MinkowskiPooling池化(下)
MinkowskiPooling池化(下)
MinkowskiPoolingTranspose
class MinkowskiEngine.MinkowskiPoolingTranspose(kernel_size, stride, dilation=1, kernel_generator=None, dimension=None)
稀疏张量的池转置层。
展开功能,然后将其除以贡献的非零元素的数量。
__init__(kernel_size, stride, dilation=1, kernel_generator=None, dimension=None)
用于稀疏张量的高维解卷层。
Args:
kernel_size (int, optional): 输出张量中内核的大小。如果未提供,则region_offset应该是 RegionType.CUSTOM并且region_offset应该是具有大小的2D矩阵N×D 这样它列出了所有D维度的 N 偏移量。.
stride (int, or list, optional): stride size of the convolution layer. If non-identity is used, the output coordinates will be at least stride ×× tensor_stride away. When a list is given, the length must be D; each element will be used for stride size for the specific axis.
dilation (int, or list, optional): 卷积内核的扩展大小。给出列表时,长度必须为D,并且每个元素都是轴特定的膨胀。所有元素必须> 0。
kernel_generator (MinkowskiEngine.KernelGenerator, optional): 定义自定义内核形状。
dimension(int):定义所有输入和网络的空间的空间尺寸。例如,图像在2D空间中,网格和3D形状在3D空间中。
cpu() → T
将所有模型参数和缓冲区移至CPU。
返回值:
模块:selfcuda(device: Optional[Union[int, torch.device]] = None) → T
将所有模型参数和缓冲区移至GPU。
这也使关联的参数并缓冲不同的对象。因此,在构建优化程序之前,如果模块在优化过程中可以在GPU上运行,则应调用它。
参数:
设备(整数,可选):如果指定,则所有参数均为
复制到该设备
返回值:
模块:self
double() →T
将所有浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为double数据类型。
返回值:
模块:self
float() →T
将所有浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为float数据类型。
返回值:
模块:self
forward(input: SparseTensor.SparseTensor, coords: Union[torch.IntTensor, MinkowskiCoords.CoordsKey, SparseTensor.SparseTensor] = None)
input (MinkowskiEngine.SparseTensor): Input sparse tensor to apply a convolution on.
coords ((torch.IntTensor, MinkowskiEngine.CoordsKey, MinkowskiEngine.SparseTensor), optional): If provided, generate results on the provided coordinates. None by default.
to(*args, **kwargs)
Moves and/or casts the parameters and buffers.
This can be called as
to(device=None, dtype=None, non_blocking=False)
to(dtype, non_blocking=False)
to(tensor, non_blocking=False)
to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
其签名类似于torch.Tensor.to(),但仅接受所需dtype的浮点s。另外,此方法将仅将浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为dtype (如果给定的话)。device如果给定了整数参数和缓冲区 ,但dtype不变。当 non_blocking被设置时,它试图转换/如果可能异步相对于移动到主机,例如,移动CPU张量与固定内存到CUDA设备。
请参见下面的示例。
Args:
device (torch.device): the desired device of the parameters
and buffers in this module
dtype (torch.dtype): the desired floating point type of
the floating point parameters and buffers in this module
tensor (torch.Tensor): Tensor whose dtype and device are the desired
dtype and device for all parameters and buffers in this module
memory_format (torch.memory_format): the desired memory
format for 4D parameters and buffers in this module (keyword only argument)
Returns:
Module: self
Example:
>>> linear = nn.Linear(2, 2)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]])
>>> linear.to(torch.double)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> gpu1 = torch.device("cuda:1")
>>> linear.to(gpu1, dtype=torch.half, non_blocking=True)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16, device='cuda:1')
>>> cpu = torch.device("cpu")
>>> linear.to(cpu)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16)
type(dst_type: Union[torch.dtype, str]) → T
Casts all parameters and buffers to dst_type.
