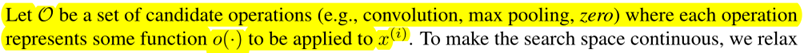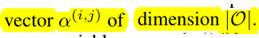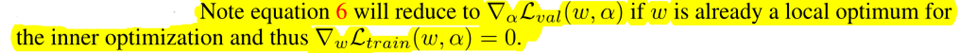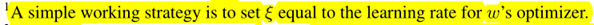2019-ICLR-DARTS: Differentiable Architecture Search-论文阅读
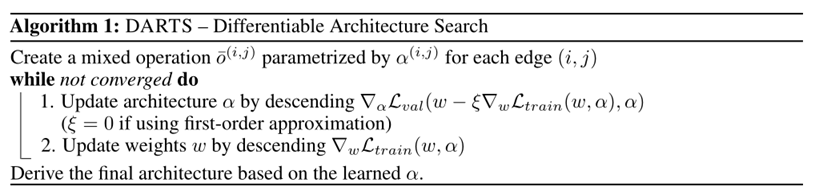
DARTS
2019-ICLR-DARTS Differentiable Architecture Search
- Hanxiao Liu、Karen Simonyan、Yiming Yang
- GitHub:2.8k stars
- Citation:557
Motivation
Current NAS method:
- Computationally expensive: 2000/3000 GPU days
- Discrete search space, leads to a large number of architecture evaluations required.
Contribution
- Differentiable NAS method based on gradient decent.
- Both CNN(CV) and RNN(NLP).
- SOTA results on CIFAR-10 and PTB.
- Efficiency: (2000 GPU days VS 4 GPU days)
- Transferable: cifar10 to ImageNet, (PTB to WikiText-2).
Method
Search Space
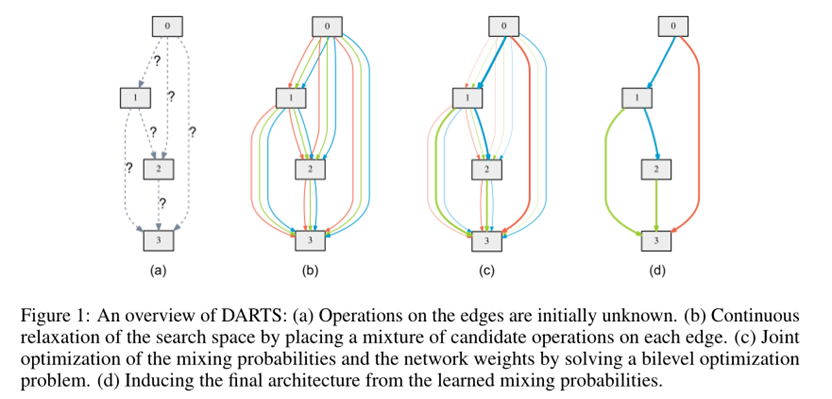
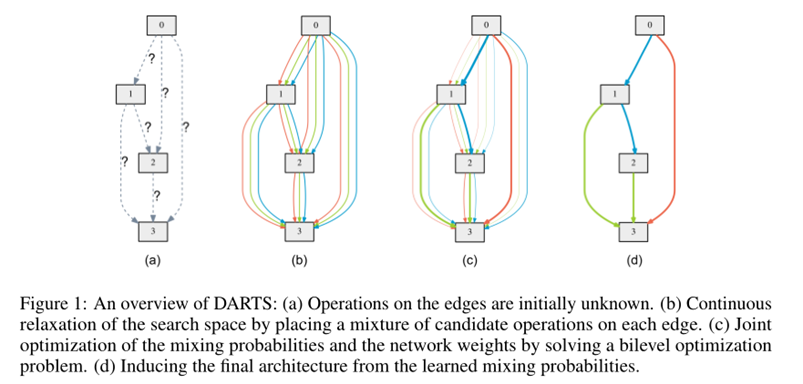
Search for a cell as the building block of the final architecture.
The learned cell could either be stacked to form a CNN or recursively connected to form a RNN.
A cell is a DAG consisting of an ordered sequence of N nodes.
\(\bar{o}^{(i, j)}(x)=\sum_{o \in \mathcal{O}} \frac{\exp \left(\alpha_{o}^{(i, j)}\right)}{\sum_{o^{\prime} \in \mathcal{O}} \exp \left(\alpha_{o^{\prime}}^{(i, j)}\right)} o(x)\)
\(x^{(j)}=\sum_{i<j} o^{(i, j)}\left(x^{(i)}\right)\)
Optimization Target
Our goal is to jointly learn the architecture α and the weights w within all the mixed operations (e.g. weights of the convolution filters).
