PAT A1099 Build A Binary Search Tree (30 分)——二叉搜索树,中序遍历,层序遍历
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
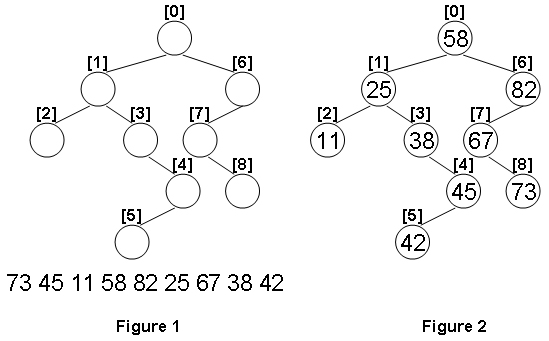
Given the structure of a binary tree and a sequence of distinct integer keys, there is only one way to fill these keys into the tree so that the resulting tree satisfies the definition of a BST. You are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of that tree. The sample is illustrated by Figure 1 and 2.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤100) which is the total number of nodes in the tree. The next N lines each contains the left and the right children of a node in the format left_index right_index, provided that the nodes are numbered from 0 to N−1, and 0 is always the root. If one child is missing, then −1 will represent the NULL child pointer. Finally N distinct integer keys are given in the last line.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of that tree. All the numbers must be separated by a space, with no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
9
1 6
2 3
-1 -1
-1 4
5 -1
-1 -1
7 -1
-1 8
-1 -1
73 45 11 58 82 25 67 38 42
Sample Output:
58 25 82 11 38 67 45 73 42
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = ;
int n;
struct node{
int data;
int l=-,r=-;
}bst[maxn];
int index=;
int q[maxn];
void inorder(int root){
if(bst[root].l!=-) inorder(bst[root].l);
bst[root].data = q[index++];
if(bst[root].r!=-) inorder(bst[root].r);
}
void level(int root){
queue<int> que;
int cnt=;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int now=que.front();
que.pop();
printf("%d",bst[now].data);
cnt++;
if(cnt!=n) printf(" ");
if(bst[now].l!=-) que.push(bst[now].l);
if(bst[now].r!=-) que.push(bst[now].r);
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
int l,r;
scanf("%d %d",&l,&r);
bst[i].l=l;
bst[i].r=r;
}
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&q[i]);
}
sort(q,q+n);
inorder();
level();
}
注意点:其实很简单的题目,又一次倒在了递归上。知道要把给定数据sort,但没想sort完后就是这棵树的中序遍历结果,只要把正常中序遍历时的打印改成赋值就能得到那棵树了。没想到中序遍历,所以自己一直在想怎么把这个有序序列一个个填到树里去,一直也没搞明白,看这题通过率0.5多,我还不会做,凉了。
看到树的题目,一般都会要建树,遍历,而对bst,一般都是要对给定序列排序的,这样能得到他的中序遍历结果,有助于建树
PAT A1099 Build A Binary Search Tree (30 分)——二叉搜索树,中序遍历,层序遍历的更多相关文章
- 1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分)(已知中序输出层序遍历)
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following propertie ...
- PAT 甲级 1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分)(不会做,重点复习,模拟中序遍历)
1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分) A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a bin ...
- PAT-1099(Build A Binary Search Tree)Java实现+二叉排序树的中序遍历和层次遍历
Build A Binary Search Tree PAT-1099 本题有意思的一个点就是:题目已经给出了一颗排序二叉树的结构,需要根据这个结构和中序遍历序列重构一棵二叉排序树. 解法:可以根据中 ...
- LeetCode 501. Find Mode in Binary Search Tree (找到二叉搜索树的众数)
Given a binary search tree (BST) with duplicates, find all the mode(s) (the most frequently occurred ...
- LeetCode第[98]题(Java):Validate Binary Search Tree(验证二叉搜索树)
题目:验证二叉搜索树 难度:Medium 题目内容: Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST). ...
- LeetCode OJ:Recover Binary Search Tree(恢复二叉搜索树)
Two elements of a binary search tree (BST) are swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing ...
- LeetCode OJ:Validate Binary Search Tree(合法的二叉搜索树)
Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST). Assume a BST is defined as ...
- LeetCode OJ:Binary Search Tree Iterator(二叉搜索树迭代器)
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the ro ...
- [LeetCode] 98. Validate Binary Search Tree(是否是二叉搜索树) ☆☆☆
描述 解析 二叉搜索树,其实就是节点n的左孩子所在的树,每个节点都小于节点n. 节点n的右孩子所在的树,每个节点都大于节点n. 定义子树的最大最小值 比如:左孩子要小于父节点:左孩子n的右孩子要大于n ...
随机推荐
- [HTML/CSS]有一种节点叫做文本节点
HTML可以看成是由节点(node)组成的树结构 我们一般都是在<p>节点里面写字符串. 在上图中,<p>节点和字符串之间有一个text, 这个text就是文本节点. 我们可以 ...
- ajax文件上传-FormData()
HTML: <form action=""> <input type="file" id="file1" name=&qu ...
- 移动端安卓手机不能识别border 0.5px解决方案
由于安卓手机无法识别border 0.5px,因此我们要用0.5px的话必须要借助css3中的-webkit-transform:scale缩放来实现, 原理:将伪元素的宽设为200%,height设 ...
- java集合类学习
以下基于jdk1.8 一. 集合类关系图 1. 接口关系图 2.集合中的类,(不包含线程安全的) 二.ArrayList 1.类定义 /** * 用“可伸缩数组”来实现List接口.实现了所有List ...
- 安卓开发_浅谈Fragment之事务添加Fragment对象
我们都知道给一个activity动态添加fragment的时候 有下面几种添加方式 看一下布局文件 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schema ...
- Expo大作战(三十四)--expo sdk api之LinearGradient(线性渐变),KeepAwake(保持屏幕不休眠),IntentLauncherAndroid,Gyroscope,
简要:本系列文章讲会对expo进行全面的介绍,本人从2017年6月份接触expo以来,对expo的研究断断续续,一路走来将近10个月,废话不多说,接下来你看到内容,讲全部来与官网 我猜去全部机翻+个人 ...
- (网页)angularjs中的验证input输入框只能输入数字和小数点
百度的资料:自己记录看下 把js的验证方法改成angular可使用的方法 AngularJS文件的写法: $scope.clearNoNum = function(obj,attr){ //先把非数字 ...
- 上下文管理器——with语句的实现
前言 with语句的使用给我们带来了很多的便利,最常用的可能就是关闭一个文件,释放一把锁. 既然with语句这么好用,那我也想让我自己写的代码也能够使用with语句,该怎么实现? 下面具体介绍怎样实现 ...
- oracle FLASHBACK TABLE
闪回表 -- 开启行迁移 ALTER TABLE employees_test ENABLE ROW MOVEMENT; UPDATE employees_test SET salary = sala ...
- 【数据结构】约瑟夫问题 C语言链表实现
1.首先,我们先来了解一下什么是约瑟夫环问题: 讲一个比较有意思的故事:约瑟夫是犹太军队的一个将军,在反抗罗马的起义中,他所率领的军队被击溃,只剩下残余的部队40余人,他们都是宁死不屈的人,所以不愿投 ...
