矩池云 | 教你如何使用GAN为口袋妖怪上色

在之前的Demo中,我们使用了条件GAN来生成了手写数字图像。那么除了生成数字图像以外我们还能用神经网络来干些什么呢?
在本案例中,我们用神经网络来给口袋妖怪的线框图上色。
第一步: 导入使用库
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
tf.enable_eager_execution()
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import clear_output
口袋妖怪上色的模型训练过程中,需要比较大的显存。为了保证我们的模型能在2070上顺利的运行,我们限制了显存的使用量为90%, 来避免显存不足的引起的错误。
config = tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.9
session = tf.compat.v1.Session(config=config)
定义需要使用到的常量。
BUFFER_SIZE = 400
BATCH_SIZE = 1
IMG_WIDTH = 256
IMG_HEIGHT = 256
PATH = 'dataset/'
OUTPUT_CHANNELS = 3
LAMBDA = 100
EPOCHS = 10
第二步: 定义需要使用的函数
图片数据加载函数,主要的作用是使用Tensorflow的io接口读入图片,并且放入tensor的对象中,方便后续使用
def load(image_file):
image = tf.io.read_file(image_file)
image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image)
w = tf.shape(image)[1]
w = w // 2
input_image = image[:, :w, :]
real_image = image[:, w:, :]
input_image = tf.cast(input_image, tf.float32)
real_image = tf.cast(real_image, tf.float32)
return input_image, real_image
tensor对象转成numpy对象的函数
在训练过程中,我会可视化一些训练的结果以及中间状态的图片。Tensorflow的tensor对象无法直接在matplot中直接使用,因此我们需要一个函数,将tensor转成numpy对象。
def tensor_to_array(tensor1):
return tensor1.numpy()
第三步: 数据可视化
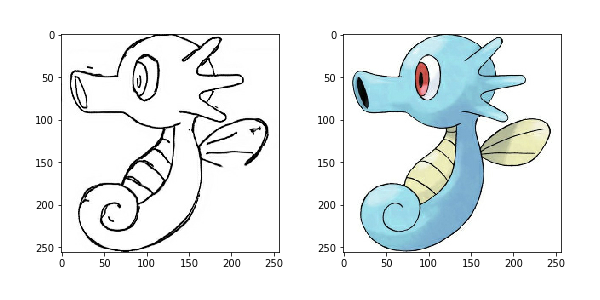
我们先来看下我们的训练数据长成什么样。
我们每张数据图片分成了两个部分,左边部分是线框图,我们用来作为输入数据,右边部分是上色图,我们用来作为训练的目标图片。
我们使用上面定义的load函数来加载一张图片看下
input, real = load(PATH+'train/114.jpg')
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(tensor_to_array(input)/255.0)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(tensor_to_array(real)/255.0)
第四步: 数据增强
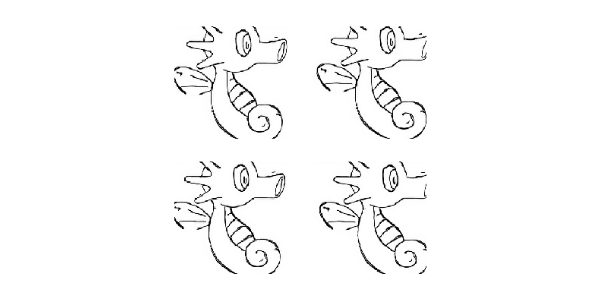
由于我们的训练数据不够多,我们使用数据增强来增加我们的样本。从而让小样本的数据也能达到更好的效果。
我们采取如下的数据增强方案:
- 图片缩放, 将输入数据的图片缩放到我们指定的图片的大小
- 随机裁剪
- 数据归一化
- 左右翻转
def resize(input_image, real_image, height, width):
input_image = tf.image.resize(input_image, [height, width], method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)
real_image = tf.image.resize(real_image, [height, width], method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)
return input_image, real_image
def random_crop(input_image, real_image):
stacked_image = tf.stack([input_image, real_image], axis=0)
cropped_image = tf.image.random_crop(stacked_image, size=[2, IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, 3])
return cropped_image[0], cropped_image[1]
def random_crop(input_image, real_image):
stacked_image = tf.stack([input_image, real_image], axis=0)
cropped_image = tf.image.random_crop(stacked_image, size=[2, IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, 3])
