从Socket入门到BIO,NIO,multiplexing,AIO
Socket入门
最简单的Server端读取Client端内容的demo
public class Server {
public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9000);
Socket s = ss.accept();
InputStream input = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = input.read(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
}
打开浏览器,输入localhost:9000
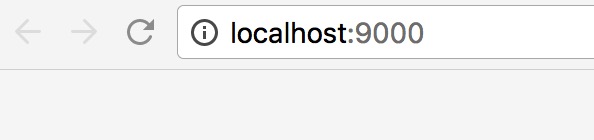
可以看到控制台输出了如下内容(HTTP请求头)
或者命令行输入:telnet localhost 9000 , 然后按下ctrl+] 然后再输入: send 发送的内容 , 然后就可以再IDEA控制台看到send的内容了.
但是现在手头是Mac系统,不知道为啥send不好使....windows下测过,肯定好使.
最简单的Server端写入到Client端内容的demo
public class Server2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket ssocket = new ServerSocket(9000);
Socket socket = ssocket.accept();
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("http/1.0 200 OK\nContent-Type:text/html;charset:GBK\n\nhello".getBytes());
os.flush();
os.close();
}
}
可以在浏览器输入localhost:9000来请求内容 , http响应头的那部分会被浏览器解析掉.所以只输出一段hello
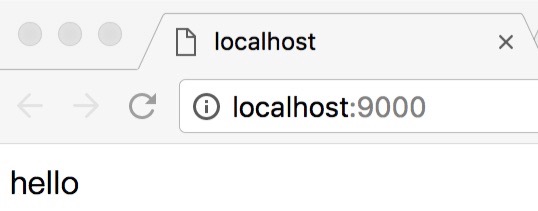
或者可以使用telnet localhost 9000来访问, 得到的结果就是那段写入的内容

最简单的Client端写入到Server端的Demo
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost",9000);
OutputStream output = socket.getOutputStream();
output.write("你好".getBytes());
output.close();
socket.close();
}
}
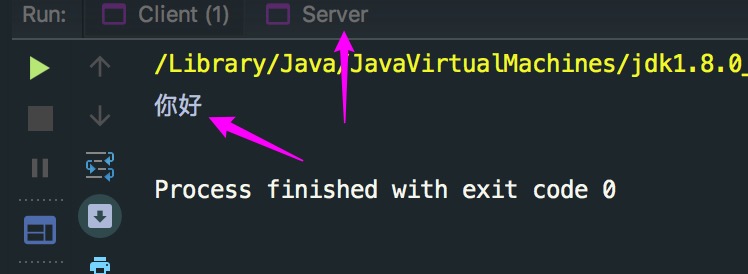
注:需要先运行上面的Server类, 然后再运行这个Client. 然后再点击Server的控制台标签, 就会发现Server类的控制台输已经出了"你好"字样.
最简单的用Client端来模拟浏览器http请求Demo
用socket作为Client来模拟浏览器访问网站, 来获取网站的html内容.以www.sohu.com 为例...为什么选sohu呢? 你试试百度,会报302....
public class Client2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Socket socket = new Socket("www.sohu.com", 80);
InputStream input = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream output = socket.getOutputStream();
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
//http协议中请求行,必须,不然不会被识别为HTTP
str.append("GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n");
//http协议中的请求头
str.append("Host: www.sohu.com\r\n");
str.append("Connection: Keep-Alive\r\n");
// 用于模拟浏览器的user-agent
str.append("user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_13_1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36\r\n");
//这里一定要一个回车换行,表示消息头完,不然服务器会一直等待,认为客户端没发送完
str.append("\r\n");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
output.write(str.toString().getBytes());
while (true) {
int len = input.read(bytes);
if (len > 0) {
String result = new String(bytes, 0, len);
System.out.println(result);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
运行后, 前面是http响应头, 后面是html代码
改进Server类, 循环读取
前面提到的"最简单的Server端读取Client端内容的demo"这段代码, 也就是Server类. 其实不管客户端发来多少内容, 都只能读取1024字节以内的数据. 因为代码就是这么写的....
下面进行改进, 让他循环读取, 直到读完为止.
public class Server3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9000);
Socket s = ss.accept();
InputStream input = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
int len = input.read(bytes);
// 如果读到了内容,说明得输出啊
if (len > 0) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
// 如果没读取到内容,或者没读满bytes数组 说明读完了, 不用再读下一次了, 该退出循环了.
if (len < bytes.length) {
break;
}
}
}
}
可以配合着用前文中的Client类来进行测试.先跑Server来监听端口, 再运行Client发送请求. 去看Server类的控制台是否输出相应的内容.
