OpenCASCADE Linear Extrusion Surface
OpenCASCADE Linear Extrusion Surface
Abstract. OpenCASCADE linear extrusion surface is a generalized cylinder. Such a surface is obtained by sweeping a curve (called the “extruded curve” or “basis”) in a given direction (referred to as the direction of extrusion and defined by a unit vector). The u parameter is along the extruded curve. The v parameter is along the direction of extrusion. The form of a surface of linear extrusion is generally a ruled surface. It can be a cylindrical surface, or a planar surface.
Key Words. OpenCASCADE, Extrusion Surface, Sweeping
1. Introduction
一般柱面(The General Cylinder)可以由一段或整个圆弧沿一个方向偏移一定的距离得到。如下图所示:
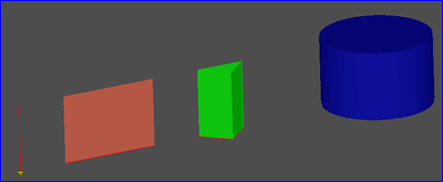
Figure 1.1 Extrusion Shapes
当将顶点拉伸时,会生成一条边;当将边拉伸时,会生成面;当将Wire拉伸时,会生成Shell,当将面拉伸时,会生成体。当将曲线沿一个方向拉伸时,会形成一个曲面,如果此方向为直线,则会生成一般柱面。如果此方向是曲线时,会生成如下图所示曲面:
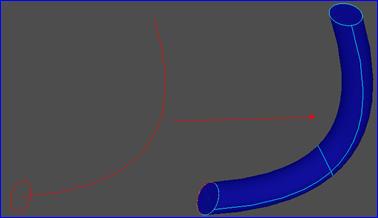
Figure 1.2 Swept surface/ loft surface
本文主要介绍将曲线沿直线方向拉伸的算法,即一般柱面生成算法。并将生成的曲面在OpenSceneGraph中进行显示。
2.Cylinder Surface Definition
设 W是一个单位向量,C(u)是定义在节点矢量U上,权值为wi的p次NURBS曲线。我们要得到一般柱面S(u,v)的表达式,S(u,v)是通过将 C(u)沿方向W平行扫描(sweep)距离d得到的。记扫描方向的参数为v, 0<v<1,显然,S(u,v)必须满足以下两个条件:
v 对于固定的u0, S(u0, v)为由C(u0)到C(u0)+dW的直线段;
v 对于固定的v0:
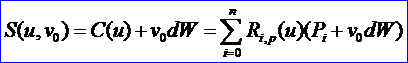
所要求的柱面的表达式为:
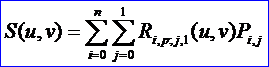
S(u,v)定义在节点矢量U和V上,这里V={0,0,1,1},U为C(u)的节点矢量。控制顶点由Pi,0=Pi和Pi,1=Pi+dW给出,权值wi,0=wi,1=wi。如下图所示为一般柱面:
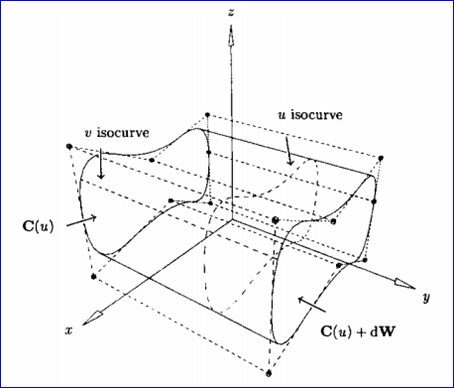
Figure 2.1 A general cylinder obtained by translating C(u) a distance d along W.
