heartbeat单独提供高可用服务
1.简介
heartbeat是人所众知高可用软件。但是在以前,heartbeat是Linux-ha项目里一大堆提供高可用组件的集合体:
- Messaging Layer(消息传递层)
- local resource manager(LRM,本地资源管理,cluster glue的一个功能)
- stonith(爆头,cluster glue的一个功能)
- Resource Agent(RA,资源代理)、
- cluster resource manager(CRM,集群资源管理器,现在独立出去的pacemaker)。
现在,由于linux-ha将很多这些组件都分离为一个个单独的软件,heartbeat已经只代表消息层(取代它的是corosync)。而且linux-ha项目团队已经不再维护heartbeat,目前能从官方获取到的最新版本是Heartbeat 3.0.6,在epel中可获取到"Heartbeat 3.0.4"版本的rpm包。
虽然Heartbeat只代表高可用集群的消息传递层,但它结合cluster glue和resource agent也可以提供高可用服务,这正是本文的内容。相比于corosync+pacemaker,heartbeat要轻量级的多,配置起来也简单许多。相应的,它的功能和完整性要简陋的多,它只支持两个heartbeat节点(结合pacemaker可多于两节点),且加载资源的速度比较慢。
当然,既然heartbeat是消息传递层,它也能配合pacemaker,但是不建议如此。而且这样搭配时,各个组件的版本要求很严格。
2.安装heartbeat
如果使用yum安装,可以配置epel源。注意,在centos7的epel上,已经没有heartbeat了。
release=`grep -o "[0-9]" /etc/redhat-release | head -1`
cat <<eof>/etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo
[epel]
name=epelrepo
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/${release}Server/\$basearch
gpgcheck=0
enable=1
eof
yum -y install heartbeat
可以看到,安装heartbeat的时候,同时还会安装cluster-glue和resource-agent。
然后提供配置文件。
cp -a /usr/share/doc/heartbeat-3.0.4/{ha.cf,haresources,authkeys} /etc/ha.d/
chmod 600 /etc/ha.d/authkeys
2.1 编译安装heartbeat
不建议编译安装heartbeat,heartbeat这个程序本身附带的很多脚本在路径指定上很混乱,安装后很可能需要到处修改脚本中关于路径的变量。
如果要编译安装heartbeat,则必须先安装cluster-glue和resource-agent,建议这3个程序安装在同一路径下。
(1).安装依赖包。
yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake libtool glib2-devel libxml2-devel bzip2 bzip2-devel e2fsprogs-devel libxslt-devel libtool-ltdl-devel asciidoc
创建好所需组和所有者,在编译cluster-glue会设置一些文件的属组和属主分别为haclient、hacluster,因此名称必须为这两个。
groupadd -g 65 haclient
useradd -g 65 -u 17 hacluster
(2).编译cluster-glue。
tar xf Cluster\ Glue\ 1.0.12.bz2
cd Reusable-Cluster-Components-glue--0a7add1d9996/
./autogen.sh
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/heartbeat LIBS=/lib64/libuuid.so.1
make
make install
如果make时有如下错误:
./.libs/libplumb.so: undefined reference to `uuid_parse'
./.libs/libplumb.so: undefined reference to `uuid_generate'
./.libs/libplumb.so: undefined reference to `uuid_copy'
./.libs/libplumb.so: undefined reference to `uuid_is_null'
./.libs/libplumb.so: undefined reference to `uuid_unparse'
./.libs/libplumb.so: undefined reference to `uuid_clear'
./.libs/libplumb.so: undefined reference to `uuid_compare'
collect2: ld returned 1 exit status
gmake[2]: *** [ipctest] Error 1
gmake[2]: Leaving directory `/root/Reusable-Cluster-Components-glue--0a7add1d9996/lib/clplumbing'
gmake[1]: *** [all-recursive] Error 1
gmake[1]: Leaving directory `/root/Reusable-Cluster-Components-glue--0a7add1d9996/lib'
make: *** [all-recursive] Error 1
解决方法:在configure中使用LIBS指向正确的库文件,64位使用/lib64,32位使用/lib
./configure LIBS=/lib64/libuuid.so.1
如果是如下错误:
gmake[2]: a2x: Command not found
解决方法:yum install asciidoc
可以看下cluster-glue提供了哪些命令。
[root@xuexi ~]# ls /usr/local/heartbeat/sbin/
cibsecret ha_logger hb_report lrmadmin meatclient stonith
从此不难看出,cluster-glue是整个ha的核心组件,除了crm、messageing layer、resource agent,所有的功能包括最基本的功能都是它提供的。例如,日志记录,stonith,lrm等。
