TensorFlow的图切割模块——Graph Partitioner
背景
功能描述
Graph Partition切割流程
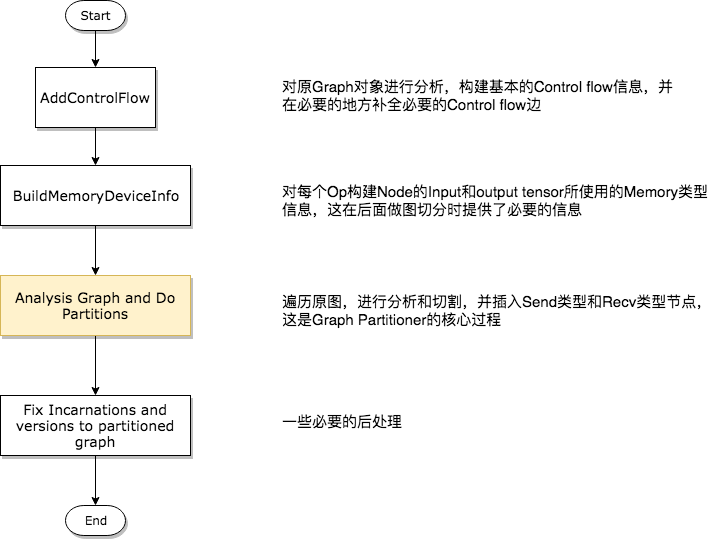
第一步——分析构建Control Flow相关信息
GraphInfo g_info;
if (!opts.control_flow_added) {
// Add the "code" for distributed execution of control flow. Code is
// added only for the frames that are placed on multiple devices. The
// new graph is an equivalent transformation of the original graph and
// has the property that it can be subsequently partitioned arbitrarily
// (down to the level of individual device) for distributed execution.
status = AddControlFlow(opts, g, &g_info);
if (!status.ok()) return status;
}
第二步——构建Op的Input和Output Memory类型信息
// MemoryType is used to describe whether input or output Tensors of
// an OpKernel should reside in "Host memory" (e.g., CPU memory) or
// "Device" Memory (CPU memory for CPU devices, GPU memory for GPU
// devices).
enum MemoryType {
DEVICE_MEMORY = ,
HOST_MEMORY = ,
};
#define REGISTER_GPU_KERNEL(type) \
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("Reshape") \
.Device(DEVICE_GPU) \
.HostMemory("shape") \
.TypeConstraint<type>("T") \
.TypeConstraint<int32>("Tshape"), \
ReshapeOp); \
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("Reshape") \
.Device(DEVICE_GPU) \
.HostMemory("shape") \
.TypeConstraint<type>("T") \
.TypeConstraint<int64>("Tshape"), \
ReshapeOp);
上面的宏显示,虽然Reshape Op确实在GPU上有注册的实现版本,但是它依然要使用HostMemory。另外,某些Tensor的类型也决定了其是否可以被放置到Device Memory上,一般情况下float类型的数据对于计算设备是非常友好的,而String类型就不是这样,所以在types.cc文件中规定了一些强制被放在HostMemory的数据类型,如下代码所示。
bool DataTypeAlwaysOnHost(DataType dt) {
// Includes DT_STRING and DT_RESOURCE.
