【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 3—多分类逻辑回归和神经网络
作业说明
Exercise 3,Week 4,使用Octave实现图片中手写数字 0-9 的识别,采用两种方式(1)多分类逻辑回归(2)多分类神经网络。对比结果。
(1)多分类逻辑回归:实现 lrCostFunction 计算代价和梯度。实现 OneVsAll 使用 fmincg 函数进行训练。使用 OneVsAll 里训练好的 theta 对 X 的数据类型进行预测,得到平均准确率。
(2)多分类神经网络:两层 theta 权重值在 ex3weights 里已提供。参数不需要调,只需要在 predict 里进行矩阵计算,即可得到分类结果。
数据集 :ex3data1.mat 。手写数字图片数据,5000个样例。每张图片20px * 20px,也就是一共400个特征。数据集X维度为5000 * 400
ex3weights.mat。神经网络每一层的权重。
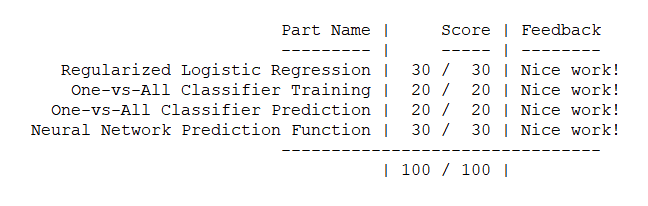
文件清单
ex3.m - Octave/MATLAB script that steps you through part 1
ex3 nn.m - Octave/MATLAB script that steps you through part 2
ex3data1.mat - Training set of hand-written digits
ex3weights.mat - Initial weights for the neural network exercise
submit.m - Submission script that sends your solutions to our servers
displayData.m - Function to help visualize the dataset
fmincg.m - Function minimization routine (similar to fminunc)
sigmoid.m - Sigmoid function
[*] lrCostFunction.m - Logistic regression cost function
[*] oneVsAll.m - Train a one-vs-all multi-class classier
[*] predictOneVsAll.m - Predict using a one-vs-all multi-class classier
[*] predict.m - Neural network prediction function
* 为必须要完成的
结论
因为Octave里数组下标从1开始。所以这里将分类结果0用10替代。预测结果中的1-10代表图片数字为1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0
矩阵运算 tricky 的地方在于维度对应,哪里需要转置很关键。
多分类逻辑回归模型
一、在数据集X里随机选择100个数字,绘制
displayData.m:
function [h, display_array] = displayData(X, example_width)
%DISPLAYDATA Display 2D data in a nice grid
% [h, display_array] = DISPLAYDATA(X, example_width) displays 2D data
% stored in X in a nice grid. It returns the figure handle h and the
% displayed array if requested. % Set example_width automatically if not passed in
if ~exist('example_width', 'var') || isempty(example_width)
example_width = round(sqrt(size(X, )));
end % Gray Image
colormap(gray); % Compute rows, cols
[m n] = size(X);
example_height = (n / example_width); % Compute number of items to display
display_rows = floor(sqrt(m));
display_cols = ceil(m / display_rows); % Between images padding
pad = ; % Setup blank display
display_array = - ones(pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad), ...
pad + display_cols * (example_width + pad)); % Copy each example into a patch on the display array
curr_ex = ;
for j = :display_rows
for i = :display_cols
if curr_ex > m,
break;
end
% Copy the patch % Get the max value of the patch
max_val = max(abs(X(curr_ex, :)));
display_array(pad + (j - ) * (example_height + pad) + (:example_height), ...
pad + (i - ) * (example_width + pad) + (:example_width)) = ...
