基于深度学习的人脸识别系统(Caffe+OpenCV+Dlib)【二】人脸预处理
前言
基于深度学习的人脸识别系统,一共用到了5个开源库:OpenCV(计算机视觉库)、Caffe(深度学习库)、Dlib(机器学习库)、libfacedetection(人脸检测库)、cudnn(gpu加速库)。
用到了一个开源的深度学习模型:VGG model。
最终的效果是很赞的,识别一张人脸的速度是0.039秒,而且最重要的是:精度高啊!!!
CPU:intel i5-4590
GPU:GTX 980
系统:Win 10
OpenCV版本:3.1(这个无所谓)
Caffe版本:Microsoft caffe (微软编译的Caffe,安装方便,在这里安利一波)
Dlib版本:19.0(也无所谓
CUDA版本:7.5
cudnn版本:4
libfacedetection:6月份之后的(这个有所谓,6月后出了64位版本的)
这个系列纯C++构成,有问题的各位朋同学可以直接在博客下留言,我们互相交流学习。
====================================================================
本篇是该系列的第二篇博客,介绍我如何设计人脸检测与预处理的接口。
思路
人脸检测与预处理作为人脸识别的步骤之一,其质量能够直接影响识别的精度。而如何在保持精度的条件下最大化运行速度也是需要注意的地方。这里我们不使用OpenCV自带的分类器,而使用一个开源的windows平台下的人脸检测库。具体可以看我的这篇博客:
http://blog.csdn.net/mr_curry/article/details/51804072
那么首先,我们先需要检测出人脸。新建FaceDetect.h,FaceRotate.h,FaceProcessing.h,一个FaceDetect.cpp,FaceProcessing.cpp开始编写。(这里假定你已经添加好dlib的属性表了)
注:下面的人脸预处理函数,是IEEE数据库上的一篇论文所述的方法,2011年的
FaceDetect.h:(提供一个总的接口)
#include "facedetect-dll.h"
#include <opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
// define
Mat Facedetect(Mat frame);
//dlib的配置函数 后面几章会讲
void Dlib_Prodefine();FaceRotate.h:(用于关键点矫正)
#include <dlib/image_processing/frontal_face_detector.h>
#include <dlib/image_processing/render_face_detections.h>
#include <dlib/image_processing.h>
#include <dlib/gui_widgets.h>
#include <dlib/image_io.h>
#include<dlib/opencv/cv_image.h>
#include <dlib/opencv.h>
using namespace dlib;
frontal_face_detector detector = get_frontal_face_detector();
shape_predictor sp;//Already getFaceProcessing.h:(用于对人脸进行预处理)
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
Mat FaceProcessing(const Mat &img_, double gamma = 0.2, double sigma0 = 1, double sigma1 = -2, double mask = 0, double do_norm = 10);FaceProcessing.cpp:
#include"FaceProcessing.h"
int gauss(float x[], float y[], int length, float sigma);
Mat gaussianfilter(Mat img, double sigma0, double sigma1, double shift1, double shift2);
Mat FaceProcessing(const Mat &img_, double gamma = 0.2, double sigma0 = 1, double sigma1 = -2, double mask = 0, double do_norm = 10);
//找出矩阵中的最大值或最小值,输入MAX,或MIN
double MatMaxMin(Mat im, String flag = "MAX")
{
double value = im.ptr<float>(0)[0];
if (flag == "MAX")
{
for (int i = 0; i<im.rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j<im.cols; j++)
if (im.ptr<float>(i)[j]>value)
value = im.ptr<float>(i)[j];
return value;
}
else if (flag == "MIN")
{
for (int i = 0; i<im.rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j<im.cols; j++)
if (im.ptr<float>(i)[j]<value)
value = im.ptr<float>(i)[j];
return value;
}
return -1;
}
//高斯滤波
Mat gaussianfilter(Mat img, double sigma0, double sigma1, double shift1 = 0, double shift2 = 0)
{
int i, j;
sigma0 = (float)sigma0;
sigma1 = (float)sigma1;
shift1 = (float)shift1;
shift2 = (float)shift2;
Mat img2 = img;
Mat img3 = img;
Mat imgResult;
//将数据存入横向高斯模板中
int rowLength = (int)(floor(3.0*sigma0 + 0.5 - shift1) - ceil(-3.0*sigma0 - 0.5 - shift1) + 1);
int rowBegin = (int)ceil(-3.0*sigma0 - 0.5 - shift1);
float rowArray[30], Gx[30];
for (i = 0; i < rowLength; i++)
{
rowArray[i] = rowBegin + i;
}
gauss(rowArray, Gx, rowLength, sigma0);
Mat kx = Mat(1, rowLength, CV_32F); //转换成mat类型
float *pData1 = kx.ptr<float>(0);
for (i = 0; i < rowLength; i++)
{
pData1[i] = Gx[i];
}
//将数据存入纵向高斯模板中
int colLength = (int)(floor(3.0*sigma1 + 0.5 - shift2) - ceil(-3.0*sigma1 - 0.5 - shift2) + 1);
int colBegin = (int)ceil(-3.0*sigma1 - 0.5 - shift2);
float colArray[30], Gy[30];