switch (dt) {
case DT_STRING:
case DT_STRING_REF:
case DT_RESOURCE:
return true;
default:
return false;
}
}
第三步——对原图进行分析,并产出切割后的多个子图
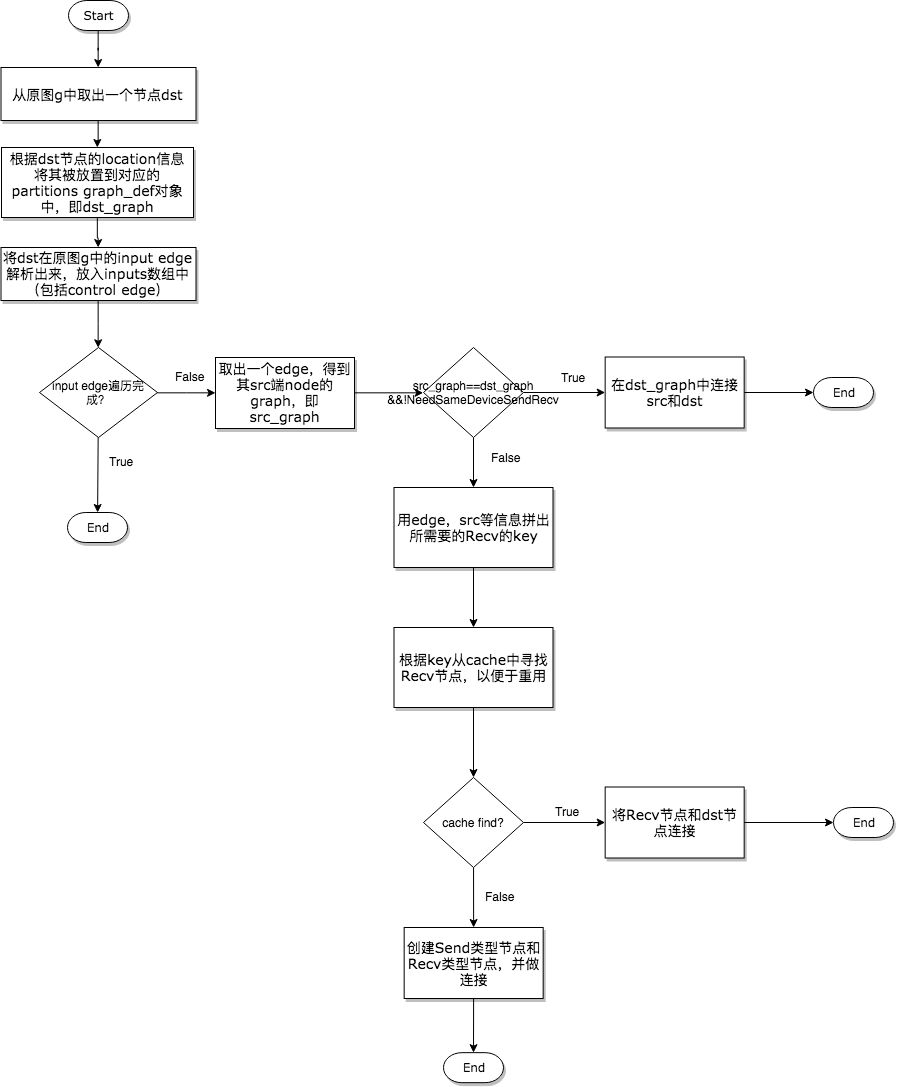
// Check whether there is already a send/recv pair transferring
// the same tensor/control from the src to dst partition.
const bool on_host = IsDstInputOnHost(edge, g_info);
DupRecvKey key{src->id(), edge->src_output(), dst_graph, on_host};
auto iter = dup_recv.find(key);
if (iter != dup_recv.end()) {
// We found one. Reuse the data/control transferred already.
const string& recv_node_name = iter->second.recv->name();
if (edge->IsControlEdge()) {
AddInput(dst_def, recv_node_name, Graph::kControlSlot);
} else {
AddInput(dst_def, recv_node_name, );
}
ref_control_inputs.push_back(recv_node_name); // We want the start_time for the recv to be the smallest of the start
// times of it's consumers. So we update this whenever we use a recv,
// and write it out to the attribute at the end of the subroutine
if (iter->second.start_time > recv_start_time) {
iter->second.start_time = recv_start_time;
}
continue;
}
const FunctionLibraryDefinition* flib_def = opts.flib_def;
if (flib_def == nullptr) {
flib_def = &g->flib_def();
} // Set versions, function library and send/recv incarnation.
for (auto& it : *partitions) {
GraphDef* gdef = &it.second;
*gdef->mutable_versions() = g->versions();
// Prune unreachable functions from `flib_def` before adding them to `gdef`.