return cropped_image[0], cropped_image[1]
我们将上述的增强方案做成一个函数,其中左右翻转是随机进行
@tf.function()
def random_jitter(input_image, real_image):
input_image, real_image = resize(input_image, real_image, 286, 286)
input_image, real_image = random_crop(input_image, real_image)
if tf.random.uniform(()) > 0.5:
input_image = tf.image.flip_left_right(input_image)
real_image = tf.image.flip_left_right(real_image)
return input_image, real_image
数据增强的效果
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
for i in range(4):
input_image, real_image = random_jitter(input, real)
plt.subplot(2, 2, i+1)
plt.imshow(tensor_to_array(input_image)/255.0)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
第五步: 训练数据的准备
定义训练数据跟测试数据的加载函数
def load_image_train(image_file):
input_image, real_image = load(image_file)
input_image, real_image = random_jitter(input_image, real_image)
input_image, real_image = normalize(input_image, real_image)
return input_image, real_image
def load_image_test(image_file):
input_image, real_image = load(image_file)
input_image, real_image = resize(input_image, real_image, IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH)
input_image, real_image = normalize(input_image, real_image)
return input_image, real_image
使用tensorflow的DataSet来加载训练和测试数据, 定义我们的训练数据跟测试数据集对象
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.list_files(PATH+'train/*.jpg')
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(load_image_train, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
train_dataset = train_dataset.cache().shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE)
train_dataset = train_dataset.batch(1)
test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.list_files(PATH+'test/*.jpg')
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(load_image_test)
test_dataset = test_dataset.batch(1)
第六步: 定义模型
口袋妖怪的上色,我们使用的是GAN模型来训练, 相比上个条件GAN生成手写数字图片,这次的GAN模型的复杂读更加的高。
我们先来看下生成网络跟判别网络的整体结构
生成网络
生成网络使用了U-Net的基本框架,编码阶段的每一个Block我们使用, 卷积层->BN层->LeakyReLU的方式。解码阶段的每一个Block我们使用, 反卷积->BN层->Dropout或者ReLU。其中前三个Block我们使用Dropout, 后面的我们使用ReLU。每一个编码层的Block输出还连接了与之对应的解码层的Block. 具体可以参考U-Net的skip connection.
定义编码Block
def downsample(filters, size, apply_batchnorm=True):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
result = tf.keras.Sequential()
result.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters, size, strides=2, padding='same', kernel_initializer=initializer, use_bias=False))
if apply_batchnorm:
result.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
result.add(tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU())
return result
