使用Python scikit-learn 库实现神经网络算法
1:神经网络算法简介
2:Backpropagation算法详细介绍
3:非线性转化方程举例
4:自己实现神经网络算法NeuralNetwork
5:基于NeuralNetwork的XOR实例
6:基于NeuralNetwork的手写数字识别实例
7:scikit-learn中BernoulliRBM使用实例
8:scikit-learn中的手写数字识别实例
一:神经网络算法简介
1:背景
以人脑神经网络为启发,历史上出现过很多版本,但最著名的是backpropagation
2:多层向前神经网络(Multilayer Feed-Forward Neural Network)
多层向前神经网络组成部分
输入层(input layer),隐藏层(hiddenlayer),输出层(output layer)
3:设计神经网络结构
4:算法验证——交叉验证法(Cross- Validation)
解读: 有一组输入集A,B,可以分成三组,第一次以第一组为训练集,求出一个准确度,第二次以第二组作为训练集,求出一个准确度,求出准确度,第三次以第三组作为训练集,求出一个准确度,然后对三个准确度求平均值
二:Backpropagation算法详细介绍
1:通过迭代性来处理训练集中的实例
2:输入层输入数
经过权重计算得到第一层的数据,第一层的数据作为第二层的输入,再次经过权重计算得到结果,结果和真实值之间是存在误差的,然后根据误差,反向的更新每两个连接之间的权重
3:算法详细介绍
输入:D : 数据集,| 学习率(learning rate),一个多层前向神经网络



 Tj:真实值,Qj表示预测值
Tj:真实值,Qj表示预测值 Errk 表示前一层的误差, Wjk表示前一层与当前点的连接权重
Errk 表示前一层的误差, Wjk表示前一层与当前点的连接权重 l:指学习比率(变化率),手工指定,优化方法是,随着数据的迭代逐渐减小
l:指学习比率(变化率),手工指定,优化方法是,随着数据的迭代逐渐减小 l:同上
l:同上4:结合实例讲解算法
0.9对用的是L,学习率
测试代码如下:
1.NeutralNetwork.py文件代码
#coding:utf-8 import numpy as np #定义双曲函数和他们的导数
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x) def tanh_deriv(x):
return 1.0 - np.tanh(x)**2 def logistic(x):
return 1/(1 + np.exp(-x)) def logistic_derivative(x):
return logistic(x)*(1-logistic(x)) #定义NeuralNetwork 神经网络算法
class NeuralNetwork:
#初始化,layes表示的是一个list,eg[10,10,3]表示第一层10个神经元,第二层10个神经元,第三层3个神经元
def __init__(self, layers, activation='tanh'):
"""
:param layers: A list containing the number of units in each layer.
Should be at least two values
:param activation: The activation function to be used. Can be
"logistic" or "tanh"
"""
if activation == 'logistic':
self.activation = logistic
self.activation_deriv = logistic_derivative
elif activation == 'tanh':
self.activation = tanh
self.activation_deriv = tanh_deriv self.weights = []
#循环从1开始,相当于以第二层为基准,进行权重的初始化
for i in range(1, len(layers) - 1):
#对当前神经节点的前驱赋值
self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i - 1] + 1, layers[i] + 1))-1)*0.25)
#对当前神经节点的后继赋值
self.weights.append((2*np.random.random((layers[i] + 1, layers[i + 1]))-1)*0.25) #训练函数 ,X矩阵,每行是一个实例 ,y是每个实例对应的结果,learning_rate 学习率,
# epochs,表示抽样的方法对神经网络进行更新的最大次数
def fit(self, X, y, learning_rate=0.2, epochs=10000):
X = np.atleast_2d(X) #确定X至少是二维的数据
temp = np.ones([X.shape[0], X.shape[1]+1]) #初始化矩阵
temp[:, 0:-1] = X # adding the bias unit to the input layer
X = temp
y = np.array(y) #把list转换成array的形式 for k in range(epochs):
#随机选取一行,对神经网络进行更新
i = np.random.randint(X.shape[0])
a = [X[i]] #完成所有正向的更新
for l in range(len(self.weights)):
a.append(self.activation(np.dot(a[l], self.weights[l])))
#
error = y[i] - a[-1]
deltas = [error * self.activation_deriv(a[-1])] #开始反向计算误差,更新权重
for l in range(len(a) - 2, 0, -1): # we need to begin at the second to last layer
deltas.append(deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T)*self.activation_deriv(a[l]))
deltas.reverse()
for i in range(len(self.weights)):
layer = np.atleast_2d(a[i])
delta = np.atleast_2d(deltas[i])
self.weights[i] += learning_rate * layer.T.dot(delta) #预测函数
def predict(self, x):
x = np.array(x)
temp = np.ones(x.shape[0]+1)
temp[0:-1] = x
a = temp
for l in range(0, len(self.weights)):
a = self.activation(np.dot(a, self.weights[l]))
return a
2、测试代码
#coding:utf-8
'''
#基于NeuralNetwork的XOR(异或)示例
import numpy as np
from NeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork nn = NeuralNetwork([2,2,1], 'tanh')
X = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]])
y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0])
nn.fit(X, y)
for i in [[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1,1]]:
print(i,nn.predict(i))
'''
'''
#基于NeuralNetwork的手写数字识别示例
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,classification_report
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from NeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork digits = load_digits()