*gdef->mutable_library() = flib_def->ReachableDefinitions(*gdef).ToProto(); // Traverse the graph to fill every send/recv op's incarnation
// information.
SetIncarnation(opts, gdef);
}
Send和Recv节点对插入的三种情况
在代码中,声明插入Send和Recv节点的代码段非常简单,如下所示。
// Need to split edge by placing matching send/recv nodes on
// the src/dst sides of the edge.
NodeDef* send = AddSend(opts, g_info, src_graph, edge, send_from,
send_start_time, &status);
if (!status.ok()) return status; NodeDef* real_recv = nullptr;
NodeDef* recv =
AddRecv(opts, g_info, dst_graph, edge, &real_recv, &status);
if (!status.ok()) return status;
但是对于不同的情况却有着丰富的处理逻辑,所以下面在展示示意图的同时,会将相关的代码段摘出来做展示。
在同一个Device上插入Send和Recv节点对
因为同一个Device上的Send和Recv节点在执行过程中实际上Memory Copy,而Recv的kernel又是异步的,所以需要有一种机制保证保证Recv一定要在Send之后执行,因此需要在Send和Recv之间插入一个Control Edge,从图的依赖上保证它们的执行顺序。
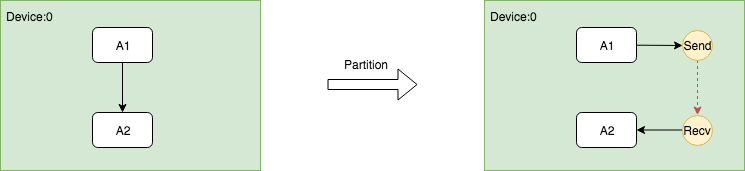
这个过程的关键是在插入Send和Recv节点之后,需要插入额外的Control Edge,代码如下。
// Fix up the control flow edge.
// NOTE(yuanbyu): 'real_recv' must be the real recv node.
if (src_graph == dst_graph) {
// For same device send/recv, add a control edge from send to recv.
// This prevents the asynchronous recv kernel from being scheduled
// before the data is available.
AddInput(real_recv, send->name(), Graph::kControlSlot);
}
跨Device根据DataFlow插入Send和Recv节点对
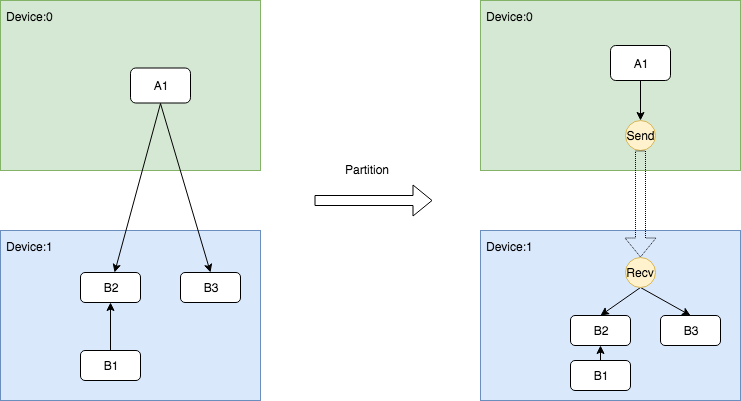
跨Device根据ControlFlow插入Send和Recv节点对
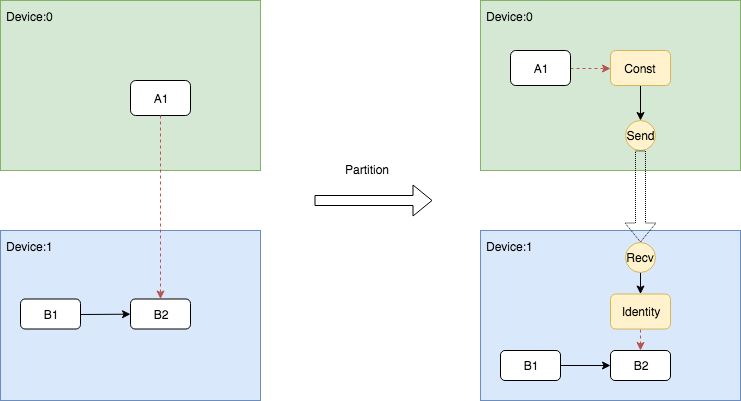
NodeDefBuilder::NodeOut send_from;
if (edge->IsControlEdge()) {
// Insert a dummy const node that will generate a tiny
// data element to be sent from send to recv.
