在LaTeX中使用颜色 Using colours in LaTeX
Using colours in LaTeX
There are several elements in LATEX whose colour can be changed to improve the appearance of the document. Colours can be manually defined to a desired tone using several models, this article explains how.
Contents |
Introduction
The simplest manner to use colours in your LATEX document is by importing the package color or xcolor. Both packages provide a common set of commands for colour manipulation, but the latter is more flexible and supports a larger number of colour models. Below an example:
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage[utf8]{inputenc}
\usepackage[english]{babel}
\usepackage{color}
\begin{document}
This example shows different examples on how to use the \texttt{color} package
to change the colour of elements in \LaTeX.
\begin{itemize}
\color{blue}
\item First item
\item Second item
\end{itemize}
\noindent
{\color{red} \rule{\linewidth}{0.5mm} }
\end{document}

Note: In all the examples the package xcolor can be used instead of color
In this example, the package color is imported with
\usepackage{color}
then the command \color{blue} sets the blue colour for the current block of text. In this case for theitemize environment.
The colour of a second block of text, delimited by { and }, is set to red with the command \color{red}, then a 0.5mm-thick horizontal ruler is inserted by \rule{\linewidth}{0.5mm}.
The amount of available colour names depends on the driver, usually the next colours can be used with any driver: white, black, yellow, green, blue, purple cyan and magenta.
See the reference guide for more colours supported by other drivers.
Open an example of the color package in ShareLaTeX
Basic usage
The colour system provided by the packages color and xcolor is built around the idea of colour models, the colour mode and the colour names supported by a driver vary.
The model based on colour names is very intuitive, even though the list of available names is limited, usually provides enough options. Below an example:
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage[utf8]{inputenc}
\usepackage[english]{babel}
\usepackage[usenames, dvipsnames]{color}
\begin{document}
This example shows different examples on how to use the \texttt{color} package
to change the colour of elements in \LaTeX.
\begin{itemize}
\color{ForestGreen}
\item First item
\item Second item
\end{itemize}
\noindent
{\color{RubineRed} \rule{\linewidth}{0.5mm} }
The background colour of some text can also be \textcolor{red}{easily} set. For
instance, you can change to orange the background of \colorbox{BurntOrange}{this
text} and then continue typing.
\end{document}

There are a few changes in this example compared to the one presented in the introduction. First, the command to import the color package has two additional parameters:
usenamesMakes the names in the corresponding driver name model available. This option can be omitted in xcolor.dvipsnamesMakes the colour names for the driver dvips available, if the package color is imported, this option must be used in conjunction withusenames. From this new set of colour names, the example uses: ForestGreen, RubineRed and BurntOrange. See the reference guide for a complete list of possible colours.
Other possible drivers are: xdvi, dvipdf, pdftex, dvipsone, dviwin, emtex, truetex and xtex.
Two new commands are also presented in the example:
\textcolor{red}{easily}- Changes the colour of inline text. Takes two parameters, the colour to use and the text whose colour is changed. In the example the word
easilyis printed inred
\colorbox{BurntOrange}{this text}- Changes the background colour of the text passed as second parameter. In the example the words
this textare printed inBurntOrange.
Open an example of the color package in ShareLaTeX
Creating your own colours
It is possible to define your own colours, the manner in which the colour is defined depends on the preferred model. Below an example using the 4 colour models typically supported by any driver.
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage[utf8]{inputenc}
\usepackage[english]{babel}
\usepackage[usenames, dvipsnames]{color}
\definecolor{mypink1}{rgb}{0.858, 0.188, 0.478}
\definecolor{mypink2}{RGB}{219, 48, 122}
\definecolor{mypink3}{cmyk}{0, 0.7808, 0.4429, 0.1412}
\definecolor{mygray}{gray}{0.6}
\begin{document}
User-defined colours with different colour models:
\begin{enumerate}
\item \textcolor{mypink1}{Pink with rgb}
\item \textcolor{mypink2}{Pink with RGB}
\item \textcolor{mypink3}{Pink with cmyk}
\item \textcolor{mygray}{Gray with gray}
\end{enumerate}
\end{document}

