logistic regression model
logistic regression model
logistic regression model
逻辑回归模型一般指的是二项分类的逻辑回归模型,也是非常经典的模型,它主要的决策函数是 ,给定数据的情况下,来求取Y属于1或者0的概率。具体的,我们可以做如下表示:
,给定数据的情况下,来求取Y属于1或者0的概率。具体的,我们可以做如下表示:
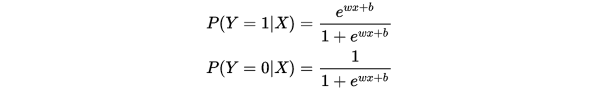
这里, 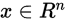 是输入,
是输入,  是输出,
是输出,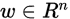 和
和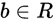 是模型参数,
是模型参数, 是内积。
是内积。
当然这里的决策函数化简后就是众所周知的sigmoid函数。这里我们使用更为通用的hypothesis来表示函数,具体如下:
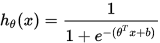
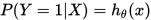
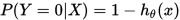
loss fuction
当我们的假设函数 确定后,我们就需要来确定真实值与假设函数值之间能量损失。通俗的讲,我们的目标就是要求假设函数的值无限逼近真实值,是的二者的差值达到最小。从而得到最有的参数
确定后,我们就需要来确定真实值与假设函数值之间能量损失。通俗的讲,我们的目标就是要求假设函数的值无限逼近真实值,是的二者的差值达到最小。从而得到最有的参数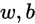 。
。
我们可以使用极大似然函数来求解我们的模型参数。0, 1综合起来得到:

求最大似然估计:
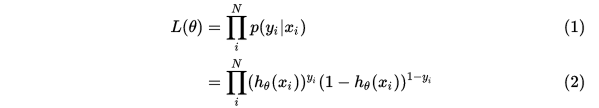
求取对数:
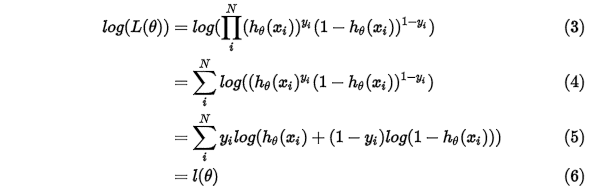
得到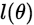 之后,我们就可以通过梯度下降法或者牛顿法来求得参数
之后,我们就可以通过梯度下降法或者牛顿法来求得参数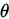 ,也就是
,也就是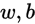
这里我们假设loss function 为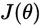 可得到:
可得到:
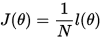
使用梯度下降法来求取模型参数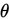 :
:
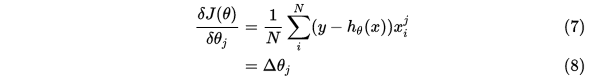
梯度公式更新参数求解:
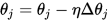
这样子就可以求解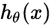 的模型参数了。当模型参数确定后就可以用来对数据进行分类了。
的模型参数了。当模型参数确定后就可以用来对数据进行分类了。
softmax
多元逻辑回归,顾名思义就是考虑多分类问题的逻辑回归方法。
它的假设函数为:
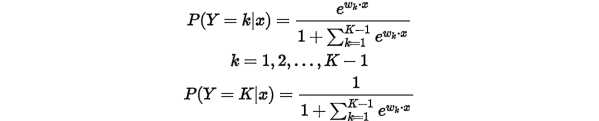
不过这个看着貌似有点繁琐,在Andrew Ng的文章中给出了一个更直观的表现形式:
对于给定的测试输入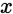 ,我们想用假设函数针对每一个类别j估算出概率值
,我们想用假设函数针对每一个类别j估算出概率值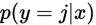 。也就是说,我们想估计
。也就是说,我们想估计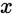 的每一种分类结果出现的概率。因此,我们的假设函数将要输出一个
的每一种分类结果出现的概率。因此,我们的假设函数将要输出一个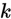 维的向量(向量元素的和为1)来表示这
维的向量(向量元素的和为1)来表示这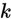 个估计的概率值。 具体地说,我们的假设函数
个估计的概率值。 具体地说,我们的假设函数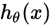 形式如下:
形式如下:

这里需要注意的是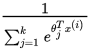 这一项对概率分布进行归一化,是的概率之和为1.
这一项对概率分布进行归一化,是的概率之和为1.
