【状压dp】cf906C. Party
需要稍加分析结论;还有一些小细节
Arseny likes to organize parties and invite people to it. However, not only friends come to his parties, but friends of his friends, friends of friends of his friends and so on. That's why some of Arseny's guests can be unknown to him. He decided to fix this issue using the following procedure.
At each step he selects one of his guests A, who pairwise introduces all of his friends to each other. After this action any two friends of Abecome friends. This process is run until all pairs of guests are friends.
Arseny doesn't want to spend much time doing it, so he wants to finish this process using the minimum number of steps. Help Arseny to do it.
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 22; 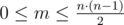 ) — the number of guests at the party (including Arseny) and the number of pairs of people which are friends.
) — the number of guests at the party (including Arseny) and the number of pairs of people which are friends.
Each of the next m lines contains two integers u and v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n; u ≠ v), which means that people with numbers u and v are friends initially. It's guaranteed that each pair of friends is described not more than once and the graph of friendship is connected.
Output
In the first line print the minimum number of steps required to make all pairs of guests friends.
In the second line print the ids of guests, who are selected at each step.
If there are multiple solutions, you can output any of them.
题目大意
给定一些关系(u,v)代表两个人是朋友。每次可以选择一个人i,使i的朋友都相互变成朋友。问最少需要选择多少人,使得所有的人都能够相互认识。
题目分析
一些初步的想法
一开始比较自然地会考虑完全子图的情况。
那么有一个想法是:能不能把这整个完全子图给看成一个人?既然他们互相认识,那么这样它连出的边可以等效吗?
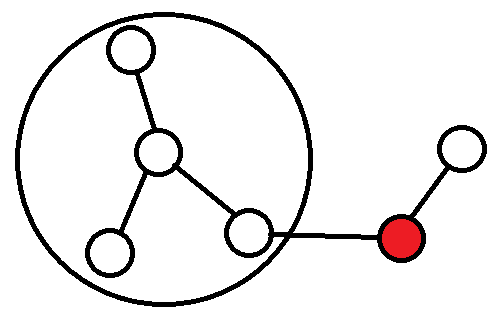
但这个想法的问题在于,这个完全子图的关系“不可拓展”,也就是说在他们的朋友介绍新朋友时,新加进来的人并不能和其他人认识。
那么贪心?
考虑到新加进人的过程是不可逆的。那么能不能够贪心地每次选尽可能多的点呢?
这样似乎还没有找到反例。但是这个做法的潜在危险在于其复杂度基于答案大小,有可能会因为答案数过大而TLE/MLE.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = ; int n,m,ans,id;
struct node
{
int val,vis[maxn],pr[maxn],deg[maxn];
std::bitset<maxn> mp[maxn];
bool legal()
{
for (int i=; i<=n; i++)
if (mp[i].count() < n) return ;
return ;
}
void print()
{
for (int i=; i<=val; i++)
printf("%d ",pr[i]);
puts("");
}
}now,tmp,chg;
std::queue<node> q; int read()
{
char ch = getchar();
int num = ;
bool fl = ;
for (; !isdigit(ch); ch=getchar())
if (ch=='-') fl = ;
for (; isdigit(ch); ch=getchar())
num = (num<<)+(num<<)+ch-;
if (fl) num = -num;
return num;
}
int main()
{
freopen("party.in","r",stdin);
freopen("party.out","w",stdout);
n = read(), m = read(), now.val = , ans = INF;
for (int i=; i<=n; i++) now.mp[i][i] = ;
for (int i=; i<=m; i++)
{
int u = read(), v = read();
