poj 3068 Bridge Across Islands
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |||
| Total Submissions: 11196 | Accepted: 3292 | Special Judge | ||
Description
Thousands of thousands years ago there was a small kingdom located in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. The territory of the kingdom consists two separated islands. Due to the impact of the ocean current, the shapes of both the islands became convex polygons. The king of the kingdom wanted to establish a bridge to connect the two islands. To minimize the cost, the king asked you, the bishop, to find the minimal distance between the boundaries of the two islands.

Input
The input consists of several test cases.
Each test case begins with two integers N, M. (3 ≤ N, M ≤ 10000)
Each of the next N lines contains a pair of coordinates, which describes the position of a vertex in one convex polygon.
Each of the next M lines contains a pair of coordinates, which describes the position of a vertex in the other convex polygon.
A line with N = M = 0 indicates the end of input.
The coordinates are within the range [-10000, 10000].
Output
For each test case output the minimal distance. An error within 0.001 is acceptable.
Sample Input
4 4
0.00000 0.00000
0.00000 1.00000
1.00000 1.00000
1.00000 0.00000
2.00000 0.00000
2.00000 1.00000
3.00000 1.00000
3.00000 0.00000
0 0
Sample Output
1.00000 题意:求两个凸包之间的最近距离
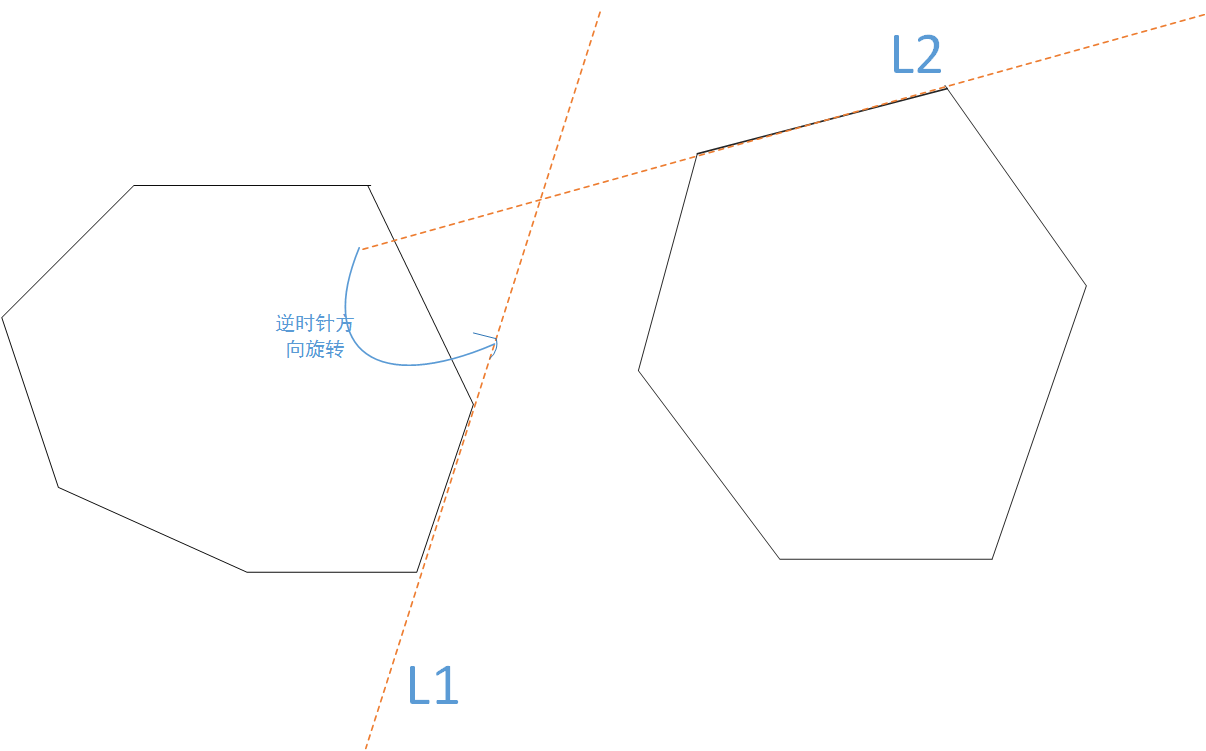
思路:找到第一个凸包的右下角的顶点和第二个凸包左上角的顶点,第一个凸包从右下角顶点开始与逆时针方向的下一个顶点作直线,暂且固定这条直线,第二个凸包的左上角的顶点也与逆时针方向下一个顶点结合作直线,判断两条直线方向,若第二条直线需要逆时针转动才能转到第一条直线的方向,那么第二条直线继续逆时针旋转,即
逆时针方向找到接下来一个顶点,这个顶点与上一个顶点形成新的直线,直到当前形成的直线与第一条直线平行或者需要顺时针旋转才能转到第一条直线的方向为止停止转动,并计算当前的两条直线所在的线段的距离,更新最短距离。之后第一条直线逆时针转动到下一个方向后继续固定,重复上述算法。。
AC代码:
Source Code Problem: User: ach11090913
Memory: 980K Time: 172MS
Language: C++ Result: Accepted
Source Code
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
#define EPS 1e-10
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
const int N_MAX = *+;
double add(double a,double b) {
if (abs(a + b) < EPS*(abs(a) + abs(b)))return ;
return a + b;
} struct P {
double x, y;
P(){}
P(double x,double y):x(x),y(y) {}
P operator +(P p) {
return P(add(x, p.x), add(y, p.y));
}
P operator -(P p) {
return P(add(x, -p.x), add(y, -p.y));
}
P operator *(P p) {
return P(x*p.x, y*p.y);
}
bool operator <(const P& p)const {
if (x != p.x)return x < p.x;
else return y < p.y;
}
double dot(P p) {
