《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第四章(BeanFactory生命周期)









package com.smart; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.*; public class Car implements BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean{
private String brand;
private String color;
private int maxSpeed; private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private String beanName; //默认构造函数
public Car(){System.out.println("调用Car()构造函数");} //带参构造函数
public Car(String brand, String color, int maxSpeed) {
this.brand = brand;
this.color = color;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
} //未带参方法
public void introduce() {
System.out.println("brand:" + brand + ";color:" + color + ";maxSpeed:" + maxSpeed);
} public String getBrand() {
return brand;
} public void setBrand(String brand) {
System.out.println("调用setBrand()设置属性");
this.brand = brand;
} public String getColor() {
return color;
} public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
} public int getMaxSpeed() {
return maxSpeed;
} public void setMaxSpeed(int maxSpeed) {
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
} // BeanFactoryAware接口方法
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory().");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
} // BeanNameAware接口方法
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println("调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName().");
this.beanName = s;
} // DisposableBean接口方法
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用DisposableBean.destroy().");
} // InitializingBean接口方法
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用InitialingBean.afterPropertiesSet().");
} // 通过<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始方法
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("调用init-method属性指定的myInit(), 将maxSpeed设置为240");
this.maxSpeed = 240;
} //同过<bean>的destroy-method属性指定的销毁方法
public void myDestroy() {
System.out.println("调用destroy-method属性指定的myDestroy().");
} }

package com.smart.beanfactory; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter; import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor; public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter { @Override
// 1.接口方法,在实例化Bean前调用
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 1-1. 仅对容器中的car Bean进行处理
if ("car".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation().");
}
return null;
} @Override
// 2.接口方法,在实例化Bean后调用
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("car".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("调用InstantiationAwarePostProcessor.postProcessorAfterInstantiation().");
}
return true;
} @Override
// 3.接口方法,在设置某个属性时调用
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 3-1. 仅对容器中的car Bean进行处理, 还可以同过pds入参进行过滤
if ("car".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("调用InstantiationAwarePostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues().");
}
return pvs;
}
}

package com.smart.beanfactory; import com.smart.Car;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("car".equals(beanName)) {
Car car = (Car) bean;
if (car.getColor() == null) {
System.out.println("调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()," +
"若color为空,设置为默认黑色");
car.setColor("黑色");
}
}
return bean;
} public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("car".equals(beanName)) {
Car car = (Car) bean;
if (car.getMaxSpeed() >= 200) {
System.out.println("调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization()," +
"将maxSpeed设置为200");
car.setMaxSpeed(200);
}
}
return bean;
}
}

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.smart.Car"
init-method="myInit"
destroy-method="myDestroy"
p:brand="红旗CA72"
p:maxSpeed="200"/> </beans>


package com.smart.beanfactory; import com.smart.Car;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; public class BeanLifeCycle {
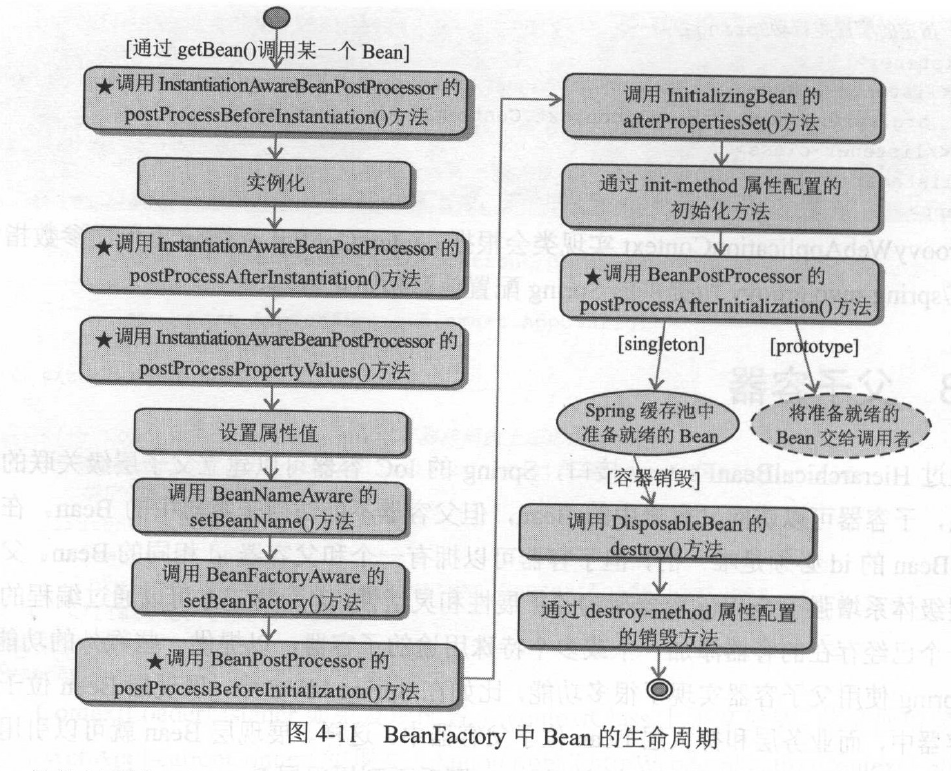
public static void lifeCycleInBeanFactory() {
// 1. 装载配置文件并启动容器
Resource res = new ClassPathResource("beans.xml");
BeanFactory bf = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((DefaultListableBeanFactory) bf);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res); //后处理器的实际调用顺序与注册顺序无关,在具有多个后处理器的情况下,必须通过实现
//org.springframework.core.Ordered接口来确定调用顺序
// 2. 向容器中注册MyBeanPostProcessor后处理器
((ConfigurableBeanFactory) bf).addBeanPostProcessor(new MyBeanPostProcessor());
// 3. 向容器中注册MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器
((ConfigurableBeanFactory) bf).addBeanPostProcessor(new MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor()); // 4. 第一次从容器中获得car, 将触发容器实例化该Bean,这将引发Bean生命周期方法的调用
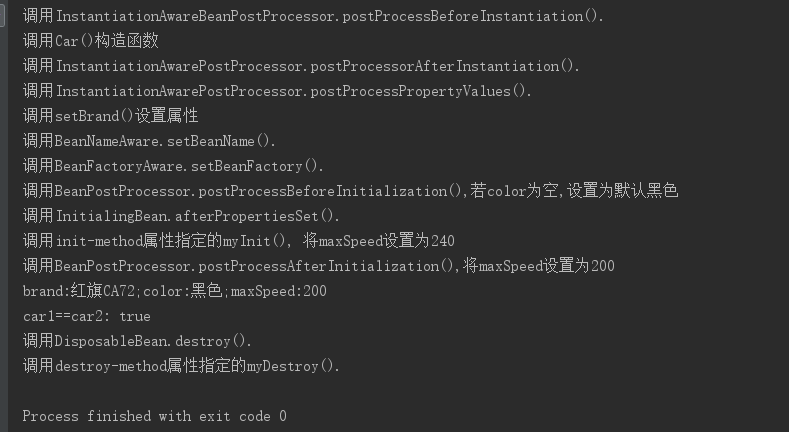
Car car1 = (Car) bf.getBean("car");
car1.introduce();
car1.setColor("红色"); // 5. 第二次从容器中获取car, 直接从缓存池中获取
Car car2 = (Car) bf.getBean("car"); // 6. 查看car1和car2是否指向同一引用
System.out.println("car1==car2: " + (car1 == car2)); // 7. 关闭容器
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) bf).destroySingleton("car"); } public static void main(String[] args) {
lifeCycleInBeanFactory();
}
}