(3).编译resource-agent。
tar xf resource-agents-3.9.6.tar.gz
cd resource-agents-3.9.6
./autogen.sh
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/heartbeat
make
make install
(4).编译heartbeat。
tar xf heartbeat\ 3.0.6.bz2
cd Heartbeat-3-0-958e11be8686/
./bootstrap
export CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -I/usr/local/heartbeat/include -L/usr/local/heartbeat/lib"
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/heartbeat --with-daemon-user=hacluster --with-daemon-group=haclient LIBS=/lib64/libuuid.so.1
make
make install
如果出现如下错误:
【configure时错误:】
configure: error: in `/root/Heartbeat-3-0-958e11be8686':
configure: error: Core development headers were not found
解决方法:
export CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -I/usr/local/heartbeat/include -L/usr/local/heartbeat/lib"
【make时错误:】
/usr/local/heartbeat/include/heartbeat/glue_config.h:105:1: error: "HA_HBCONF_DIR" redefined
In file included from ../include/lha_internal.h:38,
from strlcpy.c:1:
../include/config.h:390:1: error: this is the location of the previous definition
gmake[1]: *** [strlcpy.lo] Error 1
gmake[1]: Leaving directory `/root/Heartbeat-3-0-958e11be8686/replace'
make: *** [all-recursive] Error 1
解决方法1:
删除/usr/local/heartbeat/include/heartbeat/glue_config.h 中的第105行
#define HA_HBCONF_DIR "/etc/ha.d/"
sed -i '105d' /usr/local/heartbeat/include/heartbeat/glue_config.h
解决方法2:configure上加上忽略错误选项
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/heartbeat --with-daemon-user=hacluster --with-daemon-group=haclient LIBS=/lib64/libuuid.so.1 --enable-fatal-warnings=no
(5).编译后配置。
mkdir -p /usr/local/heartbeat/usr/lib/ocf/lib/heartbeat
cp -a /usr/lib/ocf/lib/heartbeat/ocf-* /usr/local/heartbeat/usr/lib/ocf/lib/heartbeat/
ln -s /usr/local/heartbeat/lib64/heartbeat/plugins/RAExec/* /usr/local/heartbeat/lib/heartbeat/plugins/RAExec/
ln -s /usr/local/heartbeat/lib64/heartbeat/plugins/* /usr/local/heartbeat/lib/heartbeat/plugins/
ln -s /usr/local/heartbeat/share/heartbeat /usr/share/heartbeat
提供配置文件:
cd /usr/local/heartbeat
cp -a share/doc/heartbeat/{ha.cf,haresources,authkeys} etc/ha.d/
chmod 600 etc/ha.d/authkeys
加入服务器启动列表:
chkconfig --add heartbeat
chkconfig --level 2345 heartbeat on
设置环境变量PATH:
echo 'export PATH=/usr/local/heartbeat/sbin:/usr/local/heartbeat/bin:$PATH' >/etc/profile.d/ha.sh
chmod +x /etc/profile.d/ha.sh
source /etc/profile.d/ha.sh
设置man PATH:
echo 'MANPATH /usr/local/heartbeat/share/man' >>/etc/man.config3.heartbeat相关配置文件
heartbeat配置文件有3个:
- 密钥文件authkeys,用在messaging layer下各节点之间的认证,防止外界主机随意加入节点(600权限);
- heartbeat核心配置文件,ha.cf;
- 资源管理配置文件:haresources;
它们的生效位置在/etc/ha.d/目录下,但是初始时在此目录下并没有这3个文件,它们的样例配置文件在/usr/share/docs/heartbeat-$$version/目录下,可以将它们复制到/etc/ha.d目录下。
#以下是yum安装,非编译安装的操作
cp /usr/share/doc/heartbeat-3.0.4/{authkeys,ha.cf,haresources} /etc/ha.d/
3.1 配置文件ha.cf
ha.cf的部分内容如下。该文件看起来很多,但如果不结合pacemaker,其实要修改的就几项,包括node和bcast/mcast以及auto_failback,有时还配置下ping和log。注意该文件从上往下读取,指令的配置位置很重要,因此一般不要修改它们的出现顺序。
