关于语法节点Tree、类型Type和符号Symbol
每个语法节点Tree都有Type属性,部分的语法节点有Symbol属性,如下:

与Symbol类型与Type类型之间的关系如下:
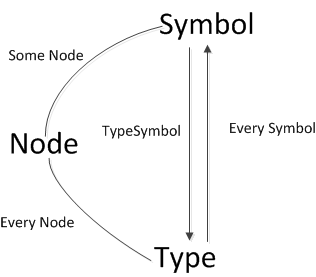
下面是Symbol与Type之间的关系:
(1)MethodSymbol("finalize").type = MethodType("()void").tsym=
ClassSymbol("Method").type=ClassType("Method").tsym=ClassSymbol("Method")
(2)TypeVar("M").tsym=TypeSymbol("M").type=TypeVar("M").tsym
(3)PackageSymbol("java").type = PackageType("java").tsym=PackageSymbol("java")
(4)VarSymbol("length").type=Type("int").tsym=ClassSymbol("int").type=Type("int").tsym=ClassSymbol("int")
下面是Node与Type之间的关系:
class Outer{
class Inner{}
}
public class Test01 extends Outer.Inner{
public Test01(Outer o){
o.super();
}
}
Outer.Inner是一个树节点,如果这个节点中的type有值,则直接返回即可,不用再进行标注。
关于Node、Symbol与Type举一个例子,如下:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class TestScope<T1 extends InputStream,T2>{
public void test(){
TestScope<FileInputStream,?> x = null;
}
}
截图如下:
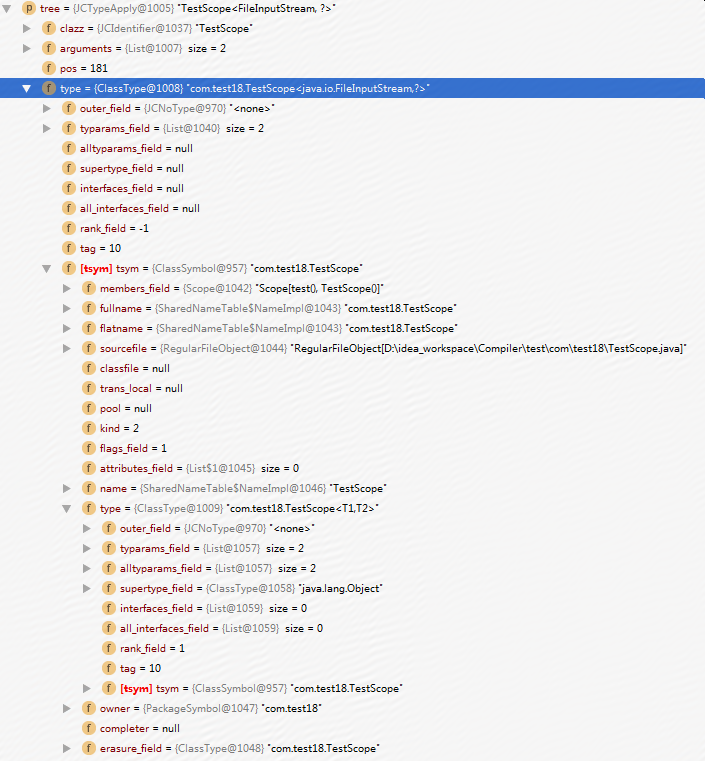
JCTypeApply的Node结点中没有Symbol属性,但是每个Node中都有Type属性,其值如上图蓝色部分。
ClassSymbol的Symbol结点中,由于每个Symbol中都有TypeSymbol类型的属性,这个属性值为com.test18.TestScope<T1,T2>
ClassType的Type结点中,由于每个Type中都有Symbol属性,这个属性的值为com.test18.TestScope
1、Symbol
对于Symbol来说:

Symbol中既有Symbol类型属性也有Type类型的属性,如下:
/** The type of this symbol.
*/
public Type type;
/** The owner of this symbol.
*/
public Symbol owner;
/** The completer of this symbol.
*/
public Completer completer;
/** A cache for the type erasure of this symbol.
*/
public Type erasure_field;
所以每个Symbol类型都有type属性。
而标注Symbol类型的是Kinds枚举类型,代码如下:
/** Internal symbol kinds, which distinguish between elements of
* different subclasses of Symbol. Symbol kinds are organized so they can be or'ed to sets.
*/
public class Kinds {
private Kinds() {} // uninstantiable
/** The empty set of kinds.
*/
public final static int NIL = 0;
/** The kind of package symbols.