具体的代价函数如下:

以看到,Softmax代价函数与logistic 代价函数在形式上非常类似,只是在Softmax损失函数中对类标记的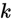 个可能值进行了累加。注意在Softmax回归中将
个可能值进行了累加。注意在Softmax回归中将 分类为类别
分类为类别 的概率为:
的概率为:
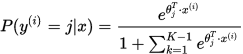

基于python的logistic regression代码
代码来自《机器学习实战》这本书
#!/usr/bin/python
# encoding: utf-8
"""
@version: 1.0
@author: Fly
@license: Apache Licence
@contact: luyfuyu@gmail.com
@site: https://www.flyuuu.cn
@software: PyCharm
@file: logistic_regression.py
"""
import numpy as np
import math
def load_dataset(filename="./data/lr_testSet.txt"):
data_matrix = []
label_matrix = []
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
line_list = line.strip().split()
data_matrix.append([1.0, float(line_list[0]), float(line_list[1])])
label_matrix.append(int(line_list[2]))
return data_matrix, label_matrix
def sigmoid(x):
return 1/(1 + np.exp(-x))
def grandient_ascent(intput_data, class_labels, maxiter=500):
data_matrix = np.mat(intput_data)
label_matrix = np.mat(class_labels).transpose()
m,n = data_matrix.shape
alpha = 0.001
weights = np.ones((n,1))
for k in range(maxiter):
h = sigmoid(data_matrix * weights)
error = label_matrix - h
weights = weights + alpha * data_matrix.transpose() * error
return weights
def stoc_ascent(intput_data, class_lables):
data_matrix = np.mat(intput_data)
label_matrix = class_lables
m, n = data_matrix.shape
alpha = 0.001
weights = np.ones(n)
for i in range(m):
h = sigmoid(data_matrix[i] * weights)
error = label_matrix[i] - h
weights = weights + alpha * data_matrix[i] * error
return weights
def plotBestFit(weights):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dataMat, labelMat=load_dataset()
dataArr = np.array(dataMat)
n = np.shape(dataArr)[0]
xcord1 = []
ycord1 = []
xcord2 = []
ycord2 = []
for i in range(n):
if int(labelMat[i])== 1:
xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2])
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s=30, c='red', marker='s')
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s=30, c='green')
x = np.arange(-3.0, 3.0, 0.1)
y = ((- weights[0] - weights[1] * x) / weights[2]).tolist()[0]
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('X1')
plt.ylabel('X2')
plt.show()
def stocGradAscent1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter=150):
m,n = np.shape(dataMatrix)
weights = np.ones(n) #initialize to all ones
for j in range(numIter):
dataIndex = list(range(m))
for i in range(m):
alpha = 4/(1.0+j+i)+0.0001 #apha decreases with iteration, does not
randIndex = int(np.random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))#go to 0 because of the constant
h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[randIndex]*weights))
error = classLabels[randIndex] - h
weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[randIndex]
del(dataIndex[randIndex])
return weights
def classifyVector(inX, weights):
prob = sigmoid(sum(inX*weights))
if prob > 0.5:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0
def colicTest():
frTrain = open('./data/horseColicTraining.txt'); frTest = open('./data/horseColicTest.txt')
trainingSet = []
trainingLabels = []
for line in frTrain.readlines():
currLine = line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr =[]
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
trainingSet.append(lineArr)
trainingLabels.append(float(currLine[21]))
trainWeights = stocGradAscent1(np.array(trainingSet), trainingLabels, 1000)
errorCount = 0
numTestVec = 0.0
for line in frTest.readlines():
numTestVec += 1.0
currLine = line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr =[]
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
if int(classifyVector(np.array(lineArr), trainWeights))!= int(currLine[21]):
errorCount += 1
errorRate = (float(errorCount)/numTestVec)
print("the error rate of this test is: %f" % errorRate)
return errorRate
def multiTest():
numTests = 10; errorSum=0.0
for k in range(numTests):
errorSum += colicTest()
print ("after %d iterations the average error rate is: %f" % (numTests, errorSum/float(numTests)))
if __name__ == "__main__":
filename = "./data/lr_testSet.txt"
x, y = load_dataset(filename)
weights = grandient_ascent(x, y)
plotBestFit(weights)
multiTest()
logistic regression model的更多相关文章
- Stanford机器学习---第三讲. 逻辑回归和过拟合问题的解决 logistic Regression & Regularization
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7716281 本栏目(Machine learning)包括单参数的线性回归.多参数的线性回归 ...
