springIOC源码接口分析(九):Environment
先贴一下接口继承关系图,spring容器启动的时候会初始化环境,所以此接口相关接口非常有必要进行了解:
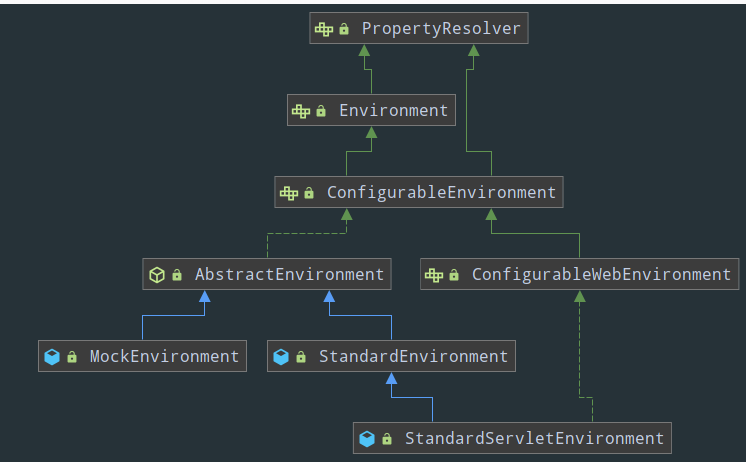
一 PropertyResolver接口
Environment继承了该接口,PropertyResolver接口用于在properties文件,yml文件,xml文件,甚至是一些nosql等文件解析一系列的属性值,
以及解析字符串中的属性表达式的接口,如${foo}/abc,foo对应的属性值为123,解析后为123/abc。
接口方法定义:
public interface PropertyResolver {
/**
* 判断是够存在key对应的属性值
*/
boolean containsProperty(String key);
/**
* 获取key对应的属性值
*/
@Nullable
String getProperty(String key);
/**
* 获取key对应的属性值,如果没有则返回传递的默认值
*/
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
/**
* 获取key对应的属性值,并解析为对应类型:
* 例如:
* Environment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
* Integer age = environment.getProperty("ages", Integer.class,5);
*/
@Nullable
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* 如果没有返回一个默认的对应类型值
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
/**
* 获取不到会抛异常
*/
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 获取不到或者获取到类型无法解析会抛异常
*/
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 根据传入的字符串将其中${}解析成对应key的属性值,比如:
* ${age}/test 解析为 24/test 并返回
*/
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
/**
* 无法解析会报错
*/
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
二 PropertyResolver实现
1 ConfigurablePropertyResolver
该接口定义了如何对组件本身进行配置。如:刚刚提到获取value时可以指定任意类型,这依赖于ConversionService进行类型转换,当前接口就提供了对ConversionService的设置和获取。
另外,可以配置属性占位符的格式,包括:占位符前缀(默认为"${")、占位符后缀(默认为"}")、占位符值分隔符(默认为":",用于分隔propertyName和defaultValue)。
组件还可以设置哪些属性是必须存在的,还可以校验必须存在的属性是否真的存在(不存在的话会抛出异常)。具体接口如下:
public interface ConfigurablePropertyResolver extends PropertyResolver {
/**
* 获取ConversionService,主要用于类型转换
*/
ConfigurableConversionService getConversionService();
/**
* 设置获取ConversionService
*/
void setConversionService(ConfigurableConversionService conversionService);
/**
* 设置占位符前缀格式(默认为"${")、占位符后缀(默认为"}")
*/
void setPlaceholderPrefix(String placeholderPrefix);
/**
* 设置占位符后缀格式(默认为"}")
*/
void setPlaceholderSuffix(String placeholderSuffix);
/**
* 设置占位符分隔符有(默认为":") 用于分隔propertyName和defaultValue 比如 ${age:25}
*/
void setValueSeparator(@Nullable String valueSeparator);
/**
* 设置遇到无法解析的占位符时是否引发异常,即是否忽略
*/
void setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(boolean ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders);
/**
* 设置哪些属性必须存在
*/
void setRequiredProperties(String... requiredProperties);
/**
* 校验设置了必须存在的属性是否真的存在,只要有一个不存在会抛出异常
*/
void validateRequiredProperties() throws MissingRequiredPropertiesException;
}
2 AbstractPropertyResolver
上述两个接口的抽象实现类。它实现了ConfigurablePropertyResolver接口的所有方法。
关于PropertyResolver接口方法,还有1个getPropertyAsRawString方法需要子类实现.
