Tree--二叉树BinarySearchTree
BinarySearchTreeMap的实现
1 public interface Map<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
2 void put(K k, V v);
3
4 V get(K k);
5
6 void delete(K k);
7
8 boolean contains(K k);
9
10 boolean isEmpty();
11
12 int size();
13
14 int size(K lo, K hi);
15
16 K min();
17
18 K max();
19
20 K floor(K k);
21
22 K ceiling(K k);
23
24 // the number of keys less than key
25 int rank(K k);
26
27 K select(int k);
28
29 void deleteMin();
30
31 void deleteMax();
32
33 // keys in [lo , hi] in sorted order
34 Iterable<K> keys(K lo, K hi);
35
36 Iterable<K> keys();
37 }
Map Interface
二叉树的定义
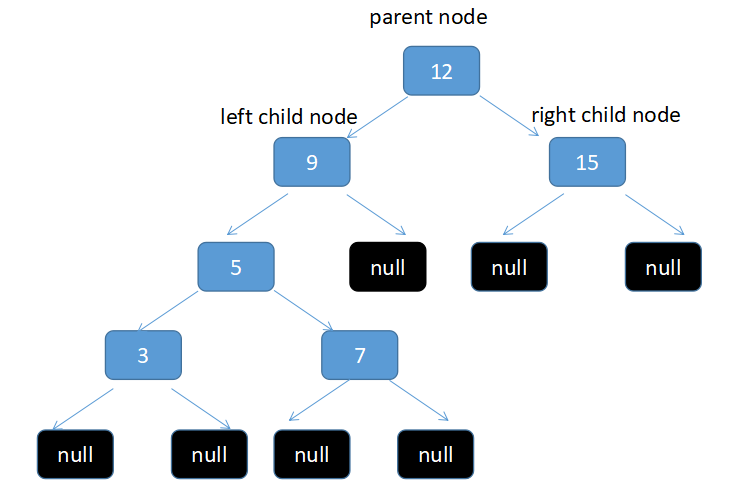
在计算机科学中,二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree)。二叉树常被用于实现二叉查找树和二叉堆。二叉树的左子节点 < 父节点 < 右子节点
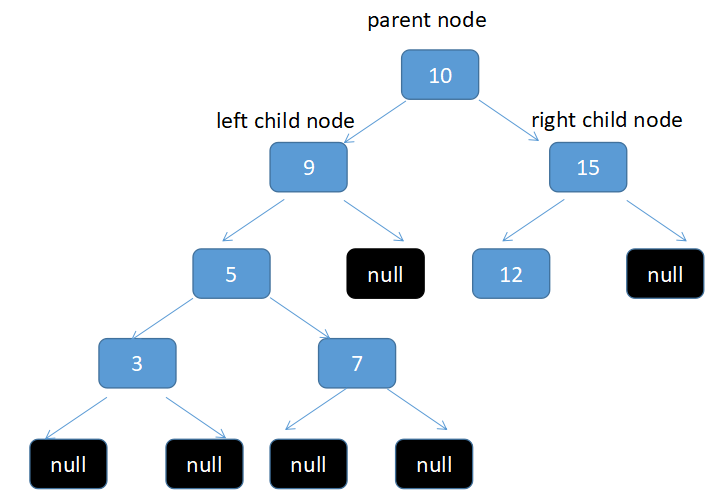
这是typical的二叉树的样子, null 代表子节点为空,从这张图可以看出,左子节点 9 小于 父节点 10 小于 右子节点
1 private class Node<K, V> {
2 private K k;
3 private V v;
4 private Node<K, V> left;
5 private Node<K, V> right;
6 private int size;
7 Node(K k, V v) { this.k = k; this.v = v; }
