项目总结二:人脸识别项目(Face Recognition for the Happy House)
一、人脸验证问题(face verification)与人脸识别问题(face recognition)
1、人脸验证问题(face verification): 输入 数据库
Image Image
ID ID
通过输入的ID找到数据库里的Image,然后将Image与输入的Image比较,判断图片是不是同一个人。一对一问题,通过监督学习即可解决。例如高铁站的门禁系统。
2、人脸识别问题(face recognition): 输入 数据库
Image Image *100
ID * 100
假设数据库里有100张图片,通过分别计算输入图片与数据库里所有图片 的d函数的的值,即如果d>阈值τ,则不是同一个人;如果d<阈值τ,则是同一个人。1对k的问题,需要解决一次学习问题(One-shot learning problem),这意味着在大多数人脸识别应用中,你需要通过单单一张图片或者单单一个人脸样例就能去识别这个人。例如Andrew NG展示的百度员工上班的门禁系统。
二、模型

By using a 128-neuron fully connected layer as its last layer, the model ensures that the output is an encoding vector of size 128.By computing a distance between two encodings and thresholding(0.7), you can determine if the two pictures represent the same person.
1、Siamese 网络(Siamese network)
对于两个不同的输入,运行相同的卷积神经网络,然后比较它们,这一般叫做Siamese网络架构。怎么训练这个Siamese神经网络呢?不要忘了这两个网络有相同的参数,所以你实际要做的就是训练一个网络,它计算得到的编码(encoding)可以用于计算距离 ,它可以告诉你两张图片是否是同一个人。
,它可以告诉你两张图片是否是同一个人。
2、Inception 模型
(1)Inception 模块
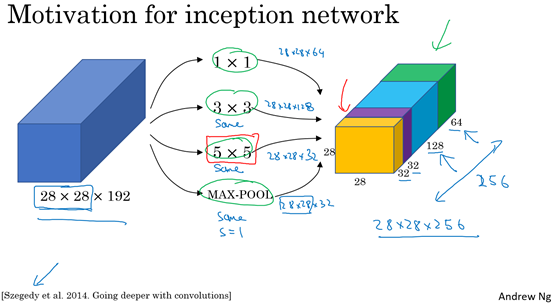
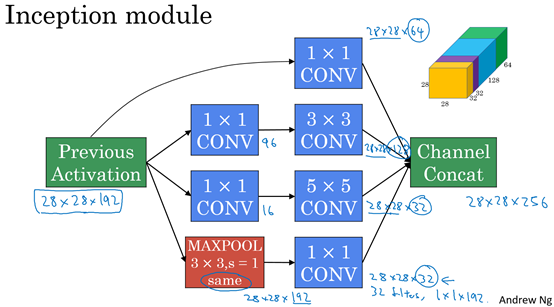
将学这些模块组合起来,构筑就可以构建Inception网络。
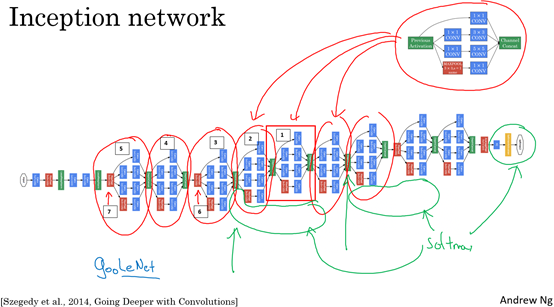
(2)实现Inception Network的代码
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
from numpy import genfromtxt
from keras import backend as K
from keras.layers import Conv2D, ZeroPadding2D, Activation, Input, concatenate
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers.normalization import BatchNormalization
from keras.layers.pooling import MaxPooling2D, AveragePooling2D
import fr_utils
from keras.layers.core import Lambda, Flatten, Dense def inception_block_1a(X):
"""
Implementation of an inception block
""" X_3x3 = Conv2D(96, (1, 1), data_format='channels_first', name ='inception_3a_3x3_conv1')(X)
X_3x3 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name = 'inception_3a_3x3_bn1')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = Activation('relu')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = ZeroPadding2D(padding=(1, 1), data_format='channels_first')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = Conv2D(128, (3, 3), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3a_3x3_conv2')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3a_3x3_bn2')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = Activation('relu')(X_3x3) X_5x5 = Conv2D(16, (1, 1), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3a_5x5_conv1')(X)
X_5x5 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3a_5x5_bn1')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = Activation('relu')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = ZeroPadding2D(padding=(2, 2), data_format='channels_first')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = Conv2D(32, (5, 5), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3a_5x5_conv2')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3a_5x5_bn2')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = Activation('relu')(X_5x5) X_pool = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, data_format='channels_first')(X)
X_pool = Conv2D(32, (1, 1), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3a_pool_conv')(X_pool)
X_pool = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3a_pool_bn')(X_pool)
X_pool = Activation('relu')(X_pool)
X_pool = ZeroPadding2D(padding=((3, 4), (3, 4)), data_format='channels_first')(X_pool) X_1x1 = Conv2D(64, (1, 1), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3a_1x1_conv')(X)
X_1x1 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3a_1x1_bn')(X_1x1)
X_1x1 = Activation('relu')(X_1x1) # CONCAT
inception = concatenate([X_3x3, X_5x5, X_pool, X_1x1], axis=1) return inception def inception_block_1b(X):
X_3x3 = Conv2D(96, (1, 1), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3b_3x3_conv1')(X)
X_3x3 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3b_3x3_bn1')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = Activation('relu')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = ZeroPadding2D(padding=(1, 1), data_format='channels_first')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = Conv2D(128, (3, 3), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3b_3x3_conv2')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3b_3x3_bn2')(X_3x3)
X_3x3 = Activation('relu')(X_3x3) X_5x5 = Conv2D(32, (1, 1), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3b_5x5_conv1')(X)