down_model = downsample(3, 4)
定义解码Block
def upsample(filters, size, apply_dropout=False):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
result = tf.keras.Sequential()
result.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(filters, size, strides=2, padding='same', kernel_initializer=initializer, use_bias=False))
result.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
if apply_dropout:
result.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5))
result.add(tf.keras.layers.ReLU())
return result
up_model = upsample(3, 4)
定义生成网络模型
def Generator():
down_stack = [
downsample(64, 4, apply_batchnorm=False), # (bs, 128, 128, 64)
downsample(128, 4), # (bs, 64, 64, 128)
downsample(256, 4), # (bs, 32, 32, 256)
downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 16, 16, 512)
downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 8, 8, 512)
downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 4, 4, 512)
downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 2, 2, 512)
downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 1, 1, 512)
]
up_stack = [
upsample(512, 4, apply_dropout=True), # (bs, 2, 2, 1024)
upsample(512, 4, apply_dropout=True), # (bs, 4, 4, 1024)
upsample(512, 4, apply_dropout=True), # (bs, 8, 8, 1024)
upsample(512, 4), # (bs, 16, 16, 1024)
upsample(256, 4), # (bs, 32, 32, 512)
upsample(128, 4), # (bs, 64, 64, 256)
upsample(64, 4), # (bs, 128, 128, 128)
]
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(OUTPUT_CHANNELS, 4,
strides=2,
padding='same',
kernel_initializer=initializer,
activation='tanh') # (bs, 256, 256, 3)
concat = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate()
inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None,None,3])
x = inputs
skips = []
for down in down_stack:
x = down(x)
skips.append(x)
skips = reversed(skips[:-1])
for up, skip in zip(up_stack, skips):
x = up(x)
x = concat([x, skip])
x = last(x)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=x)
generator = Generator()
判别网络
判别网络我们使用PatchGAN, PatchGAN又称之为马尔可夫判别器。传统的基于CNN的分类模型有很多都是在最后引入了一个全连接层,然后将判别的结果输出。然而PatchGAN却不一样,它完全由卷积层构成,最后输出的是一个纬度为N的方阵。然后计算矩阵的均值作真或者假的输出。从直观上看,输出方阵的每一个输出,是模型对原图中的一个感受野,这个感受野对应了原图中的一块地方,也称之为Patch,因此,把这种结构的GAN称之为PatchGAN。
PatchGAN中的每一个Block是由卷积层->BN层->Leaky ReLU组成的。
在我们的这个模型中,最后一层我们的输出的纬度是(Batch Size, 30, 30, 1), 其中1表示图片的通道。
每个30x30的输出对应着原图的70x70的区域。详细的结构可以参考这篇论文。
def Discriminator():
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
inp = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None, None, 3], name='input_image')
