Install TightVNC Server in RHEL/CentOS and Fedora to Access Remote Desktops
Virtual Networking Computing (VNC) is a Kind of remote sharing system that makes it possible to take control of any other computer connected to internet. Keyboard and mouse clicks can easily transmit from one computer to another. It helps administrator and technical staff to manage their servers and desktops without being to the same location physically.
VNC is an open source application created in late 1990′s. It is independent and is compatible with Windows and Unix/Linux. Means a normal Windows based user can interact with Linux based system without any hazel.
To use VNC you must have TCP/IP connection and VNC viewer client to connect to a computer running VNC server component. The server transmits a duplicate display of a remote computer to the viewer.
This artilce demonstrates how to install VNC Server using TightVNC a much enhanced version of a older VNC program, with GNOME Desktop remote access on RHEL, CentOS andFedora systems.
Step 1: Installing GNOME Desktop
If you’ve installed a minimal version of Operating System, which gives only a command-line interface not GUI. Then you need to install a GUI (Graphical User Interface) withGNOME Desktop. The GNOME desktop provides a lightweight desktop environment that works very well on remote VNC desktops.
[root@tecmint ~]# yum groupinstall "X Window System" "Desktop"
Step 2: Installing TightVNC Server
TightVNC a remote desktop control software that enables us to connect to remote desktops. To install, use the following yum command as shown below.
[root@tecmint ~]# yum -y install tigervnc-server xorg-x11-fonts-Type1
Step 3: Create a Normal VNC User
Create a normal user, that will be used to connect to remote desktop. For example, I’ve used “tecmint” as a user, you can choose your own username.
[root@tecmint ~]# useradd tecmint
[root@tecmint ~]# passwd tecmint
Changing password for user tecmint.
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
Step 4: Set VNC Password for User
Create a new password for newly created user. Login to the user (su – tecmint) and run ‘vncpasswd‘ to set the VNC password for the user.
Note : This password is for accessing VNC remote desktop, and the password we created instep 3 is for accessing SSH.
[root@tecmint ~]# su - tecmint
[tecmint@tecmint ~]$ vncpasswd
Password:
Verify:
The above command ask you to supply password twice and creates “.vnc” directory under user’s home directory with passwd file inside it. You can check the password file is created, by using following command.
# ls -l /home/tecmint/.vnc
-rw------- 1 tecmint tecmint 8 Jul 14 21:33 passwd
Now exit from user login and return to root user login.
[tecmint@tecmint ~]$ exit
exit
Step 5: Create VNC Xstartup Script
Create the xstartup script as root user. This can be created by starting the VNC server.
[root@tecmint ~]# /etc/init.d/vncserver start Starting VNC server: 1:tecmint
New 'tecmint.com:1 (tecmint)' desktop is tecmint.com:1 Starting applications specified in /home/tecmint/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/tecmint/.vnc/tecmint.com:1.log
[ OK ]
Next, check whether xstartup script is created under (tecmint) user’s home directory, do “ls -l” command.
[root@tecmint ~]# ls -l /home/tecmint/.vnc/
-rw-------. 1 tecmint tecmint 8 Jul 15 12:27 passwd
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 tecmint tecmint 654 Oct 11 2012 xstartup
Once, it created, set a desktop resolution in xstartup file. For this, you must stop running VNC service.
[root@tecmint ~]# /etc/init.d/vncserver stop Shutting down VNC server: 1:tecmint [ OK ]
Step 6: Setting Xstarup Resolution
Open file “/etc/sysconfig/vncservers” file your choice of editor. Here I’m using “nano” editor. Create new VNC Session for “tecmint” with below command. where “-geomerty” is used define desktop resolution.
[root@tecmint ~]# nano /etc/sysconfig/vncservers
And add following lines to it at the bottom of file. Save and close it.
## Single User ##
VNCSERVERS="1:tecmint"
VNCSERVERARGS[1]="-geometry 1280x1024"
If you’re dealing with multiple users, first create a vncpasswd for all user’s as described above in step 4, and then add those user’s to the VNCSERVERS line and add aVNCSERVERARGS[x] entry as shown below. Where ‘x‘ is the ID number.
## Multiple Users ##
VNCSERVERS="2:ravi 3:navin 4:avishek"
VNCSERVERARGS[2]="-geometry 1280x1024"
VNCSERVERARGS[3]="-geometry 1280x1024"
VNCSERVERARGS[4]="-geometry 1280x1024"
Step 7: Starting TightVNC Server
After making all changes, run the following command to start again the VNC server. Before starting VNC session to “tecmint” user, let me give you a small intro about Port Numbers and ID‘s. By Default VNC runs on Port 5900 and ID:0 (which is for root user). In our scenario I’ve created tecmint, ravi, navin and avishek. So, the ports andid’s are used by these users as follows
User's Port's ID's
5900 root :0
5901 tecmint :1
5902 ravi :2
5903 navin :3
5904 avishek :4
So, here user “tecmint” will get port 5901 and id as :1 and so on. If you’ve created another user say (user5) then he will get port 5905 and id:5 and so on for each user you creates.