X_5x5 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3b_5x5_bn1')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = Activation('relu')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = ZeroPadding2D(padding=(2, 2), data_format='channels_first')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = Conv2D(64, (5, 5), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3b_5x5_conv2')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3b_5x5_bn2')(X_5x5)
X_5x5 = Activation('relu')(X_5x5) X_pool = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=(3, 3), data_format='channels_first')(X)
X_pool = Conv2D(64, (1, 1), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3b_pool_conv')(X_pool)
X_pool = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3b_pool_bn')(X_pool)
X_pool = Activation('relu')(X_pool)
X_pool = ZeroPadding2D(padding=(4, 4), data_format='channels_first')(X_pool) X_1x1 = Conv2D(64, (1, 1), data_format='channels_first', name='inception_3b_1x1_conv')(X)
X_1x1 = BatchNormalization(axis=1, epsilon=0.00001, name='inception_3b_1x1_bn')(X_1x1)
X_1x1 = Activation('relu')(X_1x1) inception = concatenate([X_3x3, X_5x5, X_pool, X_1x1], axis=1) return inception def inception_block_1c(X):
X_3x3 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_3c_3x3',
cv1_out=128,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
cv2_out=256,
cv2_filter=(3, 3),
cv2_strides=(2, 2),
padding=(1, 1)) X_5x5 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_3c_5x5',
cv1_out=32,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
cv2_out=64,
cv2_filter=(5, 5),
cv2_strides=(2, 2),
padding=(2, 2)) X_pool = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, data_format='channels_first')(X)
X_pool = ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0, 1), (0, 1)), data_format='channels_first')(X_pool) inception = concatenate([X_3x3, X_5x5, X_pool], axis=1) return inception def inception_block_2a(X):
X_3x3 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_4a_3x3',
cv1_out=96,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
cv2_out=192,
cv2_filter=(3, 3),
cv2_strides=(1, 1),
padding=(1, 1))
X_5x5 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_4a_5x5',
cv1_out=32,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
cv2_out=64,
cv2_filter=(5, 5),
cv2_strides=(1, 1),
padding=(2, 2)) X_pool = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=(3, 3), data_format='channels_first')(X)
X_pool = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X_pool,
layer='inception_4a_pool',
cv1_out=128,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
padding=(2, 2))
X_1x1 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_4a_1x1',
cv1_out=256,
cv1_filter=(1, 1))
inception = concatenate([X_3x3, X_5x5, X_pool, X_1x1], axis=1) return inception def inception_block_2b(X):
#inception4e
X_3x3 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_4e_3x3',
cv1_out=160,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
cv2_out=256,
cv2_filter=(3, 3),
cv2_strides=(2, 2),
padding=(1, 1))
X_5x5 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_4e_5x5',
cv1_out=64,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
cv2_out=128,
cv2_filter=(5, 5),
cv2_strides=(2, 2),
padding=(2, 2)) X_pool = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, data_format='channels_first')(X)
X_pool = ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0, 1), (0, 1)), data_format='channels_first')(X_pool) inception = concatenate([X_3x3, X_5x5, X_pool], axis=1) return inception def inception_block_3a(X):
X_3x3 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_5a_3x3',
cv1_out=96,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
cv2_out=384,
cv2_filter=(3, 3),
cv2_strides=(1, 1),
padding=(1, 1))
X_pool = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=(3, 3), data_format='channels_first')(X)
X_pool = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X_pool,
layer='inception_5a_pool',
cv1_out=96,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
padding=(1, 1))
X_1x1 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_5a_1x1',
cv1_out=256,
cv1_filter=(1, 1)) inception = concatenate([X_3x3, X_pool, X_1x1], axis=1) return inception def inception_block_3b(X):
X_3x3 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_5b_3x3',
cv1_out=96,
cv1_filter=(1, 1),
cv2_out=384,
cv2_filter=(3, 3),
cv2_strides=(1, 1),
padding=(1, 1))
X_pool = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, data_format='channels_first')(X)