X = digits.data
y = digits.target
X -= X.min()
X /= X.max() nn =NeuralNetwork([64,100,10],'logistic')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)
labels_train = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_train)
labels_test = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_test)
print "start fitting"
nn.fit(X_train,labels_train,epochs=3000)
predictions = []
for i in range(X_test.shape[0]):
o = nn.predict(X_test[i])
predictions.append(np.argmax(o))
print confusion_matrix(y_test, predictions)
print classification_report(y_test, predictions)
''' #scikit-learn中的手写数字识别实例
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.ndimage import convolve
from sklearn import linear_model, datasets, metrics
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.neural_network import BernoulliRBM
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline ###############################################################################
# Setting up def nudge_dataset(X, Y): direction_vectors = [
[[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]], [[0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]], [[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0]], [[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0]]] shift = lambda x, w: convolve(x.reshape((8, 8)), mode='constant',
weights=w).ravel()
X = np.concatenate([X] +
[np.apply_along_axis(shift, 1, X, vector)
for vector in direction_vectors])
Y = np.concatenate([Y for _ in range(5)], axis=0)
return X, Y # Load Data
digits = datasets.load_digits()
X = np.asarray(digits.data, 'float32')
X, Y = nudge_dataset(X, digits.target)
X = (X - np.min(X, 0)) / (np.max(X, 0) + 0.0001) # 0-1 scaling X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=0) # Models we will use
logistic = linear_model.LogisticRegression()
rbm = BernoulliRBM(random_state=0, verbose=True) classifier = Pipeline(steps=[('rbm', rbm), ('logistic', logistic)]) ###############################################################################
# Training # Hyper-parameters. These were set by cross-validation,
# using a GridSearchCV. Here we are not performing cross-validation to
# save time.
rbm.learning_rate = 0.06
rbm.n_iter = 20
# More components tend to give better prediction performance, but larger
# fitting time
rbm.n_components = 100
logistic.C = 6000.0 # Training RBM-Logistic Pipeline
classifier.fit(X_train, Y_train) # Training Logistic regression
logistic_classifier = linear_model.LogisticRegression(C=100.0)
logistic_classifier.fit(X_train, Y_train) ###############################################################################
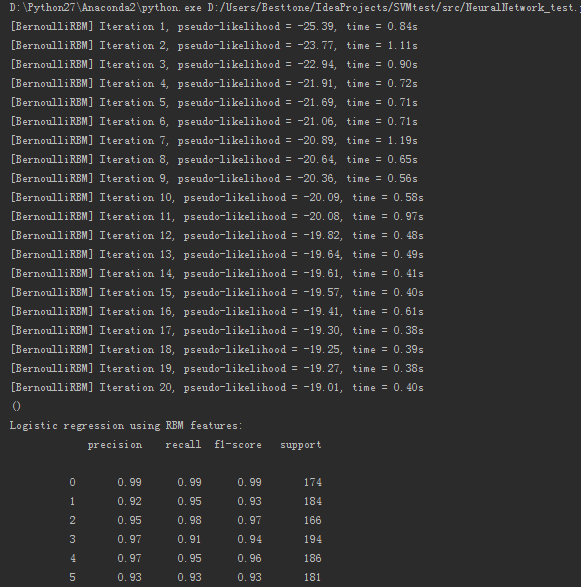
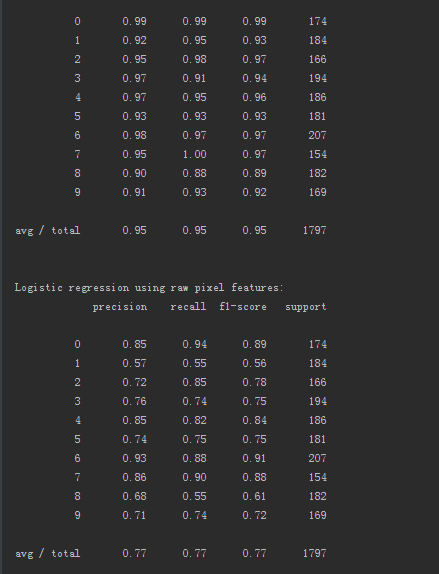
# Evaluation print()
print("Logistic regression using RBM features:\n%s\n" % (
metrics.classification_report(
Y_test,
classifier.predict(X_test)))) print("Logistic regression using raw pixel features:\n%s\n" % (
metrics.classification_report(
Y_test,
logistic_classifier.predict(X_test)))) ###############################################################################
# Plotting plt.figure(figsize=(4.2, 4))
for i, comp in enumerate(rbm.components_):
plt.subplot(10, 10, i + 1)
plt.imshow(comp.reshape((8, 8)), cmap=plt.cm.gray_r,
interpolation='nearest')
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.suptitle('100 components extracted by RBM', fontsize=16)
plt.subplots_adjust(0.08, 0.02, 0.92, 0.85, 0.08, 0.23) plt.show() '''
from sklearn.neural_network import BernoulliRBM
X = [[0,0],[1,1]]
y = [0,1]
clf = BernoulliRBM().fit(X,y)
测试结果如下:
使用Python scikit-learn 库实现神经网络算法的更多相关文章
- python复杂网络库networkx:算法
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/54020333 Networks算法Algorithms 最短路径Shortest Paths shor ...