VLOG() << "Send/Recv control: " << src->assigned_device_name() << "["
<< src->name() << "] -> " << dst->assigned_device_name() << "["
<< dst->name() << "]";
NodeDef* dummy = AddDummyConst(opts, src_graph, edge, &status);
if (!status.ok()) return status;
// Set the start time for this dummy node.
if (opts.scheduling_for_recvs) {
AddNodeAttr("_start_time", send_start_time, dummy);
}
AddInput(dummy, src->name(), Graph::kControlSlot);
send_from.Reset(dummy->name(), , DT_FLOAT);
} else {
send_from.Reset(src->name(), edge->src_output(), EdgeType(edge));
}
Indentity即相关依赖的插入逻辑被写在了AddRecv中,下面展示了这个片段。
// Add the cast node (from cast_dtype to dtype) or an Identity node.
if (dtype != cast_dtype) {
const string cast_op = (host_memory) ? "_HostCast" : "Cast";
NodeDefBuilder cast_builder(opts.new_name(src->name()), cast_op);
cast_builder.Attr("DstT", dtype);
cast_builder.Device(dst->assigned_device_name())
.Input(recv->name(), , cast_dtype);
NodeDef* cast = gdef->add_node();
*status = cast_builder.Finalize(cast);
if (!status->ok()) return nullptr;
return cast;
} else if (edge->IsControlEdge()) {
// An Identity is only needed for control edges.
NodeDefBuilder id_builder(opts.new_name(src->name()), "Identity");
id_builder.Device(dst->assigned_device_name())
.Input(recv->name(), , cast_dtype);
NodeDef* id = gdef->add_node();
*status = id_builder.Finalize(id);
if (!status->ok()) return nullptr;
return id;
} else {
return recv;
}
关于使用bfloat16压缩通信
TensorFlow支持通过使用bfloat16减少通信量,虽然bfloat16理论上是有损精度的,但是大量的实践证明这个精度损失是基本感知不到的。bfloat16的通信功能可以通过以下配置项打开,只要在创建Session时传入打开该功能的config即可。
graph_options = tf.GraphOptions(enable_bfloat16_sendrecv=True)
session_config = tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)
总结
TensorFlow的图切割模块——Graph Partitioner的更多相关文章
- Tensorflow中的图(tf.Graph)和会话(tf.Session)详解
Tensorflow中的图(tf.Graph)和会话(tf.Session) Tensorflow编程系统 Tensorflow工具或者说深度学习本身就是一个连贯紧密的系统.一般的系统是一个自治独立的 ...
- 图数据库 Nebula Graph 的数据模型和系统架构设计
Nebula Graph:一个开源的分布式图数据库.作为唯一能够存储万亿个带属性的节点和边的在线图数据库,Nebula Graph 不仅能够在高并发场景下满足毫秒级的低时延查询要求,而且能够提供极高的 ...
- TensorFlow框架(1)之Computational Graph详解
1. Getting Start 1.1 import TensorFlow应用程序需要引入编程架包,才能访问TensorFlow的类.方法和符号.如下所示的方法: import tensorflow ...
- tensorflow 优化图
当我们把训练好的tensorflow训练图拿来进行预测时,会有多个训练时生成的节点,这些节点是不必要的,我们需要在预测的时候进行删除. 下面以bert的图为例,进行优化 def optimize_gr ...