for (i = 0; i<colLength; i++)
{
colArray[i] = colBegin + i;
}
gauss(colArray, Gy, colLength, sigma1);
Mat ky = Mat(colLength, 1, CV_32F);
float *pData2;
for (i = 0; i < colLength; i++)
{
pData2 = ky.ptr<float>(i);
pData2[0] = Gy[i];
}
filter2D(img, img2, img.depth(), kx, Point(-1, -1));
filter2D(img2, imgResult, img2.depth(), ky, Point(-1, -1));
return imgResult;
}
//行列卷积
int gauss(float x[], float y[], int length, float sigma)
{
int i;
float sum = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i<length; i++)
{
x[i] = exp(-pow(x[i], 2) / (2 * pow(sigma, 2)));
sum += x[i];
}
for (i = 0; i<length; i++)
{
y[i] = x[i] / sum;
}
return 1;
}
Mat FaceProcessing(const Mat &img_, double gamma , double sigma0 , double sigma1, double mask , double do_norm)
{
Mat img;
img_.convertTo(img, CV_32F);
Mat imT1, imT2;
int rows = img.rows;
int cols = img.cols;
Mat im = img;
int b = floor(3 * abs(sigma1));//左右扩充边缘的距离
Mat imtemp(Size(cols + 2 * b, rows + 2 * b), CV_32F, Scalar(0));//保存扩充的图形
Mat imtemp2(Size(cols, rows), CV_32F, Scalar(0));
float s = 0.0;
//Gamma correct input image to increase local contrast in shadowed regions.
if (gamma == 0)
{
double impixeltemp = 0;
double Max = MatMaxMin(im, "MAX");//等价于max(1,max(max(im)))
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
{
impixeltemp = log(im.ptr<float>(i)[j] + Max / 256);
im.ptr<float>(i)[j] = impixeltemp;
}
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
im.ptr<float>(i)[j] = pow(im.ptr<float>(i)[j], gamma);
}
float *pData1;
//run prefilter, if any
if (sigma1)
{
double border = 1;
if (border) //add extend-as-constant image border to reduce
//boundary effects
{
for (int i = 0; i<rows + 2 * b - 1; i++)
{
pData1 = imtemp.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols + 2 * b - 1; j++){
//中间
if (i >= b&&i<im.rows + b&&j >= b&&j<im.cols + b)
pData1[j] = im.ptr<float>(i - b)[j - b];
//左上
else if (i<b&&j<b)
pData1[j] = im.ptr<float>(0)[0];
//右上
else if (i<b&&j >= im.cols + b&&j<cols + 2 * b)
pData1[j] = im.ptr<float>(0)[cols - 1];
//左下
else if (i >= im.rows + b&&i<rows + 2 * b&&j<b)
pData1[j] = im.ptr<float>(rows - 1)[0];
//右下
else if (i >= im.rows + b&&j >= im.cols + b)
pData1[j] = im.ptr<float>(im.rows - 1)[im.cols - 1];
//上方
else if (i<b&&j >= b&&j<im.cols + b)
pData1[j] = im.ptr<float>(0)[j - b];
//下方
else if (i >= im.rows + b&&j >= b&&j<im.cols + b)
pData1[j] = im.ptr<float>(im.rows - 1)[j - b];
//左方
else if (j<b&&i >= b&&i<im.rows + b)
pData1[j] = im.ptr<float>(i - b)[0];
//右方
else if (j >= im.cols + b&&i >= b&&i<im.rows + b)
pData1[j] = im.ptr<float>(i - b)[im.cols - 1];/**/
}
}
}
else
{
if (sigma0>0)
{
imT1 = gaussianfilter(imtemp, sigma0, sigma0);
imT2 = gaussianfilter(imtemp, -sigma1, -sigma1);
imtemp = imT1 - imT2;
//imtemp=gaussianfilter(imtemp,sigma0,sigma0)-gaussianfilter(imtemp,-sigma1,-sigma1);
}
else
imtemp = imtemp - gaussianfilter(imtemp, -sigma1, -sigma1);
}
if (border)
{
//再取回中间部分
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = im.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
pData1[j] = imtemp.ptr<float>(i + b)[j + b];
}
}
// test=im.ptr<float>(19)[19];
}
/*
% Global contrast normalization. Normalizes the spread of output
% values. The mean is near 0 so we don't bother to subtract
% it. We use a trimmed robust scatter measure for resistance to
% outliers such as specularities and image borders that have
% different values from the main image. Usually trim is about
% 10.
