Java中CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier
Java编程思想中的例子
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; class TaskPortion implements Runnable{ private static int count;
private final int id=count++;
private final CountDownLatch latch;
private static Random random=new Random(47); public TaskPortion(CountDownLatch latch) {
this.latch = latch;
} public void run() {
try {
doWork();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
latch.countDown(); } public void doWork() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(1000));
System.out.println(this+"complete"); }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TaskPortion: "+String.format("%1$-2d",id);
}
}
class WaitingTask implements Runnable{ private final CountDownLatch latch;
private static int count;
private final int id=count++; public WaitingTask(CountDownLatch latch) {
this.latch = latch;
}
public void run() {
try {
latch.await();
System.out.println(this);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "waiting task pass"+String.format("%1$-2d",id);
}
}
public class CountDownLatchDemo { private static final int SIZE=20;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
CountDownLatch latch=new CountDownLatch(SIZE);
for (int i=0;i<SIZE;i++)
executorService.execute(new TaskPortion(latch)); //
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
executorService.execute(new WaitingTask(latch));
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
}
countdownlatch中有个计数器,当计数器减少到0的时候,释放所有等待的线程,coutDown()会让计数器的值减少,调用await()的线程将会进入等待状态,直到调用countdownlatch使得计数器数值减少到0,所有等待的线程都会开始执行。
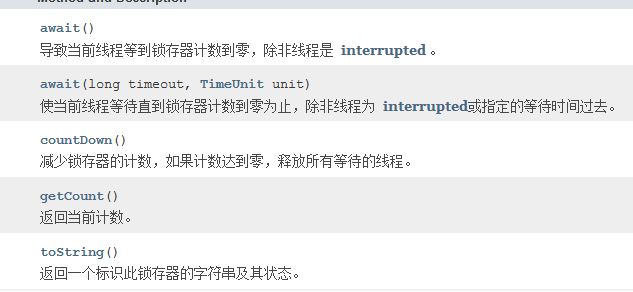
CyclicBarrier
这个相对于上面的countdownlatch来说,这种可以重复的使用,而且await()已经具备countdownlatch中的countdown()和await()两种方法的作用。(前者await()被线程调用一次计数减一,后者不会,只能通过countdown())
首先了解他的构造方法。
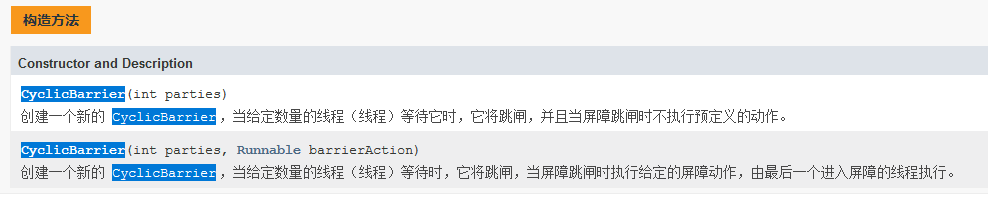
方法

自己独立敲了一段书上的模拟赛马的demo(来自于Java编程思想)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.*; class Horse implements Runnable{
private CyclicBarrier barrier; //ByclicBarrier用来控制本类的在释放屏障之前的动作,由构造函数传入
private int stride=0; //马跑得轨迹
private static int count; //马的数量
private final int id=count++; //设置马的id
private Random random = new Random(47); //模拟赛马 public Horse(CyclicBarrier barrier) {
this.barrier = barrier;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try{
while(!Thread.interrupted()){ //这里模拟赛马的过程
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
barrier.await();
stride+=random.nextInt(3);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Horse "+id+" ";
}
public String getTrack(){
StringBuilder s=new StringBuilder();//返回马当前到达屏障之后走的路径
for (int i = 0; i < stride; i++) {
s.append("=");
}
return s.toString();
}
public int getStride() {
return stride; //马走了多少
} public int getId() {
return id;
}
}
class HorseRace {
private int nhorse;
private ExecutorService exec;
private final int FINISH_LINE = 75;
private CyclicBarrier barrier;
List<Horse> horses = new ArrayList<Horse>();
private String track;
public HorseRace(int nhorse, ExecutorService executorService) {
exec = executorService;
this.nhorse = nhorse;
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < FINISH_LINE; i++) {
s.append("=");
}
track = s.toString();
System.out.println(s.toString());
barrier = new CyclicBarrier(nhorse, () -> { //表达式中定义了释放屏障之前的动作,打印当前所有马的路程并且判断是否有的码已经到达终点
System.out.println(track);
for (Horse horse : horses) {
System.out.println(horse.getTrack());
if (horse.getStride() > FINISH_LINE) {
System.out.println(horse.getId() + " won");
exec.shutdownNow();
return;
}
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < nhorse; i++) {
Horse horse = new Horse(barrier);
exec.execute(horse);
horses.add(horse);
}
}
}
public class HorseRaceDeno {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
new HorseRace(7, executorService);
}
}
两者区别总结:
CyclicBarrier:是可以重重复使用的,只有等待线程积累到一定的数量的时候才会释放屏障,在释放屏障的时候还可以使用接口初始化CyclicBarrier变量(在里面定义释放屏障之前的动作,可以是释放线程池,终止上面所说的线程)。也可以使用只有int数据类型创建CyclicBarrier变量,这样只有在释放屏障的时候没有多余的动作。
CountDownLatch:含有两个重要的方法CountDown()和await(),前者调用一次,CountDownLatch对象就会计数减少一次。await()导致当前线程等待计数器减少到零为止,除非出现中断的情况,而且CountDownLatch只有一次的机会,只会阻塞线程一次。
触发屏障的事件不同:前者只有足够的线程调用await时候才会触发线程,后者是计数器减少到零的时候才会触发屏障,但是导致计数器减少的可能只是一个线程。
Java中CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier的更多相关文章
- Java中CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier的使用和比较
CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier同为Java1.5开始引入的,应用于多线程编程中的一种工具,二者用途十分相近,十分容易混淆. CountDownLatch CountDownL ...