The command \definecolor takes three parameters: the name of the new colour, the model, and the colour definition. Roughly speaking, each number represent how much of each colour you add to the mix that makes up the final colour.
- rgb: Red, Green, Blue. Three comma-separated values between 0 and 1 define the components of the colour.
- RGB: The same as rgb, but the numbers are integers between 0 and 255.
- cmyk: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and blacK. Comma-separated list of four numbers between 0 and 1 that determine the colour according to the additive model used in most printers.
- gray: Grey scale. A single number between 0 and 1.
In the example, mypink1, mypink2 and mypink3 define the same colour but for different models. You can actually see that the one defined by cmyk is slightly different.
Colours defined by either model can later be used within your document not only to set the colour of the text, but for any other element that takes a colour as parameter, for instance tables (you must add the parameter table to the preamble), graphic elements created with TikZ, plots, vertical rulers in multicolumn documents and code listings.
Open an example of the color package in ShareLaTeX
xcolor-only colour models
There are some additional commands that are only available with the package xcolor, these enable support for more colour models and friendly colour mixing.
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage[utf8]{inputenc}
\usepackage[english]{babel}
\usepackage[dvipsnames]{xcolor}
\colorlet{LightRubineRed}{RubineRed!70!}
\colorlet{Mycolor1}{green!10!orange!90!}
\definecolor{Mycolor2}{HTML}{00F9DE}
\begin{document}
This document present several examples on how to use the \texttt{color} package
to change the colour of elements in \LaTeX.
\begin{itemize}
\item \textcolor{Mycolor1}{First item}
\item \textcolor{Mycolor2}{Second item}
\end{itemize}
\noindent
{\color{LightRubineRed} \rule{\linewidth}{1mm} }
\noindent
{\color{RubineRed} \rule{\linewidth}{1mm} }

Three new colours are defined in this example, each one in a different manner.
\colorlet{LightRubineRed}{RubineRed!70!}- A new colour named LightRubineRed is created, this colour has 70% the intensity of the original RubineRedcolour. You can think of it as a mixture of 70% RubineRed and 30% white. Defining colours in this way is great to obtain different tones of a main colour, common practice in corporate brands. In the example, you can see the original RubineRed and the new LightRubineRed used in two consecutive horizontal rulers.
\colorlet{Mycolor1}{green!10!orange!90!}- A colour named Mycolor1 is created with 10% green and 90%orange. You can use any number of colours to create new ones with this syntax.
\definecolor{Mycolor2}{HTML}{00F9DE}- The colour Mycolor2 is created using the
HTMLmodel. Colours in this model must be created with 6 hexadecimal digits, the characters A,B,C,D,E and F must be upper-case.
The colour models that only xcolor support are:
- cmy cyan, magenta, yellow
- hsb hue, saturation, brightness
- HTML RRGGBB
- Gray Grey scale, a number between 1 and 15.
- wave Wave length. Between 363 and 814.
Open an example of the xcolor package in ShareLaTeX
Setting the page background colour
The background colour of the entire page can be easily changed with \pagecolor. See the next example:
\pagecolor{black}
\color{white}