将服务器改为循环运行
之前是Server响应一个客户端就终止了,这回用while(true)来让Server不停地进行服务.
public class Server4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9000);
while (true) {
Socket s = ss.accept();
InputStream input = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
int len = input.read(bytes);
// 如果读到了内容,说明得输出啊
if (len > 0) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
// 如果没读取到内容,或者没读满bytes数组 说明读完了, 不用再读下一次了, 该退出循环了.
if (len < bytes.length) {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
可以配合着用前文中的Client类来进行测试.先跑Server来监听端口, 再运行Client发送请求. 去看Server类的控制台是否输出相应的内容.
Server运行一次就行, 一直在提供服务. 而Client这回可以运行多次了, Client运行几次, Server的控制台下就会收到几个'你好'.
BIO
同步阻塞IO, 每个线程都处理着一个客户端.客户端与线程数是1:1
public class Server5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9000);
System.out.println("服务端启动");
// 循环着监听
while (true) {
Socket s = ss.accept();
System.out.println("接收到客户端");
// 一旦接收到客户端,就开一个线程
new Thread(() -> {
//为了让代码简短,try多包一些代码...
try {
InputStream input = s.getInputStream();
OutputStream output = s.getOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
int len = input.read(bytes);
// 如果读到了内容,说明得输出啊
if (len > 0) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
// 如果没读取到内容,或者没读满bytes数组 说明读完了, 不用再读下一次了, 该退出循环了.
if (len < bytes.length) {
break;
}
}
output.write("http/1.1 200 OK\nContent-Type:text/html;charset:GBK\n\nhello".getBytes());
output.flush();
input.close();
output.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//...其实close应该出现在这里...
System.out.println("断开连接");
}
}).start();
}
}
}
可以在浏览器上用两个标签栏来访问localhost:9000来进行测试.
PIO
伪异步IO,为了避免Server5无限制地开一个新线程,使用线程池来统一管理线程.
public class Server6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9000);
System.out.println("服务端启动");
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(40);
// 循环着监听
while (true) {
Socket s = ss.accept();
System.out.println("接收到客户端");
// 一旦接收到客户端,就放入线程池
pool.submit(() -> {
//为了让代码简短,try多包一些代码...
try {
InputStream input = s.getInputStream();
OutputStream output = s.getOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
int len = input.read(bytes);
// 如果读到了内容,说明得输出啊
if (len > 0) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
// 如果没读取到内容,或者没读满bytes数组 说明读完了, 不用再读下一次了, 该退出循环了.
if (len < bytes.length) {
break;
}
}
output.write("http/1.1 200 OK\nContent-Type:text/html;charset:GBK\n\nhello".getBytes());
output.flush();
input.close();
output.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//...其实close应该出现在这里...
System.out.println("断开连接");
}
});
}
}
}
NIO
首先推荐一本书,讲的详细:

nio博客 http://ifeve.com/java-nio-all/ ,这个更适合快速入门,但原理最好还是看书..讲的很详细
所以相关原理就不在这里粘贴了....再整理也没人家讲的全面易懂,这本书还是非常推荐看的,一开始我就是在网上看各种博客(当时也知道这本书), 但直到耐下心看了这本书,才发现很多地方这里讲的非常详细, 这本书是基于api讲的, 以后需要分析看源码的话还是借助博客更好一些,网上有很多大神的源码分析
public class NIOServer {
private static int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
private static int PORT = 9000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannle = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannle.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannle.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER_SIZE));
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buf = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
// 读浏览器发送的HTTP请求
long bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buf);
while (bytesRead > 0) {
buf.flip();
while (buf.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print((char) buf.get());
}
System.out.println();
buf.clear();
bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buf);
}
//向浏览器返回HTTP请求
buf.put("http/1.1 200 OK\nContent-Type:text/html;charset:GBK\n\nhello".getBytes());
socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
buf.flip();
while (buf.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(buf);
}
// 关闭
socketChannel.close();//这样浏览器才不继续拉取
key.cancel();
}
}
}
}
}
然后再浏览器中访问localhost:9000即可看到"hello"
或者用普通SocketClient来访问
或者用如下的NIOClient访问:
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9000));
if (socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
//向服务器写入
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
String info = "hello:<" + i + ">";
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(info.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
//从服务器读取
buffer.clear();
long bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buffer);
while (bytesRead > 0) {
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print((char) buffer.get());
}
System.out.println();
buffer.clear();
bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buffer);
}
}
}
}
未完待续....
