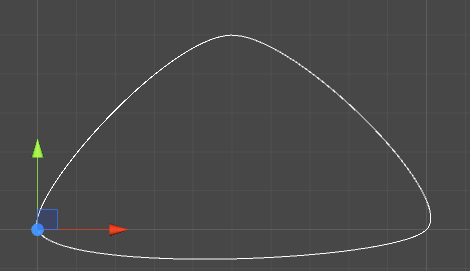
Hermite (埃尔米特)曲线
Hermite 曲线
已知曲线的两个端点坐标P0、P1,和端点处的切线R0、R1,确定的一条曲线。
参数方程
1. 几何形式
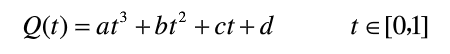
2. 矩阵形式
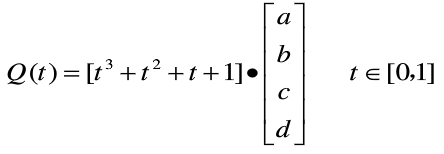
3. 推导
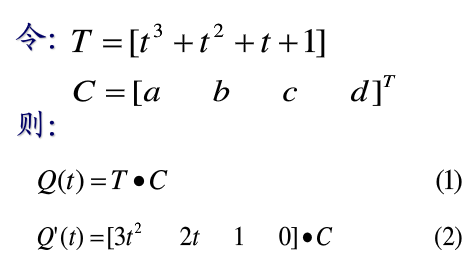




例子分析
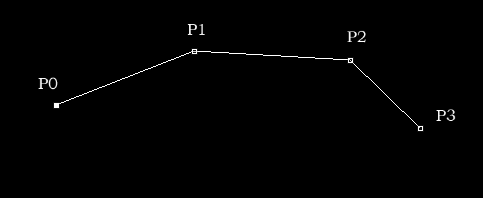
如上图有四个点,假如P0、P2是端点,那么向量R0=(P1-P0),R1=(P3-P2),将数据带入调和函数,即求得曲线。
在程序中,我们通常会使用特殊方法处理顶点之间的关系。
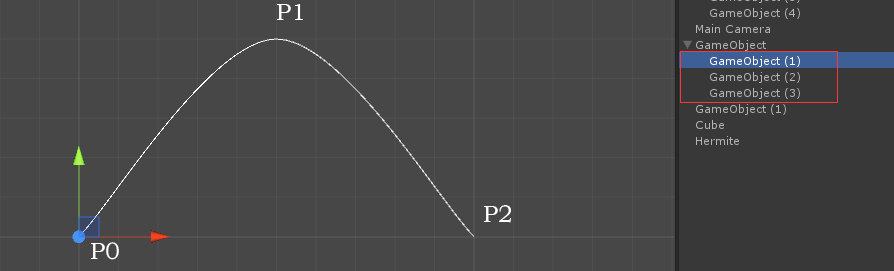
图中含有3个顶点,我们把每挨着的两个顶点看做是一条Hermite曲线,P0和P1是两个端点,那么现在,我们如何求得R1呢? 我们现在构建连个参考点F1,F2。
令 F1 = P0; F2 = P2;
那么 R1 = P1-F1; R2 = F2-P1;
然后将此值带入曲线函数,即可为求得的曲线。
程序代码
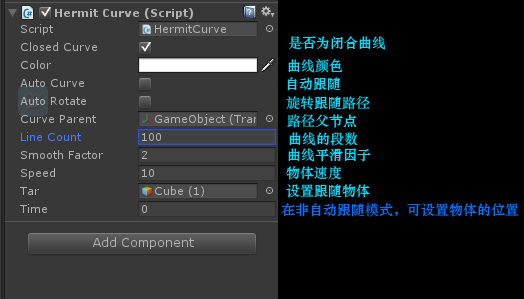
该代码是Unity脚本代码:
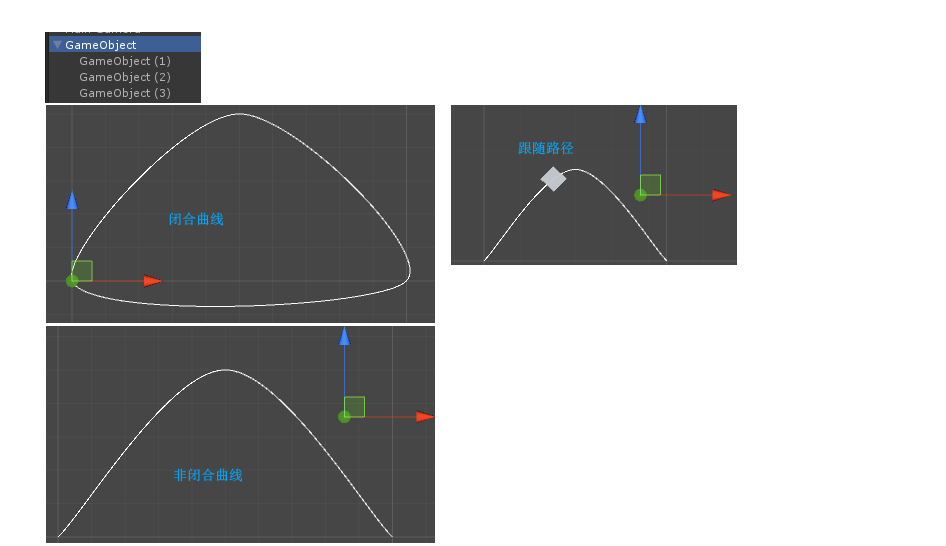
1. 实现编辑器闭合曲线和非闭合曲线的绘制;
2. 运行脚本,可以实现物体跟随曲线路径移动,可以勾选旋转跟随与不跟随;
3. 如果不进行自动跟随曲线路径,可以修改时间值,移动物体。
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class HermitCurve : Curve_Root { public Transform CurveParent;
public int lineCount;
private List<NodePath> nodePath;
public float smoothFactor = 2.0f; private Transform[] transforms;
private Vector3[] node;
public float Speed = 10.0f; Vector3 curPos;
Vector3 nextPos;
Quaternion curRotate;
Quaternion nextRotate;
float moveTime;
float curTime;
public GameObject Tar;
int index;
private Transform T; public float time; /// <summary>
/// 数据校正
/// </summary>
void DadaCorrection()
{
//根节点验证
if (CurveParent == null)
{
Debug.LogError("Please add curve the root node.");
return;
} //修正平滑因子: 2时,较为理想。
smoothFactor = smoothFactor >= 10.0f ? 10.0f : smoothFactor;
smoothFactor = smoothFactor <= 1.0f ? 1.0f : smoothFactor;
} /// <summary>
/// 计算路径节点
/// </summary>
void ComputeNode()
{
//将节点添加入链表
Component[] mTrans = CurveParent.GetComponentsInChildren(typeof(Transform));//物体和子物体的Trans
if (mTrans.Length - < )
{
Debug.LogError("Please add at least two points.");
return;
} //非闭合曲线与闭合曲线的顶点时间计算:非闭合曲线,最后个顶点的时间为1.0,闭合曲线的最后个顶点的时间为倒数第二个顶点,因为他的最后个点是原点。
float t;
if (closedCurve)
{
t = 1.0f / (mTrans.Length - );
nodePath = new List<NodePath>();
for (int i = ; i < mTrans.Length; i++)//根节点不参与路径节点的计算
{
nodePath.Add(new NodePath(mTrans[i].transform.position, (i - ) * t));
}
//闭合曲线完整的节点
AddClosedCurveNode();
}
else
{
t = 1.0f / (mTrans.Length - );
