[Kotlin Tutorials 21] 协程的取消
协程的取消
本文讨论协程的取消, 以及实现时可能会碰到的几个问题.
本文属于合辑: https://github.com/mengdd/KotlinTutorials
协程的取消
取消的意义: 避免资源浪费, 以及多余操作带来的问题.
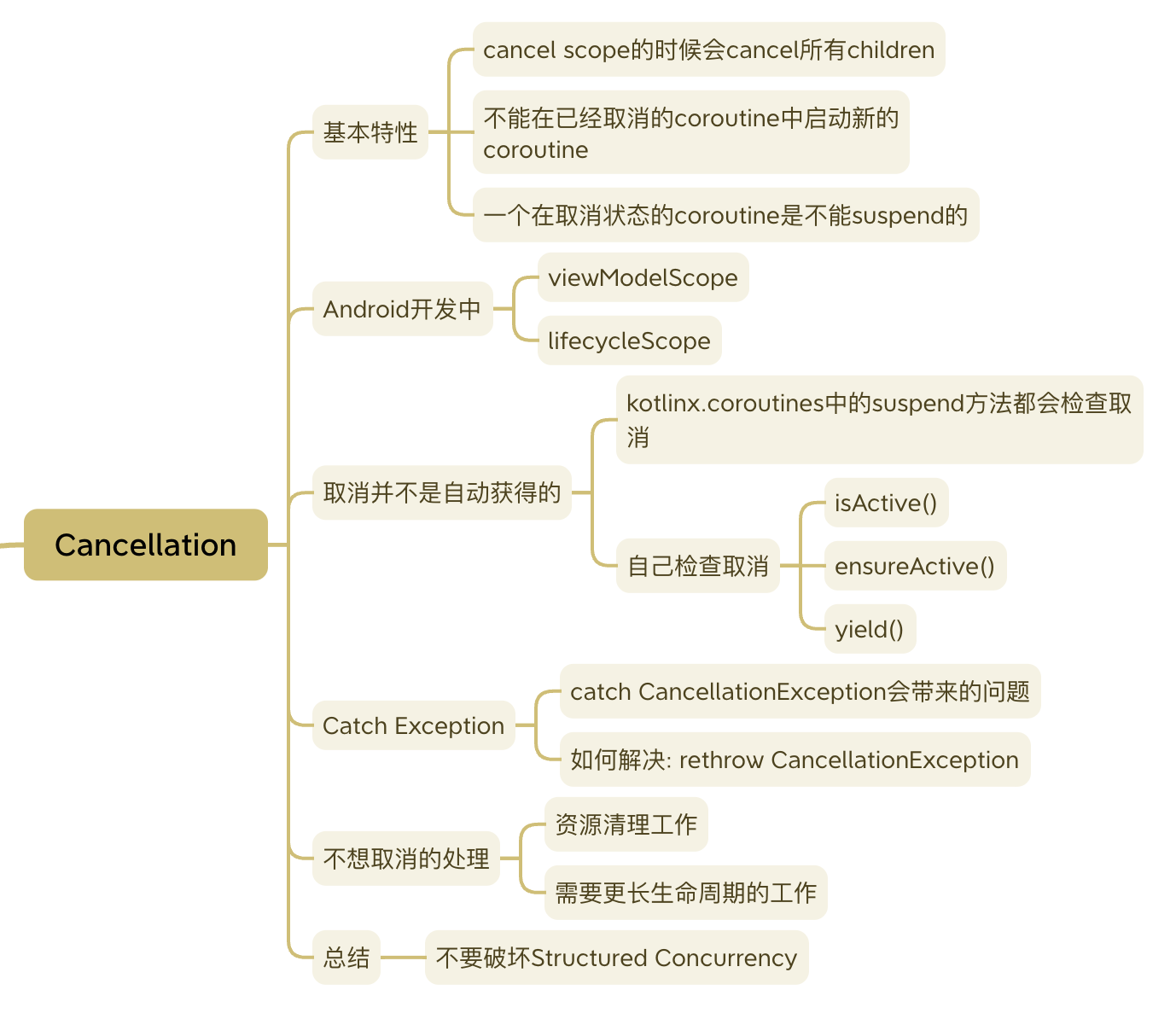
基本特性:
- cancel scope的时候会cancel其中的所有child coroutines.