*/
public final static int PCK = 1 << 0;
/** The kind of type symbols (classes, interfaces and type variables).
*/
public final static int TYP = 1 << 1;
/** The kind of variable symbols.
*/
public final static int VAR = 1 << 2;
/** The kind of values (variables or non-variable expressions), includes VAR.
*/
public final static int VAL = (1 << 3) | VAR;
/** The kind of methods.
*/
public final static int MTH = 1 << 4;
/** The error kind, which includes all other kinds.
*/
public final static int ERR = (1 << 5) - 1;
/** The set of all kinds.
*/
public final static int AllKinds = ERR;
/** Kinds for erroneous symbols that complement the above
*/
public static final int ERRONEOUS = 1 << 6;
public static final int AMBIGUOUS = ERRONEOUS+1; // ambiguous reference
public static final int HIDDEN = ERRONEOUS+2; // hidden method or field
public static final int STATICERR = ERRONEOUS+3; // nonstatic member from static context
public static final int ABSENT_VAR = ERRONEOUS+4; // missing variable
public static final int WRONG_MTHS = ERRONEOUS+5; // methods with wrong arguments
public static final int WRONG_MTH = ERRONEOUS+6; // one method with wrong arguments
public static final int ABSENT_MTH = ERRONEOUS+7; // missing method
public static final int ABSENT_TYP = ERRONEOUS+8; // missing type
public enum KindName implements Formattable {
ANNOTATION("kindname.annotation"),
CONSTRUCTOR("kindname.constructor"),
INTERFACE("kindname.interface"),
ENUM("kindname.enum"),
STATIC("kindname.static"),
TYPEVAR("kindname.type.variable"),
BOUND("kindname.type.variable.bound"),
VAR("kindname.variable"),
VAL("kindname.value"),
METHOD("kindname.method"),
CLASS("kindname.class"),
STATIC_INIT("kindname.static.init"),
INSTANCE_INIT("kindname.instance.init"),
PACKAGE("kindname.package");
private String name;
KindName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return name;
}
public String getKind() {
return "Kindname";
}
public String toString(Locale locale, Messages messages) {
String s = toString();
return messages.getLocalizedString(locale, "compiler.misc." + s);
}
}
/** A KindName representing a given symbol kind
*/
public static KindName kindName(int kind) {
switch (kind) {
case PCK: return KindName.PACKAGE;
case TYP: return KindName.CLASS;
case VAR: return KindName.VAR;
case VAL: return KindName.VAL;
case MTH: return KindName.METHOD;
default : throw new AssertionError("Unexpected kind: "+kind);
}
}
/** A KindName representing a given symbol
*/
public static KindName kindName(Symbol sym) {
switch (sym.getKind()) {
case PACKAGE:
return KindName.PACKAGE;
case ENUM:
return KindName.ENUM;
case ANNOTATION_TYPE:
case CLASS:
return KindName.CLASS;
case INTERFACE:
return KindName.INTERFACE;
case TYPE_PARAMETER:
return KindName.TYPEVAR;
case ENUM_CONSTANT:
case FIELD:
case PARAMETER:
case LOCAL_VARIABLE:
case EXCEPTION_PARAMETER:
case RESOURCE_VARIABLE:
return KindName.VAR;
case CONSTRUCTOR:
return KindName.CONSTRUCTOR;
case METHOD:
return KindName.METHOD;
case STATIC_INIT:
return KindName.STATIC_INIT;
case INSTANCE_INIT:
return KindName.INSTANCE_INIT;
default:
if (sym.kind == VAL)
// I don't think this can happen but it can't harm
// playing it safe --ahe
return KindName.VAL;
else
throw new AssertionError("Unexpected kind: "+sym.getKind());
}
}
/** A set of KindName(s) representing a set of symbol's kinds.
*/
public static EnumSet<KindName> kindNames(int kind) {
EnumSet<KindName> kinds = EnumSet.noneOf(KindName.class);
if ((kind & VAL) != 0)
kinds.add(((kind & VAL) == VAR) ? KindName.VAR : KindName.VAL);
if ((kind & MTH) != 0) kinds.add(KindName.METHOD);
if ((kind & TYP) != 0) kinds.add(KindName.CLASS);
if ((kind & PCK) != 0) kinds.add(KindName.PACKAGE);
return kinds;
}
/** A KindName representing the kind of a given class/interface type.