*/
if (do_norm)
{
double a = 0.1;
double trim = abs(do_norm);
//im = im./mean(mean(abs(im).^a))^(1/a);
imtemp2 = abs(im);
//cvPow(&im,&im,a)//为每个元素求pow
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = imtemp2.ptr<float>(i);//imtemp2为零矩阵
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
pData1[j] = pow(imtemp2.ptr<float>(i)[j], a);
}
//求平均值s
s = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = imtemp2.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
s += imtemp2.ptr<float>(i)[j];
}
s /= (im.rows*im.cols);
double temp = pow(s, 1 / a);
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = im.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
pData1[j] = pData1[j] / temp;//点除
}
//im = im./mean(mean(min(trim,abs(im)).^a))^(1/a);
imtemp2 = abs(im);
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = imtemp2.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
if (pData1[j]>trim)
pData1[j] = trim;//min(trim,abs(im))
}
//cvPow(&im,&im,a);////为每个元素求pow
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = imtemp2.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
pData1[j] = pow(pData1[j], a);
}
//求平均值
s = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = imtemp2.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
s += pData1[j];
}
s /= (im.rows*im.cols);
temp = pow(s, 1 / a);//
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = im.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
pData1[j] = pData1[j] / temp;//点除
}
if (do_norm>0)
{//im = trim*tanh(im/trim);
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = im.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
pData1[j] = trim*tanh(pData1[j] / trim);
}
}
}
//归一化处理
double Min;
Min = MatMaxMin(im, "MIN");//找到矩阵的最小值
for (int i = 0; i<rows; i++)
{
pData1 = im.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j<cols; j++)
pData1[j] += Min;
}
//im.convertTo(im, CV_32F, 1.0/255.0);
normalize(im, im, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);
//normalize(im,im,0,255,NORM_MINMAX);
/* for(int i=0;i<rows;i++)
{
pData1=im.ptr<float>(i);
for(int j=0;j<cols;j++)
pData1[j]*=255;
}*/
im.convertTo(im, CV_8UC1);
return im;
}FaceDetect.cpp:
#include <FaceDetect.h>
#include <FaceRotate.h>
#include <FaceProcessing.h>
void Dlib_Prodefine()
{
deserialize("shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat") >> sp;//读入标记点文件
}
Mat Facedetect(Mat frame)//脸是否存在
{
Mat gray,error;