8 Node(K k, V v, int size) { this.k = k; this.v = v; this.size = size;}
9 }
Node(节点)对象
二叉树的插入操作
假设我们依次插入 10 , 9, 15, 5 , 7 这5个元素到二叉树中。see what will happen 这是个动态图
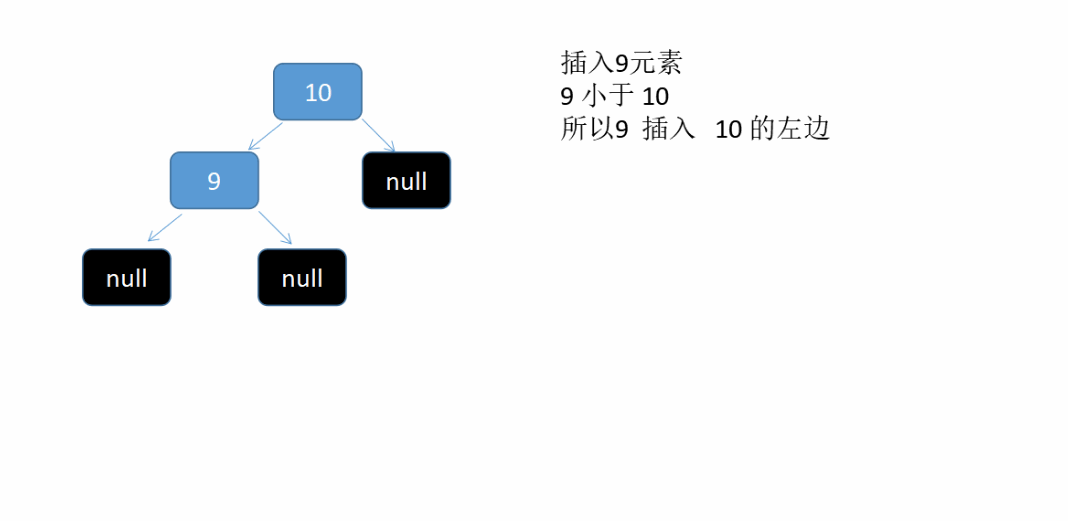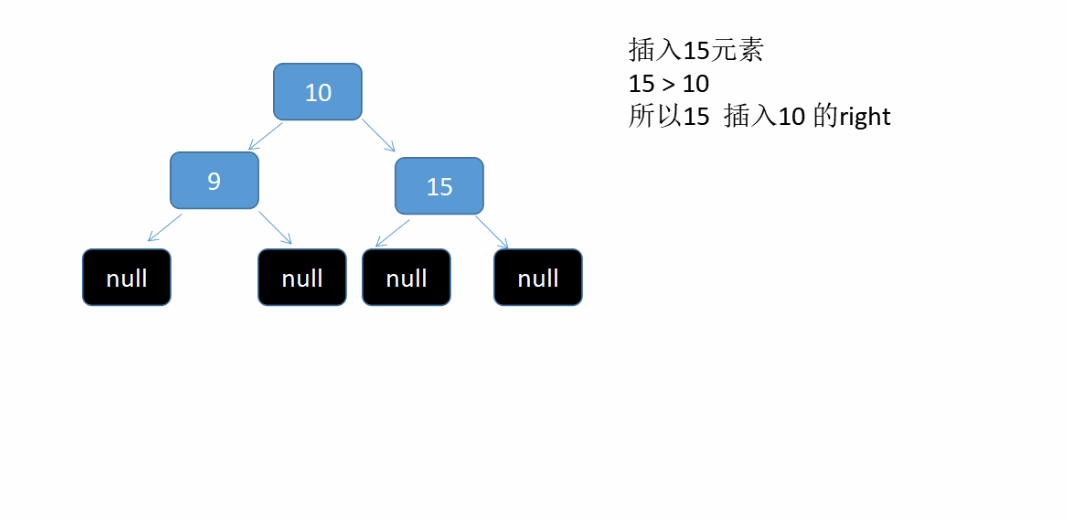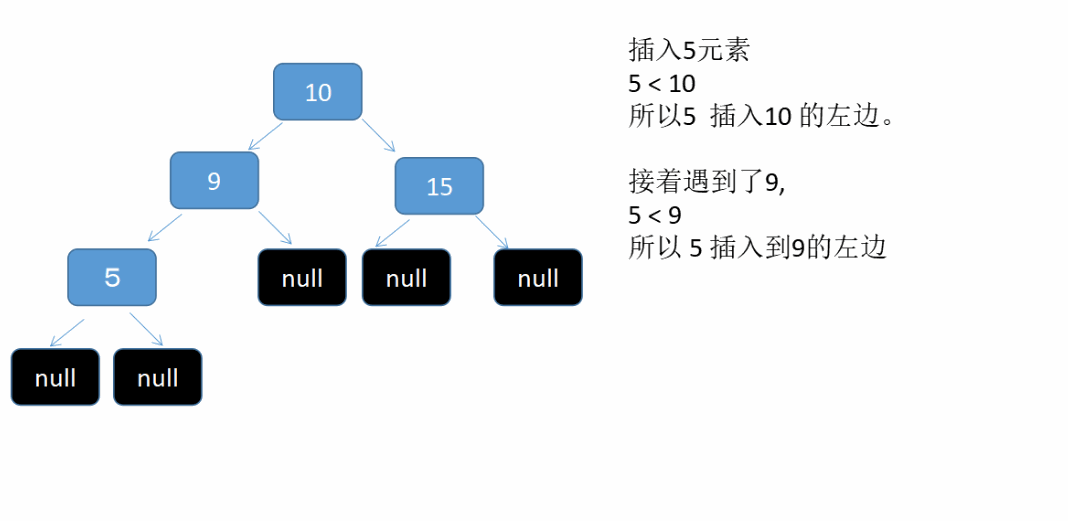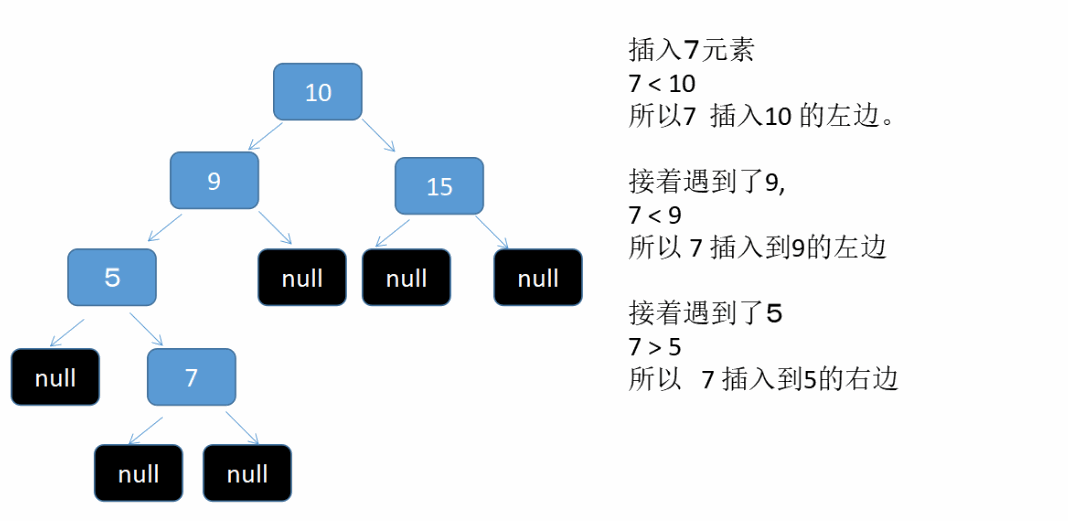
1 @Override
2 public void put(K k, V v) {
3 root = put(root, k, v); //root 是根节点
4 }
5
6 private Node<K, V> put(Node<K, V> node, K k, V v) {
7 if (node == null) return new Node<>(k, v, 1);
8 int cmp = node.k.compareTo(k);
9 if (cmp > 0) { //node的k大一点 放到左边的数中
10 node.left = put(node.left, k, v);
11 } else if (cmp < 0) { //node的k小一点 放到右边的数中
12 node.right = put(node.right, k, v);
13 } else node.v = v;
14
15 node.size = size(node.left) + size(node.right) + 1;
16 return node;
17 }
put operation (插入)
二叉树的get 方法
get方法简单来说就是要找到那个key相同的对象。比如我们要在「10 , 9, 15, 5 , 7 」上图所示中找到 7
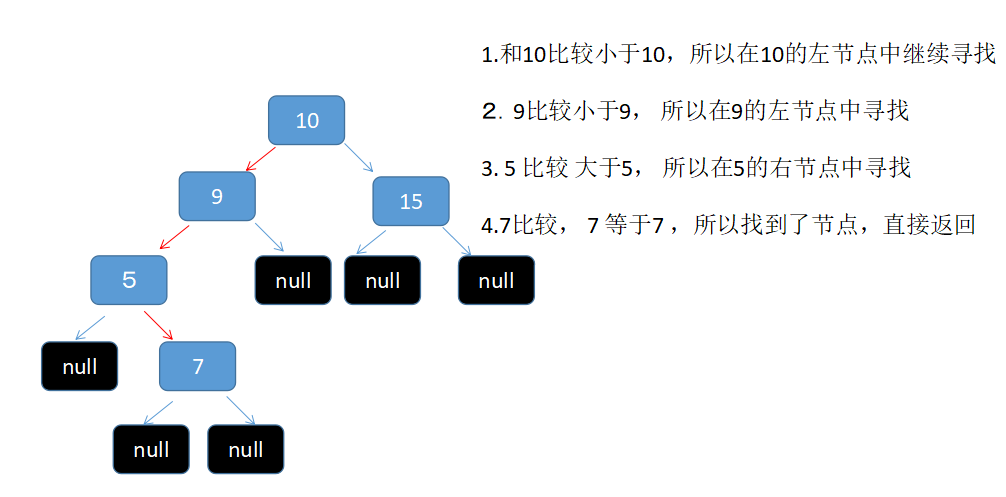
1 @Override
2 public V get(K k) {
3 return get(root, k);
4 }
5
6 private V get(Node<K, V> node, K k) {
7
8 if (node == null) return null; //not find