return add(x*p.x,y*p.y);
}
double det(P p) {
return add(x*p.y, -y*p.x);
}
double norm() {
return x*x + y*y;
}
double abs() {
return sqrt(norm());
} };
bool cmp_y1(const P&p,const P&q) {
if (p.y != q.y)
return p.y < q.y;
return p.x > q.x;
} struct Segment {
P p1, p2;
Segment(P p1=P(),P p2=P()):p1(p1),p2(p2) {}
};
typedef Segment Line;
typedef vector<P>Polygon; inline double cross(P A, P B, P C)
{
return (B - A).det(C - A);
} double getDistanceLP(Line l,P p) {
return fabs((l.p2 - l.p1).det(p - l.p1)) / ((l.p2 - l.p1).abs());
} double getDistanceSP(Segment s,P p) {
if ((s.p2 - s.p1).dot(p - s.p1) < 0.0)return (p - s.p1).abs();
if ((s.p1 - s.p2).dot(p - s.p2) < 0.0)return (p - s.p2).abs();
return getDistanceLP(s, p);
} double getDistance(Segment s1,Segment s2) {
return min(min(getDistanceSP(s1,s2.p1),getDistanceSP(s1,s2.p2)),
min(getDistanceSP(s2,s1.p1),getDistanceSP(s2,s1.p2)));
} Polygon po1, po2;
int N, M; vector<P> judge_clockwise(vector<P>p) {
for (int i = ; i < p.size()-;i++) {
//double tmp = (p[i + 1] - p[i]).det(p[i + 2] - p[i + 1]);
double tmp = cross(p[i], p[i + ], p[i + ]);
if (tmp > EPS)return p;
else if (tmp < -EPS) {
reverse(p.begin(), p.end());
return p;
}
}
return p;
} double solve() {
int i = , j = ;
for (int k = ; k < N;k++) {
if (!cmp_y1(po1[i], po1[k]))i = k;//i为凸包右下角
}
for (int k = ; k < M; k++) {
if (cmp_y1(po2[j], po2[k]))j = k;//j为凸包左上角
}
double res = INF;
for (int k = ; k< N;k++) {
while ((po1[i] - po1[(i + ) % N]).det(po2[(j + ) % M] - po2[j]) < ) j = (j + ) % M;
Segment s1, s2;
s1.p1 = po1[i], s1.p2 = po1[(i + ) % N],s2.p1=po2[j],s2.p2=po2[(j+)%M];
res = min(res, getDistance(s1, s2));
//cout << s1.p1.x << " " << s1.p1.y << " " << s1.p2.x << " " << s1.p2.y <<" " << s2.p1.x << " " << s2.p1.y << " " << s2.p2.x <<" "<< s2.p2.y << endl;
i = (i + ) % N;
}
return res;
} int main() { while (scanf("%d%d",&N,&M)&&N) {
po1.clear();
po2.clear();
for (int i = ; i < N;i++) {
double x, y;
scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y);
po1.push_back(P(x,y));
}
po1=judge_clockwise(po1);
for (int i = ; i < M;i++) {
double x, y;
scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);
po2.push_back(P(x,y));
}
po2=judge_clockwise(po2);
printf("%.5f\n",solve());
}
return ;
}
poj 3068 Bridge Across Islands的更多相关文章
- POJ 3608 Bridge Across Islands [旋转卡壳]
Bridge Across Islands Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 10455 Accepted: ...