Arguments:
dst_type (type or string): the desired type
Returns:
Module: self
MinkowskiGlobalPooling
class MinkowskiEngine.MinkowskiGlobalPooling(average=True, mode=<GlobalPoolingMode.AUTO: 0>)
将所有输入功能集中到一个输出。
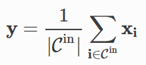
将稀疏坐标减少到原点,即将每个点云减少到原点,返回batch_size点的数量[[0,0,…,0],[0,0,…,1] ,, [0, 0,…,2]],其中坐标的最后一个元素是批处理索引。
Args:
average (bool): 当为True时,返回平均输出。如果不是,则返回所有输入要素的总和。
cpu() → T
将所有模型参数和缓冲区移至CPU。
返回值:
模块:自我
Module: self
cuda(device: Optional[Union[int, torch.device]] = None) → T
将所有模型参数和缓冲区移至GPU。
这也使关联的参数并缓冲不同的对象。因此,在构建优化程序之前,如果模块在优化过程中可以在GPU上运行,则应调用它。
参数:
device (int, optional): if specified, all parameters will be
copied to that device
Returns:
Module: self
double() → T
将所有浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为double数据类型。
Returns:
Module: self
float() → T
将所有浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为float数据类型。
返回值:
模块:self
forward(input)
to(*args, **kwargs)
移动和/或强制转换参数和缓冲区。
这可以称为
to(device=None, dtype=None, non_blocking=False)
to(dtype, non_blocking=False)
to(tensor, non_blocking=False)
to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
其签名类似于torch.Tensor.to(),但仅接受所需dtype的浮点s。另外,此方法将仅将浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为dtype (如果给定的话)。device如果给定了整数参数和缓冲区 ,dtype不变。当 non_blocking被设置时,它试图转换/如果可能异步相对于移动到主机,例如,移动CPU张量与固定内存到CUDA设备。
请参见下面的示例。
Args:
device (torch.device): the desired device of the parameters
and buffers in this module
dtype (torch.dtype): the desired floating point type of
the floating point parameters and buffers in this module
tensor (torch.Tensor): Tensor whose dtype and device are the desired
dtype and device for all parameters and buffers in this module
memory_format (torch.memory_format): the desired memory
format for 4D parameters and buffers in this module (keyword only argument)
Returns:
Module: self
Example:
>>> linear = nn.Linear(2, 2)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]])
>>> linear.to(torch.double)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> gpu1 = torch.device("cuda:1")
>>> linear.to(gpu1, dtype=torch.half, non_blocking=True)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16, device='cuda:1')
>>> cpu = torch.device("cpu")
>>> linear.to(cpu)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16)
type(dst_type: Union[torch.dtype, str]) → T
Casts all parameters and buffers to dst_type.
Arguments:
dst_type (type or string): the desired type
Returns:
Module: self
MinkowskiPooling池化(下)的更多相关文章
- MinkowskiPooling池化(上)
MinkowskiPooling池化(上) 如果内核大小等于跨步大小(例如kernel_size = [2,1],跨步= [2,1]),则引擎将更快地生成与池化函数相对应的输入输出映射. 如果使用U网 ...
- 卷积和池化的区别、图像的上采样(upsampling)与下采样(subsampled)
1.卷积 当从一个大尺寸图像中随机选取一小块,比如说 8x8 作为样本,并且从这个小块样本中学习到了一些特征,这时我们可以把从这个 8x8 样本中学习到的特征作为探测器,应用到这个图像的任意地方中去. ...
- 【小白学PyTorch】21 Keras的API详解(下)池化、Normalization层
文章来自微信公众号:[机器学习炼丹术].作者WX:cyx645016617. 参考目录: 目录 1 池化层 1.1 最大池化层 1.2 平均池化层 1.3 全局最大池化层 1.4 全局平均池化层 2 ...
- 测试EntityFramework,Z.EntityFramework.Extensions,原生语句在不同的查询中的表现。原来池化与非池化设定是有巨大的影响的。
Insert测试,只测试1000条的情况,多了在实际的项目中应该就要另行处理了. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using Syste ...