9 else if (node.k.compareTo(k) > 0) { //node的k大一点 放到左边的数中
10 return get(node.left, k);
11 } else if (node.k.compareTo(k) < 0) { //node的k小一点 放到右边的数中
12 return get(node.right, k);
13 } else { //equal
14 return node.v;
15 }
16
17 }
get operation
二叉树的删除操作
其实想象一下,当你删除一个node的时候,你需要找一个替代node来代替这个node。
这里又分3种情况。首先假设你有如下的树结构

1.第一种情况是这个删除的节点的左右节点都是null。
比如我要删除3节点。其实只要直接把3节点reset 为null 就可以了。变成如下
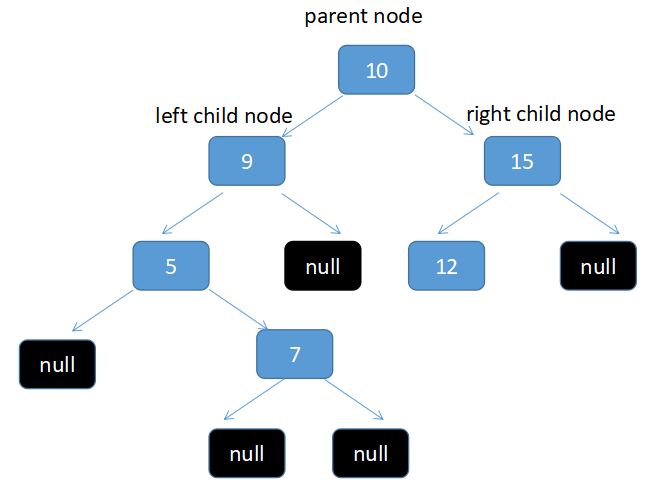
2.第二种情况是删除的节点的2个子节点中有一个子节点为null
比如我要删除15。 15 的左节点是12 右节点是 null,所以符合这个情况
这个时候只需要直接把需要删除的节点 reset 为 非空的子节点就可以了
所以在这里只需要把15的值替代为12
3.第三种情况是删除的节点的2个子节点都不为null,
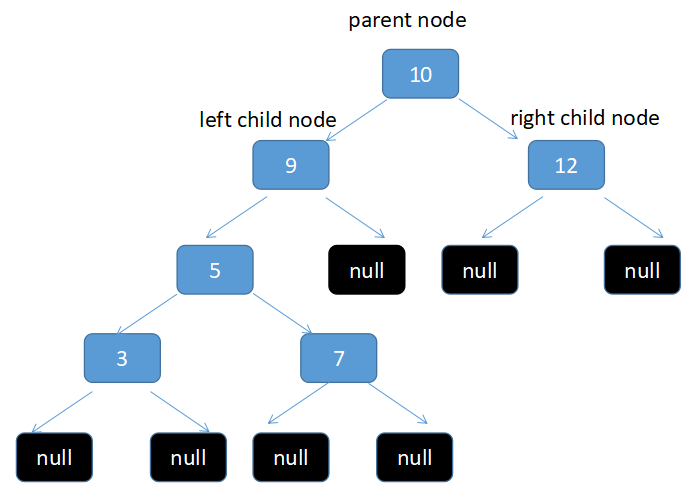
这个时候其实可以有2个选择,一个是把删除的节点替换为右子节点为根节点的那个树中最小的节点
比如我要删除10, 右节点为15(二叉树的删除操作的那个图,不是上面的那个图),15这个节点为根节点的树中总共有2个元素(15和12),12是最小的。所以把需要删除的节点替换为12。删除后如下
另外一种选择是把左节点为根节点的树中最大的值取出来,把需要删除的那个节点替换为这个左节点最大的元素(2个选择没什么区别)
1 @Override
2 public void delete(K k) {
3 delete(root, k);
4 }
5 //delete the k in the node tree and reset the size prorperty of this tree and subtrees to correct value
6 private Node<K, V> delete(Node<K, V> node, K k) {