cvtColor(frame, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
int * pResults = NULL;
pResults = facedetect_frontal_tmp((unsigned char*)(gray.ptr(0)), gray.cols, gray.rows, gray.step, 1.2f, 5, 24);
int peopleNUM = (pResults ? *pResults : 0);
for (int i = 0; i < peopleNUM; i++)//代表有几张人脸(pResults ? *pResults : 0)
{
short * p = ((short*)(pResults + 1)) + 6 * i;
Rect opencvRect(p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3]);
//gray = gray(opencvRect);
dlib::rectangle dlibRect((long)opencvRect.tl().x, (long)opencvRect.tl().y, (long)opencvRect.br().x - 1, (long)opencvRect.br().y - 1);
dlib::full_object_detection shape = sp(dlib::cv_image<uchar>(gray), dlibRect);//标记点
std::vector<full_object_detection> shapes;
shapes.push_back(shape);//把点保存在了shape中
dlib::array<array2d<rgb_pixel>> face_chips;
extract_image_chips(dlib::cv_image<uchar>(gray), get_face_chip_details(shapes), face_chips);
Mat pic = toMat(face_chips[0]);
cvtColor(pic, pic, CV_BGR2GRAY);
resize(pic, pic, Size(224, 224));
return FaceProcessing(pic);
}
return error;//如果没有检测出人脸 将返回一个空矩阵
}在上述代码中,关于dlib的array2d< rgb_pixel >类型与Mat类型的转换可以在这里进行体现:
dlib::array<array2d<rgb_pixel>> face_chips;
extract_image_chips(dlib::cv_image<uchar>(gray), get_face_chip_details(shapes), face_chips);
Mat pic = toMat(face_chips[0]);
其中face_chips[0]即为一个array2d< rgb_pixel >的类型,可以通过toMat函数进行转换。
将Mat类型转换为array2d< rgb_pixel >则可以用:
Mat gray;
dlib::cv_image<uchar>(gray);在这个地方,我们特别需要注意,还要转换一次灰度:
cvtColor(pic, pic, CV_BGR2GRAY);
resize(pic, pic, Size(224, 224));
return FaceProcessing(pic);为什么?因为在测试过程中我发现,dlib函数中的toMat函数返回的不是CV_BGR2GRAY(OpenCV中的灰度图像类型),如果这里你不加,那么这个预处理将会只卷积左半部分脸。
我们可以看看识别的效果。调用FaceDetect()函数接口:
Dlib_Prodefine();
//Caffe_Prodefine();
Mat lena = imread("lena.jpg");
imshow("Face Detect", Facedetect(lena));
waitKey(0);当然,这个地方,在进行检测之前,我们最好还是先判断FaceDetect(lena)是否为空,再进行Imshow.
检测与处理图片效果显示:
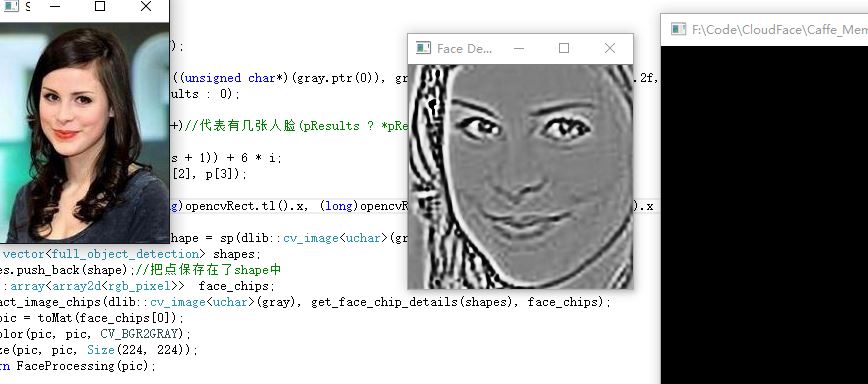
为什么要把图片最后转换为224*224的尺寸?因为:Vgg网络模型接收的就是224*224的尺寸,后面还会讲这个东西。
基于深度学习的人脸识别系统(Caffe+OpenCV+Dlib)【二】人脸预处理的更多相关文章
- 基于深度学习的中文语音识别系统框架(pluse)
目录 声学模型 GRU-CTC DFCNN DFSMN 语言模型 n-gram CBHG 数据集 本文搭建一个完整的中文语音识别系统,包括声学模型和语言模型,能够将输入的音频信号识别为汉字. 声学模型 ...
- 【OCR技术系列之四】基于深度学习的文字识别(3755个汉字)
上一篇提到文字数据集的合成,现在我们手头上已经得到了3755个汉字(一级字库)的印刷体图像数据集,我们可以利用它们进行接下来的3755个汉字的识别系统的搭建.用深度学习做文字识别,用的网络当然是CNN ...
- 【OCR技术系列之四】基于深度学习的文字识别
上一篇提到文字数据集的合成,现在我们手头上已经得到了3755个汉字(一级字库)的印刷体图像数据集,我们可以利用它们进行接下来的3755个汉字的识别系统的搭建.用深度学习做文字识别,用的网络当然是CNN ...
