python写web服务器
#coding = utf-8
from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer class RequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
Page = '''
<html>
<body>
<p>Hello, world!</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
#重载do_GET方法
def do_GET(self):
self.send_response(200) #发送状态码,200是ok
self.send_header('Content-Type', 'text/html')
'''
发送http头部信息,text/html指HTML格式
另外还有诸如text/plain纯文本格式,image/gif GIF图片格式
通过头部信息浏览器就知道如何处理所发来的内容了
另外还有self.send_header('Content-Encoding','gzip')是指让浏览器按照压缩方式处理内容
另外还有很多。。。
'''
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(self.Page.encode()) #---------------------------------------------------------------------- if __name__ == '__main__':
serverAddress = ('', 8080)
server = HTTPServer(serverAddress, RequestHandler)
server.serve_forever()
简单的web服务器
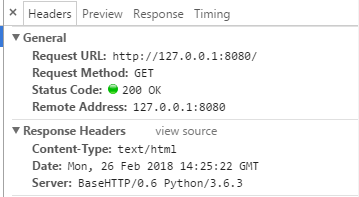
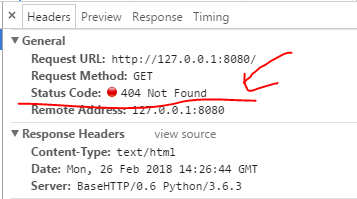
如果我把self.send_response(200)状态码改为404,那么就会出现下述情况:
#coding = utf-8
from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer class RequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
#<tr>代表一行,<td>代表一列
Page = '''
<html>
<body>
<table>
<tr> <td>Header</td> <td>Value</td> </tr>
<tr> <td>Date and time</td> <td>{date_time}</td> </tr>
<tr> <td>Client host</td> <td>{client_host}</td> </tr>
<tr> <td>Client port</td> <td>{client_port}</td> </tr>
<tr> <td>Command</td> <td>{command}</td> </tr>
<tr> <td>Path</td> <td>{path}</td> </tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
''' def do_GET(self):
page = self.create_page()
self.send_content(page) def send_content(self, page):
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header('Content-Type', 'text/html')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(page.encode()) def create_page(self):
values = {
'date_time': self.date_time_string(),
'client_host': self.client_address[0],
'client_port': self.client_address[1],
'command': self.command,
'path': self.path
}
page = self.Page.format(**values)
'''
字符串格式化函数
通过字典设置参数
site = {'name': '菜鸟教程', 'url': 'www.runoob.com'}
print('网站名:{name}, 地址:{url}'.format(**site))
'''
return page #---------------------------------------------------------------------- if __name__ == '__main__':
serverAddress = ('', 8080)
server = HTTPServer(serverAddress, RequestHandler)
server.serve_forever()
显示请求的信息

#coding = utf-8
from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer
import sys, os class serverException(Exception):
'''服务器内部错误'''
pass class RequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
errorPage = """\
<html>
<body>
<h1>Error accessing {path}</h1>
<p>{msg}</p>
</body>
</html>
""" def do_GET(self):
try:
fullPath = os.getcwd() + self.path
if not os.path.exists(fullPath): #不存在就报错
raise serverException("'{0}' not found".format(self.path))
elif os.path.isfile(fullPath): #如果是文件,则打开
self.handle_file(fullPath)
else: #其余情况
raise serverException("Unknown object '{0}'".format(self.path))
except Exception as msg:
self.handle_error(msg) def handle_error(self, msg):
content = self.errorPage.format(path=self.path, msg=msg)
self.send_content(content, 404) def send_content(self, page, status=200):
self.send_response(status)
self.send_header('Content-Type', 'text/html')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(page.encode()) def handle_file(self, fullPath):
try:
f = open(fullPath, 'r') #python3要注意是以r读还是rb读
content = f.read()
self.send_content(content)
except IOError as msg:
msg = "'{0}' cannot be read: {1}".format(self.path, msg)
self.handle_error(msg) #---------------------------------------------------------------------- if __name__ == '__main__':
serverAddress = ('', 8080)
server = HTTPServer(serverAddress, RequestHandler)
server.serve_forever()
响应静态页面
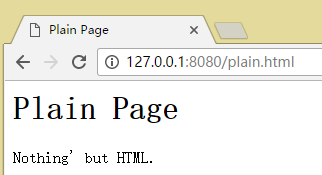
在这里的话需要把plain.html这个文件放在代码相同目录下。
测试情况如下:

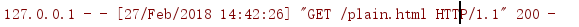
#coding = utf-8
from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer
import sys, os class serverException(Exception):
'''服务器内部错误'''
pass '''
将不同的情况单独写成一个类,最后将这些类保存在一个列表之中,这样最后遍历列表即可,不需要if-elif了
'''
class case_no_file(object):
'''路径不存在'''
def test(self, handler):
return not os.path.exists(handler.fullPath)
def act(self, handler):
raise serverException("'{0}' not found".format(handler.path)) class case_is_file(object):
'''路径是文件'''
def test(self, handler):
return os.path.isfile(handler.fullPath)
def act(self, handler):
handler.handle_file(handler.fullPath) class case_always_fail(object):
'''不满足时的默认处理类'''
def test(self, handler):
return True
def act(self, handler):
raise serverException("Unknown object '{0}'".format(handler.Path)) class case_directory_index_file(object):
'''进入根目录时显示主页'''
def index_path(self, handler):
return os.path.join(handler.fullPath, 'index.html') #前后合并