7 if (node == null) return null; //没有找到这个node
8
9 int cmp = node.k.compareTo(k);
10 if (cmp > 0) {
11 node.left = delete(node.left, k);
12 node.size = size(node.left) + size(node.right) + 1;
13 return node;
14 } else if (cmp < 0) {
15 node.right = delete(node.right, k);
16 node.size = size(node.left) + size(node.right) + 1;
17 return node;
18 } else { //hit the key
19 if (node.right == null) //if the right node is null then just replace this node with left node
20 return node.left;
21 else if (node.left == null) // if the left node is null then just replace this node with right node
22 return node.right;
23 else {
24 return deleteMin(node.right); // if both the subnodes are not null replace this node with the smallest node in the right sub node
25 }
26 }
27 }
28
29 //删除从参数node开始的最小的node
30 private Node<K, V> deleteMin(Node<K, V> node) {
31 return delete(node, min(node));
32 }
33
34 private Node<K, V> deleteMax(Node<K, V> node) {
35 return delete(node, max(node));
36 }
37
38 @Override
39 public void deleteMin() {
40 deleteMin(root);
41 }
42
43 @Override
44 public void deleteMax() {
45 deleteMax(root);
46 }
47
48 @Override
49 public K min() {
50 return min(root);
51 }
52
53 //get the smallest node in the given node
54 private K min(Node<K, V> node) {
55 if (node == null) return null;
56 for (; node.left != null; node = node.left);
57 return node.k;
58 }
59
60 @Override
61 public K max() {
62 return max(root);
63 }
64 //get the most max node in the given node
65 private K max(Node<K, V> node) {
66 if (node == null) return null;
67 for (node = root; node.right != null; node = node.right);
68 return node.k;
69 }
delete operation 删除操作
分析
BinarySearchTree 有一个最大的缺点,就是如果插入的元素是ordered,比如我插入 1 2 3 4 5 6 这样子,元素都会排在一边。这样子查找起来路径很长,效率很低。
如果插入的元素是随机的,那么所有的get put 操作的时间复杂度应该是 和 log2(N) 成正比的
具体的实现可以参考这个。https://github.com/Cheemion/algorithms/blob/master/src/com/algorithms/tree/BinarySearchTreeMap.java
有什么错误的地方欢迎大家指正哈
Tree--二叉树BinarySearchTree的更多相关文章
- Leetcode 101 Symmetric Tree 二叉树
判断一棵树是否自对称 可以回忆我们做过的Leetcode 100 Same Tree 二叉树和Leetcode 226 Invert Binary Tree 二叉树 先可以将左子树进行Invert B ...