now.mp[u][v] = , now.mp[v][u] = ;
}
q.push(now);
while (q.size())
{
tmp = q.front(), q.pop();
if (tmp.legal()){
ans = tmp.val;
printf("%d\n",ans);
tmp.print();
break;
}
bool fnd = ;
while (!fnd){
id = ;
for (int i=; i<=n; i++)
if (!tmp.vis[i]){
tmp.deg[i] = tmp.mp[i].count();
if (tmp.deg[i] > tmp.deg[id]) id = i;
}
for (int i=; i<=n; i++)
if (tmp.deg[i]==tmp.deg[id]){
bool upd = ;
chg = tmp, chg.val++;
chg.vis[i] = , chg.pr[chg.val] = i;
for (int j=; j<=n; j++)
for (int k=; k<=n; k++)
if (j!=k&&chg.mp[i][j]&&chg.mp[i][k]&&!chg.mp[j][k])
chg.mp[k][j] = chg.mp[j][k] = , upd = ;
if (upd) fnd = , q.push(chg);
else tmp.vis[i] = ;
}
}
}
return ;
}
状压dp
注意到特殊的数据范围,考虑状压。
首先明确两个结论:
- 答案与合并顺序无关
- 对图$G=\{V,E\}$中一个完全子图$G'=\{V',E'\}$中的点$x\in V'$进行操作后,其所在的完全子图$G''=\{V'+V_x,E'+E_x\},E_x=\{x,V_x\}\in E$。换句话说就是操作集合内的点能使集合变大。
第一条是因为操作点$x$之后$\forall (x,y_i)$,$y_i$之间都存在边,那么下一步选取$y_i$时会把其他的$y_j$也都连在一起;第二条比较容易理解。
那么用$f[i]$表示$i$的二进制状态下,这些人相互认识的最小代价。
于是转移就是经典的状压转移;顺便再记录一下转移的位置就好了。
需要注意的细节是原图是否已经连通,那么这个就是预处理的时候再判断一下。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
const int maxn = ;
const int maxs = ;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; bool fnd;
int n,m,mx;
int s[maxn],f[maxs],fa[maxs],pr[maxs]; int read()
{
char ch = getchar();
int num = ;
bool fl = ;
for (; !isdigit(ch); ch=getchar())
if (ch=='-') fl = ;
for (; isdigit(ch); ch=getchar())
num = (num<<)+(num<<)+ch-;
if (fl) num = -num;
return num;
}
void fndScheme(int st)
{
if (fa[st]) fndScheme(fa[st]);
printf("%d ",pr[st]);
}
int main()
{
// freopen("party.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("party.out","w",stdout);
memset(f, 0x3f3f3f3f, sizeof f);
n = read(), m = read(), mx = (<<n)-;
for (int i=; i<n; i++) s[i+] = <<i;
for (int i=; i<=m; i++)
{
int x = read()-, y = read()-;
s[x+] |= <<y, s[y+] |= <<x;
}
fnd = ;
for (int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
f[s[i]] = , pr[s[i]] = i;
if (s[i]!=mx) fnd = ;
}
if (fnd){
puts("");
return ;
}
for (int st=; st<=mx; st++)
if (f[st]!=INF){
for (int i=; i<=n; i++)
if (((st>>(i-))&)&&(f[st]+ < f[st|s[i]])){
f[st|s[i]] = f[st]+;
fa[st|s[i]] = st;
pr[st|s[i]] = i;
}
}
printf("%d\n",f[mx]);
fndScheme(mx);
return ;
}
END
【状压dp】cf906C. Party的更多相关文章
- BZOJ 1087: [SCOI2005]互不侵犯King [状压DP]
1087: [SCOI2005]互不侵犯King Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 3336 Solved: 1936[Submit][ ...
- nefu1109 游戏争霸赛(状压dp)
题目链接:http://acm.nefu.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problemShow.php?problem_id=1109 //我们校赛的一个题,状压dp,还在的人用1表示,被淘汰 ...
- poj3311 TSP经典状压dp(Traveling Saleman Problem)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3311 题意:一个人到一些地方送披萨,要求找到一条路径能够遍历每一个城市后返回出发点,并且路径距离最短.最后输出最短距离即可.注意:每一 ...