# 如果logfile/debugfile/logfacility都没有设置,则等价于设置了"use_logd yes"
# 且use_logd设置为yes后,logfile/debugfile/logfacility的设置都失效
#
# Note on logging:
# If all of debugfile, logfile and logfacility are not defined,
# logging is the same as use_logd yes. In other case, they are
# respectively effective. if detering the logging to syslog,
# logfacility must be "none".
#
# File to write debug messages to
#debugfile /var/log/ha-debug
#
#
# File to write other messages to
#
#logfile /var/log/ha-log
#
#
# Facility to use for syslog()/logger
#
logfacility local0
#
#
# A note on specifying "how long" times below...
#
# The default time unit is seconds
# 10 means ten seconds
#
# You can also specify them in milliseconds
# 1500ms means 1.5 seconds
#
#
# keepalive: how long between heartbeats?
# 发送心跳信息的时间间隔,默认每两秒发送一次心跳信息
#keepalive 2
#
# deadtime: how long-to-declare-host-dead?
#
# If you set this too low you will get the problematic
# split-brain (or cluster partition) problem.
# See the FAQ for how to use warntime to tune deadtime.
# 指定若备节点在30秒内未收到主节点心跳信号,则判定主节点死亡,并接管主服务器资源
#deadtime 30
#
# warntime: how long before issuing "late heartbeat" warning?
# See the FAQ for how to use warntime to tune deadtime.
# 指定心跳延迟的时间为10秒,10秒内备节点不能接收主节点心跳信号,即往日志写入警告日志,但不会切换服务
#warntime 10
#
#
# Very first dead time (initdead)
#
# On some machines/OSes, etc. the network takes a while to come up
# and start working right after you've been rebooted. As a result
# we have a separate dead time for when things first come up.
# It should be at least twice the normal dead time.
# 定义第一次死亡判定时间,即第一个heartbeat启动后等待第二个heartbeat启动,
# 第二个启动后才会启动高可用服务、启动VIP等。若在此时间内第二个节点未启动则
# 判定其dead,然后才启动高可用服务和VIP,这是双方为形成高可用群集的等待时间。
# 此时间至少要是deadtime的两倍
#initdead 120
#
#
# What UDP port to use for bcast/ucast communication?
# 心跳信息端口
#udpport 694
#
# Baud rate for serial ports...
# 支持两种方式发送心跳信息,一是以太网(广播组播单播),一是串行线,在heartbeat3中,baud已经废弃
#baud 19200
#
# serial serialportname ...
#serial /dev/ttyS0 # Linux
#serial /dev/cuaa0 # FreeBSD
#serial /dev/cuad0 # FreeBSD 6.x
#serial /dev/cua/a # Solaris
#
#
# What interfaces to broadcast heartbeats over?
#
#bcast eth0 # Linux
#bcast eth1 eth2 # Linux
#bcast le0 # Solaris
#bcast le1 le2 # Solaris
#
# Set up a multicast heartbeat medium
# mcast [dev] [mcast group] [port] [ttl] [loop]
#
# [dev] device to send/rcv heartbeats on
# [mcast group] multicast group to join (class D multicast address
# 224.0.0.0 - 239.255.255.255)
# [port] udp port to sendto/rcvfrom (set this value to the
# same value as "udpport" above)
# [ttl] the ttl value for outbound heartbeats. this effects
# how far the multicast packet will propagate. (0-255)
# Must be greater than zero.
# [loop] toggles loopback for outbound multicast heartbeats.
# if enabled, an outbound packet will be looped back and
# received by the interface it was sent on. (0 or 1)
# Set this value to zero.
#
#
#mcast eth0 225.0.0.1 694 1 0