- Leetcode 110 Balanced Binary Tree 二叉树
判断一棵树是否是平衡树,即左右子树的深度相差不超过1. 我们可以回顾下depth函数其实是Leetcode 104 Maximum Depth of Binary Tree 二叉树 /** * Def ...
- [CareerCup] 4.7 Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree 二叉树的最小共同父节点
4.7 Design an algorithm and write code to find the first common ancestor of two nodes in a binary tr ...
- [LeetCode] 111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree ☆(二叉树的最小深度)
[Leetcode] Maximum and Minimum Depth of Binary Tree 二叉树的最小最大深度 (最小有3种解法) 描述 解析 递归深度优先搜索 当求最大深度时,我们只要 ...
- UVA.548 Tree(二叉树 DFS)
UVA.548 Tree(二叉树 DFS) 题意分析 给出一棵树的中序遍历和后序遍历,从所有叶子节点中找到一个使得其到根节点的权值最小.若有多个,输出叶子节点本身权值小的那个节点. 先递归建树,然后D ...
- [LeetCode] 111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree 二叉树的最小深度
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth. The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shor ...
- [LeetCode] 543. Diameter of Binary Tree 二叉树的直径
Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a b ...
- [LeetCode] Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree 二叉树的序列化和去序列化
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so tha ...
- [LeetCode] Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree 二叉树的最小共同父节点
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree. According ...
- [LeetCode] Minimum Depth of Binary Tree 二叉树的最小深度
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth. The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shor ...
随机推荐
- SSM使用Ueditor
富文本编辑器(UEditor) 1. 下载UEditor富文本编辑器 建议下载 utf8-jsp 版本的,结构目录如下: 下载地址:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Nq0oJB ...
- Java 将JSON反射到实体类
通过服务间调用拿到的数据返回的格式是JSON,如果你当前这个服务有实体数据类型可以对应上,那么就可以轻松愉快的搞定. 如果数据格式对不上,例如这个JSON里面有些数据是我们不想要的,这样我们实体的数据 ...
- php 之根据mysql字段 批量生成 array 数组
ci框架 验证字段 需要 生成类似为: array('field' => 'admin_id','label' => '账号ID','rules' => 'integer'), ...
- php之4个坐标点判断是否为矩形和正方形
代码 <?php $a=[0,0]; $b=[0,1]; $c=[1,1]; $d=[1,0]; $ar=array($a,$b,$c,$d); $a1=[]; // 0 1 2 3 forea ...
- python0why study python
Python 越来越火爆 Python 在诞生之初,因为其功能不好,运转功率低,不支持多核,根本没有并发性可言,在计算功能不那么好的年代,一直没有火爆起来,甚至很多人根本不知道有这门语言. 随着时代的 ...
- 对Spark硬件配置的建议
对于Spark开发人员来说,一个比较普遍的问题就是如何合理的配置Spark的硬件?当然如何合理的对Spark集群进行硬件配置要视情况而定,在这里给出以下建议: 存储系统 在大数据领域,有一句" ...
- php 检测敏感字
public function getMin($content){//调用接口 $content_url ="http://www.ju1.cn/index.php/Index/add.ht ...
- VMware 虚拟机下CentOS 7连接网络
查看主机网络配置 ipconfig 1.在centos打开终端命令 2. 输入命令 cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ 进入文件 输入 ls查看此文件夹下的文件 3 ...
- Python图像读写方法对比
训练视觉相关的神经网络模型时,总是要用到图像的读写.方法有很多,比如matplotlib.cv2.PIL等.下面比较几种读写方式,旨在选出一个最快的方式,提升训练速度. 实验标准 因为训练使用的框架是 ...
- 【linux】helloword原理分析及实战
目录 前言 linux中hello word原理 hello word 实战 学习参考 前言 hello word 著名演示程序,哈哈 下面在 arm linux 下展示一下hello world,便 ...