这个方法用于直接返回获取到的value值(不进行占位符替换),一般的getProperty方法默认都会替换掉value值中的占位符后返回
3 PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
该类是体系中唯一的完整实现类。它以PropertySources属性源集合(内部持有属性源列表List<PropertySource>)为属性值的来源,
按序遍历每个PropertySource,获取到一个非null的属性值则返回,实现了getPropertyAsRawString方法,并继承了父抽象类已经实现好的方法
三 PropertySources接口
PropertySources接口定义是保存一个或者多个PropertySource对象,继承自Iterable<PropertySource<?>>,定义了多个PropertySource的迭代接口。
只有一个默认的实现类MutablePropertySources,通过CopyOnWriteArrayList保存多个PropertySource对象,并增加了维护PropertySource在列表中的具体位置的接口
接口定义了三个方法:
public interface PropertySources extends Iterable<PropertySource<?>> {
/**
* 获取泛型PropertySource的stream流
*/
default Stream<PropertySource<?>> stream() {
return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);
}
/**
* 是否含有给定的key
*/
boolean contains(String name);
/**
* 根据给定key获取PropertySource
*/
@Nullable
PropertySource<?> get(String name);
}
其只有一个实现类MutablePropertySources:
public class MutablePropertySources implements PropertySources {
//PropertySource对象集合
private final List<PropertySource<?>> propertySourceList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
@Override
@Nullable
public PropertySource<?> get(String name) {
// 此处用indexOf迭代,因为PropertySource重写了equals方法,使得只比较key就可以,named返回一个指定
//key的空实现,value默认是new Object,来进行查找索引
int index = this.propertySourceList.indexOf(PropertySource.named(name));
return (index != -1 ? this.propertySourceList.get(index) : null);
}
//......一些迭代方法的实现
}
四 PropertySource抽象类
PropertySource是抽象类,表示一个键值对,用于存放(key-value)键值对的抽象,value可以是任意类型,注意该类重写了equals()和hashCode()方法,
提供了一个named(String name)方法用于构造基于name的PropertySource的空实现,从而便于PropertySource 集合中查找指定属性名的PropertySource:
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
protected final String name; // key
protected final T source; // value
//构造器
public PropertySource(String name, T source) {
Assert.hasText(name, "Property source name must contain at least one character");
Assert.notNull(source, "Property source must not be null");
this.name = name;
this.source = source;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public PropertySource(String name) {
this(name, (T) new Object());
}
/**
* 获取key
*/
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
/**
* 获取value
*/
public T getSource() {
return this.source;
}
/**
* 是否包含给定key的属性
*/
public boolean containsProperty(String name) {
return (getProperty(name) != null);
}
/**
* 获取key对应的value
*/
@Nullable
public abstract Object getProperty(String name);
/**
* 重写equals,如果两个属性的key,即name相等,也返回true
* ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals:传入的对象都不等于null,则返回equals方法结果
* 此处如果name字符串都不等于null,且相等则返回true
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
return (this == other || (other instanceof org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource &&
ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.name, ((org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource<?>) other).name)));
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.name);
}/**
* 根据给定的name构造一个子类ComparisonPropertySource的实现,value默认是一个new Object()
*/
public static org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource<?> named(String name) {