#
# Set up a unicast / udp heartbeat medium
# ucast [dev] [peer-ip-addr]
#
# [dev] device to send/rcv heartbeats on
# [peer-ip-addr] IP address of peer to send packets to
#
# 单播心跳,需指定对方心跳接口地址
#ucast eth0 192.168.1.2
#
#
# About boolean values...
#
# Any of the following case-insensitive values will work for true:
# true, on, yes, y, 1
# Any of the following case-insensitive values will work for false:
# false, off, no, n, 0
#
#
#
# auto_failback: determines whether a resource will
# automatically fail back to its "primary" node, or remain
# on whatever node is serving it until that node fails, or
# an administrator intervenes.
#
# The possible values for auto_failback are:
# on - enable automatic failbacks
# off - disable automatic failbacks
# legacy - enable automatic failbacks in systems
# where all nodes do not yet support
# the auto_failback option.
#
# auto_failback "on" and "off" are backwards compatible with the old
# "nice_failback on" setting.
#
# See the FAQ for information on how to convert
# from "legacy" to "on" without a flash cut.
# (i.e., using a "rolling upgrade" process)
#
# The default value for auto_failback is "legacy", which
# will issue a warning at startup. So, make sure you put
# an auto_failback directive in your ha.cf file.
# (note: auto_failback can be any boolean or "legacy")
# 主节点恢复重新上线后,是否自动接管服务
auto_failback on
#
# 以下是fence设备相关
# Basic STONITH support
# Using this directive assumes that there is one stonith
# device in the cluster. Parameters to this device are
# read from a configuration file. The format of this line is:
#
# stonith <stonith_type> <configfile>
#
# NOTE: it is up to you to maintain this file on each node in the
# cluster!
#
#stonith baytech /etc/ha.d/conf/stonith.baytech
#
# STONITH support
# You can configure multiple stonith devices using this directive.
# The format of the line is:
# stonith_host <hostfrom> <stonith_type> <params...>
# <hostfrom> is the machine the stonith device is attached
# to or * to mean it is accessible from any host.
# <stonith_type> is the type of stonith device (a list of
# supported drives is in /usr/lib/stonith.)
# <params...> are driver specific parameters. To see the
# format for a particular device, run:
# stonith -l -t <stonith_type>
#
#
# Note that if you put your stonith device access information in
# here, and you make this file publically readable, you're asking
# for a denial of service attack ;-)
#
# To get a list of supported stonith devices, run
# stonith -L
# For detailed information on which stonith devices are supported
# and their detailed configuration options, run this command:
# stonith -h
#
#stonith_host * baytech 10.0.0.3 mylogin mysecretpassword