[root@tecmint ~]# /etc/init.d/vncserver start Starting VNC server: 1:tecmint
New 'tecmint.com:1 (tecmint)' desktop is tecmint.com:1 Starting applications specified in /home/tecmint/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/tecmint/.vnc/tecmint.com:1.log 2:ravi
New 'tecmint.com:2 (ravi)' desktop is tecmint.com:2 Starting applications specified in /home/ravi/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/ravi/.vnc/tecmint.com:2.log 3:navin
New 'tecmint.com:3 (navin)' desktop is tecmint.com:3 Starting applications specified in /home/navin/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/navin/.vnc/tecmint.com:3.log 4:avishek
New 'tecmint.com:4 (avishek)' desktop is tecmint.com:4 Starting applications specified in /home/avishek/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/avishek/.vnc/tecmint.com:4.log [ OK ]
Step 8: Open VNC Ports on Firewall
Open port on iptables, say for user (tecmint) at 5901.
[root@tecmint ~]# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 5901 -j ACCEPT
For multiple users, ravi, navin and avishek. I open ports 5902, 5903 and 5904respectively.
[root@tecmint ~]# iptables -I INPUT 5 -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp -m multiport --dports 5902:5904 -j ACCEPT
Restart Iptables service.
[root@tecmint ~]# service iptables save
[root@tecmint ~]# service iptables restart
Step 9: Download VNC Client
Now go to your Windows or Linux machine and download VNC Viewer client and install in your system to access the desktop.
Step 10: Connect to Remote Desktop Using Client
After you installed the VNC Viewer client, open it you’ll get similar to below screen. Enter VNC Server IP address along with VNC ID (i.e 1) for user tecmint.
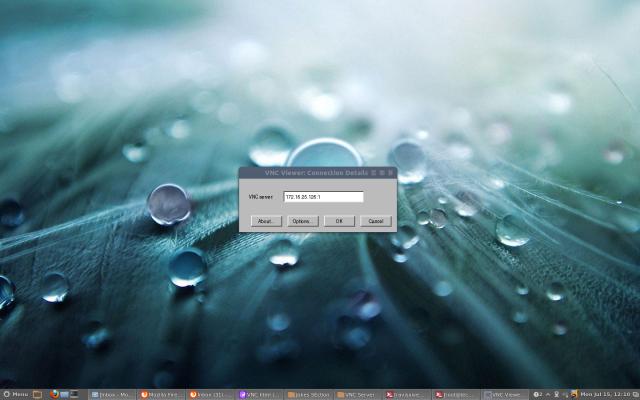
Enter VNC Server IP Address
Enter password that we created with “vncpasswd” command.
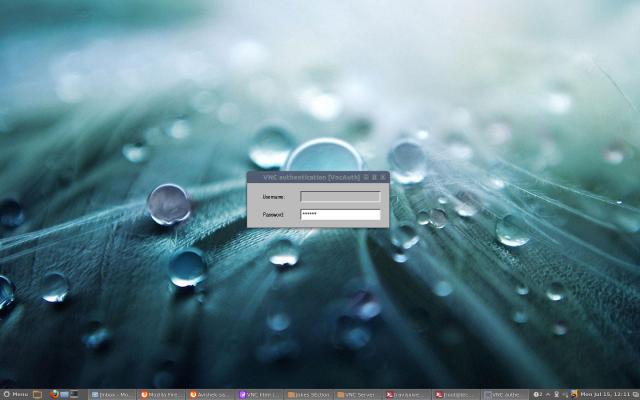
Enter VNC User Password
That’s it, you connected to your Remote Desktop.
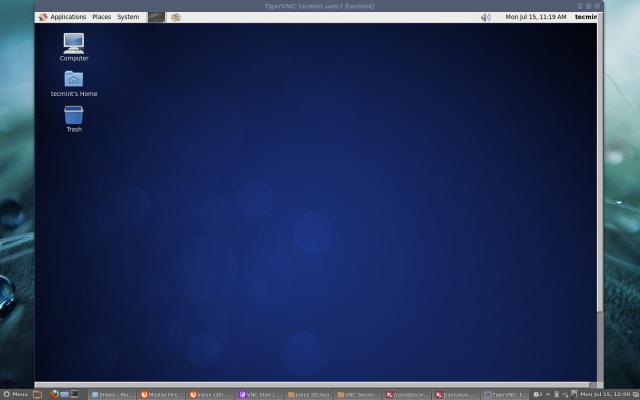
VNC Remote Desktop
Read Also : Access VNC Desktop from Web Browser
from:http://www.tecmint.com/install-tightvnc-remote-desktop/
Install TightVNC Server in RHEL/CentOS and Fedora to Access Remote Desktops的更多相关文章
- Installation of NVIDIA Drivers in RHEL/CentOS and Fedora
1.首先安装所需的软件: # yum groupinstall "Development Tools" # yum install kernel-devel kernel-head ...