return new org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource.ComparisonPropertySource(name);
}
/**
* value是new Object()的子类
*/
public static class StubPropertySource extends org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource<Object> {
public StubPropertySource(String name) {
super(name, new Object());
}
/**
* 子类对象如果获取属性,永远返回null
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String getProperty(String name) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 继承StubPropertySource的子类,调用其他方法都抛异常
*/
static class ComparisonPropertySource extends org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource.StubPropertySource {
private static final String USAGE_ERROR =
"ComparisonPropertySource instances are for use with collection comparison only";
public ComparisonPropertySource(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public Object getSource() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(USAGE_ERROR);
}
@Override
public boolean containsProperty(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(USAGE_ERROR);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public String getProperty(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(USAGE_ERROR);
}
}
}
PropertySource还有许多实现类,增加获取各种属性的方法,比如获取系统属性,jvm启动属性,map类型属性等等,这里就不写了,可查看源码
五 Environment接口规范
Environment实现扩展了PropertyResolver接口,定义了代表当前应用程序所处的运行环境的方法,接口方法定义如下:
/**
* 返回激活的profile配置文件环境后缀,比如 dev,test
*/
String[] getActiveProfiles(); /**
* 返回默认的profile配置环境,默认是default
*/
String[] getDefaultProfiles(); @Deprecated
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles); /**
* 判断给定环境是否存在,有一个存在返回true,比如:environment.acceptsProfiles(Profiles.of("dev","test"))
*/
boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles);
该接口继承关系如图:
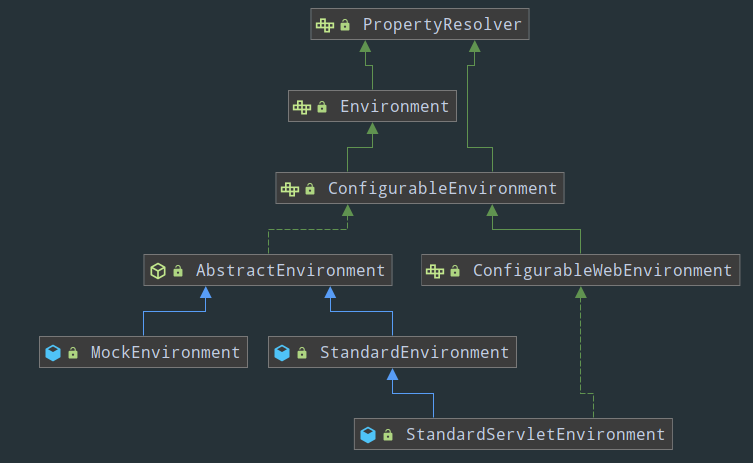
1 ConfigurableEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment接口实现了Environment, ConfigurablePropertyResolver,主要是对Environment接口进行扩展,
Environment接口中有获取激活的默认的配置环境等方法,在此接口中添加了设置这些环境等方法,并增加了
getPropertySources方法来获取PropertySources属性,以便于获取属性集合,还添加了一些获取系统属性,合并(merger)属性集合等方法
此接口方法定义如下:
/**
* 根据环境后缀设置激活的profile文件
*/
void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles); /**
* 添加激活的配置文件
*/
void addActiveProfile(String profile); /**
* 如果没有其他文件就设置默认的激活配置文件
*/
void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles); /**
* 获取PropertySources接口,用来操作PropertySource属性集合
*/
MutablePropertySources getPropertySources(); /**
* 获取系统环境设置,获取这个System类的getProperties()方法,如果获取不到就使用一个有效key再次尝试获取,下面方法也是一样的
*/
Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties(); /** * 获取系统环境 */
Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment(); /** * 将给定父环境的活动配置文件、默认配置文件合并到此(子)环境各自的集合的属性源。 * 如果有相同名称的,丢弃父环境的使用当前子环境的 */
void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent);
2 AbstractEnvironment
AbstractEnvironment抽象类实现了ConfigurableEnvironment接口,并且实现了接口定义的所有方法,并且在构造器里定义了一个初始化的protected
方法,空实现,以供子类进行各自初始化:
构造器:
/**
* Create a new {@code Environment} instance, calling back to
* {@link #customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources)} during construction to
* allow subclasses to contribute or manipulate {@link PropertySource} instances as
* appropriate.