从Socket入门到BIO,NIO,multiplexing,AIO的更多相关文章
- Java BIO NIO 与 AIO
回顾 上一章我们介绍了操作系统层面的 IO 模型. 阻塞 IO 模型. 非阻塞 IO 模型. IO 复用模型. 信号驱动 IO 模型(用的不多,知道个概念就行). 异步 IO 模型. 并且介绍了 IO ...
- 从Socket入门到BIO,PIO,NIO,multiplexing,AIO(未完待续)
Socket入门 最简单的Server端读取Client端内容的demo public class Server { public static void main(String [] args) t ...
- BIO,NIO与AIO的区别
Java NIO : 同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个请求一个线程,即客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接有I/O请求时才启动一个线程进行处理.Java AIO(NIO.2 ...
- Java的BIO,NIO和AIO的区别于演进
作者:公众号:我是攻城师 前言 Java里面的IO模型种类较多,主要包括BIO,NIO和AIO,每个IO模型都有不一样的地方,那么这些IO模型是如何演变呢,底层的原理又是怎样的呢? 本文我们就来聊聊. ...
- Socket网络通信——IO、NIO、AIO介绍以及区别
一 基本概念 Socket又称"套接字",应用程序通常通过"套接字"向网路发出请求或者应答网络请求. Socket和ServerSocket类位于java.ne ...
- 关于BIO NIO和AIO的理解
转载自 :http://blog.csdn.net/anxpp/article/details/51512200 1.BIO编程 1.1.传统的BIO编程 网络编程的基本模型是C/S模型,即两个进程间 ...
- BIO、NIO、AIO入门认识
同步.异步.阻塞.非阻塞概念理解. 同步: 比如在执行某个逻辑业务,在没有得到结果之前一直处于等待阻塞状态,得到结果后才继续执行 异步: 比如在执行某个逻辑业务,在没有得到结果可以去干其他的事情,等待 ...
- JAVA SOCKET 通信总结 BIO、NIO、AIO ( NIO 2) 的区别和总结
1 同步 指的是用户进程触发IO操作并等待或者轮询的去查看IO操作是否就绪 自己上街买衣服,自己亲自干这件事,别的事干不了.2 异步 异步是指用户进程触发IO操作以后便开始做自己的事情,而当IO操作已 ...
- 也谈BIO | NIO | AIO (Java版--转)
关于BIO | NIO | AIO的讨论一直存在,有时候也很容易让人混淆,就我的理解,给出一个解释: BIO | NIO | AIO,本身的描述都是在Java语言的基础上的.而描述IO,我们需要从两个 ...
随机推荐
- Json序列化、反序列化
引用 using Newtonsoft.Json; using Newtonsoft.Json.Converters; 把Json字符串反序列化为对象 1.目标对象 = JavaScriptConve ...
- 浅谈this关键字
在我学习this关键字的时候,通过查找资料总结出一些this的特殊用法, 供大家参考,代码里面有我总结的分析过程! 箭头函数里的this: var username = "全局"; ...
- 类似fabric主机管理demo
类似于fabric的主机管理系统 可以批量对主机进行操作 批量上传文件 批量下载文件 批量执行命令 demo代码 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -* ...
- python网络编程基础知识整理
- CSS3之box-shadow
1.属性简介 box-shadow:颜色值|inset|none|!important 2.浏览器兼容性 (1)IE不兼容,IE9和IE10未知: (2)火狐3.5(包含3.5)以上兼容 (3)Chr ...
- Linux显示包含全部的文件系统
Linux显示包含全部的文件系统 youhaidong@youhaidong-ThinkPad-Edge-E545:~$ df -a 文件系统 1K-blocks 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点 /dev ...
- 芝麻HTTP:Python爬虫进阶之Scrapy框架安装配置
初级的爬虫我们利用urllib和urllib2库以及正则表达式就可以完成了,不过还有更加强大的工具,爬虫框架Scrapy,这安装过程也是煞费苦心哪,在此整理如下. Windows 平台: 我的系统是 ...
- 同一张表省市县sql查询
一,表的结构 SELECT * FROM t_unionpay_areacode t SELECT * FROM t_unionpay_areacode t WHERE t.`name`LIKE &q ...
- python利用jieba进行中文分词去停用词
中文分词(Chinese Word Segmentation) 指的是将一个汉字序列切分成一个一个单独的词. 分词模块jieba,它是python比较好用的分词模块.待分词的字符串可以是 unicod ...
- [BZOJ1385] [Baltic2000] Division expression (数学)
Description 除法表达式有如下的形式: X1/X2/X3.../Xk 其中Xi是正整数且Xi<=1000000000(1<=i<=k,K<=10000) 除法表达式应 ...