- 由浅入深了解Thrift之客户端连接池化
一.问题描述 在上一篇<由浅入深了解Thrift之服务模型和序列化机制>文章中,我们已经了解了thrift的基本架构和网络服务模型的优缺点.如今的互联网圈中,RPC服务化的思想如火如荼.我 ...
- Deep Learning 学习随记(七)Convolution and Pooling --卷积和池化
图像大小与参数个数: 前面几章都是针对小图像块处理的,这一章则是针对大图像进行处理的.两者在这的区别还是很明显的,小图像(如8*8,MINIST的28*28)可以采用全连接的方式(即输入层和隐含层直接 ...
- 池化 - Apache Commons Pool
对于那些创建耗时较长,或者资源占用较多的对象,比如网络连接,线程之类的资源,通常使用池化来管理这些对象,从而达到提高性能的目的.比如数据库连接池(c3p0, dbcp), java的线程池 Execu ...
- 对象池化技术 org.apache.commons.pool
恰当地使用对象池化技术,可以有效地减少对象生成和初始化时的消耗,提高系统的运行效率.Jakarta Commons Pool组件提供了一整套用于实现对象池化的框架,以及若干种各具特色的对象池实现,可以 ...
- 高可用的池化 Thrift Client 实现(源码分享)
本文将分享一个高可用的池化 Thrift Client 及其源码实现,欢迎阅读源码(Github)并使用,同时欢迎提出宝贵的意见和建议,本人将持续完善. 本文的主要目标读者是对 Thrift 有一定了 ...
随机推荐
- 播放视频插件swfobject.js与Video Html5
播放视频的方法: 方法一. 使用HTML5播放 <video src="./files/Clip_480_5sec_6mbps_h264.mp4" width="1 ...
- [转]gitlab ci/cd 发布
转自 https://meigit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/configure_gitlab_i18n_and_create_gitlab_ci_with_gitlab_ru ...
- Win64 驱动内核编程-3.内核里使用内存
内核里使用内存 内存使用,无非就是申请.复制.设置.释放.在 C 语言里,它们对应的函数是:malloc.memcpy.memset.free:在内核编程里,他们分别对应 ExAllocatePool ...
- Win64 驱动内核编程-14.回调监控文件
回调监控文件 使用 ObRegisterCallbacks 实现保护进程,其实稍微 PATCH 下内核,这个函数还能实现文件操作监视.但可惜只能在 WIN7X64 上用.因为在 WIN7X64 上 P ...
- 【vue-01】快速入门
什么是vue vue是渐进式的JavaScript框架 什么是渐进式? 你可以在原有大系统的上面,把一两个组件改用vue实现,:也可以整个项目用vue全家桶开发. vue是一个轻量级的MVVM ...
- liunx中文件夹不能删除怎么操作
1.运行rm -rf 文件名称 2.不能删除对应文件并且提示"rm: cannot remove './.user.ini': Operation not permitted" 操 ...
- python-内置函数-文件操作
文件操作 用的最多的就是r+,w+和a+都有局限性 w+是先清空,然后再写,之后再读 a+是无论如何调整指针位置,写时都在文件最后追加 而r+可以通过调整指针位置来确定写入的位置 文件操作之with处 ...
- MySQL密码复杂度与密码过期策略介绍
前言: 年底了,你的数据库是不是该巡检了?一般巡检都会关心密码安全问题,比如密码复杂度设置,是否有定期修改等.特别是进行等保评测时,评测机构会要求具备密码安全策略.其实 MySQL 系统本身可以设置密 ...
- Codeforces Round #694 (Div. 2)
A. Strange Partition 题意:就是求最小和最大的bi/x向上取整的和. 思路:见题解:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45900709/article/detai ...
- “深度评测官”——记2020BUAA软工软件案例分析作业
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 2020春季计算机学院软件工程(罗杰 任建) 这个作业的要求在哪里 个人博客作业-软件案例分析 我在这个课程的目标是 完成一次完整的软件开发经历并以博客的方式记录开发 ...