* @see #customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources)
*/
public AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
}
初始化方法:
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
}
3 StandardEnvironment
StandardEnvironment类继承了上面的抽象类AbstractEnvironment,标准环境,普通Java应用时使用,会自动注册System.getProperties() 和 System.getenv()到环境,
覆写了父类定义的初始化方法进行系统属性的初始化,MapPropertySource和SystemEnvironmentPropertySource都是属性类PropertySource的子类实现,都是对资源的抽象:
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
4 ConfigurableWebEnvironment
此接口实现了ConfigurableEnvironment接口,只定义了一个方法,用来对web环境的属性进行初始化的,定义的环境在web项目启动时会 进行调用:
public interface ConfigurableWebEnvironment extends ConfigurableEnvironment {
void initPropertySources(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig);
}
比如springboot项目启动web环境调用地方:
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
if (environment instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) { // 判断是否是web环境的接口
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) environment)
.initPropertySources(this.servletContext, null); //调用初始化方法
}
}
5 StandardServletEnvironment
StandardServletEnvironment继承了StandardEnvironment类,还实现了ConfigurableWebEnvironment接口定义的初始化方法用来初始化注册ServletConfig(DispatcherServlet)、ServletContext
标准的servlet环境,在web项目环境时使用,初始化时候除了调用父类初始化方法进行系统属性的初始化之外还会自动注册JNDI实例到环境:
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
//调用父类的初始化方法
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
//此方法在web项目启动的时候会调用
@Override
public void initPropertySources(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig);
}
还有一个MockEnvironment实现类也继承了抽象类,是测试的时候模拟使用的
6 自定义环境配置
因为上面抽象类构造器里面提供了一个空实现的初始化方法,我们可以看到初始化属性都是在子类里面完成的,
所以spring提供了这个接口来方方便我们进行自定义环境配置,只需要实现抽象父类,然后在上面提到的初始化方法里面进行自定义设置即可,spring是真心强大!
六 实际应用
ApplicationContext等容器虽然没有直接继承Environment接口,但是继承了一个EnvironmentCapable接口:
该接口只定义了一个方法,即获取容器方法:
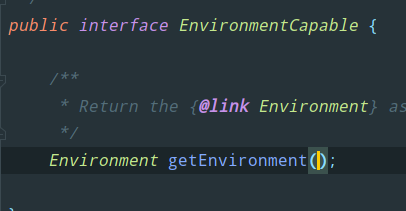
从而在容器实现类中通过该方法返回Environment对象(实现类中有引用属性),来使用此接口功能:

开发中使用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext application = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = application.getEnvironment();
Integer age = environment.getRequiredProperty("age",Integer.class);
String str = environment.resolvePlaceholders("/${age}/hou");
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(environment.getDefaultProfiles()));
}
springIOC源码接口分析(九):Environment的更多相关文章
- springIOC源码接口分析(三):ApplicationContext
一 新增方法 主要都是获取容器基本信息的一些接口,比如获取名称,id和启动时间戳,获取AutowireCapableBeanFactory等接口 二 继承接口 ApplicationContext继承 ...
- springIOC源码接口分析(八):AutowireCapableBeanFactory
参考博文: https://blog.csdn.net/f641385712/article/details/88651128 一 接口规范 从宏观上看,AutowireCapableBeanFact ...
- springIOC源码接口分析(十一):ConfigurableApplicationContext
一 实现接口 关系图: ConfigurableApplicationContext接口实现了三个接口,ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable, Applic ...
- springIOC源码接口分析(七):ApplicationEventPublisher
一 定义方法 此接口主要是封装事件发布功能的接口,定义了两个方法: /** * 通知应用所有已注册且匹配的监听器此ApplicationEvent */ default void publishEve ...
- springIOC源码接口分析(六):ResourceLoader
参考博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/jixp/articles/10702486.html 一 定义方法 Spring提供了ResourceLoader接口用于实现不同的Res ...