\(\min _{\alpha} \mathcal{L}_{v a l}\left(w^{*}(\alpha), \alpha\right)\) ......(3)
s.t. \(\quad w^{*}(\alpha)=\operatorname{argmin}_{w} \mathcal{L}_{\text {train}}(w, \alpha)\) .......(4)
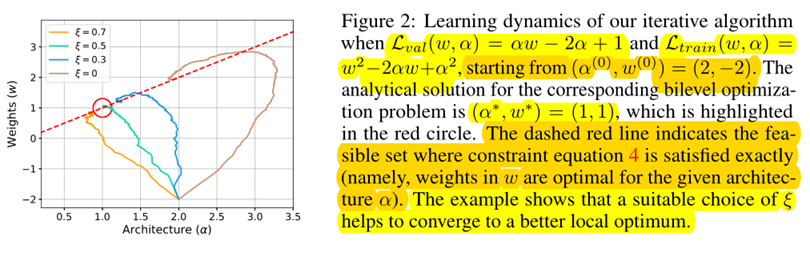
The idea is to approximate w∗(α) by adapting w using only a single training step, without solving the inner optimization (equation 4) completely by training until convergence.
\(\nabla_{\alpha} \mathcal{L}_{v a l}\left(w^{*}(\alpha), \alpha\right)\) ......(5)
\(\approx \nabla_{\alpha} \mathcal{L}_{v a l}\left(w-\xi \nabla_{w} \mathcal{L}_{t r a i n}(w, \alpha), \alpha\right)\) ......(6)
- When ξ = 0, the second-order derivative in equation 7 will disappear.
- ξ = 0 as the first-order approximation,
- ξ > 0 as the second-order approximation.
Discrete Arch
To form each node in the discrete architecture, we retain the top-k strongest operations (from distinct nodes) among all non-zero candidate operations collected from all the previous nodes.
we use k = 2 for convolutional cells and k = 1 for recurrent cellsThe strength of an operation is defined as \(\frac{\exp \left(\alpha_{o}^{(i, j)}\right)}{\sum_{o^{\prime} \in \mathcal{O}} \exp \left(\alpha_{o^{\prime}}^{(i, j)}\right)}\)
Experiments
We include the following operations in O:
- 3 × 3 and 5 × 5 separable convolutions,
- 3 × 3 and 5 × 5 dilated separable convolutions,
- 3 × 3 max pooling,
- 3 × 3 average pooling,
- identity (skip connection?)
- zero.
All operations are of
- stride one (if applicable)
- the feature maps are padded to preserve their spatial resolution.
We use the
- ReLU-Conv-BN order for convolutional operations,
- Each separable convolution is always applied twice
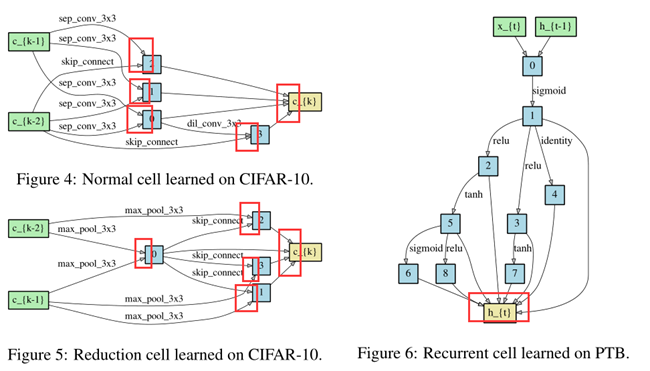
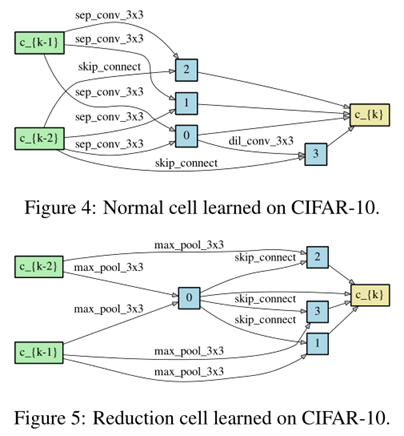
- Our convolutional cell consists of N = 7 nodes, the output node is defined as the depthwise concatenation of all the intermediate nodes (input nodes excluded).
The first and second nodes of cell k are set equal to the outputs of cell k−2 and cell k−1
Cells located at the 1/3 and 2/3 of the total depth of the network are reduction cells, in which all the operations adjacent to the input nodes are of stride two.
The architecture encoding therefore is (αnormal, αreduce),
where αnormal is shared by all the normal cells
and αreduce is shared by all the reduction cells.