*/
public static KindName typeKindName(Type t) {
if (t.tag == TYPEVAR ||
t.tag == CLASS && (t.tsym.flags() & COMPOUND) != 0)
return KindName.BOUND;
else if (t.tag == PACKAGE)
return KindName.PACKAGE;
else if ((t.tsym.flags_field & ANNOTATION) != 0)
return KindName.ANNOTATION;
else if ((t.tsym.flags_field & INTERFACE) != 0)
return KindName.INTERFACE;
else
return KindName.CLASS;
}
/** A KindName representing the kind of a a missing symbol, given an
* error kind.
* */
public static KindName absentKind(int kind) {
switch (kind) {
case ABSENT_VAR:
return KindName.VAR;
case WRONG_MTHS: case WRONG_MTH: case ABSENT_MTH:
return KindName.METHOD;
case ABSENT_TYP:
return KindName.CLASS;
default:
throw new AssertionError("Unexpected kind: "+kind);
}
}
}
Symbol可以通过访问模式来访问各个结点,定义如下:
(1)Symbol.Visitor<R, P>
符号类中定义的访问者模式接口如下:
/**
* A visitor for symbols. A visitor is used to implement operations
* (or relations) on symbols. Most common operations on types are
* binary relations and this interface is designed for binary
* relations, that is, operations on the form
* Symbol × P → R.
* <!-- In plain text: Type x P -> R -->
*
* @param <R> the return type of the operation implemented by this
* visitor; use Void if no return type is needed.
* @param <P> the type of the second argument (the first being the
* symbol itself) of the operation implemented by this visitor; use
* Void if a second argument is not needed.
*/
public interface Visitor<R,P> {
R visitClassSymbol(ClassSymbol s, P arg);
R visitMethodSymbol(MethodSymbol s, P arg);
R visitPackageSymbol(PackageSymbol s, P arg);
R visitOperatorSymbol(OperatorSymbol s, P arg);
R visitVarSymbol(VarSymbol s, P arg);
R visitTypeSymbol(TypeSymbol s, P arg);
R visitSymbol(Symbol s, P arg);
}
(2)Types中的DefaultSymbolVisitor<R,S>
/**
* A default visitor for symbols. All visitor methods except
* visitSymbol are implemented by delegating to visitSymbol. Concrete
* subclasses must provide an implementation of visitSymbol and can
* override other methods as needed.
*
* @param <R> the return type of the operation implemented by this
* visitor; use Void if no return type is needed.
* @param <S> the type of the second argument (the first being the
* symbol itself) of the operation implemented by this visitor; use
* Void if a second argument is not needed.
*/
public static abstract class DefaultSymbolVisitor<R,S> implements Symbol.Visitor<R,S> {
final public R visit(Symbol s, S arg) { return s.accept(this, arg); }
public R visitClassSymbol(ClassSymbol s, S arg) { return visitSymbol(s, arg); }
public R visitMethodSymbol(MethodSymbol s, S arg) { return visitSymbol(s, arg); }
public R visitOperatorSymbol(OperatorSymbol s, S arg) { return visitSymbol(s, arg); }
public R visitPackageSymbol(PackageSymbol s, S arg) { return visitSymbol(s, arg); }
public R visitTypeSymbol(TypeSymbol s, S arg) { return visitSymbol(s, arg); }
public R visitVarSymbol(VarSymbol s, S arg) { return visitSymbol(s, arg); }
}
2、Type

对于每个Type类型来说,只限定有TypeSymbol类型的属性,也就是包、类和类型变量对应的符号。
// The defining class / interface / package / type variable public TypeSymbol typeSymbol; // 只有ClassSymbol与PackageSymbol继承了TypeSymbol
标注每个Type类型的为TypeTags,代码如下:
/** An interface for type tag values, which distinguish between different sorts of types.
*/
public class TypeTags {
private TypeTags() {} // uninstantiable
/** The tag of the basic type `byte'.
*/
public static final int BYTE = 1;
/** The tag of the basic type `char'.
*/
public static final int CHAR = BYTE+1;
/** The tag of the basic type `short'.
*/
public static final int SHORT = CHAR+1;
/** The tag of the basic type `int'.
*/
public static final int INT = SHORT+1;
/** The tag of the basic type `long'.
*/
public static final int LONG = INT+1;
/** The tag of the basic type `float'.
*/
public static final int FLOAT = LONG+1;
/** The tag of the basic type `double'.
*/
public static final int DOUBLE = FLOAT+1;
/** The tag of the basic type `boolean'.
*/
public static final int BOOLEAN = DOUBLE+1;
/** The tag of the type `void'.
*/
public static final int VOID = BOOLEAN+1;
/** The tag of all class and interface types.