其中OpenCASCADE中一般柱面的表达式如下所示:
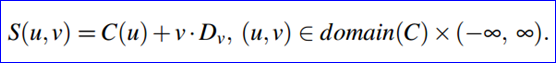
其取值范围的代码如下所示:
//=======================================================================
//function : Bounds
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
void Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion::Bounds ( Standard_Real& U1,
Standard_Real& U2,
Standard_Real& V1,
Standard_Real& V2 ) const { V1 = -Precision::Infinite(); V2 = Precision::Infinite();
U1 = basisCurve->FirstParameter(); U2 = basisCurve->LastParameter();
}
由上代码可知,参数在v方向上是趋于无穷的;在u方向上参数的范围为曲线的范围。计算柱面上点的方法代码如下所示:
//=======================================================================
//function : D0
//purpose :
//=======================================================================
void Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion::D0 (const Standard_Real U,
const Standard_Real V,
Pnt& P) const { XYZ Pxyz = direction.XYZ();
Pxyz.Multiply (V);
Pxyz.Add (basisCurve->Value (U).XYZ());
P.SetXYZ(Pxyz);
}
即将柱面上点先按V方向来计算,再按U方向来计算,最后将两个方向的值相加即得到柱面上的点。
由上述代码可知,OpenCASCADE中一般柱面没有使用NURBS曲面来表示。根据这个方法,可以将任意曲线沿给定的方向来得到一个柱面,这个曲线可以是直线、圆弧、圆、椭圆等。关于柱面上更多算法,如求微分等,可以参考源程序。
3.Display the Surface
还是在OpenSceneGraph中来对一般柱面进行可视化,来验证结果。因为OpenSceneGraph的简单易用,显示曲面的程序代码如下所示:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2013 to current year. All Rights Reserved.
*
* File : Main.cpp
* Author : eryar@163.com
* Date : 2014-11-23 10:18
* Version : OpenCASCADE6.8.0
*
* Description : Test the Linear Extrusion Surface of OpenCASCADE.
*
* Key Words : OpenCascade, Linear Extrusion Surface, General Cylinder
*
*/ // OpenCASCADE.
#define WNT
#include <Precision.hxx> #include <gp_Circ.hxx> #include <Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion.hxx> #include <GC_MakeCircle.hxx>
#include <GC_MakeSegment.hxx>
#include <GC_MakeArcOfCircle.hxx> #pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib") // OpenSceneGraph.
#include <osgViewer/Viewer>
#include <osgViewer/ViewerEventHandlers> #include <osgGA/StateSetManipulator> #pragma comment(lib, "osgd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgGAd.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "osgViewerd.lib") const double TOLERANCE_EDGE = 1e-;
const double APPROXIMATION_DELTA = 0.05; /**
* @brief Render 3D geometry surface.
*/
osg::Node* BuildSurface(const Handle_Geom_Surface& theSurface)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geode> aGeode = new osg::Geode(); Standard_Real aU1 = 0.0;
Standard_Real aV1 = 0.0;
Standard_Real aU2 = 0.0;
Standard_Real aV2 = 0.0;
Standard_Real aDeltaU = 0.0;
Standard_Real aDeltaV = 0.0; theSurface->Bounds(aU1, aU2, aV1, aV2); // trim the parametrical space to avoid infinite space.
Precision::IsNegativeInfinite(aU1) ? aU1 = -1.0 : aU1;
Precision::IsInfinite(aU2) ? aU2 = 1.0 : aU2; Precision::IsNegativeInfinite(aV1) ? aV1 = -1.0 : aV1;
Precision::IsInfinite(aV2) ? aV2 = 1.0 : aV2; // Approximation in v direction.
aDeltaU = (aU2 - aU1) * APPROXIMATION_DELTA;
aDeltaV = (aV2 - aV1) * APPROXIMATION_DELTA; for (Standard_Real u = aU1; (u - aU2) <= TOLERANCE_EDGE; u += aDeltaU)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> aLine = new osg::Geometry();
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> aPoints = new osg::Vec3Array(); for (Standard_Real v = aV1; (v - aV2) <= TOLERANCE_EDGE; v += aDeltaV)
{
gp_Pnt aPoint = theSurface->Value(u, v); aPoints->push_back(osg::Vec3(aPoint.X(), aPoint.Y(), aPoint.Z()));
} // Set vertex array.
aLine->setVertexArray(aPoints);
aLine->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, , aPoints->size())); aGeode->addDrawable(aLine.get());
} // Approximation in u direction.
for (Standard_Real v = aV1; (v - aV2) <= TOLERANCE_EDGE; v += aDeltaV)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> aLine = new osg::Geometry();
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> aPoints = new osg::Vec3Array(); for (Standard_Real u = aU1; (u - aU2) <= TOLERANCE_EDGE; u += aDeltaU)
{
gp_Pnt aPoint = theSurface->Value(u, v); aPoints->push_back(osg::Vec3(aPoint.X(), aPoint.Y(), aPoint.Z()));
} // Set vertex array.
aLine->setVertexArray(aPoints);
aLine->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, , aPoints->size())); aGeode->addDrawable(aLine.get());
} return aGeode.release();
} /**
* @brief Build the test scene.