reshape(X(curr_ex, :), example_height, example_width) / max_val;
curr_ex = curr_ex + ;
end
if curr_ex > m,
break;
end
end % Display Image
h = imagesc(display_array, [- ]); % Do not show axis
axis image off drawnow; end
ex3.m里的调用
load('ex3data1.mat'); % training data stored in arrays X, y
m = size(X, );
% Randomly select data points to display
rand_indices = randperm(m);
sel = X(rand_indices(:), :);
displayData(sel);
运行效果如下:

二、代价函数
注意:θ0不参与正则化。
正则化逻辑回归的代价函数如下,分为三项:
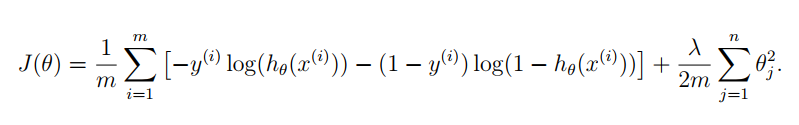
梯度下降算法如下:


lrCostFunction.m:
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda) m = length(y); % number of training examples temp = theta; temp() = ; % because we don't add anything for j = 0 % 第一项
part1 = -y' * log(sigmoid(X * theta));
% 第二项
part2 = ( - y)' * log(1 - sigmoid(X * theta)); % 正则项
regTerm = lambda / / m * temp' * temp;
J = / m * (part1 - part2) + regTerm; % 梯度
grad = / m * X' *((sigmoid(X * theta) - y)) + lambda / m * temp; grad = grad(:); end
正则化之后的代价函数同时返回代价 J 和 grad 梯度。这里和上个星期实现的二分类逻辑回归代码是一样的。
三、训练oneVsAll多分类模型
week2逻辑回归分类的目标是区分两种类型。写好代价函数之后,调用一次 fminunc 函数,得到 theta、就可以画出 boundary。
但是多分类中需要训练 K 个分类器,所以多了一个 oneVsAll.m。其实就是循环 K 次,得到一个 theta矩阵(row 为 K,column为特征值个数)。
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda) % Some useful variables
m = size(X, );
n = size(X, ); % You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + ); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, ) X]; initial_theta = zeros(n + , ); options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', ); % Run fmincg to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
for i = : num_labels,
[theta] = ...
fmincg(@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == i), lambda)), ...
initial_theta, options);
all_theta(i,:) = theta';
end;
end
多分类使用的 Octave 函数是 fmincg 不是 fminunc,fmincg更适合参数多的情况。
注意这里用到了 y == i,这个操作将 y 中每个数据和 i 进行比较。得到的矩阵中(这里是向量)相同的为1,不同的为0。
ex3.m 里的调用
lambda = 0.1;
[all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda);
四、使用OneVsAll分类器进行预测
predictOneVsAll.m
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X) m = size(X, );
num_labels = size(all_theta, ); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, ), ); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, ) X]; temp = X * all_theta';
[x, p] = max(temp,[],); end
将 X 与 theta 相乘得到预测结果,得到一个 5000*10 的矩阵,每行对应一个分类结果(只有一个1,其余为0)。
题目要求返回的矩阵 p 是一个 5000*1 的矩阵。每行是 1-K 的数字。使用 max 函数,得到两个返回值。第一个 x 是一个全1的向量,没用。第二个是 1 所在的 index,也就是对应的类别。
ex3.m 中的调用:
pred = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X);
fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * );
三层神经网络
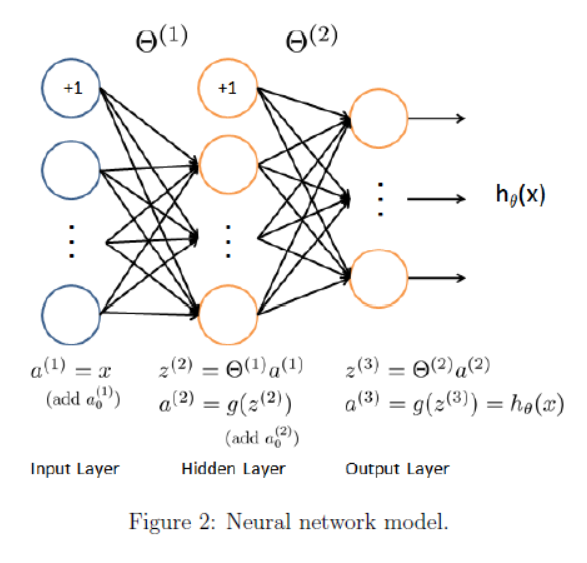
这里g(z) 使用 sigmoid 函数。
神经网络中,从上到下的每个原点是 feature 特征 x0, x1, x2...,不是实例。计算过程其实就是 feature 一层一层映射的过程。一层转换之后,feature可能变多、也可能变少。下一层 i+1层 feature 的个数是通过权重矩阵里当前 θ(i) 的 row 行数来控制。
两层权重 θ 已经在 ex3weights.mat 里给出。从a1映射到a2权重矩阵 θ1为 25 * 401,从a2映射到a3权重矩阵 θ2为10 * 26。因为最后有10个分类。(这意味着运算的时候要注意转置)
一、使用OneVsAll分类器进行预测
权重已经在文件中给出了,只需要矩阵相乘,预测就好了
predict.m :
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label of an input given a trained neural network
% p = PREDICT(Theta1, Theta2, X) outputs the predicted label ofxgiven the
% trained weights of a neural network (Theta1, Theta2) % Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned neural network. You should set p to a
% vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels.