- logistic regression的一些问题,不平衡数据,时间序列,求解惑
Logistic Regression 1.在有时间序列的特征数据中,怎么运用LR? 不光是LR,其他的模型也是. 有很多基本的模型变形之后,变成带时序的模型.但,个人觉得,这类模型大多不靠谱. 我觉 ...
- Machine Learning - 第3周(Logistic Regression、Regularization)
Logistic regression is a method for classifying data into discrete outcomes. For example, we might u ...
- Python实践之(七)逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
机器学习算法与Python实践之(七)逻辑回归(Logistic Regression) zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 机器学习算法与Pyth ...
- Logistic Regression:银行贷款申请审批实例
问题定义 这是一个贷款的审批问题,假设你是一个银行的贷款审批员,现在有客户需要一定额度的贷款,他们填写了个人的信息(信息在datas.txt中给出),你需要根据他们的信息,建立一个分类模型,判断是否可 ...
- 【机器学习】Octave 实现逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
ex2data1.txt ex2data2.txt 本次算法的背景是,假如你是一个大学的管理者,你需要根据学生之前的成绩(两门科目)来预测该学生是否能进入该大学. 根据题意,我们不难分辨出这是一种二分 ...
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning(week2)Logistic Regression with a Neural Network mindset(实现一个图像识别算法)
Logistic Regression with a Neural Network mindset You will learn to: Build the general architecture ...
- 课程一(Neural Networks and Deep Learning),第二周(Basics of Neural Network programming)—— 4、Logistic Regression with a Neural Network mindset
Logistic Regression with a Neural Network mindset Welcome to the first (required) programming exerci ...
- 机器学习算法与Python实践之(七)逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/20319673 机器学习算法与Python实践之(七)逻辑回归(Logistic Regression) z ...
随机推荐
- C++_class_powerpoint_1.2
用英文编写(复制黏贴)果然比较吃力啊,果然还是要写中文. Expressions and Statements Operator summary Scope resolution class::m ...
- [SpringMVC]定义多个前缀映射的问题
转自:https://penciltim.iteye.com/blog/501073 我在web.xml里面定义多个dispatch-servlet的前缀映射,像下面这样 <!-- Servle ...
- Coursera Algorithms Programming Assignment 2: Deque and Randomized Queue (100分)
作业原文:http://coursera.cs.princeton.edu/algs4/assignments/queues.html 这次作业与第一周作业相比,稍微简单一些.有三个编程练习:双端队列 ...
- Redis(五)-数据库
Redis是一个字典结构的存储服务器,而实际上一个Redis实例提供了多个用来存储数据的字典,客户端可以将制定的书存储在哪个字典中,这与关系书库实例中可以i创建多个数据库类似,所以可以将其中的每个字典 ...
- Spring Boot (20) 拦截器
动态资源和静态资源 拦截器可以算是aop的一种实现,专门拦截对动态资源的后台请求,也就是拦截对控制层的请求,主要用于判断用户是否有权限请求后台.拦截器不会拦截静态资源,如spring boot默认静态 ...
- 全局设置border-box
全局设置 border-box 很好,更符合我们通常对一个「盒子」尺寸的认知.,其次它可以省去一次又一次的加加减减,它还有一个关键作用——让有边框的盒子正常使用百分比宽度.但是使用了 border-b ...
- linux ssh 经常断开 的解决方法
1.现象 在linux ,用ssh进行远程连接时,经常会发生长时间后断线,或者是无响应,就像卡住的感觉(键盘输入不进去). 2.解决方法 在ssh客户端的linux设置 # sudo vim /etc ...
- Inception搭建
Inception安装Inception是集审核.执行.回滚于一体的一个自动化运维系统,它是根据MySQL代码修改过来的,用它可以很明确的,详细的,准确的审核MySQL的SQL语句,它的工作模式和My ...
- halcon 模板匹配 -- 转化 vector_angle_to_rigid
********************************模板匹配 ********************create_shape_model创建模板,这个函数有许多参数,其中金字塔的级数由N ...
- dell inspiron 15 3000 装XP win7 等GHOST系统方法
dell inspiron 装XP win7 等GHOST系统方法 . 开机按F2,进入BIOS .在 BIOS 的Boot菜单下,将Secure Boot 改为 Disabled . 将Boot L ...