- day-11 python自带库实现2层简单神经网络算法
深度神经网络算法,是基于神经网络算法的一种拓展,其层数更深,达到多层,本文以简单神经网络为例,利用梯度下降算法进行反向更新来训练神经网络权重和偏向参数,文章最后,基于Python 库实现了一个简单神经 ...
- Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习
转自:http://my.oschina.net/u/175377/blog/84420#OSC_h2_23 Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习 Warning 警告:有些没能理解的 ...
- day-9 sklearn库和python自带库实现最近邻KNN算法
K最近邻(k-Nearest Neighbor,KNN)分类算法,是一个理论上比较成熟的方法,也是最简单的机器学习算法之一.该方法的思路是:如果一个样本在特征空间中的k个最相似(即特征空间中最邻近)的 ...
- Python实现神经网络算法识别手写数字集
最近忙里偷闲学习了一点机器学习的知识,看到神经网络算法时我和阿Kun便想到要将它用Python代码实现.我们用了两种不同的方法来编写它.这里只放出我的代码. MNIST数据集基于美国国家标准与技术研究 ...
- scikit learn 模块 调参 pipeline+girdsearch 数据举例:文档分类 (python代码)
scikit learn 模块 调参 pipeline+girdsearch 数据举例:文档分类数据集 fetch_20newsgroups #-*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于神经网络算法在智能医疗诊断中的应用探索代码简要展示
#K-NN分类 import os import sys import time import operator import cx_Oracle import numpy as np import ...
- python 各种开源库
测试开发 来源:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ea6f7fb69501 Web UI测试自动化 splinter - web UI测试工具,基于selnium封装. 链接 sel ...
- Python常用的库简单介绍一下
Python常用的库简单介绍一下fuzzywuzzy ,字符串模糊匹配. esmre ,正则表达式的加速器. colorama 主要用来给文本添加各种颜色,并且非常简单易用. Prettytable ...
随机推荐
- yii2GridView的简单使用
GridView::widget([ 'dataProvider' => $dataProvider,// 你传过来的ActiveDataProvider // 'filterModel' =& ...
- 无线路由器wan口和lan口ip同网段导致无法上网解决办法
环境 本地网段为192.168.0.0/24 路由器默认网段也是192.168.0.0/24 设置好路由器wan口DHCP自动获取ip以后无法上网 解决办法 把路由器是lan口地址设置为192.168 ...
- [ASP.NET]从Request.Url获取根网址的最简单方法
在拼接绝对路径的网址时,经常需要从Request.Url中获取根网址(比如http://www.cnblogs.com),然后与相对路径一起拼接为绝对路径. 以前的做法如下: var uri = Re ...
- 虚拟机中CentoOs配置ip且连网
1.修改"VMware Network Adapter VMnet8",配置IP 2.打开虚拟机,"编辑" => "虚拟网络编辑器", ...
- pandas的merge方法
数据合并时可以使用merge方法,对两个dataFrame根据某一个series合并,这个方法非常好用,只要找到了合并的标准,新的数据就可以重构出来. 1.命令: pd.merge() on:列名,j ...
- python及numpy,pandas易混淆的点
https://blog.csdn.net/happyhorizion/article/details/77894035 初接触python觉得及其友好(类似matlab),尤其是一些令人拍案叫绝不可 ...
- BBS - 文章详细页、点赞、踩灭
一.文章详细页 文章详细页:1.链接:<div><h5><a href="/blog/{{ article.user.username }}/articles/ ...
- 2014年百度之星程序设计大赛 - 资格赛 1001 Energy Conversion
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章.未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/sr19930829/article/details/26003661 Energy Conversi ...
- django基础之FBV与CBV,ajax序列化补充,Form表单
目录: FBV与CBV ajax序列化补充 Form表单(一) 一.FBV与CBV 1.什么是FBV.CBV? django书写view时,支持两种格式写法,FBV(function bases vi ...
- 为什么要同时重写equals和hashcode
原文地址https://blog.csdn.net/tiantiandjava/article/details/46988461 原文地址https://blog.csdn.net/lijiecao0 ...