- 一旦取消一个scope, 你将不能再在其中launch新的coroutine.
- 一个在取消状态的coroutine是不能suspend的.
如果一个coroutine抛出了异常, 它将会把这个exception向上抛给它的parent, 它的parent会做以下三件事情:
- 取消其他所有的children.
- 取消自己.
- 把exception继续向上传递.
Android开发中的取消
在Android开发中, 比较常见的情形是由于View生命周期的终止, 我们需要取消一些操作.
通常我们不需要手动调用cancel()方法, 那是因为我们利用了一些更高级的包装方法, 比如:
viewModelScope: 会在ViewModel onClear的时候cancel.lifecycleScope: 会在作为Lifecycle Owner的View对象: Activity, Fragment到达DESTROYED状态时cancel.
取消并不是自动获得的
all suspend functions from kotlinx.coroutines are cancellable, but not yours.
kotlin官方提供的suspend方法都会有cancel的处理, 但是我们自己写的suspend方法就需要自己留意.
尤其是耗时或者带循环的地方, 通常需要自己加入检查, 否则即便调用了cancel, 代码也继续在执行.
有这么几种方法:
isActive()ensureActive()yield(): 除了ensureActive以外, 会出让资源, 比如其他工作不需要再往线程池里加线程.
一个在循环中检查coroutine是否依然活跃的例子:
fun main() = runBlocking {
val startTime = currentTimeMillis()
val job = launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
var nextPrintTime = startTime
var i = 0
while (isActive) { // cancellable computation loop
// print a message twice a second
if (currentTimeMillis() >= nextPrintTime) {
println("job: I'm sleeping ${i++} ...")
nextPrintTime += 500L
}
}
}
delay(1300L) // delay a bit
println("main: I'm tired of waiting!")
job.cancelAndJoin() // cancels the job and waits for its completion
println("main: Now I can quit.")
}
输出:
job: I'm sleeping 0 ...
job: I'm sleeping 1 ...
job: I'm sleeping 2 ...
main: I'm tired of waiting!
main: Now I can quit.
catch Exception和runCatching
众所周知catch一个很general的Exception类型可能不是一个好做法.
因为你以为捕获了A, B, C异常, 结果实际上还有D, E, F.
捕获具体的异常类型, 在开发阶段的快速失败会帮助我们更早定位和解决问题.
协程还推出了一个"方便"的runCatching方法, catchThrowable.
让我们写出了看似更"保险", 但却更容易破坏取消机制的代码.
如果我们catch了CancellationException, 会破坏Structured Concurrency.
看这个例子:
fun main() = runBlocking {
val job = launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
println("my long time function start")
myLongTimeFunction()
println("my other operations ==== ") // this line should not be printed when cancelled
}
delay(1300L) // delay a bit
println("main: I'm tired of waiting!")
job.cancelAndJoin() // cancels the job and waits for its completion
println("main: Now I can quit.")
}
private suspend fun myLongTimeFunction() = runCatching {
var i = 0
while (i < 10) {
// print a message twice a second
println("job: I'm sleeping ${i++} ...")
delay(500)
}
}
输出:
my long time function start
job: I'm sleeping 0 ...
job: I'm sleeping 1 ...
job: I'm sleeping 2 ...
main: I'm tired of waiting!
my other operations ====
main: Now I can quit.
当job cancel了以后后续的工作不应该继续进行, 然而我们可以看到log仍然被打印出来, 这是因为runCatching把异常全都catch了.
这里有个open issue讨论这个问题: https://github.com/Kotlin/kotlinx.coroutines/issues/1814
CancellationException的特殊处理
如何解决上面的问题呢? 基本方案是把CancellationException再throw出来.
比如对于runCatching的改造, NowInAndroid里有这么一个方法suspendRunCatching:
private suspend fun <T> suspendRunCatching(block: suspend () -> T): Result<T> = try {
Result.success(block())
} catch (cancellationException: CancellationException) {
throw cancellationException
} catch (exception: Exception) {
Log.i(
"suspendRunCatching",
"Failed to evaluate a suspendRunCatchingBlock. Returning failure Result",
exception
)
Result.failure(exception)
}
上面的例子改为用这个suspendRunCatching方法替代runCatching就修好了.