The command \pagecolor{black} set the page colour to black. This is a switch command, meaning it will take effect in the entire document unless another switch command is used to revert it. \nopagecolor will change the background back to normal.
Open an example of the color package in ShareLaTeX
Reference guide
Basic colour names available in LATEX
white, black, red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, yellow
Colour names available with the dvipsnames option
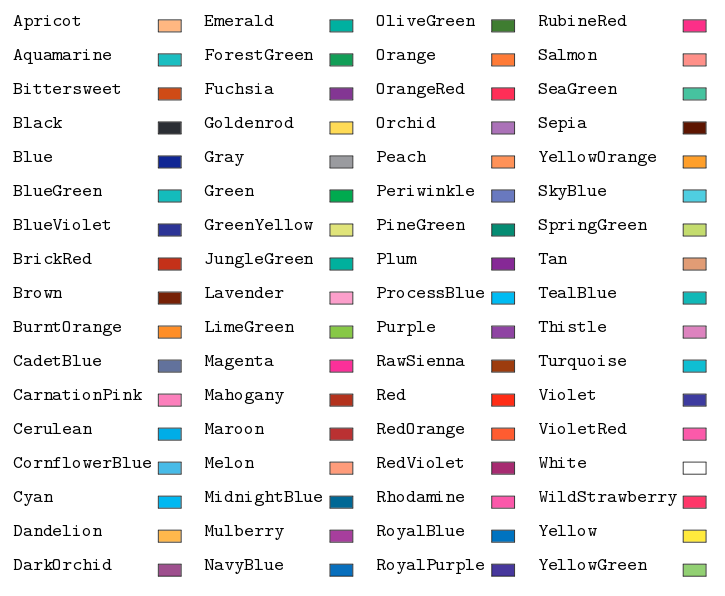
Other drivers have more colour names available, links to documentations in the further reading section.
Open an example of the xcolor package in ShareLaTeX
from: https://www.sharelatex.com/learn/Using_colours_in_LaTeX
在LaTeX中使用颜色 Using colours in LaTeX的更多相关文章
- Latex中如何设置字体颜色(3种方式)
Latex中如何设置字体颜色(三种方式) 1.直接使用定义好的颜色 \usepackage{color} \textcolor{red/blue/green/black/white/cyan/ma ...
- Latex中画出函数文件的调用关系拓扑图
流程图,思维导图,拓扑图通常能把我们遇到的一些复杂的关系结构用图形的方式展现出来.在Latex中要想画这样的拓扑图,有一个很好用的绘图工具包 pgf/tikz . 1.pgf/tikz的安装:pgf/ ...
- LaTeX中Python代码的语法高亮
LaTeX中Python代码的语法高亮 本文中,"{}"中的字母为LaTeX或Python的包名,只有"Pygments"是Python的包,其他都是LaTeX ...
- 如何在latex 中插入EPS格式图片
如何在latex 中插入EPS格式图片 第一步:生成.eps格式的图片 1.利用visio画图,另存为pdf格式的图片 利用Adobe Acrobat裁边,使图片大小合适 另存为.eps格式,如下图所 ...
- Latex中插入C语言代码
Latex是一个文本排版的语言,能排版出各种我们想要的效果.而且用代码排版的优点是易于修改板式,因此在文本内容的排版时,Latex应用十分广泛. 当我们需要在Latex中插入代码时,就需要用到 \us ...
- 计算机中的颜色XIV——快速变换颜色的V分量
基本知识回顾: 计算机中的颜色Color,用RGB模式存储(用R.G.B三个分量表示颜色,每个分量的范围是0—255). 而计算机中的颜色除了用RGB模式表示以外,常见的还有HSV模式(或者是HSB. ...
- paper 48: Latex中如何制作参考文献
文章写到现在,最后一步就要大功告成了!reference,let's go! 一.用Google来做Latex的bib文件 1. 打开scholar.google.com 2. 定制 Schola ...
- Latex中关于参考文献的一些经验
又到了继春节后的又一个投稿高峰,在Latex中写参考文献时经常会出现这样那样的问题,而且出版社不同比如IEEE与Elaver,需要引入的包也有不同.在search解决方案时,发现一篇有用的博文,转载一 ...
- The usage method of reference with bibtex in Latex【latex中参考文献的使用方法】
如何在latex中以Bibtex文件方式引用参考文献? 以IEEEtran模板为例: 1.制作bibtex参考文献库.方法如下: ①建立myreference.bib文件: ②在Google scho ...
随机推荐
- python 单变量线性回归
单变量线性回归(Linear Regression with One Variable)¶ In [54]: #初始化工作 import random import numpy as np imp ...
- Codeforces 486E LIS of Sequence
LIS of Sequence 我们先找出那些肯定不会再LIS里面. 然后我们从前往后扫一次, 当前位置为 i , 看存不存在一个 j 会在lis上并且a[ j ] > a[ i ], 如果满足 ...
- python的异常处理及异常类定义
python的异常处理语法和大多数语言相似: try: try块的语句... except exceptiontype1 as var:#使用as语句获得本次捕获到的异常的实例var except块语 ...
- MOXA的Nport5600初始密码
今天第一次弄Nport,看了半天手册没找到初始密码,网上也搜不到,按照说明书上想打电话问问,发现根本是空号... 后来灵感一来试了一下,居然是:moxa
- mysql where 条件中的字段有NULL值时的sql语句写法
比如你有一个sql语句联表出来之后是这样的 id name phone status 1 张三 ...
- nodejs备忘总结(一) -- 基础入门
什么是NodeJS JS是脚本语言,脚本语言都需要一个解析器才能运行.对于写在HTML页面里的JS,浏览器充当了解析器的角色.而对于需要独立运行的JS,NodeJS就是一个解析器. 每一种解析器都是一 ...
- 允许mysql远程用户连接。
默认mysql是禁止远程用户连接的.连接提示: 1045,“Access denied for user 'root'@'192.168.100.1' (using password:YES)&quo ...
- FireDAC 下的 Sqlite [12] - 备忘录(草草结束这个话题了)
该话题的继续延伸主要就是 SQL 的语法了, 草草收场的原因是现在的脑筋已经进入了 IntraWeb 的世界. 相关备忘会随时补充在下面: //连接多个数据库的参考代码: FDConnection1. ...
- .net core在Linux ARM板上运行
最近接了个临时任务,给别的项目组的机器人平台上开发个小程序,那机器人上跑的是ARM平台,ubuntu的系统. 本来打算用C++写的,由于最近用.net core较多,鉴于其在linux平台良好的兼容性 ...
- python websocket-client connection
参考:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/websocket-client/ https://www.cnblogs.com/saryli/p/6702260.html i ...
