linux下c语言的多线程编程
我们在写linux的服务的时候,经常会用到linux的多线程技术以提高程序性能
多线程的一些小知识:
一个应用程序可以启动若干个线程。
线程(Lightweight Process,LWP),是程序执行的最小单元。
一般一个最简单的程序最少会有一个线程,就是程序本身,也就是主函数(单线程的进程可以简单的认为只有一个线程的进程)
一个线程阻塞并不会影响到另外一个线程。
多线程的进程可以尽可能的利用系统CPU资源。
1创建线程
先上一段在一个进程中创建一个线程的简单的代码,然后慢慢深入。
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<errno.h> void * func(void * arg)
{
printf("func run...\n");
return NULL;
}
int main()
{ pthread_t t1;
int err = pthread_create(&t1,NULL,func,NULL);
if(err!=)
{
printf("thread_create Failed:%s\n",strerror(errno)); }else{
printf("thread_create success\n");
}
sleep();
return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread,const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine)(void*), void *arg);
在main函数里面我们调用上面的函数进行创建一个线程。
函数参数:
第一个参数:pthread_t代表创建线程的唯一标识,是一个结构体,需要我们创建好后,将这个结构体的指针传递过去。
第二个参数:pthread_attr_t,代表创建这个线程的一些配置,比如分配栈的大小等等。。一般我们可以填NULL,代表默认的创建线程的配置
第三个参数:代表一个函数的地址,创建线程时,会调用这个函数,函数的返回值是void*,函数的参数也是void*,一般格式就像void * func(void * arg){}
第四个参数:代表调用第三个函数传递的参数
函数返回值:
函数成功返回0,如果不等于0则代表函数调用失败,此时通过strerror(errno)可以打印出具体的错误。
注意:每个线程都拥有一份errno副本,不同的线程拥有不同的errno
最后通过gcc编译
gcc 1createthread.c -c -o 1createthread.o
gcc 1createthread.o -o thr1 -lpthread
编译的时候需要加上-lpthread 用来链接libpthread.so动态库,不然会提示找不到function
函数调用返回结果
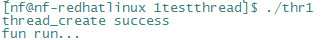
问题:为什么调用sleep函数
答:可能新创建的线程还没运行到打印的方法主线程就结束了,而主线程结束,所有线程都会结束了。
2线程挂起
有时候我们在一个线程中创建了另外一个线程,主线程要等到创建的线程返回了,获取该线程的返回值后主线程才退出。这个时候就需要用到线程挂起。
int pthread_join(pthread_t th, void **thr_return);。
pthread_join函数用于挂起当前线程,直至th指定的线程终止为止。
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<errno.h> void * func(void * arg)
{
int i=;
for(;i<;i++)
{
printf("func run%d\n",i);
sleep();
}
int * p = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*p=; return p; }
int main()
{ pthread_t t1,t2;
int err = pthread_create(&t1,NULL,func,NULL);
if(err!=)
{
printf("thread_create Failed:%s\n",strerror(errno)); }else{
printf("thread_create success\n");
}
void *p=NULL;
pthread_join(t1,&p);
printf("线程退出:code=%d\n",*(int*)p);
return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
函数执行结果
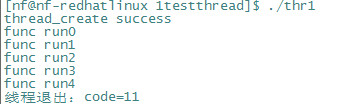
我们主函数一直在等待创建的线程执行完,并且得到了线程执行结束的返回值
3线程终止
进程终止时exit()函数,那么线程终止是什么呢?
线程终止的三种情况:
- 线程只是从启动函数中返回,返回值是线程的退出码。
- 线程可以被同一进程中的其他线程取消。
- 线程调用pthread_exit。
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<errno.h> void * func(void * arg)
{
int i=;
while()
{
if(i==)
{
int * p = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*p=;
pthread_exit(p);
}
printf("fun run %d\n",i++);
sleep();
}
return NULL; }
int main()
{ pthread_t t1,t2;
int err = pthread_create(&t1,NULL,func,NULL);
if(err!=)
{
printf("thread_create Failed:%s\n",strerror(errno)); }else{
printf("thread_create success\n");
}
void *p=NULL;
pthread_join(t1,&p);
printf("线程退出:code=%d",*(int*)p);
return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
void pthread_exit(void *arg);
pthread_exit函数的参数就跟正常线程结束return的使用时一样的,都会被等待它结束的主线程获取到。
函数运行结果:
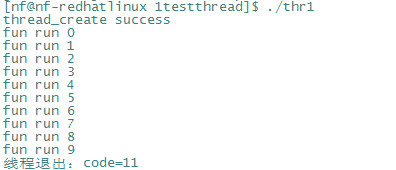
4线程分离
int pthread_detach(pthread_t th);
pthread_detach函数使线程处于被分离状态。
如果不等待一个线程,同时对线程的返回值不感兴趣,可以设置这个线程为被分离状态,让系统在线程退出的时候自动回收它所占用的资源。
一个线程不能自己调用pthread_detach改变自己为被分离状态,只能由其他线程调用pthread_detach。
5线程取消
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t th);
pthread_cancel函数允许一个线程取消th指定的另一个线程。
函数成功,返回0,否则返回非0。
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<errno.h> void * func1(void * arg)
{
while()