%
% Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max
% function can also return the index of the max element, for more
% information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you
% can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row.
%0 % Add ones to thexdata matrix
a1 = [ones(m, 1) X]; %5000x401
a2 = sigmoid(a1 * Theta1'); %5000x401乘以401x25得到5000x25。即把401个feature映射到25 a2 = [ones(m, 1) a2]; %5000x26
a3 = sigmoid(a2 * Theta2'); %5000x26乘以26x10得到5000x10。即把26个feature映射到10 [x,p] = max(a3,[],2); %和上面逻辑回归多分类一样,最后使用 max 函数获得分类结果。
% ========================================================================= end
二、预测结果
em3_nn.m 里的调用
%% Setup the parameters you will use for this exercise
input_layer_size = 400; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
hidden_layer_size = 25; % 25 hidden units
num_labels = 10; % 10 labels, from 1 to 10
% (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10) load('ex3weights.mat'); pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X); fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * 100); % To give you an idea of the network's output, you can also run
% through the examples one at the a time to see what it is predicting. % Randomly permute examples 随机获取数字,显示预测结果
rp = randperm(m); for i = 1:m
% Display
fprintf('\nDisplaying Example Image\n');
displayData(X(rp(i), :)); pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X(rp(i),:));
fprintf('\nNeural Network Prediction: %d (digit %d)\n', pred, mod(pred, 10)); % Pause with quit option
s = input('Paused - press enter to continue, q to exit:','s');
if s == 'q'
break
end
end
运行结果:
准确率 Training Set Accuracy: 97.520000

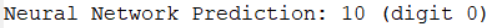

这里我比较疑惑的一点是。代码中没对 0 进行特殊处理,为什么能预测成10。后来一想 整个计算过程都是权重矩阵控制的,给的 weights 文件里已经是调整好的结果了,0 就是会被分类成10。
所以神经网络最主要的还是调参啊,调 θ 矩阵。
三、关于矩阵相乘
矩阵这里转置总是出问题。仔细思考一下
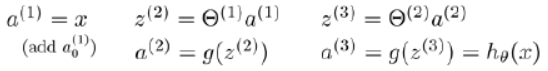
(1)假设只有一个实例 x,而且它像图中一样是一个列向量。那根据神经网络的公式,最相符的应该是 θ(i) * x。最后的得到的是 K 维列向量。
(2)但实际情况中,训练数据通常一行一个实例。如果严格按图和公式去计算,(θ(i) * XT)T 就需要将 X 先转置过来,最后再转置回去。应该是下面的代码,但是明显能看出比上面的方法麻烦:
a1 = [ones(, m); X']; %401x5000
a2 = sigmoid(Theta1 * a1); %25x401 乘以 401x5000 得到25x5000 a2 = [ones(, m); a2]; %26x5000
a3 = sigmoid(Theta2 * a2); %10x26 乘以 26x5000 得到10x5000 a3 = a3'; % 5000x10
(3)所以用 X * θ(i)T 替换 (θ(i) * XT)T
a1 = [ones(m, ) X]; %5000x401
a2 = sigmoid(a1 * Theta1'); %5000x401乘以401x25得到5000x25。即把401个feature映射到25 a2 = [ones(m, ) a2]; %5000x26
a3 = sigmoid(a2 * Theta2'); %5000x26乘以26x10得到5000x10。即把26个feature映射到10
https://github.com/madoubao/coursera_machine_learning/tree/master/homework/machine-learning-ex3/ex3
【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 3—多分类逻辑回归和神经网络的更多相关文章
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 4—反向传播神经网络
课程笔记 Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 9_Neural Networks learning 作业说明 Exercise 4,Week 5,实现反向传播 ba ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 1 线性回归
作业说明 Exercise 1,Week 2,使用Octave实现线性回归模型.数据集 ex1data1.txt ,ex1data2.txt 单变量线性回归必须实现,实现代价函数计算Computin ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 2——逻辑回归
作业说明 Exercise 2,Week 3,使用Octave实现逻辑回归模型.数据集 ex2data1.txt ,ex2data2.txt 实现 Sigmoid .代价函数计算Computing ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Multi-class Classification and Neural Networks
作业文件 machine-learning-ex3 1. 多类分类(Multi-class Classification) 在这一部分练习,我们将会使用逻辑回归和神经网络两种方法来识别手写体数字0到9 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Logistic Regression
编程作业文件: machine-learning-ex2 1. Logistic Regression (逻辑回归) 有之前学生的数据,建立逻辑回归模型预测,根据两次考试结果预测一个学生是否有资格被大 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业: Linear Regression
编程作业有两个文件 1.machine-learning-live-scripts(此为脚本文件方便作业) 2.machine-learning-ex1(此为作业文件) 将这两个文件解压拖入matla ...