*/
public static final int CLASS = VOID+1;
/** The tag of all array types.
*/
public static final int ARRAY = CLASS+1;
/** The tag of all (monomorphic 单一同态的) method types.
*/
public static final int METHOD = ARRAY+1;
/** The tag of all package "types".
*/
public static final int PACKAGE = METHOD+1;
/** The tag of all (source-level) type variables.
*/
public static final int TYPEVAR = PACKAGE+1;
/** The tag of all type arguments.
*/
public static final int WILDCARD = TYPEVAR+1;
/** The tag of all polymorphic (method-) types.
*/
public static final int FORALL = WILDCARD+1;
/** The tag of the bottom type <null>.
*/
public static final int BOT = FORALL+1;
/** The tag of a missing type.
*/
public static final int NONE = BOT+1;
/** The tag of the error type.
*/
public static final int ERROR = NONE+1;
/** The tag of an unknown type
*/
public static final int UNKNOWN = ERROR+1;
/** The tag of all instantiatable type variables.
*/
public static final int UNDETVAR = UNKNOWN+1;
/** The number of type tags.
*/
public static final int TypeTagCount = UNDETVAR+1;
/** The maximum tag of a basic type.
*/
public static final int lastBaseTag = BOOLEAN;
/** The minimum tag of a partial type
*/
public static final int firstPartialTag = ERROR;
}
Javac为Type结果定义了访问者接口,如下:
(1)Type.Visitor<R, S>
类型Type中定义的访问者模式:
/**
* A visitor for types. A visitor is used to implement operations
* (or relations) on types. Most common operations on types are
* binary relations and this interface is designed for binary
* relations, that is, operations on the form
* Type × S → R.
* <!-- In plain text: Type x S -> R -->
*
* @param <R> the return type of the operation implemented by this
* visitor; use Void if no return type is needed.
* @param <S> the type of the second argument (the first being the
* type itself) of the operation implemented by this visitor; use
* Void if a second argument is not needed.
*/
public interface Visitor<R,S> {
R visitClassType(ClassType t, S s);
R visitWildcardType(WildcardType t, S s);
R visitArrayType(ArrayType t, S s);
R visitMethodType(MethodType t, S s);
R visitPackageType(PackageType t, S s);
R visitTypeVar(TypeVar t, S s);
R visitCapturedType(CapturedType t, S s);
R visitForAll(ForAll t, S s);
R visitUndeterminedVar(UndeterminedVar t, S s);
R visitErrorType(ErrorType t, S s);
R visitType(Type t, S s);
}
(2)Types中的DefaultTypeVisitor<R,S>,SimpleTypeVisitor<R,S>
/**
* A default visitor for types. All visitor methods except
* visitType are implemented by delegating to visitType. Concrete
* subclasses must provide an implementation of visitType and can
* override other methods as needed.
*
* @param <R> the return type of the operation implemented by this
* visitor; use Void if no return type is needed.
* @param <S> the type of the second argument (the first being the
* type itself) of the operation implemented by this visitor; use
* Void if a second argument is not needed.
*/
public static abstract class DefaultTypeVisitor<R,S> implements Type.Visitor<R,S> {
final public R visit(Type t, S s) { return t.accept(this, s); }
public R visitClassType(ClassType t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
public R visitWildcardType(WildcardType t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
public R visitArrayType(ArrayType t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
public R visitMethodType(MethodType t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
public R visitPackageType(PackageType t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
public R visitTypeVar(TypeVar t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
public R visitCapturedType(CapturedType t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
public R visitForAll(ForAll t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
public R visitUndeterminedVar(UndeterminedVar t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
public R visitErrorType(ErrorType t, S s) { return visitType(t, s); }
}
/**
* A <em>simple</em> visitor for types. This visitor is simple as
* captured wildcards, for-all types (generic methods), and
* undetermined(未确定的) type variables (part of inference) are hidden.
* Captured wildcards are hidden by treating them as type
* variables and the rest are hidden by visiting their qtypes.
*
* @param <R> the return type of the operation implemented by this
* visitor; use Void if no return type is needed.
* @param <S> the type of the second argument (the first being the
* type itself) of the operation implemented by this visitor; use
* Void if a second argument is not needed.
*/
public static abstract class SimpleTypeVisitor<R,S> extends DefaultTypeVisitor<R,S> {
@Override
public R visitCapturedType(CapturedType t, S s) {
return visitTypeVar(t, s);
}
@Override
public R visitForAll(ForAll t, S s) {
return visit(t.qtype, s);
}
@Override
public R visitUndeterminedVar(UndeterminedVar t, S s) {
return visit(t.qtype, s);
}
}
关于语法节点Tree、类型Type和符号Symbol的更多相关文章
- 关于类型Type
每一个JC语法节点都含有type属性,因为做为所有JC语法节点的父节点JCTree含有type属性.其继承关系如下图. 下面看一下Type类的定义及重要的属性. public class Type i ...