#stonith_host ken3 rps10 /dev/ttyS1 kathy 0
#stonith_host kathy rps10 /dev/ttyS1 ken3 0
#
#
# 看门狗是一个计时器。如果自身60秒不心跳了,则本节点会重启
# Watchdog is the watchdog timer. If our own heart doesn't beat for
# a minute, then our machine will reboot.
# NOTE: If you are using the software watchdog, you very likely
# wish to load the module with the parameter "nowayout=0" or
# compile it without CONFIG_WATCHDOG_NOWAYOUT set. Otherwise even
# an orderly shutdown of heartbeat will trigger a reboot, which is
# very likely NOT what you want.
#
#watchdog /dev/watchdog #看门狗fence设备,Linux自带的软watchdog
#
# Tell what machines are in the cluster
# node nodename ... -- must match uname -n
# 必须配置的node,必须和uname -n的结果一致
#node ken3
#node kathy
#
# Less common options...
#
# Treats 10.10.10.254 as a psuedo-cluster-member
# Used together with ipfail below...
# note: don't use a cluster node as ping node
#
# 通过ping参考ip检测本节点对外的网络连通性,需要配合ipfail进程。当ping不通时将down掉本节点
# ping_group是通过ping一组ip来检查ip的连通性,防止因对方节点故障而误以为自己坏了。
# 只有当组中所有节点都ping不通才认为自己坏了。和ping只能使用二选一
# 不要使用集群节点作为ping的参考ip,一般ping的对象都是网关
#ping 10.10.10.254
#ping_group group1 172.16.103.254 172.16.103.212
# 随heartbeat启动、停止而启动停止的进程,它是pacemaker在heartbeat中的实现
#respawn hacluster /usr/local/lib/heartbeat/ipfail
# 指定哪个用户、组可以连通使用某进程,此处为ipfail
#apiauth ipfail gid=haclient uid=hacluster
综上,必须要配置的就是三项:node、bcast/mcast、auto_failback。它们在文件中的位置顺序是先bcast/mcast/ucast,再auto_failback,最后才是node。偶尔还需配置ping来检测自身网络。
例如,以下是两个heartbeat节点,分别两个网卡,使用广播方式从eth0发送心跳信息的配置。
logfile /var/log/ha-log
logfacility local0
bcast eth0
#mcast eth1 225.0.0.193 694 1 0
auto_failback yes
node node1.longshuai.com
node node2.longshuai.com
ping 192.168.100.1
respawn hacluster /usr/local/lib/heartbeat/ipfail
apiauth ipfail gid=haclient uid=hacluster
因为使用的是广播,两台服务器上的ha.cf文件是完全一样的。如果是通过多播或单播的方式发送心跳信息,则两台服务器的ha.cf在mcast/ucast指令配置参数上是不一样的。
另外需注意,heartbeat主节点重启heartbeat或重启系统,当前正运行的heartbeat会发出通告给备节点,使其快速接管资源,而不是按照配置文件中定义的deadtime来获取资源的。同理,当再次启动的时候,如果设置了failback,会发送通告迅速收回资源。
3.2 配置文件authkeys
chmod 600 authkeys
以下为authkeys的内容。两个节点上该文件的内容一致。
#auth 1
#1 crc
#2 sha1 HI!
#3 md5 Hello!
auth 3
3 md5 6hy6Y6NCdVInax1PlGlvFyIMm/k
使用的是md5格式,使用sha1更安全。后面的是一段随机数,这里用随机数来做md5加密。随机数的生成方式有很多种。如:
openssl rand -base64 20
3.3 配置文件haresources