- Google Chrome 55 Released – Install on RHEL/CentOS 7/6 and Fedora 25-20
Google Chrome is a freeware web browser developed by Google Inc. Google Chrome team proudly announce ...
- Install LAMP Server (Apache, MariaDB, PHP) On CentOS/RHEL/Scientific Linux 7
Install LAMP Server (Apache, MariaDB, PHP) On CentOS/RHEL/Scientific Linux 7 By SK - August 12, 201 ...
- Install Apache 2.2.15, MySQL 5.5.34 & PHP 5.5.4 on RHEL/CentOS 6.4/5.9 & Fedora 19-12 [转]
Step 1: Installing Remi Repository ## Install Remi Repository on Fedora , , , , ## rpm -Uvh http://d ...
- How to install 64-bit Google Chrome 28+ on 64-bit RHEL/CentOS 6 or 7
How to install 64-bit Google Chrome 28+ on 64-bit RHEL/CentOS 6 or 7 The problem Google developers s ...
- 转: How to Install MongoDB 3.2 on CentOS/RHEL & Fedora (简单易懂)
from: http://tecadmin.net/install-mongodb-on-centos-rhel-and-fedora/ MongoDB (named from “huMONGOus ...
- [转载]How to Install Google Chrome 39 in CentOS/RHEL 6 and Fedora 19/18
FROM: http://tecadmin.net/install-google-chrome-in-centos-rhel-and-fedora/ Google Chrome is a freewa ...
- How to install redis server on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
在本教程中,我们将学习如何在CentOS 7 / RHEL 7上安装Redis服务器. redis的缩写是REmote DIctionary Server. 它是最流行的开源,高级键值缓存和存储之一. ...
- RHEL/CentOS/Fedora各种源(EPEL、Remi、RPMForge、RPMFusion)配置
最新文章:Virson’s Blog CentOS默认自带CentOS-Base.repo源,但官方源中去除了很多有版权争议的软件,而且安装的软件也不是最新的稳定版.Fedora自带的源中也找不到很多 ...
随机推荐
- qt数据库多线程问题的解决(QSqlDatabase只能在创建它的线程中使用)
Qt数据库由QSqlDatabase::addDatabase()生成的QSqlDatabase只能在创建它的线程中使用, 在多线程中共用连接或者在另外一个线程中创建query都是不支持的几乎国内没有 ...
- HDU 3584 Cube
题目大意:给定一个体积为N*N*N立方体,每个单位小立方体A[x][y][z]里有一个值,初始值全部为0,我们可以对立方体进行一下两种操作: 0表示查询A[x][y][z]的奇偶性 1表示对子立方体的 ...
- leetcode_question_70 Climbing Stairs
You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top. Each time you can either climb ...
- jdbc操作步骤和preparedStatment相比Statment的好处
java操纵数据库封装了一组API,通过这组API可以透明的操作各种数据库,一般来讲,操纵数据库的步骤是: 一. try{ 1.加载数据库驱动 Class.forName("数据库驱动类&q ...
- Cstyle的札记,Freertos内核具体解释,第0篇
Freertos是一个硬实时内核,支持众多的微处理器架构,我们能够从它的官网(www.freertos.ort)下载它的sourcecode,同一时候也能够看出它支持了几十种的微处理器架构,这 ...
- (译)Node.js的模块-exports和module.exports
原文标题:Node.js Module – exports vs module.exports 原文链接:http://www.hacksparrow.com/node-js-exports-vs-m ...
- CSS技巧!像table一样布局div
摘自:http://www.cnblogs.com/hnyei/archive/2011/09/19/2181442.html 许多网页设计师都喜欢,将两个或者多个容器等高的并排放置,并在里面展示每个 ...
- 如何使用SublimeText风格的代码高亮样式 添加Zed Coding(EMMET)插件
因为觉得博客园自带的代码高亮样式很单一,不符合作为前端的我的审美习惯,于是下定决心要想办法折腾出一个方法来应用上另外一套代码高亮样式. 虽然探索的过程是很痛苦的,但最后还是成功了,但也不枉付出的那些努 ...
- 使用PHP搭建自己的MVC框架
一.什么是MVC MVC模式(Model-View-Controller)是软件工程中的一种软件架构模式,把软件系统分为三个基本部分:模型(Model).视图(View)和控制器(Controller ...
- nginx根据条件跳转+跳转规则
好的参考博文: nginx rewrite规则 自己写的时候参考这两个 Nginx 伪静态Rewrite,重定向Location配置总结(转) nginx rewrite规则语法 一.输入子目录跳转 ...