tar = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None, None, 3], name='target_image')
# (batch size, 256, 256, channels*2)
x = tf.keras.layers.concatenate([inp, tar])
# (batch size, 128, 128, 64)
down1 = downsample(64, 4, False)(x)
# (batch size, 64, 64, 128)
down2 = downsample(128, 4)(down1)
# (batch size, 32, 32, 256)
down3 = downsample(256, 4)(down2)
# (batch size, 34, 34, 256)
zero_pad1 = tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D()(down3)
# (batch size, 31, 31, 512)
conv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 4, strides=1, kernel_initializer=initializer, use_bias=False)(zero_pad1)
batchnorm1 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(conv)
leaky_relu = tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(batchnorm1)
# (batch size, 33, 33, 512)
zero_pad2 = tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D()(leaky_relu)
# (batch size, 30, 30, 1)
last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(1, 4, strides=1, kernel_initializer=initializer)(zero_pad2)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=[inp, tar], outputs=last)
discriminator = Discriminator()
第七步: 定义损失函数和优化器
**
**
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
**
def discriminator_loss(disc_real_output, disc_generated_output):
real_loss = loss_object(tf.ones_like(disc_real_output), disc_real_output)
generated_loss = loss_object(tf.zeros_like(disc_generated_output), disc_generated_output)
total_disc_loss = real_loss + generated_loss
return total_disc_loss
def generator_loss(disc_generated_output, gen_output, target):
gan_loss = loss_object(tf.ones_like(disc_generated_output), disc_generated_output)
l1_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(target - gen_output))
total_gen_loss = gan_loss + (LAMBDA * l1_loss)
return total_gen_loss
generator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)
discriminator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)
第八步: 定义CheckPoint函数
由于我们的训练时间较长,因此我们会保存中间的训练状态,方便后续加载继续训练
checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(generator_optimizer=generator_optimizer,
discriminator_optimizer=discriminator_optimizer,
generator=generator,
discriminator=discriminator)
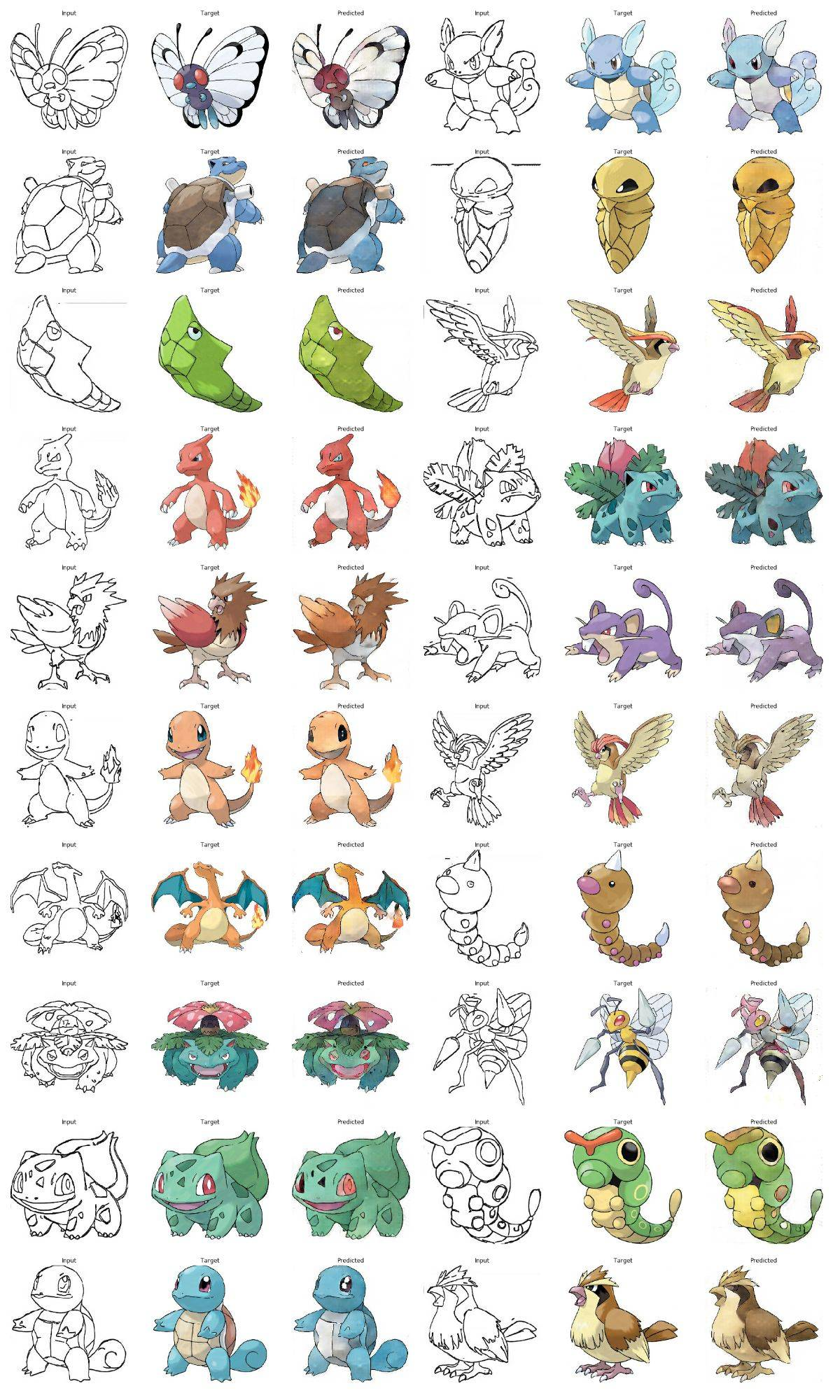
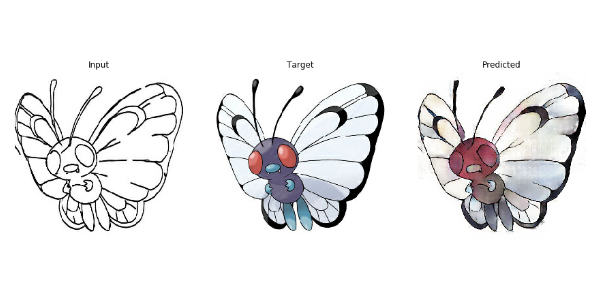
如果我们保存了之前的训练的结果,我们加载保存的数据。然后我们应用上次保存的模型来输出下我们的测试数据。
def generate_images(model, test_input, tar):
prediction = model(test_input, training=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
display_list = [test_input[0], tar[0], prediction[0]]
title = ['Input', 'Target', 'Predicted']