- 基于深度学习的回声消除系统与Pytorch实现
文章作者:凌逆战 文章代码(pytorch实现):https://github.com/LXP-Never/AEC_DeepModel 文章地址(转载请指明出处):https://www.cnblog ...
- VulDeePecker:基于深度学习的脆弱性检测系统
最近的两款软件,VUDDY和VulPecker,假阴性率高而假阳性率低,用于检测由代码克隆引发的漏洞.而如果用于非代码克隆引起的漏洞则会出现高误报率. 本文使用深度学习处理程序中的代码片段,不应由专家 ...
- 深度学习(PYTORCH)-2.python调用dlib提取人脸68个特征点
在看官方教程时,无意中发现别人写的一个脚本,非常简洁. 官方教程地址:http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/data_loading_tutorial.html# ...
- 基于深度学习的人脸识别系统(Caffe+OpenCV+Dlib)【一】如何配置caffe属性表
前言 基于深度学习的人脸识别系统,一共用到了5个开源库:OpenCV(计算机视觉库).Caffe(深度学习库).Dlib(机器学习库).libfacedetection(人脸检测库).cudnn(gp ...
- 基于深度学习的人脸识别系统(Caffe+OpenCV+Dlib)【三】VGG网络进行特征提取
前言 基于深度学习的人脸识别系统,一共用到了5个开源库:OpenCV(计算机视觉库).Caffe(深度学习库).Dlib(机器学习库).libfacedetection(人脸检测库).cudnn(gp ...
- 基于深度学习的人脸识别系统系列(Caffe+OpenCV+Dlib)——【四】使用CUBLAS加速计算人脸向量的余弦距离
前言 基于深度学习的人脸识别系统,一共用到了5个开源库:OpenCV(计算机视觉库).Caffe(深度学习库).Dlib(机器学习库).libfacedetection(人脸检测库).cudnn(gp ...
随机推荐
- 关于Maven报错的一些解决办法(别处贴的)
1.警告:The tag handler class for "s:form"(org.apache.struts2.views.jsp.ui.FormTag) was not f ...
- amaze ui表格斑马纹效果
amaze ui表格斑马纹效果 需要注意的是样式的写法,都是 am-table- ,很好记的 如果是条纹就是striped,如果是hover状态就是hover 用法很简单,点对应class,不同的cl ...
- CSU 8月月赛 Decimal 小数化分数
http://acm.csu.edu.cn/OnlineJudge/problem.php?id=1303 这个OJ很容易跪所以我贴一下题目 Description 任意一个分数都是有理数,对于任意一 ...
- POJ 1279 Art Gallery 半平面交/多边形求核
http://poj.org/problem?id=1279 顺时针给你一个多边形...求能看到所有点的面积...用半平面对所有边取交即可,模版题 这里的半平面交是O(n^2)的算法...比较逗比.. ...
- shutdown---系统关机
shutdown命令用来系统关机命令.shutdown指令可以关闭所有程序,并依用户的需要,进行重新开机或关机的动作. 语法 shutdown(选项)(参数) 选项 -c:当执行“shutdown - ...
- Wget使用
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/A7BRny wget / curl 是两个比较方便的测试http功能的命令行工具,大多数情况下,测试http功能主要是查看请求响应 头 ...
- iOS 基于第三方QQ授权登录
基于iOS实现APP的第三方QQ登陆.接入第三方SDK时的一个主要的步骤: 1,找到相关的开放平台.QQ互联平台,http://connect.qq.com/: 2,注冊成功后创建自己的APP.填写一 ...
- 使用wpaint绘图软件时:Uncaught DOMException: Failed to execute 'drawImage' on 'CanvasRenderingContext2D': The image argument is a canvas element with a width or height of 0.
使用wpaint绘图软件时:Uncaught DOMException: Failed to execute 'drawImage' on 'CanvasRenderingContext2D': Th ...
- 用Navicat连接MySQL数据库出现1251错误:密码方式错误
原因:因为MySQL8.0是最新版密码保存方式,而图形化数据库管理工具还是原先的密码保存方式. 解决方式: 用CMD命令号方式进入MySQL use mysql: ALTER USER 'root'@ ...
- java list 容器的ConcurrentModificationException
java中的很多容器在遍历的同时进行修改里面的元素都会ConcurrentModificationException,包括多线程情况和单线程的情况.多线程的情况就用说了,单线程出现这个异常一般是遍历( ...