- Andrew NG 机器学习编程作业3 Octave
问题描述:使用逻辑回归(logistic regression)和神经网络(neural networks)识别手写的阿拉伯数字(0-9) 一.逻辑回归实现: 数据加载到octave中,如下图所示: ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Support Vector Machines
作业: machine-learning-ex6 1. 支持向量机(Support Vector Machines) 在这节,我们将使用支持向量机来处理二维数据.通过实验将会帮助我们获得一个直观感受S ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias/Variance
作业文件: machine-learning-ex5 1. 正则化线性回归 在本次练习的前半部分,我们将会正则化的线性回归模型来利用水库中水位的变化预测流出大坝的水量,后半部分我们对调试的学习算法进行 ...
随机推荐
- SWF文件加密、混淆
简单说下SWF文件的混淆原理,(已经明白的请跳过本段):我们的AS源代码被编译完成后,SWF内部会形成一个字符串映射表,包含源码里出现的所有字符串(类名,包名,成员变量名,常量等).一个数字(相当于地 ...
- tf随笔-1
生成新的计算图,并完成常量初始化,在新的计算 图中完成加法计算 import tensorflow as tf g1=tf.Graph() with g1.as_default(): value=[1 ...
- sysbench安装for oracle
RHEL7.2+ 1.依赖包安装 * autoconf * automake * cdbs * debhelper (>= 9) * docbook-xml * docbook-xsl * li ...
- Linux 下spark安装
一.安装前提: 1.java环境(jdk1.8) 2.scala环境(2.0) 3.python 环境(3.5) :注如果使用pyspark的话,这个才是必须的. 二.spark安装 在官网下载安装 ...
- R+markdown+LaTeX 中文编译解决方案
一丢丢前言 很久之前曾试图以Rmarkdown编译pdf文档,无奈怎么鼓捣都会error,搜索了很久都没能找到比较好的解决方案.在配置上将编译器调成了xeLaTeX后就不了了之.这两天心血来潮研究了一 ...
- 深入分析AIDL原理
深入分析AIDL原理 分类: Android2011-11-18 17:29 6522人阅读 评论(1) 收藏 举报 descriptorcallbackservicenullinterfaceser ...
- C#进阶之路(七)反射的应用
反射在C#中的应用还是很多的,但它对代码的性能有一定影响. 反射的性能: 使用反射来调用类型或者触发方法,或者访问一个字段或者属性时clr 需要做更多的工作:校验参数,检查权限等等,所以速度是非常慢的 ...
- Nginx 反向代理与负载均衡详解
序言 Nginx的代理功能与负载均衡功能是最常被用到的,关于nginx的基本语法常识与配置已在Nginx 配置详解中有说明,这篇就开门见山,先描述一些关于代理功能的配置,再说明负载均衡详细. Ngin ...
- oscache使用经历
oscache作为一款老的本地缓存,应用场景主要有页面缓存和对象缓存.这里拿在maven项目中使用oscache作为对象缓存举例说明下用法: 1.导入jar包 <dependency> & ...
- FPGA与嵌入式一点见解
FPGA:即现场可编程门阵列,它是在PAL.GAL.CPLD等可编程器件的基础上进一步发展的产物.它是作为专用集成电路(ASIC)领域中的一种半定制电路而出现的,既解决了定制电路的不足,又克服了原有可 ...