for i in range(3):
plt.subplot(1, 3, i+1)
plt.title(title[i])
plt.imshow(tensor_to_array(display_list[i]) * 0.5 + 0.5)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
ckpt_manager = tf.train.CheckpointManager(checkpoint, "./", max_to_keep=2)
if ckpt_manager.latest_checkpoint:
checkpoint.restore(ckpt_manager.latest_checkpoint)
for inp, tar in test_dataset.take(20):
generate_images(generator, inp, tar)

第九步: 训练
在训练中,我们输出第一张图片来查看每个epoch给我们的预测结果带来的变化。让大家感受到其中的乐趣
每20个epoch我们保存一次状态
@tf.function
def train_step(input_image, target):
with tf.GradientTape() as gen_tape, tf.GradientTape() as disc_tape:
gen_output = generator(input_image, training=True)
disc_real_output = discriminator([input_image, target], training=True)
disc_generated_output = discriminator([input_image, gen_output], training=True)
gen_loss = generator_loss(disc_generated_output, gen_output, target)
disc_loss = discriminator_loss(disc_real_output, disc_generated_output)
generator_gradients = gen_tape.gradient(gen_loss,
generator.trainable_variables)
discriminator_gradients = disc_tape.gradient(disc_loss,
discriminator.trainable_variables)
generator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(generator_gradients,
generator.trainable_variables))
discriminator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(discriminator_gradients,
discriminator.trainable_variables))
def fit(train_ds, epochs, test_ds):
for epoch in range(epochs):
start = time.time()
for input_image, target in train_ds:
train_step(input_image, target)
clear_output(wait=True)
for example_input, example_target in test_ds.take(1):
generate_images(generator, example_input, example_target)
if (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0:
ckpt_save_path = ckpt_manager.save()
print ('保存第{}个epoch到{}\n'.format(epoch+1, ckpt_save_path))
print ('训练第{}个epoch所用的时间为{:.2f}秒\n'.format(epoch + 1, time.time()-start))
fit(train_dataset, EPOCHS, test_dataset)
训练第8个epoch所用的时间为51.33秒。
第十步: 使用测试数据上色,查看下我们的效果
for input, target in test_dataset.take(20):
generate_images(generator, input, target)
矩池云现在已经上架 “口袋妖怪上色” 镜像;感兴趣的小伙伴可以通过矩池云官网“Jupyter 教程 Demo” 镜像中尝试使用。
矩池云 | 教你如何使用GAN为口袋妖怪上色的更多相关文章
- 矩池云上使用nvidia-smi命令教程
简介 nvidia-smi全称是NVIDIA System Management Interface ,它是一个基于NVIDIA Management Library(NVML)构建的命令行实用工具, ...
- 矩池云里查看cuda版本
可以用下面的命令查看 cat /usr/local/cuda/version.txt 如果想用nvcc来查看可以用下面的命令 nvcc -V 如果环境内没有nvcc可以安装一下,教程是矩池云上如何安装 ...
- 在矩池云上复现 CVPR 2018 LearningToCompare_FSL 环境
这是 CVPR 2018 的一篇少样本学习论文:Learning to Compare: Relation Network for Few-Shot Learning 源码地址:https://git ...
