POJ 1251 Jungle Roads - C语言 - Kruskal算法
Description
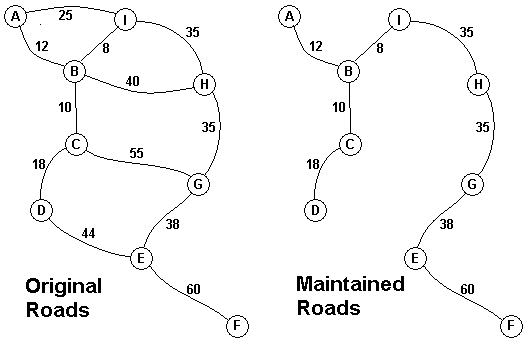
The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money was spent on extra roads between villages some years ago. But the jungle overtakes roads relentlessly, so the large road network is too expensive to maintain. The Council of Elders must choose to stop maintaining some roads. The map above on the left shows all the roads in use now and the cost in aacms per month to maintain them. Of course there needs to be some way to get between all the villages on maintained roads, even if the route is not as short as before. The Chief Elder would like to tell the Council of Elders what would be the smallest amount they could spend in aacms per month to maintain roads that would connect all the villages. The villages are labeled A through I in the maps above. The map on the right shows the roads that could be maintained most cheaply, for 216 aacms per month. Your task is to write a program that will solve such problems.
Input
The input consists of one to 100 data sets, followed by a final line containing only 0. Each data set starts with a line containing only a number n, which is the number of villages, 1 < n < 27, and the villages are labeled with the first n letters of the alphabet, capitalized. Each data set is completed with n-1 lines that start with village labels in alphabetical order. There is no line for the last village. Each line for a village starts with the village label followed by a number, k, of roads from this village to villages with labels later in the alphabet. If k is greater than 0, the line continues with data for each of the k roads. The data for each road is the village label for the other end of the road followed by the monthly maintenance cost in aacms for the road. Maintenance costs will be positive integers less than 100. All data fields in the row are separated by single blanks. The road network will always allow travel between all the villages. The network will never have more than 75 roads. No village will have more than 15 roads going to other villages (before or after in the alphabet). In the sample input below, the first data set goes with the map above.
Output
The output is one integer per line for each data set: the minimum cost in aacms per month to maintain a road system that connect all the villages. Caution: A brute force solution that examines every possible set of roads will not finish within the one minute time limit.
Sample Input
9
A 2 B 12 I 25
B 3 C 10 H 40 I 8
C 2 D 18 G 55
D 1 E 44
E 2 F 60 G 38
F 0
G 1 H 35
H 1 I 35
3
A 2 B 10 C 40
B 1 C 20
0
Sample Output
216
30
题解
题目的核心是:构造一棵最小生成树。我采用的是 Kruskal 算法来解决此问题。
定义如下结构体保存路线信息:
struct node {
char u, v;// 起点和终点
int cost;// 花费
} roads[MAX_ROADS];// 路线
int roads_num;
Kruskal 算法构造最小生成树的步骤如下:
- 初始化每个顶点为一棵树,根结点是自己
- 遍历所有边,找到花费最小的边
- 如果这条边的两点属于同一棵树,那么不用处理
- 如果这条边的两点属于不同的树,那么将这两棵树合并(修改一个根结点的父结点为另一个根结点)
- 重复第2步,直到所有顶点都属于同一棵树为止
对于此题而言,只需要在2.2中将花费加起来,最后的和就是最小花费。
C代码
/*********************************************************************
File: 1251 -- Jungle Roads
Result: Accepted
Memory: 340K
Time: 0MS
Language: GCC
Code Length: 2028B
Version: 1.3
From: https://www.cnblogs.com/wowpH/p/11908562.html
Author: wowpH
Date: 2019-11-22 15:18:59
*********************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_N 26
#define MAX_ROADS 75
struct node {
char u, v;// 起点和终点
int cost;// 花费
} roads[MAX_ROADS];// 路线
int roads_num;
int father[MAX_N];// 父结点,用于并查集
void input_roads(int n);
int compare(const void* a, const void* b);
int kruskal();
void init();
int merge(int u, int v);
int find(int x);
int main(void) {
int n;// 村庄个数
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF && n > 0) {
input_roads(n);// 输入路线
// 按照花费升序排序
qsort(roads, roads_num, sizeof(struct node), compare);
printf("%d\n", kruskal());// 输出最小花费
}
return 0;
}
void input_roads(int n) {
roads_num = 0;// 路线个数重置为0
char start, end;
int number, cost;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
scanf(" %c %d", &start, &number);// 输入起点和终点个数
for (int j = 0; j < number; ++j) {
scanf(" %c %d", &end, &cost);// 输入终点和花费
roads[roads_num].u = start;
roads[roads_num].v = end;
roads[roads_num].cost = cost;
++roads_num;
}
}
}
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
return (*(struct node*)a).cost - (*(struct node*)b).cost;// 升序
}
int kruskal() {// 克鲁斯卡尔算法,并查集算法实现
init();// 初始化
int min_cost = 0;// 最小花费
int u, v;// 起点,终点
for (int i = 0; i < roads_num; ++i) {
u = roads[i].u - 'A';
v = roads[i].v - 'A';
if (merge(u, v) == 0) {// 合并成功,此路线属于最小生成树
min_cost += roads[i].cost;
}
}
return min_cost;
}
void init() {// 并查集的初始化
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; ++i) {// 初始化父结点为自己
father[i] = i;
}
}
int merge(int u, int v) {// 并查集的合并
u = find(u);
v = find(v);
if (u != v) {// 不属于同一个集合,可以合并
father[v] = u;// 合并
return 0;// 成功
}
return -1;
}
int find(int x) {// 并查集的查找父结点
if (father[x] != x) {
father[x] = find(father[x]);// 压缩路径
}
return father[x];
}
中文版:
我觉得这题就是考英文的。
有 n 个村庄,之间有一些道路,为了维护道路需要花费一些钱,现在打算放弃部分道路,只维护 n-1 条道路,问最小的花费是多少?