*/
osg::Node* BuildScene(void)
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Group> aRoot = new osg::Group(); // test the linear extrusion surface.
// test linear extrusion surface of a line.
Handle_Geom_Curve aSegment = GC_MakeSegment(gp_Pnt(3.0, 0.0, 0.0), gp_Pnt(6.0, 0.0, 0.0));
Handle_Geom_Surface aPlane = new Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion(aSegment, gp::DZ()); aRoot->addChild(BuildSurface(aPlane)); // test linear extrusion surface of a arc.
Handle_Geom_Curve aArc = GC_MakeArcOfCircle(gp_Circ(gp::ZOX(), 2.0), 0.0, M_PI, true);
Handle_Geom_Surface aSurface = new Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion(aArc, gp::DY()); aRoot->addChild(BuildSurface(aSurface)); // test linear extrusion surface of a circle.
Handle_Geom_Curve aCircle = GC_MakeCircle(gp::XOY(), 1.0);
Handle_Geom_Surface aCylinder = new Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion(aCircle, gp::DZ()); aRoot->addChild(BuildSurface(aCylinder)); return aRoot.release();
} int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
osgViewer::Viewer aViewer; aViewer.setSceneData(BuildScene()); aViewer.addEventHandler(new osgGA::StateSetManipulator(
aViewer.getCamera()->getOrCreateStateSet()));
aViewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::StatsHandler);
aViewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::WindowSizeHandler); return aViewer.run(); return ;
}
上述显示方法只是显示线框的最简单的算法,只为验证一般柱面结果,不是高效算法。显示结果如下图所示:
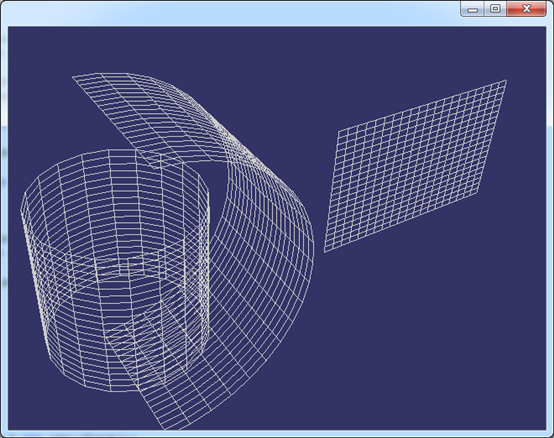
Figure 3.1 General Cylinder for: Circle, Arc, Line
如上图所示分别为对圆、圆弧和直线进行拉伸得到的一般柱面。根据这个原理可以将任意曲线沿给定方向进行拉伸得到一个柱面。
4.Conclusion
通 过对OpenCASCADE中一般柱面的类中代码进行分析可知,OpenCASCADE的这个线性拉伸柱面 Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion是根据一般柱面的定义实现的,并不是使用NURBS曲面来表示的。当需要用NURBS曲面来 表示一般柱面时,需要注意控制顶点及权值的计算取值。
5. References
1. 赵罡,穆国旺,王拉柱译. 非均匀有理B样条. 清华大学出版社. 2010
2. Les Piegl, Wayne Tiller. The NURBS Book. Springer-Verlag. 1997
3. OpenCASCADE Team, OpenCASCADE BRep Format. 2014
4. Donald Hearn, M. Pauline Baker. Computer Graphics with OpenGL. Prentice Hall. 2009
5. 莫蓉,常智勇. 计算机辅助几何造型技术. 科学出版社. 2009
PDF Version and Source Code: OpenCASCADE Linear Extrusion Surface
OpenCASCADE Linear Extrusion Surface的更多相关文章
- Geometry Surface of OpenCascade BRep
Geometry Surface of OpenCascade BRep eryar@163.com 摘要Abstract:几何曲面是参数表示的曲面 ,在边界表示中其数据存在于BRep_TFace中, ...
- Render OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph
在OpenSceneGraph中绘制OpenCascade的曲面 Render OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph eryar@163.co ...