{ printf("fun run...\n");
sleep();
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{ pthread_t t1;
if(pthread_create(&t1,NULL,func1,NULL)!=)
{
printf("thread_create Failed:%s\n",strerror(errno));
return -; }
sleep();
pthread_cancel(t1);
pthread_join(t1,NULL);
return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
函数执行结果:
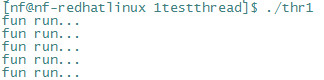
上面我们说过创建一个线程函数pthread_create的第二个参数,用来决定创建线程的一些初始化状态,这里我们 举个例子,改线程一创建就是分离状态的线程(
)
先上一段代码:
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<errno.h> void * func(void * arg)
{
int i=;
for(;i<;i++)
{
printf("func run%d\n",i);
sleep();
}
int * p = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*p=; return p; }
int main()
{ pthread_t t1; pthread_attr_t attr;//申明一个attr的结构体
pthread_attr_init(&attr);//初始化结构体
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);//设置线程为分离线程 int err = pthread_create(&t1,&attr,func,NULL);
if(err!=)
{
printf("thread_create Failed:%s\n",strerror(errno)); }else{
printf("thread_create success\n");
}
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr); pthread_join(t1,NULL);
printf("主线程退出\n");
return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
pthread_attr_t就是我们要传入的参数的结构体,一般申明的步骤有
1,申明一个pthread_attr_t对象
3,设置线程的一些属性,比如pthread_attr_setdetachstate函数就是设置该线程创建的时候为正常状态还是分离状态。
4,函数pthread_attr_destroy释放attr内存空间
pthread_attr_setdetachstate把线程属性设置为下面两个合法值之一:
|
值 |
说明 |
|
PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED |
设置线程为分离状态 |
|
PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE |
设置线程为正常状态 |
上面函数运行结果:
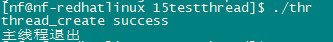
因为线程是个分离状态的,所以pthread_join挂起会失效,主线程很快运行结束,程序也就结束了,创建的线程还没来得及运行
线程同步
有时候我们多个线程处理订单扣减库存会遇到这样的问题,两个线程同时进入一段代码先查询库存,两个都查出来为还剩一件库存,第一个线程用掉这个库存后,将库存变为0,但是第二个线程刚才也查出来为1了,所以他还认为有库存,
这个时候操作就会引发我们想不到的意外,库存变为负数了!!所以这个时候就需要使用线程的同步!!
先上一段代码看看效果:
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<errno.h> void * func(void * arg)
{
int threadno =*(int*)arg;
int i=;
for(;i<;i++)
{
printf("%d thread%d \n",threadno,i);
sleep();
} return NULL; }
int main()
{ pthread_t t1,t2; int i1=,i2=;
pthread_create(&t1,NULL,func,&i1);
pthread_create(&t2,NULL,func,&i2); pthread_join(t1,NULL);
pthread_join(t2,NULL); printf("主线程退出\n");
return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
函数运行结果:
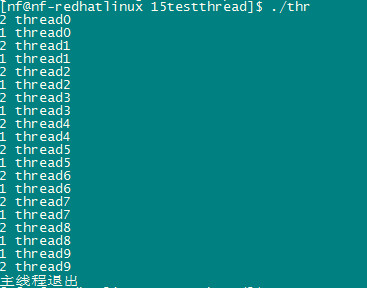
可以看到两个线程是没有规律的争相处理的,如果这段代码是扣减库存就完蛋啦!,所以我们要对这段代码进行加锁,同一时刻只能有一个线程进入操作!
先上代码:
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<errno.h> pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; void * func(void * arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//对mutex加锁,其他线程进入后将会挂起,知道这个锁被解锁 int threadno =*(int*)arg;
int i=;
for(;i<;i++)
{
printf("%d thread%d \n",threadno,i);
sleep();
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); return NULL; }
int main()
{ pthread_t t1,t2; int i1=,i2=;
pthread_create(&t1,NULL,func,&i1);
pthread_create(&t2,NULL,func,&i2); pthread_join(t1,NULL);
pthread_join(t2,NULL); printf("主线程退出\n");
return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
函数运行结果:
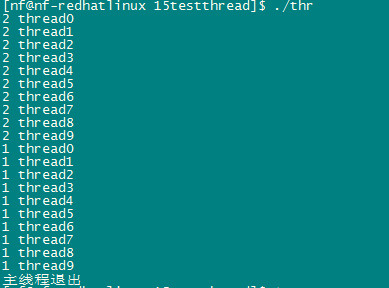
可以看到第二个线程先进入后一直运行结束,对mutex解锁后,第一个线程才能进方法里面运行!否则会挂起,一直等到锁被解锁!
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
加锁解锁函数:
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
linux下c语言的多线程编程的更多相关文章
- linux下C语言socket网络编程简例
原创文章,转载请注明转载字样和出处,谢谢! 这里给出在linux下的简单socket网络编程的实例,使用tcp协议进行通信,服务端进行监听,在收到client的连接后,发送数据给client:clie ...