- [NOIP2016]愤怒的小鸟 D2 T3 状压DP
[NOIP2016]愤怒的小鸟 D2 T3 Description Kiana最近沉迷于一款神奇的游戏无法自拔. 简单来说,这款游戏是在一个平面上进行的. 有一架弹弓位于(0,0)处,每次Kiana可 ...
- 【BZOJ2073】[POI2004]PRZ 状压DP
[BZOJ2073][POI2004]PRZ Description 一只队伍在爬山时碰到了雪崩,他们在逃跑时遇到了一座桥,他们要尽快的过桥. 桥已经很旧了, 所以它不能承受太重的东西. 任何时候队伍 ...
- bzoj3380: [Usaco2004 Open]Cave Cows 1 洞穴里的牛之一(spfa+状压DP)
数据最多14个有宝藏的地方,所以可以想到用状压dp 可以先预处理出每个i到j的路径中最小权值的最大值dis[i][j] 本来想用Floyd写,无奈太弱调不出来..后来改用spfa 然后进行dp,这基本 ...
- HDU 1074 Doing Homework (状压dp)
题意:给你N(<=15)个作业,每个作业有最晚提交时间与需要做的时间,每次只能做一个作业,每个作业超出最晚提交时间一天扣一分 求出扣的最小分数,并输出做作业的顺序.如果有多个最小分数一样的话,则 ...
- 【BZOJ1688】[Usaco2005 Open]Disease Manangement 疾病管理 状压DP
[BZOJ1688][Usaco2005 Open]Disease Manangement 疾病管理 Description Alas! A set of D (1 <= D <= 15) ...
- 【BZOJ1725】[Usaco2006 Nov]Corn Fields牧场的安排 状压DP
[BZOJ1725][Usaco2006 Nov]Corn Fields牧场的安排 Description Farmer John新买了一块长方形的牧场,这块牧场被划分成M列N行(1<=M< ...
随机推荐
- sass预编译器
突然间就不怎么想用博客写笔记了,想改用有道云笔记 sass sass是一个css的预编译程序, 是基于 ruby 的 先要去安装 ruby 在命令行中, 执行以下两句代码(安装sass的), 连网操作 ...
- code blocks无法输出中文解决方法
是CodeBlocks编译器设置问题,在CodeBlocks菜单 settings -> compiler and debugger settings -> global compiler ...
- [软件工程基础]2017.11.05 第九次 Scrum 会议
具体事项 项目交接燃尽图 每人工作内容 成员 已完成的工作 计划完成的工作 工作中遇到的困难 游心 #10 搭建可用的开发测试环境:#9 阅读分析 PhyLab 后端代码与文档:#8 掌握 Larav ...
- [Android]Android之四种常见布局
一个丰富的界面总是要由很多个控件组成的,那我们如何才能让各个控件都有条不紊地 摆放在界面上,而不是乱糟糟的呢?这就需要借助布局来实现了.布局是一种可用于放置很 多控件的容器,它可以按照一定的规律调整内 ...
- Solr创建索引问题
问题描述: 8月 19, 上午10点27:58.219 WARN com.ngdata.hbaseindexer.supervisor.IndexerSupervisor No indexer pro ...
- sql、linq和lambda查询语句比较inner join和group by组合使用及匿名类型的处理
使用EF自己做的小功能需要遇到inner join和group by组合使用及匿名类型的处理,搜了很多,基本不能满足自己的需要,所以总结了也实现了就自己写出来,已备查看及伙伴查询参考(一般的语句查询就 ...
- R17下maps新增参数的问题
今天遇到一个奇怪的问题,我之前写的一个函数在我弟弟的机器上编译出错.代码如下: %%将list [k1,v1,k2,v2...]转换成map {k1=>v1,key2=>v2...} -s ...
- jstl表达式的应用的条件
在el表达式中,有时我们要写for循环,这时我们要写 <c:forEach items="${list}" var="news" > </c: ...
- 公司项目git开发流程规范
手动修改冲突之后,git add . git commit ,git push
- javaweb-servlet生成简单的验证码
package com.serv; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.Graphics; import java.awt.image.BufferedIma ...