- <老古董>线性支持向量机中的硬间隔(hard margin)和软间隔(soft margin)是什么
_________________________________________________________________________________________________ Th ...
- Surface Normal Vector in OpenCascade
Surface Normal Vector in OpenCascade eryar@163.com 摘要Abstract:表面上某一点的法向量(Normal Vector)指的是在该点处与表面垂直的 ...
- OpenCascade Ruled Surface
OpenCascade Ruled Surface eryar@163.com Abstract. A ruled surface is formed by moving a line connect ...
- Unity Shader——Writing Surface Shaders(1)——Surface Shader Examples
这里有Surface Shader的一些例子.下面的这些例子关注使用内建的光照模型:关于如何使用自定义光照模型的例子参见Surface Shader Lighting Examples. 简单 我们将 ...
- OpenCASCADE构造一般曲面
OpenCASCADE构造一般曲面 eryar@163.com Abstract. 本文主要介绍常见的曲面如一般柱面(拉伸曲面).旋转面在OpenCASCADE中的构造方法,由此思考一般放样算法的实现 ...
- Bounding Volume Hierarchy BVH in OpenCASCADE
Bounding Volume Hierarchy BVH in OpenCASCADE eryar@163.com Abstract. Bounding Volume Hierarchy(BVH) ...
- OpenCASCADE BRep Projection
OpenCASCADE BRep Projection eryar@163.com 一网友发邮件问我下图所示的效果如何在OpenCASCADE中实现,我的想法是先构造出螺旋线,再将螺旋线投影到面上. ...
随机推荐
- 【BZOJ】3997: [TJOI2015]组合数学
题意 \(N \times M\)的网格,一开始在\((1, 1)\)每次可以向下和向右走,每经过一个有数字的点最多能将数字减1,最终走到\((N, M)\).问至少要走多少次才能将数字全部变为\(0 ...
- [BZOJ4196][NOI2015]软件包管理器
4196: [Noi2015]软件包管理器 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MBSubmit: 1040 Solved: 603[Submit][Stat ...
- Go 语言的基本数据类型
Go 语言的基本数据类型 0)变量声明 var 变量名字 类型 = 表达式 例: 其中“类型”或“= 表达式”两个部分可以省略其中的一个. 1)根据初始化表达式来推导类型信息 2)默认值初始化为0. ...
- 怎么统计指定文件夹下含有.xml格式的文件数目
如何统计指定文件夹下含有.xml格式的文件数目?如题 ------解决思路----------------------Directory.GetFiles(@"路径", " ...
- 设计模式(十三) 职责链(chain of responsibility)
软件领域中的设计模式为开发人员提供了一种使用专家设计经验的有效途径.设计模式中运用了面向对象编程语言的重要特性:封装.继承.多态,真正领悟设计模式的精髓是可能一个漫长的过程,需要大量实践经验的积累.最 ...
- Python模块之day4
模块,代码归类实现了某个功能的代码集合. 类似于函数式编程和面向过程编程,函数式编程则完成一个功能,其他代码用来调用即可,提供了代码的重用性和代码间的耦合.而对于一个复杂的功能来,可能需要多个函数才能 ...
- thrift ssl 证书整理
一.生成证书,所需机器数必须 >= 2(一台生成服务端证书,一台生成客户端证书),以下服务器以A表示服务端.B表示客户端来举例,thrift版本为0.7.01.自签名的证书的生成和测试 1)生成 ...
- 一步步学习javascript基础篇(3):Object、Function等引用类型
我们在<一步步学习javascript基础篇(1):基本概念>中简单的介绍了五种基本数据类型Undefined.Null.Boolean.Number和String.今天我们主要介绍下复杂 ...
- ASP.NET MVC 5 入门指南汇总
经过前一段时间的翻译和编辑,我们陆续发出12篇ASP.NET MVC 5的入门文章.其中大部分翻译自ASP.NET MVC 5 官方教程,由于本系列文章言简意赅,篇幅适中,从一个web网站示例开始讲解 ...
- Linux 搭建FTP服务器
介绍 本章主要介绍在Linux中搭建FTP服务器的过程,需要掌握的要点是配置文件的合理配置. 知识点 在linux中使用的FTP是vsftp FTP可以有三种登入方式分别是: 匿名登录方式:不需要用户 ...
