平台 This blog series will introduce you to some of the foundational concepts ...
随机推荐
- 苹果新的编程语言 Swift 语言进阶(十六)--泛型
泛型允许你定义一个宽松.可重用的函数或者类型,使用泛型能够避免代码的重复,也能以更清楚和抽象的方式来表达程序的意图. 泛型是Swift语言提供的强大功能之一,Swift提供的许多标准库都使用了泛型来创 ...
- iOS和OS X中的bundle
bundle也可以称之为包(package). 它在iOS和OS X中实际为一个文件夹但却当成单独的文件来对待. 每一个app都有一个bundle,并且你可以通过在xxx.app图标上右击鼠标然后选择 ...
- LeetCode之“数学”:Plus One
题目链接 题目要求: Given a non-negative number represented as an array of digits, plus one to the number. Th ...
- IOS中用到的缓存
App已经与我们形影不离了,不管在地铁上.公交上还是在会场你总能看到很多人拿出来手机,刷一刷微博,看看新闻. 据不完全统计有近一半的用户在非Wifi环境打开App,以下为一个典型iPhone和Andr ...
- C# 视频多人脸识别
上一篇内容的调整,并按 @轮回 的说法,提交到git了,https://github.com/catzhou2002/ArcFaceDemo 基本思路如下: 一.识别线程 1.获取当前图片 2.识别当 ...
- 深入浅出web服务器与python应用程序之间的联系
简单来说,Web服务器是在运行在物理服务器上的一个程序,它永久地等待客户端(主要是浏览器,比如Chrome,Firefox等)发送请求.Web 服务器接受 Http Request,返回 Respon ...
- app ionic1 微信 微博 分享功能的实现
微信分享 1.登录微信开放平台注册账户 2.创建一个移动应用 (app) 审核过后会有一个appid 之后安装插件的时候会用到 3.在这个应用上面填写 包名 和 签名 就可以了 包名和签名的 ...
- JVM的运行原理以及JDK 7增加的新特性(二)
JVM结构 Java编写的代码会按照下图的流程来执行 类装载器装载负责装载编译后的字节码,并加载到运行时数据区(Runtime Data Area),然后执行引擎执行会执行这些字节码. 类加载器(Cl ...
- vue2.0 — 移动端的输入框实时检索更新列表
我们都是行走在这世界的孤独者 - 暖暖 最近在做vue2.0的项目遇到一个移动端实事检索搜索更新列表的效果,但用户在搜索框输入客户的电话或姓名的时候,客户列表内容会做相应的更新,下面给大家看下图~· ...
- 微信小程序中自定义函数的学习使用
新手,最近在给学校搞个党费计算器.需要自己定义函数来实现某个功能. 1.无参函数: 函数都是写在js文件里面的. Page({ data:{ income1:'0', }, cal:function( ...