《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第四章(BeanFactory生命周期)的更多相关文章
- 《精通Spring4.x企业应用开发实战》第三章
这一章节主要介绍SpringBoot的使用,也是学习的重点内容,之后就打算用SpringBoot来写后台,所以提前看一下还是很有必要的. 3.SpringBoot概况 3.1.1SpringBoot发 ...
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第四章(资源访问)
package com.smart.resource; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springf ...
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第七章(创建增强类)
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第七章(AOP基础知识、jdk动态代理,CGLib动态代理)
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第七章(AOP概念)
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第六章(容器事件)
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第六章(国际化)
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第六章(引用Bean的属性值)
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第六章(使用外部属性文件)
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第六章(属性编辑器)
随机推荐
- npm ERR! fatal: unable to connect to github.com
https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_30809315/article/details/86520093 git config --global url."https:// ...
- 开发过程中,本地分支和远程跟踪分支发生了diverge
1 git基本概念梳理 1.1 git的工作目录.暂存区和HEAD指向的版本库以及branch的概念 一个branch就是整个产品的一套代码,而工作目录中就是存放的本branch最新的代码,HEAD指 ...
- redis自启动
$ vi /etc/init.d/redis # chkconfig: 2345 90 10 # description: Redis is a persistent key-value databa ...
- thinkphp5 (最棒的php开源框架)
tp5的唯一可访问目录是public,即项目根目录: http://localhost/tp5/public/ 开发规范: 类库.函数文件统一以.php为后缀 类(命名和路径)和命名空间保持一致 类文 ...
- 卸载apache服务
卸载服务,管理员身份运行命令行程序,输入 sc delete apache2.2
- LeetCode:分发饼干【455】
LeetCode:分发饼干[455] 题目描述 假设你是一位很棒的家长,想要给你的孩子们一些小饼干.但是,每个孩子最多只能给一块饼干.对每个孩子 i ,都有一个胃口值 gi ,这是能让孩子们满足胃口的 ...
- 一个商品SKU是怎么生成的
首先说一说什么是SKU.......自己百度去... 类似京东上面,未来人类S5这个台笔记本(没错,我刚入手了) 都是S5这个型号,但是因为CPU,显卡,内存,硬盘等不同,价格也不一样.CPU,显卡, ...
- TensorFlow框架(4)之CNN卷积神经网络详解
1. 卷积神经网络 1.1 多层前馈神经网络 多层前馈神经网络是指在多层的神经网络中,每层神经元与下一层神经元完全互连,神经元之间不存在同层连接,也不存在跨层连接的情况,如图 11所示. 图 11 对 ...
- 51nod 40分算法题
1737:见前2篇随笔. 1677:题意:给定一个n节点树,一个整数k,n个节点任意选k个出来,对于每一种选择方案,ans累加上使这k个点联通的最小边数,输出ans%1e9+7. 一句话题解:考虑每一 ...
- smokeping 微信报警配置
1. 准备alert脚本,用来调用微信脚本 #!/bin/bash alertname=$ target=$ losspattern=$ rtt=$ smokename="hq_to_idc ...