上面例子的输出变为:
my long time function start
job: I'm sleeping 0 ...
job: I'm sleeping 1 ...
job: I'm sleeping 2 ...
main: I'm tired of waiting!
main: Now I can quit.
不想取消的处理
可能还有一些工作我们不想随着job的取消而完全取消.
资源清理工作
finally通常用于try block之后的的资源清理, 如果其中没有suspend方法那么没有问题.
如果finally中的代码是suspend的, 如前所述, 一个在取消状态的coroutine是不能suspend的.
那么需要用一个withContext(NonCancellable).
例子:
fun main() = runBlocking {
val job = launch {
try {
repeat(1000) { i ->
println("job: I'm sleeping $i ...")
delay(500L)
}
} finally {
withContext(NonCancellable) {
println("job: I'm running finally")
delay(1000L)
println("job: And I've just delayed for 1 sec because I'm non-cancellable")
}
}
}
delay(1300L) // delay a bit
println("main: I'm tired of waiting!")
job.cancelAndJoin() // cancels the job and waits for its completion
println("main: Now I can quit.")
}
注意这个方法一般用于会suspend的资源清理, 不建议在各个场合到处使用, 因为它破坏了对coroutine执行取消的控制.
需要更长生命周期的工作
如果有一些工作需要比View/ViewModel更长的生命周期, 可以把它放在更下层, 用一个生命周期更长的scope.
可以根据不同的场景设计, 比如可以用一个application生命周期的scope:
class MyApplication : Application() {
// No need to cancel this scope as it'll be torn down with the process
val applicationScope = CoroutineScope(SupervisorJob() + otherConfig)
}
再把这个scope注入到repository中去.
如果需要做的工作比application的生命周期更长, 那么可以考虑用WorkManager.
总结: 不要破坏Structured Concurrency
Structure Concurrency为开发者提供了方便管理多个coroutines的有效方法.
基本上破坏Structure Concurrency特性的行为(比如用GlobalScope, 用NonCancellable, catch CancellationException等)都是反模式, 要小心使用.
还要注意不要随便传递job.
CoroutineContext有一个元素是job, 但是这并不意味着我们可以像切Dispatcher一样随便传一个job参数进去.
文章: Structured Concurrency Anniversary
看这里: https://github.com/Kotlin/kotlinx.coroutines/issues/1001
References & Further Reading
Kotlin官方文档的网页版和markdown版本:
Android官方文档上链接的博客和视频:
- Cancellation in coroutines
- KotlinConf 2019: Coroutines! Gotta catch 'em all! by Florina Muntenescu & Manuel Vivo
其他:
- Coroutines: first things first
- Kotlin Coroutines and Flow - Use Cases on Android
- Structured Concurrency Anniversary
- Exceptions in coroutines
- Coroutines & Patterns for work that shouldn’t be cancelled
[Kotlin Tutorials 21] 协程的取消的更多相关文章
- kotlin学习-Coroutines(协程)
协程(又名纤程),轻量级线程(建立在线程基础上,属于用户态调用),非阻塞式编程(像同步编写一样),在用户态内进行任务调度,避免与内核态过多交互问题,提高程序快速响应.协程使用挂起当前上下文替代阻塞,被 ...
- Kotlin Coroutine(协程): 二、初识协程
@ 目录 前言 一.初识协程 1.runBlocking: 阻塞协程 2.launch: 创建协程 3.Job 4.coroutineScope 5.协程取消 6.协程超时 7.async 并行任务 ...
- Kotlin Coroutine(协程): 三、了解协程
@ 目录 前言 一.协程上下文 1.调度器 2.给协程起名 3.局部变量 二.启动模式 CoroutineStart 三.异常处理 1.异常测试 2.CoroutineExceptionHandler ...
- Kotlin 协程一 —— 全面了解 Kotlin 协程
一.协程的一些前置知识 1.1 进程和线程 1.1.1基本定义 1.1.2为什么要有线程 1.1.3 进程与线程的区别 1.2 协作式与抢占式 1.2.1 协作式 1.2.2 抢占式 1.3 协程 二 ...