- 初识Haskell 二:基本操作符、类型Type、数据结构
对Discrete Mathematics Using a Computer的第一章Introduction to Haskell进行总结.环境Windows 1. 在安装了ghci后,便可以进行Ha ...
- Roslyn 语法树中的各种语法节点及每个节点的含义
使用 Roslyn 进行源码分析时,我们会对很多不同种类的语法节点进行分析.如果能够一次性了解到各种不同种类的语法节点,并明白其含义和结构,那么在源码分析的过程中将会更加得心应手. 本文将介绍 Ros ...
- 分享:根据svg节点对象类型和路径值转换坐标值
功能用处: 对svg文件的路径节点填充时会使用(相邻两个坐标区域内的四边形的填充颜色不重复). 需要对svg文件中的Path节点或者 Polyline 节点做颜色填充.并且相邻的两个区域之间的颜色不允 ...
- orcle自定义类型type/create or replace type
一.type / create or repalce type 区别联系 相同: 可用关键字create type 或者直接用type定义自定义类型, 区别: create type 变量 as ta ...
- 转载:oracle 自定义类型 type / create type
标签:type create oracle object record 一:Oracle中的类型有很多种,主要可以分为以下几类: 1.字符串类型.如:char.nchar.varchar2.nvarc ...
- oracle 自定义类型 type / create type
一:Oracle中的类型有很多种,主要可以分为以下几类: 1.字符串类型.如:char.nchar.varchar2.nvarchar2. 2.数值类型.如:int.number(p,s).integ ...
- kubernetes1.4新特性:增加新的节点健康状况类型DiskPressure
背景资料 在Kubernetes架构图中可以看到,节点(Node)是一个由管理节点委托运行任务的worker. 它能运行一个或多个Pods,节点(Node)提供了运行容器环境所需要的所有必要条件,在K ...
- cocos2dx 如何获得节点的类型
1. 需求:在所有子节点中得到是ui::Text类型的节点,并对其进行操作. 2. 解决方案:在根节点Node中有一个如下的函数: /** * Gets the description string. ...
随机推荐
- 2016-2017-2 20155223 实验二 《Java面向对象程序设计》
2016-2017-2 苏黄永郦 实验二 实验报告 前期准备工作--程序安装 -问题一 开始的时候我就在老师博客的指导下安装IDEA插件JUnit Generator V2.0.当然我的IDEA肯定没 ...
- KVM虚拟机windows系统增加硬盘
原文:http://www.ilanni.com/?p=6211 前一篇文章介绍了有关linux系统添加硬盘的方法,这次我们来介绍有关windows系统添加的相关步骤. 其实linux和windows ...
- WinRT支持GB2312
在SL年代,有第三方类库支持 http://encoding4silverlight.codeplex.com 在RT版本有点不兼容,一直没时间看.今天闲的卵疼,就来一段代码兼容一下RT版本,迟点整合 ...
- Sql语法高级应用之一:使用sql语句如何实现不同的角色看到不同的数据
前言 在常见的管理系统中,通常都有这样的需求,管理员可以看到所有数据,部门可以看到本部门的数据,组长可以看到自己组的数据,组员只能看到自己相关的数据. 一般人的做法是,根据不同的角色通过if...el ...
- 深入了解java虚拟机(JVM) 第十一章 类的加载
一.类加载机制概述 虚拟机把描述类的数据从class文件加载到内存并对数据进行效验,解析和初始化,最终形成可以被虚拟机直接使用的java类型,这就是虚拟机的类加载机制. 二.类加载的机制 类加载的过程 ...
- 【OCP-052】052最新考试题库分析整理-第7题
7.Which is true about external tables? A) The ORACLE_DATAPUMP access driver can be used to write dat ...
- API接口文档范例
- Spring-解决请求中文乱码问题
解决spring请求中文乱码问题 1.web.xml添加编码拦截器 <filter> <filter-name>CharacterEncoding</filter-nam ...
- 《快学Scala》第六章 对象 第七章 包和引入
- lamp-linux-1
LAMP编程之Linux(1) LAMP:Linux Apache MySQL PHP LNMP:Linux Nginx MySQL PHP WAMP:Windows Apache MySQL PHP ...