nodePath = new List<NodePath>();
for (int i = ; i < mTrans.Length; i++)//根节点不参与路径节点的计算
{
nodePath.Add(new NodePath(mTrans[i].transform.position, (i - ) * t));
}
//非闭合曲线完整的节点
AddCurveNode();
}
} // Use this for initialization
void Start () { DadaCorrection(); ComputeNode(); node = new Vector3[lineCount+];
//Vector3 start = nodePath[1].point;
//Vector3 end; node[] = nodePath[].point;
Vector3 end;
//绘制节点
for (int i = ; i <= lineCount; i++)
{
float ti = i / (float)lineCount;
end = GetHermitAtTime(ti);
if (node != null)
{
node[i] = end;
}
} T = new GameObject().transform; curPos = node[];
nextPos = node[];
moveTime = (nextPos - curPos).magnitude / Speed; Tar.transform.position = curPos;
Tar.transform.transform.LookAt(nextPos);
curRotate = Tar.transform.rotation;
T.position = node[];
T.LookAt(node[]);
nextRotate = T.rotation;
curTime = ;
index = ;
} // Update is called once per frame
void Update () { if (AutoCurve)
{
if (moveTime > curTime)
{
Tar.transform.position = Vector3.Lerp(curPos, nextPos, curTime / moveTime);
if (AutoRotate)
{
Tar.transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(curRotate, nextRotate, curTime / moveTime);
} curTime += Time.deltaTime;
}
else
{
if (closedCurve)
{
index = ((index + ) % (lineCount + ) == ) ? : index + ;
}
else
{
index = ((index + ) % (lineCount+) == ) ? index : index + ;
}
curPos = nextPos;
nextPos = node[index]; curTime = ;
moveTime = (nextPos - curPos).magnitude / Speed; T.position = node[index];
curRotate = nextRotate; if (closedCurve)
{
int c1;
if (index == node.Length-)
{
c1 = ;
}
else
{
c1 = index + ;
}
T.LookAt(node[c1]);
}
else
{
int c1;
if (index == node.Length - )
{
c1 = ;
}
else
{
c1 = index + ;
T.LookAt(node[c1]);
}
} nextRotate = T.rotation;
}
}
else
{
if (closedCurve)
{
if (AutoRotate)
{
time = time > 1.0f ? 0.0f : time;
time = time < 0.0f ? 1.0f : time;
Vector3 cur = GetHermitAtTime(time);
Tar.transform.position = cur; float del = 1.0f / lineCount;
Vector3 next0 = GetHermitAtTime(time + del);
Tar.transform.LookAt(next0);
}
else
{
time = time > 1.0f ? 0.0f : time;
time = time < 0.0f ? 1.0f : time;
Vector3 cur = GetHermitAtTime(time);
Tar.transform.position = cur;
}
}
else
{
if (AutoRotate)
{