- springIOC源码接口分析(五):ListableBeanFactory
一 继承关系 该接口是对BeanFactory的扩展,允许预加载bean定义的BeanFactory可以实现此接口 其目的在于使实现它的BeanFactory能够枚举所有的Bean 该接口不支持分层结 ...
- springIOC源码接口分析(四):MessageSource
一 定义方法 MessageSource接口用于支持信息的国际化和包含参数的信息的替换 这个接口定义了三个方法: public interface MessageSource { /** * 解析co ...
- springIOC源码接口分析(二):ConfigurableBeanFactory
一 继承功能 1 SingletonBeanRegistry接口 此接口是针对Spring中的单例Bean设计的.提供了统一访问单例Bean的功能,类中定义了以下方法: 2 HierarchicalB ...
- springIOC源码接口分析(一):BeanFactory
一 应用场景 BeanFactory接口定义了IOC容器的最基本功能,提供了容器应该具有的功能规范,所有的容器都应该实现这个接口 BeanFactory设计了getBean方法用来获取容器中的Bean ...
随机推荐
- HashMap面试题解答
一.HashMap的实现原理? 此题可以组成如下连环炮来问 你看过HashMap源码嘛,知道原理嘛?为什么用数组+链表?hash冲突你还知道哪些解决办法?我用LinkedList代替数组结构可以么?既 ...
- SofaBoot使用Nacos进行服务注册发现
前提 最近创业公司的项目组基于业务需要,开发一套新的微服务,考虑到选用的组件必须是主流.社区活跃.生态完善以及方便迁移到云上等因素,引入了SOFAStack全家桶.微服务开发里面,一个很重要的功能就是 ...
- 洛谷$P3645\ [APIO2015]$雅加达的摩天楼 最短路
正解:最短路 解题报告: 传送门$QwQ$ 考虑暴力连边,发现最多有$n^2$条边.于是考虑分块 对于长度$p_i$小于等于$\sqrt(n)$的边,建立子图$d=p_i$.说下关于子图$d$的定义? ...
- $SCOI2009\ windy$数 数位$dp$
\(Sol\) 数位\(dp\)常规套路题. \(dp[i][j]\)表示从低位到高位填到第\(i\)位且第\(i\)位的数字为\(j\)的方案数.答案就是\(sol(r)-sol(l+1).\)这里 ...
- FRPC 双向socket通讯 转发请求类轮子
一直在找一个能双向通讯的C#库 学识浅薄没有找到 于是封装一个预计BUG奇多的轮子 他是基于SuperSocket开发的 这样的 它跟传统的 架构不一样 它的最小架构 或者 客户端即是服务端 比如一个 ...
- .net core试水
概述 大概记录下我如何第一次使用.net core搭建一个api,由于最近.net core比较火,我也尝试着使用.net core做了一个小功能 本文主要包括 1.环境配置 2.程序编写 3.程序部 ...
- 用本地自定义域名访问远程服务器,并支持websocket和cookie
场景 在公司会有很多测试的机器,或者一些OA服务,Confluence,Jenkins,各种中间件的后台等等,都使用HTTP访问,且由于是内网机器没有域名,输入IP又要输入不同端口,访问起来比较麻烦. ...
- spring cloud 微服务之 -- 配置文件拆分之道
0-前言 在spring cloud微服务架构中,基本上每个拆分的微服务都会部署多个运行实例,这些运行实例,配置基本都是一样的,不同的是少数配置,比如端口,而这些不同的配置又是必不可少的 那我们怎么来 ...
- 「洛谷P1198」 [JSOI2008]最大数 解题报告
P1198 [JSOI2008]最大数 题目描述 现在请求你维护一个数列,要求提供以下两种操作: 1. 查询操作. 语法:Q L 功能:查询当前数列中末尾L个数中的最大的数,并输出这个数的值. 限制: ...
- 贪心 park
来总结一道非常经典的好题 这一道题是通过贪心实现的 首先看到这一题的时间复杂度 n<=100000 需要一个比较玄学的做法 我们先假设把题干改成这个样子 一圈n个车位 停在每个车位都有一定的代价 ...