在此配置文件内配置资源代理(resource agent)参数。heartbeat自身支持两种风格的RA:一种是LSB类型的程序,它的路径在/etc/init.d/下;一种是heartbeat自带的haresource,它的路径在ha.d/resource.d/目录下。
以下是heartbeat自带的RA。
[root@xuexi ~]# ls /etc/ha.d/resource.d/
apache db2 Filesystem ICP IPaddr IPsrcaddr LinuxSCSI MailTo portblock SendArp WAS Xinetd
AudibleAlarm Delay hto-mapfuncs ids IPaddr2 IPv6addr LVM OCF Raid1 ServeRAID WinPopup
需要记住其中几个:
- apache:管理httpd,需指定httpd配置文件作为该RA的参数。
- IPaddr和IPaddr2:设置IP别名(注意,是别名),IPaddr2是IPaddr的升级版,但两者可以通用。
- Filesystem:挂载文件系统。
自带的RA类似于LSB,只是它能接受参数(如start/stop/status),而LSB不能,LSB的start、stop和status参数由heartbeat自行发送。
它们都必须能接受start/stop/status参数,且必须具有幂等性。例如running状态的再次start,返回状态码为0,还是继续running,stop状态的再次stop不会报错,且状态码为0。除了对stop状态的资源进行status时返回状态码3,其他任意参数的状态码都必须为0。
如果结合pacemaker,则还支持ocf风格的程序来管理资源。
通过以下5行来说明该配置文件的配置方法。
#node-name resource1 resource2 ... resourceN
#IPaddr::135.9.8.7/24/eth0
#just.linux-ha.org 135.9.216.110 httpd
#node1 10.0.0.170 Filesystem::/dev/sda1::/data1::ext2
#node1 10.0.0.170 apache::/etc/apache/httpd.conf
- 第一行是配置语法说明,首先指定节点名,节点名必须和
uname -n一致。后面指定在此节点上运行的资源,多个资源使用空格隔开。 - 第二行中的"IPaddr"是资源代理程序,该程序在/etc/ha.d/resource.d/目录下,如果该目录下找不到就会去找/etc/init.d/目录下的程序。IPaddr后面的双冒号"::"是参数分隔符,多个参数之间使用双冒号分割,参数是传递给资源代理程序的。这一行说明的是设置在某节点上设置ip为135.9.8.7,掩码为24位,配置在eth0的别名上。它实现的是
resource.d/IPaddr 135.9.8.7/24/eth0 start|stop|status。 - 第三行说明在节点just.linux-ha.org上启用ip 135.9.216.110(IPaddr程序可省略)和httpd服务。
- 第四行说明节点node1上启用IP 10.0.0.170,成功后运行资源代理程序Filesystem,向其传入运行3个参数"/dev/sda1"、"/data1"、"ext2"。
如果不知道某个RA接什么样的参数实现怎样的功能,可以去查看ha.d/resource.d/下对应RA的程序用法(一般都是shell脚本,前几行就会写Usage)。例如,IPaddr2的前几行:
[root@xuexi ~]# vim /etc/ha.d/resource.d/IPaddr2
#!/bin/sh
#
#
# Description: wrapper of OCF RA IPaddr2, based on original heartbeat RA.
# See OCF RA IPaddr2 for more information.
#
# Author: Xun Sun <xunsun@cn.ibm.com>
# Support: linux-ha@lists.linux-ha.org
# License: GNU General Public License (GPL)
# Copyright: (C) 2005 International Business Machines
#
# This script manages IP alias IP addresses
#
# It can add an IP alias, or remove one.
#
# usage: $0 ip-address[/netmaskbits[/interface[:label][/broadcast]]] \
# {start|stop|status|monitor}
#
# The "start" arg adds an IP alias.
#
# Surprisingly, the "stop" arg removes one. :-)
例如,以下是只管理两个节点VIP资源的haresources文件内容。两个服务器上的内容相同时表示:这是一个主主模型,节点1初始时只设置20.16这个IP,节点2初始时只设置20.14这个IP,当某节点故障后,另一节点接管其上VIP。
node1.longshuai.com IPaddr2::192.168.20.16/24/eth0
node2.longshuai.com IPaddr2::192.168.20.14/24/eth0
注意:
- heartbeat只支持两个节点,没有主从之分,只能根据haresources中的节点名称来决定是否设置某资源。
- VIP这种配置在别名接口上的地址,必须要和它所在接口同网段,否则它没有对应的路由。即使它通过默认路由出去了,如果它的下一跳是Linux主机,由于Linux主机默认设置了rp_filter=1的源地址严格检查,会直接丢弃这样的数据包。如果真这样,将其设置为2(也可以设置为0,但不推荐)。
- 如果采用广播发送心跳信息,建议心跳接口地址不要和VIP所在接口主地址同网段,否则心跳信息会被各节点的对外通信接口接收,从而影响性能。