- linux下C语言实现多线程通信—环形缓冲区,可用于生产者(producer)/消费者(consumer)【转】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-28458801-id-4262445.html 操作系统:ubuntu10.04 前言: 在嵌入式开发中,只要是带操作系统的 ...
- linux下c语言实现多线程文件复制【转】
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/zxl0715/articles/5365989.html .具体思路 把一个文件分成N份,分别用N个线程copy, 每个线程只读取指定长度字节大 ...
- Linux下c语言TCP多线程聊天室
开发环境:Linux,GCC 相关知识:TCP(博客:传送门),线程 附加:项目可能还有写不足之处,有些bug没调出来(如:对在线人数的控制),希望大佬赐教. 那么话不多说,放码过来: 码云:传送门, ...
- Linux下C语言进程通讯编程
代码: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/shm.h> /*************基本的函 ...
- linux下C语言多线程编程实例
用一个实例.来学习linux下C语言多线程编程实例. 代码目的:通过创建两个线程来实现对一个数的递加.代码: //包含的头文件 #include <pthread.h> #include ...
- Linux下C语言编程实现spwd函数
Linux下C语言编程实现spwd函数 介绍 spwd函数 功能:显示当前目录路径 实现:通过编译执行该代码,可在终端中输出当前路径 代码实现 代码链接 代码托管链接:spwd.c 所需结构体.函数. ...
- Linux基础与Linux下C语言编程基础
Linux基础 1 Linux命令 如果使用GUI,Linux和Windows没有什么区别.Linux学习应用的一个特点是通过命令行进行使用. 登录Linux后,我们就可以在#或$符后面去输入命令,有 ...
- LINUX下C语言编程基础
实验二 Linux下C语言编程基础 一.实验目的 1. 熟悉Linux系统下的开发环境 2. 熟悉vi的基本操作 3. 熟悉gcc编译器的基本原理 4. 熟练使用gcc编译器的常用选项 5 .熟练使用 ...
随机推荐
- Spark 1.6升级2.x防踩坑指南
原创文章,谢绝转载 Spark 2.x自2.0.0发布到目前的2.2.0已经有一年多的时间了,2.x宣称有诸多的性能改进,相信不少使用Spark的同学还停留在1.6.x或者更低的版本上,没有升级到2. ...
- 三分钟读懂TT猫分布式、微服务和集群之路
针对入门新手的普及,有过大型网站技术架构牛人路过,别耽误浪费了时间,阅读之前,请确保有一定的网络基础,熟练使用Linux,浏览大概需要3-5分钟的时间,结尾有彩蛋. 目录 分布式 微服务 负载均衡集群 ...
- React Native底|顶部导航使用小技巧
导航一直是App开发中比较重要的一个组件,ReactNative提供了两种导航组件供我们使用,分别是:NavigatorIOS和Navigator,但是前者只能用于iOS平台,后者在ReactNati ...
- poj2942(双联通分量,交叉染色判二分图)
题意:一些骑士,他们有些人之间有矛盾,现在要求选出一些骑士围成一圈,圈要满足如下条件:1.人数大于1.2.总人数为奇数.3.有仇恨的骑士不能挨着坐.问有几个骑士不能和任何人形成任何的圆圈. 思路:首先 ...
- Httprequest 获取url 常用方法
HttpServletRequest常用获取URL的方法 1.request.getRequestURL() 返回的是完整的url,包括Http协议,端口号,servlet名字和映射路 ...
- 微软为啥让免费升Win10?
今天终于赶在截止日期之前把我的联想PC升到win10.微软这次对中国开放的持续一年的免费升级活动主要有两个原因.首先当然是"感恩Windows用户长久支持的回馈".微 ...
- 【★】RSA-什么是不对称加密算法?
不对称加密算法RSA浅析 本文主要介绍不对称加密算法中最精炼的RSA算法.我们先说结论,也就是RSA算法怎么算,然后再讲为什么. 随便选取两个不同的大素数p和q,N=p*q,r=(p-1)*(q-1) ...
- Java 多线程(一) 基础知识与概念
多线程Multi-Thread 基础 线程概念 线程就是程序中单独顺序的流控制. 线程本身不能运行,它只能用于程序中. 说明:线程是程序内的顺序控制流,只能使用分配给程序的资源和环境. 进程 进程:执 ...
- 第一次作业-----四则运算题目生成(基于java)
1.题目要求 1.除了整数以外,还要支持真分数的四则运算,真分数的运算,例如:1/6 + 1/8 = 7/24. 2.运算符为 +, −, ×, ÷. 3.并且要求能处理用户的输入,并判断对错,打分统 ...
- 团队作业4——第一次项目冲刺(Alpha版本)2nd day
一.Daily Scrum Meeting照片 二.燃尽图 三.项目进展 界面 1.四个用户登录界面已经完成. 2.界面内的功能完成了一小部分. 登陆部分 1.QQ授权已经申请,还未通过. 2.通过好 ...