time = time > 1.0f ? 1.0f : time;
time = time < 0.0f ? 0.0f : time;
Vector3 cur = GetHermitAtTime(time);
Tar.transform.position = cur; float del = 1.0f / lineCount;
Vector3 next0 = GetHermitAtTime(time + del); Tar.transform.LookAt(next0);
}
else
{
time = time > 1.0f ? 1.0f : time;
time = time < 0.0f ? 0.0f : time;
Vector3 cur = GetHermitAtTime(time);
Tar.transform.position = cur;
}
} } } /// <summary>
/// 绘制曲线
/// </summary>
void DrawCurve()
{
if (closedCurve)
{
Vector3 start = nodePath[].point;
Vector3 end; Gizmos.color = _Color;
//绘制节点
for (int i = ; i < lineCount; i++)
{
float time = i / (float)lineCount;
end = GetHermitAtTime(time);
//Debug.Log(end);
Gizmos.DrawLine(start, end); start = end;
}
Gizmos.DrawLine(start, nodePath[nodePath.Count - ].point);
}
else
{
Vector3 start = nodePath[].point;
Vector3 end; Gizmos.color = _Color;
//绘制节点
for (int i = ; i < lineCount; i++)
{
float time = i / (float)lineCount;
end = GetHermitAtTime(time);
//Debug.Log(end);
Gizmos.DrawLine(start, end);
start = end;
}
Gizmos.DrawLine(start, nodePath[nodePath.Count - ].point);
}
} /// <summary>
/// 在Scene场景中,绘制Hermite曲线
/// </summary>
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
/*数据校正*/
DadaCorrection();
/*计算顶点*/
ComputeNode();
/*计算曲线*/
DrawCurve();
} /// <summary>
/// 1. 非闭合曲线
/// </summary>
public void AddCurveNode()
{
nodePath.Insert(, nodePath[]);
nodePath.Add(nodePath[nodePath.Count - ]);
} /// <summary>
/// 2. 闭合曲线
/// </summary>
public void AddClosedCurveNode()
{
//nodePath.Insert(0, nodePath[0]);
nodePath.Add(new NodePath(nodePath[]));
nodePath[nodePath.Count - ].time = 1.0f; Vector3 vInitDir = (nodePath[].point - nodePath[].point).normalized;
Vector3 vEndDir = (nodePath[nodePath.Count - ].point - nodePath[nodePath.Count - ].point).normalized;
float firstLength = (nodePath[].point - nodePath[].point).magnitude;
float lastLength = (nodePath[nodePath.Count - ].point - nodePath[nodePath.Count - ].point).magnitude; NodePath firstNode = new NodePath(nodePath[]);
firstNode.point = nodePath[].point + vEndDir * firstLength; NodePath lastNode = new NodePath(nodePath[nodePath.Count - ]);
lastNode.point = nodePath[].point + vInitDir * lastLength; nodePath.Insert(, firstNode);