X_pool = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X_pool,
layer='inception_5b_pool',
cv1_out=96,
cv1_filter=(1, 1))
X_pool = ZeroPadding2D(padding=(1, 1), data_format='channels_first')(X_pool) X_1x1 = fr_utils.conv2d_bn(X,
layer='inception_5b_1x1',
cv1_out=256,
cv1_filter=(1, 1))
inception = concatenate([X_3x3, X_pool, X_1x1], axis=1) return inception def faceRecoModel(input_shape):
"""
Implementation of the Inception model used for FaceNet Arguments:
input_shape -- shape of the images of the dataset Returns:
model -- a Model() instance in Keras
""" # Define the input as a tensor with shape input_shape
X_input = Input(input_shape) # Zero-Padding
X = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3))(X_input) # First Block
X = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), strides = (2, 2), name = 'conv1')(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis = 1, name = 'bn1')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X) # Zero-Padding + MAXPOOL
X = ZeroPadding2D((1, 1))(X)
X = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides = 2)(X) # Second Block
X = Conv2D(64, (1, 1), strides = (1, 1), name = 'conv2')(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis = 1, epsilon=0.00001, name = 'bn2')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X) # Zero-Padding + MAXPOOL
X = ZeroPadding2D((1, 1))(X) # Second Block
X = Conv2D(192, (3, 3), strides = (1, 1), name = 'conv3')(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis = 1, epsilon=0.00001, name = 'bn3')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X) # Zero-Padding + MAXPOOL
X = ZeroPadding2D((1, 1))(X)
X = MaxPooling2D(pool_size = 3, strides = 2)(X) # Inception 1: a/b/c
X = inception_block_1a(X)
X = inception_block_1b(X)
X = inception_block_1c(X) # Inception 2: a/b
X = inception_block_2a(X)
X = inception_block_2b(X) # Inception 3: a/b
X = inception_block_3a(X)
X = inception_block_3b(X) # Top layer
X = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=(1, 1), data_format='channels_first')(X)
X = Flatten()(X)
X = Dense(128, name='dense_layer')(X) # L2 normalization
X = Lambda(lambda x: K.l2_normalize(x,axis=1))(X) # Create model instance
model = Model(inputs = X_input, outputs = X, name='FaceRecoModel') return model
3、损失函数:The Triplet Loss
raining will use triplets of images (A,P,N):
- A is an "Anchor" image--a picture of a person.
- P is a "Positive" image--a picture of the same person as the Anchor image.
- N is a "Negative" image--a picture of a different person than the Anchor image.
These triplets are picked from our training dataset. We will write (A(i),P(i),N(i)) to denote the i-th training example.
You'd like to make sure that an image A(i)of an individual is closer to the Positive P(i) than to the Negative image N(i) by at least a margin α:
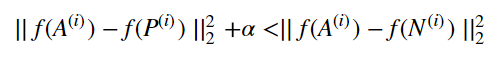
You would thus like to minimize the following "triplet cost":

Here, we are using the notation "[z]+" to denote max(z,0).
Notes:
- The term (1) is the squared distance between the anchor "A" and the positive "P" for a given triplet; you want this to be small.
- The term (2) is the squared distance between the anchor "A" and the negative "N" for a given triplet, you want this to be relatively large, so it thus makes sense to have a minus sign preceding it.
- α is called the margin. It is a hyperparameter that you should pick manually. We will use α=0.2.
Most implementations also normalize the encoding vectors to have norm equal one (i.e., ∣∣f(img)∣∣2=1); you won't have to worry about that here.
4、model compile
FRmodel.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = triplet_loss, metrics = ['accuracy'])
load_weights_from_FaceNet(FRmodel)
The pretrained model we use is inspired by Victor Sy Wang's implementation and was loaded using his code: https://github.com/iwantooxxoox/Keras-OpenFace.
5、输入输出数据类型
(1)输入数据:This network uses 96x96 dimensional RGB images as its input. Specifically, inputs a face image (or batch of m face images) as a tensor of shape (m,nC,nH,nW)=(m,3,96,96)
(2)输出数据:It outputs a matrix of shape (m,128) that encodes each input face image into a 128-dimensional vector
6、总结
- Face verification solves an easier 1:1 matching problem; face recognition addresses a harder 1:K matching problem.
- The triplet loss is an effective loss function for training a neural network to learn an encoding of a face image.