- GraphX 在图数据库 Nebula Graph 的图计算实践
不同来源的异构数据间存在着千丝万缕的关联,这种数据之间隐藏的关联关系和网络结构特性对于数据分析至关重要,图计算就是以图作为数据模型来表达问题并予以解决的过程. 一.背景 随着网络信息技术的飞速发展,数 ...
- 初识分布式图数据库 Nebula Graph 2.0 Query Engine
摘要:本文主要介绍 Query 层的整体结构,并通过一条 nGQL 语句来介绍其通过 Query 层的四个主要模块的流程. 一.概述 分布式图数据库 Nebula Graph 2.0 版本相比 1.0 ...
- 【转载】利用Unity自带的合图切割功能将合图切割成子图
虽然目前网上具有切割合图功能的工具不少,但大部分都是自动切割或者根据plist之类的合图文件切割的, 这种切割往往不可自己微调或者很难维调,导致效果不理想. 今天逛贴吧发现了一位网友写的切割合图插件很 ...
- c/c++ 有向无环图 directed acycline graph
c/c++ 有向无环图 directed acycline graph 概念: 图中点与点之间的线是有方向的,图中不存在环.用邻接表的方式,实现的图. 名词: 顶点的入度:到这个顶点的线的数量. 顶点 ...
- 图:无向图(Graph)基本方法及Dijkstra算法的实现 [Python]
一般来讲,实现图的过程中需要有两个自定义的类进行支撑:顶点(Vertex)类,和图(Graph)类.按照这一架构,Vertex类至少需要包含名称(或者某个代号.数据)和邻接顶点两个参数,前者作为顶点的 ...
随机推荐
- Codeforces Codeforces Round #484 (Div. 2) E. Billiard
Codeforces Codeforces Round #484 (Div. 2) E. Billiard 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/982/proble ...
- struts2参数传递总结
需求1:登录页面填写表单,提交后进入action,action中能够获取填入的内容.[宏观分类:页面->action] 需求2:登录action从数据库校验完毕后,跳转至主页,主页显示当前登录的 ...
- IDEL中easyui使用jstl和el出现传值不显示的问题
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding=& ...
- python网络编程 双人多人聊天
在学习网路编程时,我们首先要考虑的是其中的逻辑,我们借助打电话的形式来了解网络编程的过程, 我们打电话时属于呼叫方,接电话的属于被呼叫方,那么被呼叫方一直保持在待机状态,等待主呼叫方 呼叫,只有在被呼 ...
- kubernets基础
1.定义和功能. 1.1定义:kubernets解释为舵手或者飞行员,以Borg为主衍生出. 1.2功能:自动装箱,自我修复,水平扩展,服务发现和负载均衡,自动发布和回滚. 密钥和配置管理,存储编排, ...
- awk\sed\grep 补充
# awk\sed\grep 补充 以上命令中字符 / 在sed中作为定界符使用,也可以使用任意的定界符 sed's:test:TEXT:g' sed's|test|TEXT|g' 定界符出现在样式内 ...
- Delphi Excel导入 的通用程序
步骤: 1 连excel(自己知道其格式,最好是没个字段在数据一一对应) 2 读excel数据,填入到数据库 我这里有个函数,实现把excel表格中数据导入数据库,在一条数据导入前判断数据库中是否有该 ...
- 【CF429E】 Points and Segments(欧拉回路)
传送门 CodeForces 洛谷 Solution 考虑欧拉回路有一个性质. 如果把点抽出来搞成一条直线,路径看成区间覆盖,那么一个点从左往右被覆盖的次数等于从右往左被覆盖的次数. 发现这个性质和本 ...
- 基于Fusioncharts的报表统计
先了解fusioncharts插件,fusioncharts是一款基于XML和flash的报表组件,支持Java.PHP.AngularJS等等开发语言,所以,开发出来,加入swf文件,就可以出现动态 ...
- 仿今日头条app手机端顶部触屏滑动导航
swiper.js <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset=" ...