def test(self, handler):
return os.path.isdir(handler.fullPath) and os.path.isfile(self.index_path(handler))
def act(self, handler):
handler.handle_file(self.index_path(handler)) class RequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
caseList = [case_no_file(),
case_is_file(),
case_directory_index_file(),
case_always_fail()] errorPage = """\
<html>
<body>
<h1>Error accessing {path}</h1>
<p>{msg}</p>
</body>
</html>
""" def do_GET(self):
try:
self.fullPath = os.getcwd() + self.path
for case in self.caseList:
if case.test(self):
case.act(self)
break
except Exception as msg:
self.handle_error(msg) def handle_error(self, msg):
content = self.errorPage.format(path=self.path, msg=msg)
self.send_content(content, 404) def send_content(self, page, status=200):
self.send_response(status)
self.send_header('Content-Type', 'text/html')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(page.encode()) def handle_file(self, fullPath):
try:
f = open(fullPath, 'r') #python3要注意是以r读还是rb读
content = f.read()
self.send_content(content)
except IOError as msg:
msg = "'{0}' cannot be read: {1}".format(self.path, msg)
self.handle_error(msg) #---------------------------------------------------------------------- if __name__ == '__main__':
serverAddress = ('', 8080)
server = HTTPServer(serverAddress, RequestHandler)
server.serve_forever()
在url根目录显示主页
之前所做的是静态页面的显示,如果要显示动态页面的话就不能写成html的文件了,在这里可以使用CGI协议与脚本来实现动态页面。
服务器在收到客户端的请求后执行指定的CGI应用程序,CGI应用程序执行后再转换成服务器和浏览器能够理解的内容,比如说HTML页面。
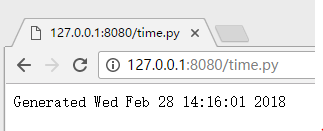
下面的例子就是做一个展示当前时间的页面,先是用python实现了一个CGI脚本time.py,当浏览器请求这个CGI脚本的时候,服务器就会去执行time.py,然后得到执行结果的一段HTML形式的字符,最后就输出即可。
在这里就用到了python库中的subprocess模块,它的功能使fork一个子进程,然后运行一个外部程序。
subprocess.check_output(args, *, stdin=None, stderr=None, shell=False, universal_newlines=False)
它的作用是执行args中的命令,并将其输出成字符串返回。
#!/usr/bin/env python
import time print('''\
<html>
<body>
<p>Generated {0}</p>
</body>
</html>
'''.format(time.asctime()))
time.py
#coding = utf-8
from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer
import sys, os
import subprocess class serverException(Exception):
'''服务器内部错误'''
pass '''
将不同的情况单独写成一个类,最后将这些类保存在一个列表之中,这样最后遍历列表即可,不需要if-elif了
'''
class case_no_file(object):
'''路径不存在'''
def test(self, handler):
return not os.path.exists(handler.fullPath)
def act(self, handler):
raise serverException("'{0}' not found".format(handler.path)) class case_is_file(object):
'''路径是文件'''
def test(self, handler):
return os.path.isfile(handler.fullPath)
def act(self, handler):
handler.handle_file(handler.fullPath) class case_always_fail(object):
'''不满足时的默认处理类'''
def test(self, handler):
return True
def act(self, handler):
raise serverException("Unknown object '{0}'".format(handler.Path)) class case_directory_index_file(object):
'''进入根目录时显示主页'''
def index_path(self, handler):
return os.path.join(handler.fullPath, 'index.html') #前后合并
def test(self, handler):
return os.path.isdir(handler.fullPath) and os.path.isfile(self.index_path(handler))
def act(self, handler):
handler.handle_file(self.index_path(handler)) class case_cgi_file(object):
'''脚本文件处理'''
def test(self, handler):
return os.path.isfile(handler.fullPath) and handler.fullPath.endswith('.py')
def act(self, handler):
handler.run_cgi(handler.fullPath) class RequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
caseList = [case_no_file(),
case_cgi_file(),
case_is_file(),
case_directory_index_file(),
case_always_fail()] errorPage = """\
<html>
<body>
<h1>Error accessing {path}</h1>
<p>{msg}</p>
</body>
</html>
""" def do_GET(self):
try:
self.fullPath = os.getcwd() + self.path
for case in self.caseList:
if case.test(self):
case.act(self)
break
except Exception as msg:
self.handle_error(msg) def handle_error(self, msg):
content = self.errorPage.format(path=self.path, msg=msg)
self.send_content(content, 404) def send_content(self, page, status=200):
self.send_response(status)
self.send_header('Content-Type', 'text/html')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(page.encode()) def handle_file(self, fullPath):
try:
f = open(fullPath, 'r') #python3要注意是以r读还是rb读
content = f.read()
self.send_content(content)
except IOError as msg:
msg = "'{0}' cannot be read: {1}".format(self.path, msg)
self.handle_error(msg) def run_cgi(self, fullPath):
data = subprocess.check_output(['python', fullPath])
self.send_content(data.decode()) #---------------------------------------------------------------------- if __name__ == '__main__':
serverAddress = ('', 8080)
server = HTTPServer(serverAddress, RequestHandler)
server.serve_forever()
main.py
python写web服务器的更多相关文章
- Python搭建Web服务器,与Ajax交互,接收处理Get和Post请求的简易结构
用python搭建web服务器,与ajax交互,接收处理Get和Post请求:简单实用,没有用框架,适用于简单需求,更多功能可进行扩展. python有自带模块BaseHTTPServer.CGIHT ...