- The same encoding can be used for verification and recognition. Measuring distances between two images' encodings allows you to determine whether they are pictures of the same person.
项目总结二:人脸识别项目(Face Recognition for the Happy House)的更多相关文章
- 转:基于开源项目OpenCV的人脸识别Demo版整理(不仅可以识别人脸,还可以识别眼睛鼻子嘴等)【模式识别中的翘楚】
文章来自于:http://blog.renren.com/share/246648717/8171467499 基于开源项目OpenCV的人脸识别Demo版整理(不仅可以识别人脸,还可以识别眼睛鼻子嘴 ...
- 基于卷积神经网络的人脸识别项目_使用Tensorflow-gpu+dilib+sklearn
https://www.cnblogs.com/31415926535x/p/11001669.html 基于卷积神经网络的人脸识别项目_使用Tensorflow-gpu+dilib+sklearn ...
- Github开源人脸识别项目face_recognition
Github开源人脸识别项目face_recognition 原文:https://www.jianshu.com/p/0b37452be63e 译者注: 本项目face_recognition是一个 ...
- 基于Python与命令行人脸识别项目(系列二)
接着系统一,继续开始我们face_recognition. Python 模块:face_recognition 在Python中,你可以导入face_recognition模块,调用丰富的API接口 ...
- 基于Python与命令行人脸识别项目(系列一)
Face Recognition 人脸识别 摘要:本项目face_recognition是一个强大.简单.易上手的人脸识别开源项目,并且配备了完整的开发文档和应用案例,方便大家使用.对于本项目可以使用 ...
- anaconda3下配置python-3.5+tensorflow-gpu-1.9.0人脸识别项目环境
https://www.cnblogs.com/31415926535x/p/10620732.html 之前为了配置tensorflow-gpu的环境又是装cuda,又是装cudnn,还有tenso ...
- Faces人脸识别项目简介
Faces人脸识别 分为两个模块,Faces文件夹下存放人脸识别算法的代码,Web文件夹下存放网站搭建的代码 详情请查看各个模块下的readme文档 项目简介 核心算法 一款基于Dlib.opencv ...
- python人脸识别项目face-recognition
该项目基于Github上面的开源项目人脸识别face-recognition,主要是对图像和视频中的人脸进行识别,在开源项目给出的例子基础上对视频人脸识别的KNN算法进行了实现. 0x1 工程项目结构 ...
- express+gulp构建项目(二)启动项目和主文件
这一次整理的内容是项目主文件和如何启动项目. 启动项目 通过nodejs官网的例子https://nodejs.org/docs/latest-v4.x/doc/api/synopsis.html我们 ...
随机推荐
- 纯css实现无限嵌套菜单
效果图: demo:关键的地方都以颜色明显标识 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>menu</title& ...
- java之路 把1到100之间的数的偶数相加
/** *把1到100之间的数的偶数相加 */ class Demo{ public static void main(String[] args){ int i =1; int sum = 0; d ...
- oracle中的日期函数的使用
TO_DATE格式(以时间:2007-11-02 13:45:25为例) Year: yy two digits 两位年 显示值:07 ...
- node 项目中 koa2 环境搭建 以及项目发布
环境搭建: 1.Koa 必须使用 7.6 以上的版本.如果你的版本低于这个要求,就要先升级 Node. 查看node版本方法:node -v 2.使用koa-generator生成器生成项目 安装ko ...
- 【Selenium】【BugList7】执行driver.find_element_by_id("kw").send_keys("Selenium"),报错:selenium.common.exceptions.InvalidArgumentException: Message: Expected [object Undefined] undefined to be a string
[版本] selenium:3.11.0 firefox:59.0.3 (64 位) python:3.6.5 [代码] #coding=utf-8 from selenium import webd ...
- Jquery.Datatable 控件后端分页实例 (后台使用ashx、aspx-webmethod)
本实例引用Datatable版本号: 1.10.16 一.传到aspx后台(webmethod) 1.添加js.css引用: <link href="/Scripts/ThirdLib ...
- shell脚本学习-循环
跟着RUNOOB网站的教程学习的笔记 for循环 与其他编程语言类似,shell支持for循环. for循环一般格式为: for var in item1 item2 ... itemN do com ...
- Notes : <Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> Chapter 3
Chapter 3-Classification .caret, .dropup > .btn > .caret { border-top-color: #000 !important; ...
- virtualenv搭建
1.准备工作 终端 网络状况良好 2.安装虚拟环境 如何安装虚拟环境: 2.1了解你的电脑中有哪些版本的python whereis python 查看当前系统中有多少跟python有关的命令 ...
- Sudoku(POJ2676/3074)
Sudoku is one of the metaphysical techniques. If you understand the essence of it, you will have the ...