nodePath.Add(lastNode);
} /// <summary>
/// 通过节点段数的时间大小,获取每段节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="t"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Vector3 GetHermitAtTime(float t)
{
//Debug.Log(t);
int k;
//最后一个顶点
if (t >= nodePath[nodePath.Count - ].time)
{
return nodePath[nodePath.Count - ].point;
}
for (k = ; k < nodePath.Count-; k++)
{
if (nodePath[k].time > t)
break;
} k = k - ;
float param = (t - nodePath[k].time) / (nodePath[k+].time - nodePath[k].time);
return GetHermitNode(k, param);
} /// <summary>
/// Herimite曲线:获取节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index">节点最近的顶点</param>
/// <param name="t"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Vector3 GetHermitNode(int index,float t)
{
Vector3 v;
Vector3 P0 = nodePath[index - ].point;
Vector3 P1 = nodePath[index].point;
Vector3 P2 = nodePath[index + ].point;
Vector3 P3 = nodePath[index + ].point; //调和函数
float h1 = * t * t * t - * t * t + ;
float h2 = - * t * t * t + * t * t;
float h3 = t * t * t - * t * t + t;
float h4 = t * t * t - t * t; v = h1 * P1 + h2 * P2 + h3 * (P2 - P0) / smoothFactor + h4 * (P3 - P1) / smoothFactor;
//Debug.Log(index + " "+ t+" "+v);
return v;
}
} /// <summary>
/// 节点类
/// </summary>
public class NodePath
{
public Vector3 point;
public float time; public NodePath(Vector3 v,float t)
{
point = v;
time = t;
} public NodePath(NodePath n)
{
point = n.point;
time = n.time;
}
}
基类代码
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections; public class Curve_Root : MonoBehaviour { //曲线是否为闭合曲线
public bool closedCurve = false; //曲线的颜色
public Color _Color = Color.white; //自动跟随路径
public bool AutoCurve = false; //旋转跟随
public bool AutoRotate = false;
}
路径漫游
在曲线函数中,参数t取值[0,1],将曲线进行分段。那么能够计算出每一个点的位置。因此,在路径漫游中,我们从原点出发,将t的增量作为下一个点位置,进行插值移动。就实现了路径漫游,同时进行朝向下一个顶点旋转,就可以使看的方向随着曲线变化。
Unity 3D 项目工程
http://download.csdn.net/detail/familycsd000/9365859
Hermite (埃尔米特)曲线的更多相关文章
- 数值分析:Hermite多项式
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/49366047 Hermite埃尔米特多项式 在数学中,埃尔米特多项式是一种经典的正交多项式族,得名于法 ...
- 骨骼蒙皮动画(SkinnedMesh Animation)的实现
http://blog.csdn.net/zjull/article/details/11529695 1.简介 骨骼蒙皮动画,简称骨骼动画,因其占用磁盘空间少并且动画效果好被广泛用于3D游戏中,它把 ...
