HDU 4121 Xiangqi 模拟题
Xiangqi
Time Limit: 20 Sec
Memory Limit: 256 MB
题目连接
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4121
Description
Now
we introduce some basic rules of Xiangqi. Xiangqi is played on a 10×9
board and the pieces are placed on the intersections (points). The top
left point is (1,1) and the bottom right point is (10,9). There are two
groups of pieces marked by black or red Chinese characters, belonging to
the two players separately. During the game, each player in turn moves
one piece from the point it occupies to another point. No two pieces can
occupy the same point at the same time. A piece can be moved onto a
point occupied by an enemy piece, in which case the enemy piece is
"captured" and removed from the board. When the general is in danger of
being captured by the enemy player on the enemy player’s next move, the
enemy player is said to have "delivered a check". If the general's player can make no move to prevent the general's capture by next enemy move, the situation is called “checkmate”.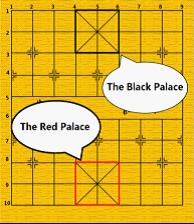
We only use 4 kinds of pieces introducing as follows: General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the “palace” unless the situation called “flying general”
General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the “palace” unless the situation called “flying general”
(see the figure above). “Flying general” means that one general can
“fly” across the board to capture the enemy general if they stand on the
same line without intervening pieces. Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces
Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its target.
Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its target. Horse:
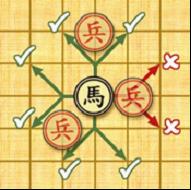
Horse:
the horses have 8 kinds of jumps to move and capture shown in the left
figure. However, if there is any pieces lying on a point away from the
horse horizontally or vertically it cannot move or capture in that
direction (see the figure below), which is called “hobbling the horse’s leg”.
Now
you are given a situation only containing a black general, a red
general and several red chariots, cannons and horses, and the red side
has delivered a check. Now it turns to black side’s move. Your job is to
determine that whether this situation is “checkmate”.
Input
There is a blank line between two test cases. The input ends by 0 0 0.
Output
For each test case, if the situation is checkmate, output a single word ‘YES’, otherwise output the word ‘NO’.
Sample Input
2 1 4
G 10 5
R 6 4
3 1 5
H 4 5
G 10 5
C 7 5
0 0 0
Sample Output
YES
NO
HINT
题意
给你一个象棋残局,黑方只剩下一个王了。现在该王走了,是否王怎么走都会死了?
题解:
1.黑方王在走的时候,可以踩死红方棋子
2.马会被蹩脚
然后没有什么坑点了,暴力模拟就好了……
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std; int n,x,y;
vector<pair<int,int> >P;
vector<pair<int,int> >H;
vector<pair<int,int> >C;
vector<pair<int,int> >G;
int dx[]={,-,,};
int dy[]={,,,-};
int vis[][];
void init()
{
P.clear();
H.clear();
C.clear();
G.clear();
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
}
int check(int xx,int yy)
{
//cout<<xx<<" "<<yy<<endl;
if(xx<||xx>)return ;
if(yy<||yy>)return ; for(int i=;i<C.size();i++)
{
int xxx = C[i].first, yyy = C[i].second;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
continue;
while(xxx<=)
{
xxx++;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
xxx = C[i].first, yyy = C[i].second;
while(xxx)
{
xxx--;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
xxx = C[i].first, yyy = C[i].second;
while(yyy<=)
{
yyy++;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
xxx = C[i].first, yyy = C[i].second;
while(yyy)
{
yyy--;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
}
//cout<<xx<<" "<<yy<<endl;
for(int i=;i<H.size();i++)
{
int xxx = H[i].first , yyy = H[i].second;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
continue;
if(xxx != && vis[xxx-][yyy]==)
{
if(xx == xxx - && yy == yyy + )
return ;
if(xx == xxx - && yy == yyy - )
return ;
}
if(xxx != && vis[xxx+][yyy]==)
{
if(xx == xxx + && yy == yyy + )
return ;
if(xx == xxx + && yy == yyy - )
return ;
}
if(yyy != && vis[xxx][yyy-]==)
{
if(xx == xxx + && yy == yyy - )
return ;
if(xx == xxx - && yy == yyy - )
return ;
}
if(yyy != && vis[xxx][yyy+]==)
{
if(xx == xxx + && yy == yyy + )
return ;
if(xx == xxx - && yy == yyy + )
return ;
}
}
//cout<<xx<<" "<<yy<<endl;
for(int i=;i<P.size();i++)
{
int xxx = P[i].first,yyy = P[i].second;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
continue;
int flag = ;
while(xxx<=)
{
xxx++;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy && flag == )
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
flag++;
}
xxx = P[i].first, yyy = P[i].second,flag = ;
while(xxx)
{
xxx--;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy && flag == )
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
flag++;
}
xxx = P[i].first, yyy = P[i].second,flag = ;
while(yyy<=)
{