4.示例:heartbeat为httpd提供高可用
这是一个没有实际意义的示例,只是为了演示heartbeat提供高可用时需要配置哪些必要的东西,以及如何提供VIP漂移(即IP资源高可用)。
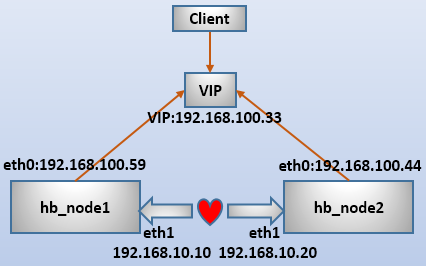
环境如下:
需要说明的是,httpd有两种管理方式:
- heartbeat只管理vip的漂移,不管理httpd的启动。这种情况要求httpd要事先在两节点启动好。
- heartbeat同时管理VIP和httpd,这时httpd不能事先启动,也不能设置开机自启动。
本文测试采用第二种方案。
(1).配置节点主机名。
# node1上执行
hostname node1.longshuai.com
sed -i "/HOSTNAME/Is/=.*$/=node1\.longshuai\.com/" /etc/sysconfig/network
# node2上执行
hostname node2.longshuai.com
sed -i "/HOSTNAME/Is/=.*$/=node2\.longshuai\.com/" /etc/sysconfig/network
(2).配置主机名解析。
# 两节点都执行
cat >>/etc/hosts<<eof
192.168.100.59 node1.longshuai.com node1
192.168.100.44 node2.longshuai.com node2
eof
(3).为心跳线接口配置主机路由。
# 在node上执行:
route add -host 192.168.10.20 dev eth1
route -n
# 在node2上执行:
route add -host 192.168.10.10 dev eth1
route -n
(4).将两节点进行时间同步。
# 两节点都执行
ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com
(5).两节点安装httpd,并设置不同页面内容以方便测试。
# node1上执行:
yum -y install httpd
echo "response from node1" >/var/www/html/index.html
# node2上执行:
yum -y install httpd
echo "response from node2" >/var/www/html/index.html
(6).提供配置文件ha.cf。由于此处采用广播方式,两节点ha.cf内容完全一致。
cp /etc/ha.d/ha.cf /etc/ha.d/ha.cf.bak
cat <<eof>/etc/ha.d/ha.cf
logfile /var/log/ha-log
logfacility local0
keepalive 2
deadtime 30
warntime 10
initdead 120
udpport 694
bcast eth1
auto_failback on
node node1.longshuai.com
node node2.longshuai.com
ping 192.168.100.1 # 虚拟机网关
respawn hacluster /usr/local/lib/heartbeat/ipfail
apiauth ipfail gid=haclient uid=hacluster
eof
(7).提供配置文件authkeys。两节点authkeys内容完全一致。
# 在node1上执行:
chmod 600 /etc/ha.d/authkeys
echo -e "auth 3\n3 md5 `openssl rand -base64 20`" >>/etc/ha.d/authkeys
scp /etc/ha.d/authkeys node2:/etc/ha.d/
(8).提供配置文件haresources,两节点内容一致。
# 在node1上执行:
cp /etc/ha.d/haresources /etc/ha.d/haresources.bak
echo "node1.longshuai.com IPaddr2::192.168.100.33/24/eth0 httpd" >/etc/ha.d/haresources
scp /etc/ha.d/haresources node2:/etc/ha.d/
最后,启动两端heartbeat节点,并通过访问VIP的web页面进行测试。可以查看日志/var/log/ha-log,看看heartbeat节点之间是如何等待对方并工作的。
heartbeat单独提供高可用服务的更多相关文章
- Nfs+Drdb+Heartbeat 数据存储高可用服务架构方案
一.方案的应用场景 适用于2千万-3千万PV架构的网站,Nfs数据存储高可用服务方案 备注:互联网排名前30左右公司常用的架构 二.生产环境方案部署原理图 三.生产环境服务器硬件配置: 生产环境中采用 ...
- 使用kuernetes提供高可用的logstash服务
在kubernetes集群中部署logstash步骤如下: 1:logstash安装文件(目前最新版本2.3.4): 2:编写Dockerfile及执行点脚本文件run.sh,并且修改logstash ...
- 每天响应数亿次请求,腾讯云如何提供高可用API服务?
每天响应数亿次请求,腾讯云如何提供高可用API服务? https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/OPwlHcqkaTT_gcwHfr5Shw 李阳 云加社区 2020-09-16 导语 | ...
- Heartbeat+LVS构建高可用负载均衡集群
1.heartbeat简介: Heartbeat 项目是 Linux-HA 工程的一个组成部分,它实现了一个高可用集群系统.心跳服务和集群通信是高可用集群的两个关键组件,在 Heartbeat 项目里 ...