- 矩池云上安装yolov4 darknet教程
这里我是用PyTorch 1.8.1来安装的 拉取仓库 官方仓库 git clone https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet 镜像仓库 git clone https: ...
- 用端口映射的办法使用矩池云隐藏的vnc功能
矩池云隐藏了很多高级功能待用户去挖掘. 租用机器 进入jupyterlab 设置vnc密码 VNC_PASSWD="userpasswd" ./root/vnc_startup.s ...
- 矩池云上安装ikatago及远程链接教程
https://github.com/kinfkong/ikatago-resources/tree/master/dockerfiles 从作者的库中可以看到,该程序支持cuda9.2.cuda10 ...
- 矩池云上编译安装dlib库
方法一(简单) 矩池云上的k80因为内存问题,请用其他版本的GPU去进行编译,保存环境后再在k80上用. 准备工作 下载dlib的源文件 进入python的官网,点击PyPi选项,搜索dilb,再点击 ...
- 如何在矩池云上运行FinRL-Libray股票交易策略框架
FinRL-Libray 项目:https://github.com/AI4Finance-LLC/FinRL-Library 选择FinRL镜像 在矩池云-主机市场选择合适的机器,并选择FinRL- ...
- 使用 MobaXterm 连接矩池云 GPU服务器
Host Name(主机名):hz.matpool.com 或 hz-t2.matpool.com,请以您 SSH 中给定的域名为准. Port(端口号):矩池云租用记录里 SSH 链接里冒号后的几位 ...
随机推荐
- git命令行-新建分支与已提交分支合并
例如要将A分支的一个commit合并到B分支: 首先切换到A分支 git checkout A git log 找出要合并的commit ID : 例如 325d41 然后切换到B分支上 git ch ...
- 阿里四面:你知道Spring AOP创建Proxy的过程吗?
Spring在程序运行期,就能帮助我们把切面中的代码织入Bean的方法内,让开发者能无感知地在容器对象方法前后随心添加相应处理逻辑,所以AOP其实就是个代理模式. 但凡是代理,由于代码不可直接阅读,也 ...
- kindof
kindof:相当于 __kindof:表示当前类或者它的子类' 类设计历史 id:可以调用任何对象方法,不能进行编译检查 @interface Person : NSObject // xcode5 ...
- linux 进程信号
转载请注明来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/hookjc/ signal 函数的使用方法简单,但并不属于 POSIX 标准,在各类 UNIX 平台上的实现不尽相同,因此其用途受 到 ...
- webpack引入css文件
需要配置 postcss 详见 官网 https://www.postcss.com.cn/
- Feign的异步调用或者MQ调用与Security的问题处理;
两大踩坑点: 一:部分框架自带有查询当前登录人的信息工具,无需各种本地线程栈ThreadLocals取Request啥的折磨自己: 二:Security自带有uri匹配的工具,没事多翻翻源码,原创方法 ...
- go基础——基本数据类型
GO语言的数据类型: /* GO语言的数据类型: 1.基本数据类型: 布尔类型:true,false 数值类型:整数,浮点,复数complex 字符串:string 2.复合数据类型 array,sl ...
- MATLAB基础学习(3)——数值数组及运算
rand('state',s)表示随机产生数的状bai态state,一般情百况du下不用指定状态.rand('state',0)作用在于如果指容定zhi状态,产生dao随机结果就相同了.一般情况下不用 ...
- Flask初探之WSGI
Flask是一个使用 Python 编写的轻量级 Web 应用框架.较其他同类型框架更为灵活.轻便.安全且容易上手.它可以很好地结合MVC模式进行开发,小型团队在短时间内就可以完成功能丰富的中小型网站 ...
- tar压缩打包实用命令总结
一.tar常用命令参数 用法:tar [参数] [文件] -v 显示指令执行过程 -c 创建压缩文件 -x 解压文件 -z 通过gzip指令处理文件 -f 指定文件 -C 解压文件到指定目录 -t - ...