- JavaSE 手写 Web 服务器(二)
原文地址:JavaSE 手写 Web 服务器(二) 博客地址:http://www.extlight.com 一.背景 在上一篇文章 <JavaSE 手写 Web 服务器(一)> 中介绍了 ...
- JavaSE 手写 Web 服务器(一)
原文地址:JavaSE 手写 Web 服务器(一) 博客地址:http://www.extlight.com 一.背景 某日,在 Java 技术群中看到网友讨论 tomcat 容器相关内容,然后想到自 ...
- (转)Python的web服务器
1.浏览器请求动态页面过程 2.WSGI Python Web Server Gateway Interface (或简称 WSGI,读作“wizgy”). WSGI允许开发者将选择web框架和web ...
- python之Web服务器案例
HTTP协议简介 1. 使用谷歌/火狐浏览器分析 在Web应用中,服务器把网页传给浏览器,实际上就是把网页的HTML代码发送给浏览器,让浏览器显示出来.而浏览器和服务器之间的传输协议是HTTP,所以: ...
- Python的web服务器
1.浏览器请求动态页面过程 2.WSGI Python Web Server Gateway Interface (或简称 WSGI,读作“wizgy”). WSGI允许开发者将选择web框架和web ...
- Python基础Web服务器案例
一.WSGI 1.PythonWeb服务器网关接口(Python Web Server Gateway Interface,缩写为WSGI) 是Python应用程序或框架和Web服务器之间的一种接口, ...
- python对web服务器做压力测试并做出图形直观显示
压力测试有很多工具啊.apache的,还有jmeter, 还有loadrunner,都比较常用. 其实你自己用python写的,也足够用. 压力测试过程中要统计时间. 比如每秒的并发数,每秒的最大响应 ...
- 用python写web一定要去破解的异步请求问题.经历web.py和tornado,完破!
1.问题 上个学期,给学校写了一个数据服务,主要从oracle里面读取一些数据供查询使用,非常快速的用web.py搭建了起来.调试顺利,测试正常,上线!接下来就是挨骂了,我铁定知道会卡,但是没想到会那 ...
随机推荐
- Linux基础命令---间歇执行命令watch
watch watch指令可以间歇性的执行程序,将输出结果以全屏的方式显示,默认是2s执行一次.watch将一直运行,直到被中断. 此命令的适用范围:RedHat.RHEL.Ubuntu.CentOS ...
- Codeforces 579A. Raising Bacteria
You are a lover of bacteria. You want to raise some bacteria in a box. Initially, the box is empty. ...
- AtCoder Regular Contest 077 D - 11
题目链接:http://arc077.contest.atcoder.jp/tasks/arc077_b Time limit : 2sec / Memory limit : 256MB Score ...
- [转载]C#中IndexOf的使用
注:此方法无法找出目标字符串第二次.第三次等出现的位置. 具体代码如下所示: 1 2 3 4 5 var array=['REG','2018','2018']; array.indexOf(‘R ...
- [转载]oracle的加密和解密
加密函数 create or replace function encrypt_des(p_text varchar2, p_key varchar2) return varchar2 isv_tex ...
- IDEA添加作者和时间信息
- 图片转化成base64字符串
package demo; import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder; import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder; import java.io.*; public ...
- Java操作Solr之SolrJ
添加SolrJ的jar包 solrj是访问Solr服务的java客户端,提供索引和搜索的请求方法,SolrJ通常在嵌入在业务系统中,通过SolrJ的API接口操作Solr服务, <depende ...
- Html5之Web存储
localStorage 方法存储的数据没有时间限制.第二天.第二周或下一年之后,数据依然可用. sessionStorage 方法针对一个session 进行数据存储.当用户关闭浏览器窗口后,数据会 ...
- 识别简单的答题卡(Bubble sheet multiple choice scanner and test grader using OMR, Python and OpenCV——jsxyhelu重新整编)
该博客转自www.pyimagesearch.com,进行了相关修改补充. Over the past few months I've gotten quite the number of reque ...