- 样条之埃尔米特(Hermite)
埃尔米特(Charles Hermite,1822—1901) 法国数学家.巴黎综合工科学校毕业.曾任法兰西学院.巴黎高等师范学校.巴黎大学教授.法兰西科学院院士.在函数论.高等代数.微分方程等方面都 ...
- 样条之埃尔米特(Hermite)插值函数
核心代码: ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 埃尔米特等距插值 /////////// ...
- Hermite曲线插值
原文 Hermite Curve Interpolation Hermite Curve Interpolation Hamburg (Germany), the 30th March 1998. W ...
- hermite插值
Hermite 插值就是要求插值函数不仅经过所给节点,而且要保证在该点的导数也相等.<备注:虽然还不理解这句话,但是还是先放这里!> 所谓样条曲线(Spline Curves)是指给定一组 ...
- Moore-Penrose Matrix Inverse 摩尔-彭若斯广义逆 埃尔米特矩阵 Hermitian matrix
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Moore-PenroseMatrixInverse.html 显然,埃尔米特矩阵主对角线上的元素都是实数的,其特征值也是实数.对于只包含实数 ...
- caffe的python接口学习(7):绘制loss和accuracy曲线
使用python接口来运行caffe程序,主要的原因是python非常容易可视化.所以不推荐大家在命令行下面运行python程序.如果非要在命令行下面运行,还不如直接用 c++算了. 推荐使用jupy ...
- 埃尔米特插值问题——用Python进行数值计算
当插值的要求涉及到对插值函数导数的要求时,普通插值问题就变为埃尔米特插值问题.拉格朗日插值和牛顿插值的要求较低,只需要插值函数的函数值在插值点与被插函数的值相等,以此来使得在其它非插值节点插值函数的值 ...
随机推荐
- 实现自己的ArrayList
最近在学习数据结构和算法,书上有个ArrayList的简单实现,写的很不错. package cn.sp.test4; import java.util.Iterator; import java.u ...
- IDEA远程调试Tomcat程序
如何使用 Idea 远程调试 Java 代码 IDEA远程调试的 基本就是在服务端先设置Tomcat服务器启动脚本catalina.bat,然后在客户端IDEA上进行参数配置,最后二者可以通过Sock ...
- 32位Oracle10g在64位CentOS下安装失败记录
环境信息:Alibaba Cloud Elastic Compute Service,CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core),16C/64GB. 使用32位Oracl ...
- CoreText的绘制流程-转
来自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7c8dc2d50101lbb1.html 使用coreText进行文本绘制,需要在工程中添加CoreText.framework, ...
- node.js学习笔记(1)
一. 安装以及环境配置 安装路径 http://nodejs.cn/download/ 多种环境选择 环境变量的配置 Step1 先检查环境变量中的系统变量里面的path,查看是否加入了nod ...
- Android Studio 导入新工程项目
1 导入之前先修改工程下相关文件 1.1 只需修改如下三个地方1.2 修改build.gradle文件 1.3 修改gradle/wrapper/gradle-wrapper.properties 1 ...
- iOS Programming Subclassing UITableViewCell
iOS Programming Subclassing UITableViewCell 1.Creating BNRItemCell UITableViewCell is a UIView subc ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册37-第10章 初始化
Chapter 10 Initialization 第10章 初始化 After a signal on the RESET pin, certain registers of the 80386 a ...
- file.seek()
语法:fileObject.seek(offset,whence) offset -- 开始的偏移量,也就是代表需要移动偏移的字节数 whence:可选,默认值为 0.给offset参数一个定义,表示 ...
- 类的封装,property特性,类与对象的绑定方法和非绑定方法,
类的封装 就是把数据或者方法封装起来 为什么要封装 封装数据的主要原因是:保护隐私 封装方法的主要原因是:隔离复杂度(快门就是傻瓜相机为傻瓜们提供的方法,该方法将内部复杂的照相功能都隐藏起来了,比如你 ...