- java并发编程中CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier的使用
在多线程程序设计中,经常会遇到一个线程等待一个或多个线程的场景,遇到这样的场景应该如何解决? 如果是一个线程等待一个线程,则可以通过await()和notify()来实现: 如果是一个线程等待多个线程 ...
- 使用Java辅助类(CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier、Semaphore)并发编程
在java 1.5中,提供了一些非常有用的辅助类来帮助我们进行并发编程,比如CountDownLatch,CyclicBarrier和Semaphore,今天我们就来学习一下这三个辅助类的用法 一.C ...
- java并发--CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier和Semaphore
在java 1.5中,提供了一些非常有用的辅助类来帮助我们进行并发编程,比如CountDownLatch,CyclicBarrier和Semaphore,今天我们就来学习一下这三个辅助类的用法. 以下 ...
- Java多线程-CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier、Semaphore
上次简单了解了多线程中锁的类型,今天要简单了解下多线程并发控制的一些工具类了. 1. 概念说明: CountDownLatch:相当于一个待执行线程计数器,当计数减为零时表示所有待执行线程都已执行完毕 ...
- Java的CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier的理解和区别
CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier的功能看起来很相似,不易区分,有一种谜之的神秘.本文将通过通俗的例子并结合代码讲解两者的使用方法和区别. CountDownLatch和Cycl ...
- Java中CountDownLatch类的使用
0.CountDownLatch作用 1) Java api中的解释:一个同步辅助类,在完成一组正在其他线程中执行的操作之前,它允许一个或多个线程一直等待. 2) CountDownLatch可以使J ...
- java面试-CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier、Semaphore谈谈你的理解
一.CountDownLatch 主要用来解决一个线程等待多个线程的场景,计数器不能循环利用 public class CountDownLatchDemo { public static void ...
- JAVA中CountDownLatch的简单示例
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CountDownLatch latch =new Count ...
随机推荐
- MongoDB的启动与停止(一)
1:启动和停止Mongodb 1)从命令行启动 执行mongod,启动MongoDB服务器,mongod有很多可配置的启动选项,可以使用mongod --help查看所有选项 -- ...
- laravel路由别名
在定义路由时使用数组键 as 指定路由名称: Route::get('user/profile', ['as' => 'profile', function () { // }]); 另外,还可 ...
- Java面试题 corejava(二)
65.JAVA 语言如何进行异常处理,关键字:throws,throw,try,catch,finally分别代表什么意义?在try 块中可以抛出异常吗?[基础] 答:Java 通过面向对象的方法进行 ...
- Spring Boot - 配置介绍
Spring Boot 针对常用的开发场景提供了一系列自动化配置来减少原本复杂而又几乎很少改动的模板配置内容,但是,我们还是需要了解如何在Spring Boot中修改这些自动化的配置,以应对一些特殊场 ...
- Windows Azure Virtual Network (13) 跨数据中心之间的虚拟网络点对点连接VNet Peering
<Windows Azure Platform 系列文章目录> 今天是大年初二,首先祝大家新年快乐,万事如意. 在笔者之前的文章中:Windows Azure Virtual Networ ...
- 删除文件夹下各级子目录中的.svn文件
建立一个文本文件,取名为removeSvn.reg(扩展名由txt改为reg),内容如下 Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHIN ...
- (dev mode) install CONSUL on ubuntu
WSL: V18.04.1 1. install $sudo apt-get update$sudo apt-get install consul wsl1017@DESKTOP-14G6K9S:~$ ...
- git 在本地拉取远程分支的代码(并不做提交操作)
1. git fetch 获取远程的所有分支 2. 在执行 git checkout -b local-branch-name origin/remote-branch 就可以将远程分支remote ...
- Ajax的异步与同步(async)
1.async值为true (异步)当ajax发送请求后,在等待server端返回的这个过程中,前台会继续 执行ajax块后面的脚本,直到server端返回正确的结果才会去执行success,也就是说 ...
- android 开发 View _5_ Paint详解
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/abcdef314159 //Paint的setStyle,Style共有3种 setStyle(Style style) Paint.Style.FI ...
