关于 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 及 tf.clip_by_value
In order to train our model, we need to define what it means for the model to be good. Well, actually, in machine learning we typically define what it means for a model to be bad. We call this the cost, or the loss, and it represents how far off our model is from our desired outcome. We try to minimize that error, and the smaller the error margin, the better our model is.
One very common, very nice function to determine the loss of a model is called "cross-entropy." Cross-entropy arises from thinking about information compressing codes in information theory but it winds up being an important idea in lots of areas, from gambling to machine learning. It's defined as:
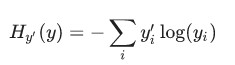
Where y is our predicted probability distribution, and y′ is the true distribution (the one-hot vector with the digit labels). In some rough sense, the cross-entropy is measuring how inefficient our predictions are for describing the truth. Going into more detail about cross-entropy is beyond the scope of this tutorial, but it's well worthunderstanding.
To implement cross-entropy we need to first add a new placeholder to input the correct answers:
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
Then we can implement the cross-entropy function, 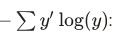
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
First, tf.log computes the logarithm of each element of y. Next, we multiply each element of y_ with the corresponding element of tf.log(y). Then tf.reduce_sum adds the elements in the second dimension of y, due to the reduction_indices=[1] parameter. Finally, tf.reduce_mean computes the mean over all the examples in the batch.
Note that in the source code, we don't use this formulation, because it is numerically unstable. Instead, we apply tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits on the unnormalized logits (e.g., we call softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits on tf.matmul(x, W) + b), because this more numerically stable function internally computes the softmax activation. In your code, consider usingtf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits instead.
大意是:如果使用 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
来计算交叉熵,则需要使用 tf.clip_by_value 来使某些求 log 的值,因为 log 会产生 none (如 log-3 ), 用它来限定不出现none,具体使用方式如下:
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(tf.clip_by_value(y_conv, 1e-10, 1.0)))但后来有人用了一个更好的方法来避免none:
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv + 1e-10))具体参见 http://stackoverflow.com/questions/33712178/tensorflow-nan-bug 的讨论。
而如果直接用 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 则你再没有上面的后顾之忧了,它自动解决了上面的问题。
关于 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 及 tf.clip_by_value的更多相关文章
- 【TensorFlow】tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits的用法
在计算loss的时候,最常见的一句话就是 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits ,那么它到底是怎么做的呢? 首先明确一点,loss是代价值,也就是我们要最小化 ...
- 深度学习原理与框架-Tensorflow卷积神经网络-卷积神经网络mnist分类 1.tf.nn.conv2d(卷积操作) 2.tf.nn.max_pool(最大池化操作) 3.tf.nn.dropout(执行dropout操作) 4.tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(交叉熵损失) 5.tf.truncated_normal(两个标准差内的正态分布)
1. tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') # 对数据进行卷积操作 参数说明:x表示输入数据,w表示卷积核, stride ...
- [TensorFlow] tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits的用法
在计算loss的时候,最常见的一句话就是tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits,那么它到底是怎么做的呢? 首先明确一点,loss是代价值,也就是我们要最小化的值 ...
- tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits的用法
http://blog.csdn.net/mao_xiao_feng/article/details/53382790 计算loss的时候,最常见的一句话就是tf.nn.softmax_cross_e ...
- tf.nn.softmax & tf.nn.reduce_sum & tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
tf.nn.softmax softmax是神经网络的最后一层将实数空间映射到概率空间的常用方法,公式如下: \[ softmax(x)_i=\frac{exp(x_i)}{\sum_jexp(x_j ...
- tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits()函数的使用方法
import tensorflow as tf labels = [[0.2,0.3,0.5], [0.1,0.6,0.3]]logits = [[2,0.5,1], [0.1,1,3]] a=tf. ...
- 1、求loss:tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None))
1.求loss: tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None)) 第一个参数log ...
- tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 分类
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None) 参数: logits:就是神经网络最后一层的输出,如果有batch ...
- 深度学习原理与框架-图像补全(原理与代码) 1.tf.nn.moments(求平均值和标准差) 2.tf.control_dependencies(先执行内部操作) 3.tf.cond(判别执行前或后函数) 4.tf.nn.atrous_conv2d 5.tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(反卷积) 7.tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(判断sess是否存在
1. tf.nn.moments(x, axes=[0, 1, 2]) # 对前三个维度求平均值和标准差,结果为最后一个维度,即对每个feature_map求平均值和标准差 参数说明:x为输入的fe ...
随机推荐
- IEnumerable扩展
void Main() { // This uses a custom 'Pair' extension method, defined below. Customers .Select (c =&g ...
- Unix系统编程()main函数的命令行参数
命令行参数输入双引号是什么效果? 好像可以去空格化.
- dirname(__FILE__) 的使用总结 1(转)
dirname(__FILE__) php中定义了一个很有用的常数,即 __file__ 这个内定常数是当前php程序的就是完整路径(路径+文件名). 即使这个文件被其他文件引用(include或re ...
- nginx php-fpm安装手记
首先下载nginx,nginx下载地址:http://www.nginx.org/download/nginx-0.8.53.tar.gz[root@winsyk ~]# mkdir -p /usr/ ...
- 【iOS越狱开发】如何将应用打包成.ipa文件
在项目开发中,我们常常需要将工程文件打包成.ipa文件,提供给越狱的iphone安装. 下面是一种方法: 1.首先应该给工程安装好配置文件(这里不再敖述),在ios device的状态下,运行成功. ...
- hdu6038 Function 函数映射
/** 题目:hdu6038 Function 链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6038 题意:给定一个a排列[0,n-1],一个b排列[0, ...
- import _mysql----ImportError: DLL load failed: %1 不是有效的 Win32 应用程序。
背景:安装了mysql,练习sql 操作,提示 ImportError DLL load failed: %1 不是有效的 Win32 应用程序 解决方法: 操作系统win10,64位,查看安装的my ...
- php linux 创建文件夹权限问题
$path = "DataMsg/"; if(is_dir($path)==false){ @mkdir($path,0777); } windows 上创建没问题.但在linux ...
- 什么是AOP和OOP,IOC和DI有什么不同?
什么是AOP和OOP,IOC和DI有什么不同? 解答: 1)面向对象编程(Object Oriented Programming,OOP,面向对象程序设计)是一种计算机编程架构.AOP是OOP的延续, ...
- Chem 3D中怎么创建立体模型
ChemDraw作为一款很受大家欢迎的化学绘图软件,其在绘制平面化学方面的功能已经非常的强大了,其实它也可以绘制3D图形.Chem 3D就是绘制3D图形的重要组件.而且为了满足不同的用户绘图的需求,可 ...