这不就是最小生成树的典型题目吗?用 Prim 算法或者 Kruskal 算法即可。
限制条件:
- 1 < n < 27
- 1 <= 道路条数 <= 100
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1251
参考:Kruskal算法
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wowpH/p/11908562.html
wowpH - cnblogs
POJ 1251 Jungle Roads - C语言 - Kruskal算法的更多相关文章
- poj 1251 Jungle Roads (最小生成树)
poj 1251 Jungle Roads (最小生成树) Link: http://poj.org/problem?id=1251 Jungle Roads Time Limit: 1000 ...
- POJ 1251 Jungle Roads(Kruskal算法求解MST)
题目: The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money w ...
- POJ 1251 Jungle Roads (prim)
D - Jungle Roads Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:10000KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Su ...
- POJ 1251 Jungle Roads (最小生成树)
题目: Description The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign ...
- POJ 1251 Jungle Roads(最小生成树)
题意 有n个村子 输入n 然后n-1行先输入村子的序号和与该村子相连的村子数t 后面依次输入t组s和tt s为村子序号 tt为与当前村子的距离 求链接全部村子的最短路径 还是裸的最小生成树咯 ...
- POJ 1251 Jungle Roads (zoj 1406) MST
传送门: http://poj.org/problem?id=1251 http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=406 P ...
- HDU 1301 Jungle Roads (最小生成树,基础题,模版解释)——同 poj 1251 Jungle Roads
双向边,基础题,最小生成树 题目 同题目 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include<stri ...
- POJ 1251 Jungle Roads
题意:嗯……没看题……看了眼图……求个最小生成树. 解法:kruskal. 代码: #include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include& ...
- [ An Ac a Day ^_^ ] [kuangbin带你飞]专题六 最小生成树 POJ 1251 Jungle Roads
题意: 有n个点 每个点上有一些道路 求最小生成树 解释下输入格式 A n v1 w1 v2 w2 A点上有n条边 A到v1权值是w1 A到v2权值是w2 思路: 字符串处理之后跑kruskal求最小 ...
随机推荐
- bzoj3745: [Coci2015]Norma 分治,单调队列
链接 bzoj 思路 首先\(\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}\sum\limits_{j=1}^{n}\sum\limits_{k=i}^{j}max(a_k)\)可以用单调队列求解.参见 ...
- mac 安装注册Charles
软件去官网下载安装即可. 下载地址:https://www.charlesproxy.com/download/ 适用于Charles任意版本的注册码Charles 4.2.7 目前是最新版,可用. ...
- c++ 朋友函数
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Address; //提前声明Address类 //声明Student类 class Stud ...
- 2019蓝桥杯Java第十题大学生B组——最短路径思想
题目: 代码: package priv.tzk.lanqiao.ten; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Scanner; public c ...
- 第01组 Alpha冲刺(1/6)
队名:007 组长博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/Linrrui/p/11845138.html 作业博客: https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fz ...
- docker swarm和compose 的使用(阿里)
基本的docker使用参考:Docker 入门 到部署Web 程序- (阿里面试常用的docker命令和优点) 昨天去阿里面试 问我如果给你5台服务器 如何部署docker,我说一个个拷贝,面试官听了 ...
- 【转】Android原生PDF功能实现
1.背景 近期,公司希望实现安卓原生端的PDF功能,要求:高效.实用. 经过两天的调研.编码,实现了一个简单Demo,如上图所示.关于安卓原生端的PDF功能实现,技术点还是很多的,为了咱们安卓开发的同 ...
- VS2015 创建C++动态库及使用
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/w_x_myself/article/details/82252646 1.dll的特点 代码复用是提高软件开发效率的重要途径.一般而言,只要某部分代 ...
- 配置HTTPS全过程
HTTPS配置全过程服务器配置https协议HTTPS,是以安全为目标的HTTP通道,简单讲是HTTP的安全版.即HTTP下加入SSL层,HTTPS的安全基础是SSL,因此加密的详细内容就需要SSL. ...
- SpringBoot项目从Git拉取代码并完成编译打包启动的sh自动脚本
操作步骤: 1.进入/home/servers/codes/xxxx-dev/目录,从git上将项目clone下来: 2.确保/usr/local/xxx/xxxx-dev目录存在: 3.确保sh脚本 ...