yyy++;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy && flag == )
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
flag++;
}
xxx = P[i].first, yyy = P[i].second,flag = ;
while(yyy)
{
yyy--;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy && flag == )
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
flag++;
}
} for(int i=;i<G.size();i++)
{
int xxx = G[i].first, yyy = G[i].second;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
continue;
while(xxx<=)
{
xxx++;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
xxx = G[i].first, yyy = G[i].second;
while(xxx)
{
xxx--;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
xxx = G[i].first, yyy = G[i].second;
while(yyy<=)
{
yyy++;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
xxx = G[i].first, yyy = G[i].second;
while(yyy)
{
yyy--;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
return ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
}
//cout<<xx<<" "<<yy<<endl;
return ;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&x,&y)!=EOF)
{
if(n== && x == && y == )
break;
init();
string cc;int xx,yy;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>cc;
scanf("%d %d",&xx,&yy);
if(cc[]=='G')
G.push_back(make_pair(xx,yy));
if(cc[]=='R')
C.push_back(make_pair(xx,yy));
if(cc[]=='H')
H.push_back(make_pair(xx,yy));
if(cc[]=='C')
P.push_back(make_pair(xx,yy));
vis[xx][yy]++;
} xx = x,yy = y;
int flag2 = ;
for(int i=;i<G.size();i++)
{
int xxx = G[i].first, yyy = G[i].second;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
continue;
while(xxx<=)
{
xxx++;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
flag2 = ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
xxx = G[i].first, yyy = G[i].second;
while(xxx)
{
xxx--;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
flag2 = ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
xxx = G[i].first, yyy = G[i].second;
while(yyy<=)
{
yyy++;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
flag2 = ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
xxx = G[i].first, yyy = G[i].second;
while(yyy)
{
yyy--;
if(xxx == xx && yyy == yy)
flag2 = ;
if(vis[xxx][yyy])
break;
}
}
if(flag2)
{
printf("NO\n");
continue;
}
int flag = ;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
xx = x + dx[i];
yy = y + dy[i];
vis[xx][yy]++;
if(!check(xx,yy))
flag ++;
vis[xx][yy]--;
}
if(flag == )
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
HDU 4121 Xiangqi 模拟题的更多相关文章
- HDU 4121 Xiangqi --模拟
题意: 给一个象棋局势,问黑棋是否死棋了,黑棋只有一个将,红棋可能有2~7个棋,分别可能是车,马,炮以及帅. 解法: 开始写法是对每个棋子,都处理处他能吃的地方,赋为-1,然后判断将能不能走到非-1的 ...
- HDU 4121 Xiangqi (算是模拟吧)
传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4121 题意:中国象棋对决,黑棋只有一个将,红棋有一个帅和不定个车 马 炮冰给定位置,这时当黑棋走,问你黑 ...
- HDU 4121 Xiangqi
模拟吧,算是... 被这个题wa到哭,真是什么都不想说了...上代码 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespac ...
- HDU 4121 Xiangqi 我老了?
Xiangqi Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Sub ...
- HDU 4431 Mahjong(模拟题)
题目链接 写了俩小时+把....有一种情况写的时候漏了...代码还算清晰把,想了很久才开写的. #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #in ...
- HDU 1234 简单模拟题
题目很简单不多说了,我只是觉得这题目的输入方式还是很有特点的 #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorit ...
- HDU 4041 Eliminate Witches! (模拟题 ACM ICPC 2011亚洲北京赛区网络赛)
HDU 4041 Eliminate Witches! (模拟题 ACM ICPC 2011 亚洲北京赛区网络赛题目) Eliminate Witches! Time Limit: 2000/1000 ...
- HDU 4452 Running Rabbits (模拟题)
题意: 有两只兔子,一只在左上角,一只在右上角,两只兔子有自己的移动速度(每小时),和初始移动方向. 现在有3种可能让他们转向:撞墙:移动过程中撞墙,掉头走未完成的路. 相碰: 两只兔子在K点整(即处 ...
- hdu 5641 King's Phone(暴力模拟题)
Problem Description In a military parade, the King sees lots of new things, including an Andriod Pho ...
随机推荐
- 【转】APUE习题4.6---测试lseek作用
原文网址:http://m.blog.csdn.net/blog/u014488381/42556509 原题:如果使用追加标志打开一个文件以便读.写,能否仍用 lseek 在任一为止开始读?能否用 ...
- Android 版本自动更新
截图如下: 代码实现如下: package com.update.apk; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import jav ...
- Oracle 课程一之Oracle体系结构
课程目标 •理解ORACLE数据库体系架构—内存结构和进程 •理解SQL在数据库中的运作流程 •理解UNDO&REDO原理 •理解commit原理 1.Oracle数据库概述 •数据库:物 ...
- 使用carrierwave出现MiniMagick::Invalid错误的解决方法
安装Imagemagick不能从源码安装,要从软件市场安装,否则会出现错误:MiniMagick::Invalid 使用make uninstall卸载后,重新在软件市场里安装,问题解决.
- c# datagridview与DataSet绑定, 列与数据库表里面的列一一对应
参考代码1: 自己模拟出数据,并分别对dataGridView赋值. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Comp ...
- adb remount 失败remount failed: Operation not permitted
1. 进入shell adb shell 2. shell下输入命令 shell@android:/ $ sushell@android:/ # mount -o rw,remount -t yaff ...
- delegate 为什么用 weak属性
weak指针主要用于“父-子”关系,父亲拥有一个儿子的strong指针,因此是儿子的所有者:但是为了阻止所有权回环,儿子需要使用weak指针指向父亲:你的viewcontroller通过strong指 ...
- SQL经典笔试题之一
本题用到下面三个关系表: CARD 借书卡. CNO 卡号,NAME 姓名,CLASS 班级 BOOKS 图书. BNO 书号,BNAME 书名,AUTHOR 作者,PRIC ...
- CentsOS7 网络自动启动
虚拟机中安装完成CentOS7后,网络总是需要手工启动才可使用,设置为自动连接的方式如下: cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ls #找到类似的文件:ifcfg-et ...
- thread.join函数,java多线程中的join函数解析
join函数的作用,是让当前线程等待,直到调用join()的 线程结束或者等到一段时间,我们来看以下代码 package mian; public class simpleplela { static ...