- Nginx (三) 使用Keepalived搭建高可用服务
Nginx可以实现高并发反向代理,实现负载均衡,但是有个问题就是Nginx是单点的.如果Nginx故障,则整个服务将会处于不可用状态.所以我们就需要想办法让nginx高可用,即使一个Nginx宕机,还 ...
- 阿里云AHAS应用高可用服务初体验
AHAS是阿里云提供的应用高可用服务(Application High Availability Service)产品. 高可用这个关键词可以说是互联网及软件开发行业热度一直很高的词语了,阿里云推出的 ...
- Heartbeat+DRBD+MySQL高可用方案
1.方案简介 本方案采用Heartbeat双机热备软件来保证数据库的高稳定性和连续性,数据的一致性由DRBD这个工具来保证.默认情况下只有一台mysql在工作,当主mysql服务器出现问题后,系统将自 ...
- Heartbeat+DRBD+MySQL高可用方案【转】
转自Heartbeat+DRBD+MySQL高可用方案 - yayun - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/gomysql/p/3674030.html 1.方案简介 本方案采用 ...
- Redis Sentinel 高可用服务搭建
阅读目录: 关于 Redis 的概念 关于 Redis Sentinel 的概念 搭建 Redis Server(master) 搭建 Redis Server(slave) 搭建 Redis Sen ...
随机推荐
- python2 => python3 踩坑集合
报错内容: ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'md5' 解析: 这是 python2 的库,python3 已经把它包含进 hashlib 库里了 解决方法 ...
- PowerDesigner 简单应用(转载)
PowerDesigner是一款功能非常强大的建模工具软件,足以与Rose比肩,同样是当今最著名的建模软件之一.Rose是专攻UML对象模型的建模工具,之后才向数据库建模发展,而PowerDesign ...
- STL中坑爹的max函数
hdu1754永远难忘的痛,参数最好不要传耗时特别长的函数,因为会调用两次,如果是递归的话,不知道多少次呢.. 切记!切记!切记! 例如: //return max(getAns(root<&l ...
- JavaScript网页全屏API
在大多数的浏览器中都有实现网页全屏显示的功能,并且大部分浏览器实现全屏显示和退出全屏显示的快捷键通常是F11和Esc两个按键.如今,W3C已经制定了关于网页全屏显示的API,利用这个API 可以实现网 ...
- 在浏览器地址栏输入URL,按下回车后究竟发生了什么?
1.DNS 在浏览器中输入URL后,首先要进行DNS解析,DNS解析的顺序为: 浏览器缓存 本地hosts文件 系统缓存 路由器缓存 DNS服务器迭代查询 2.发送请求 通过DNS得到目标的IP地址后 ...
- linux 邮件服务器
邮件通信系统协议及概念:软件角色:MUA:邮件客户端MTA:邮件服务端MDA:邮件服务端模块邮件客户端:Mail User Agent,邮件用户代理邮件服务端:Mail Transfer Agent, ...
- 关于echarts
昨天随手玩了下echarts,看见同事纠结于echarts的兼容问题. 最简单的echarts(官网的): <div id="main" style="width: ...
- FULL HD
FULL HD(全高清)是Full High Definition的简写,是指物理分辨率高达1920×1080显示(包括1080i和1080P),其中i(interlace)是指隔行扫描:P(Prog ...
- R+openNLP︱openNLP的六大可实现功能及其在R语言中的应用
每每以为攀得众山小,可.每每又切实来到起点,大牛们,缓缓脚步来俺笔记葩分享一下吧,please~ --------------------------- openNLP是NLP中比较好的开源工具,R语 ...
- Exynos4412从SD卡启动的简单网络文件系统制作
Exynos4412从SD卡启动的简单网络文件系统制作 1. 简介 嵌入式系统能够在开发板上正常运行,需要先进行系统配置,一个完整的嵌入式系统应该包含的几个部分::uboot,kernel,rootf ...