- POJ 3608 Bridge Across Islands(旋转卡壳,两凸包最短距离)
Bridge Across Islands Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 7202 Accepted: ...
- POJ 3608 Bridge Across Islands(计算几何の旋转卡壳)
Description Thousands of thousands years ago there was a small kingdom located in the middle of the ...
- POJ 3608 Bridge Across Islands --凸包间距离,旋转卡壳
题意: 给你两个凸包,求其最短距离. 解法: POJ 我真的是弄不懂了,也不说一声点就是按顺时针给出的,不用调整点顺序. 还是说数据水了,没出乱给点或给逆时针点的数据呢..我直接默认顺时针给的点居然A ...
- ●POJ 3608 Bridge Across Islands
题链: http://poj.org/problem?id=3608 题解: 计算几何,求两个凸包间的最小距离,旋转卡壳 两个凸包间的距离,无非下面三种情况: 所以可以基于旋转卡壳的思想,去求最小距离 ...
- POJ 3608 Bridge Across Islands (旋转卡壳)
[题目链接] http://poj.org/problem?id=3608 [题目大意] 求出两个凸包之间的最短距离 [题解] 我们先找到一个凸包的上顶点和一个凸包的下定点,以这两个点为起点向下一个点 ...
- poj 3608 Bridge Across Islands
题目:计算两个不相交凸多边形间的最小距离. 分析:计算几何.凸包.旋转卡壳.分别求出凸包,利用旋转卡壳求出对踵点对,枚举距离即可. 注意:1.利用向量法判断旋转,而不是计算角度:避免精度问题和TLE. ...
- POJ - 3608 Bridge Across Islands【旋转卡壳】及一些有趣现象
给两个凸包,求这两个凸包间最短距离 旋转卡壳的基础题 因为是初学旋转卡壳,所以找了别人的代码进行观摩..然而发现很有意思的现象 比如说这个代码(只截取了关键部分) double solve(Point ...
- poj 3608 Bridge Across Islands 两凸包间最近距离
/** 旋转卡壳,, **/ #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include ...
随机推荐
- python中yield的用法详解
首先我要吐槽一下,看程序的过程中遇见了yield这个关键字,然后百度的时候,发现没有一个能简单的让我懂的,讲起来真TM的都是头头是道,什么参数,什么传递的,还口口声声说自己的教程是最简单的,最浅显易懂 ...
- jfinal的配置文件详解
1.去官网下载最新的jar包(我这是JFinal-lib-2.2) tomcat+mysql 所需要的jar 2.配置web.xml <filter> <filter-name> ...
- linux 下使用 curl 访问带多参数,GET掉参数解决方案
url 为 http://mywebsite.com/index.php?a=1&b=2&c=3 web形式下访问url地址,使用 $_GET是可以获取到所有的参数 curl -s ...
- 用promise封装ajax
首先贴代码 var ajaxOptions = { url: 'url', method: 'GET', async: true, data: null, dataType: 'text', } fu ...
- 在物理机上,用U盘安装esxi虚拟化环境
一般使用U盘安装centos镜像,可使用镜像刻录工具UltraISO,详细方法参照如下链接: https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/647f0115ee55ba7f214 ...
- LeetCode之Weekly Contest 91
第一题:柠檬水找零 问题: 在柠檬水摊上,每一杯柠檬水的售价为 5 美元. 顾客排队购买你的产品,(按账单 bills 支付的顺序)一次购买一杯. 每位顾客只买一杯柠檬水,然后向你付 5 美元.10 ...
- vue里的数据
背景: 一个项目完工在即,鉴于此,前端使用了vue,写下此栏,以供日后翻阅, 会涉及到我所运用到的vue相关知识,需要一定的js基础. 默认vue的single-file-components(单文件 ...
- Python学习笔记:open函数和with临时运行环境(文件操作)
open函数 1.open函数: file=open(filename, encoding='utf-8'),open()函数是Python内置的用于对文件的读写操作,返回的是文件的流对象(而不是文件 ...
- leetcode-20-Dynamic Programming
303. Range Sum Query - Immutable 解题思路: Note里说sumRange会被调用很多次..所以简直强烈暗示要做cache啊...所以刚开始,虽然用每次都去遍历数组求和 ...
- WPF触控程序的开发(一)——有用的资源
迟来的一篇博文,每次都要撞到月末,这个月实在太忙了,除了在公司上班,还接了个单子,用wpf做一个触屏软件,类似iphone的相册功能.先说搭建开发环境吧,我是不可能去买个平板来的,再说基于win7的程 ...