- Kotlin协程解析系列(上):协程调度与挂起
vivo 互联网客户端团队- Ruan Wen 本文是Kotlin协程解析系列文章的开篇,主要介绍Kotlin协程的创建.协程调度与协程挂起相关的内容 一.协程引入 Kotlin 中引入 Corout ...
- Kotlin协程第一个示例剖析及Kotlin线程使用技巧
Kotlin协程第一个示例剖析: 上一次https://www.cnblogs.com/webor2006/p/11712521.html已经对Kotlin中的协程有了理论化的了解了,这次则用代码来直 ...
- Kotlin协程入门
开发环境 IntelliJ IDEA 2021.2.2 (Community Edition) Kotlin: 212-1.5.10-release-IJ5284.40 介绍Kotlin中的协程.用一 ...
- Android中的Coroutine协程原理详解
前言 协程是一个并发方案.也是一种思想. 传统意义上的协程是单线程的,面对io密集型任务他的内存消耗更少,进而效率高.但是面对计算密集型的任务不如多线程并行运算效率高. 不同的语言对于协程都有不同的实 ...
- Unity协程Coroutine使用总结和一些坑
原文摘自 Unity协程Coroutine使用总结和一些坑 MonoBehavior关于协程提供了下面几个接口: 可以使用函数或者函数名字符串来启动一个协程,同时可以用函数,函数名字符串,和Corou ...
- 第二章 - Java与协程
Java与协程 内核线程的局限 通过一个具体场景来解释目前Java线程面临的困境.今天对Web应用的服务要求,不论是在请求数量上还是在复杂度上,与十多年前相比已不可同日而语,这一方面是源于业务量的增长 ...
随机推荐
- Java面试——Redis
一.Redis 为什么那么快 [1]完全基于内存,绝大部分请求是纯粹的内存操作,非常快速.数据存在内存中.[2]数据结构简单,对数据操作也简单,Redis中的数据结构是专门进行设计的.[3]采用单线程 ...
- 免费Midjourney AI绘画Prompt提示词平台合集
Midjourney AI绘图最关键的地方在于Prompt提示词写的好,一个好的提示词可以让AI模型创造出更优质的绘图,以下是8个免费的Midjourney Prompt提示词辅助平台. 编辑切换 ...
- 纯CSS3实现多行文本截断
纯CSS处理多行文本展开和收起,直接上代码和效果图 1 <html> 2 <header> 3 <style> 4 .wrap { 5 position: rela ...
- Win系统下的免杀思路(总结非教程)
1.简介 在安全厂商日趋成熟的背景下,编写免杀马的难度和成本日益增长.好用新兴的开源项目在短时间内就被分析并加入特征库.笔者调研了部分开源项目,其中也有项目做了类似的分析 [1],目前能够免杀的项目初 ...
- 我没能实现始终在一个线程上运行 task
前文我们总结了在使用常驻任务实现常驻线程时,应该注意的事项.但是我们最终没有提到如何在处理对于带有异步代码的办法.本篇将接受笔者对于该内容的总结. 如何识别当前代码跑在什么线程上 一切开始之前,我们先 ...
- [JavaScript]Promise:异步编程
1 文由 某项目的需求:先要请求API1,再以API1的结果请求API2. var n, a; //var r = window.md5; var r = function (password, us ...
- Java设计模式 —— 享元模式
14 享元模式 14.1 享元模式概述 Flyweight Pattern: 运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度对象的复用. 当系统中存在大量相同或相似的对象时,它通过共享技术实现相同或相似的细粒度对象 ...
- HTML、 input;、accept 属性-规定能够通过文件上传进行提交的文件类型
定义和用法 文章地址: http://www.w3school.com.cn/tags/att_input_accept.asp accept 属性规定了可通过文件上传提交的服务器接受的文件类型. 注 ...
- 【Vue项目】尚品汇(四)Search组件开发
Search模块开发 分析:1)编写静态页面 2)编写api 3)编写vuex三大件 4)组件获取仓库数据,并进行动态展示 1 SearchSelector 1 编写api export const ...
- Linx 阶段一
Linux Linux常用命令 具体演示 1). ls 2). pwd 3). touch 4). mkdir 5). rm 使用技巧 1. 连按 Tab健自动补齐文件名 2. ll 查看当前目录文件 ...