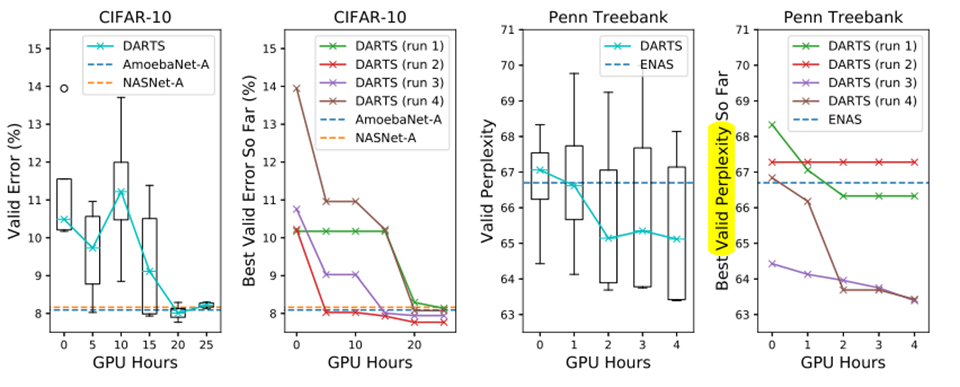
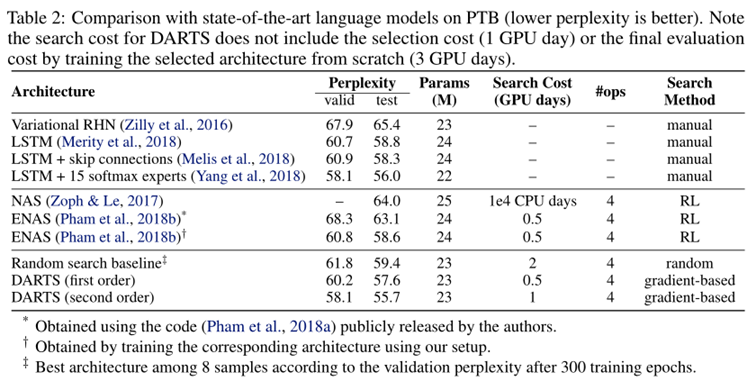
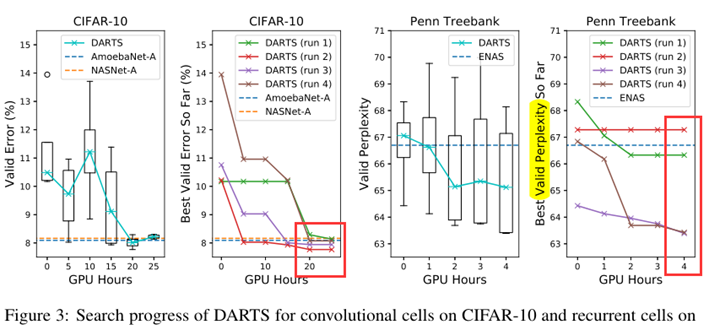
To determine the architecture for final evaluation, we run DARTS four times with different random seeds and pick the best cell based on its validation performance obtained by training from scratch for a short period (100 epochs on CIFAR-10 and 300 epochs on PTB).
This is particularly important for recurrent cells, as the optimization outcomes can be initialization-sensitive (Fig. 3)
Arch Evaluation
- To evaluate the selected architecture, we randomly initialize its weights (weights learned during the search process are discarded), train it from scratch, and report its performance on the test set.
- To evaluate the selected architecture, we randomly initialize its weights (weights learned during the search process are discarded), train it from scratch, and report its performance on the test set.
Result Analysis
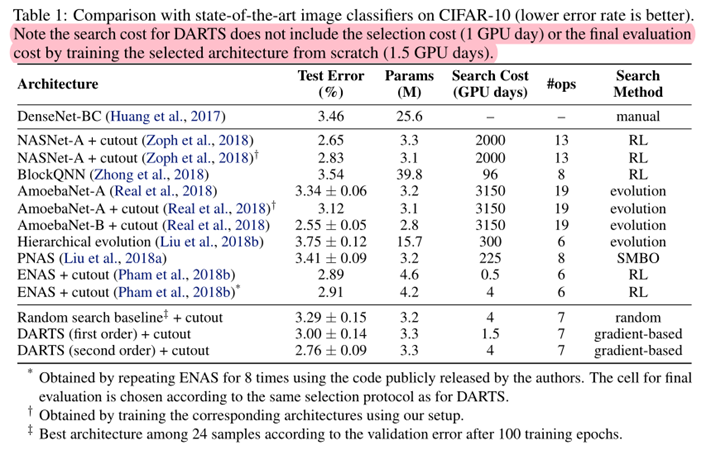
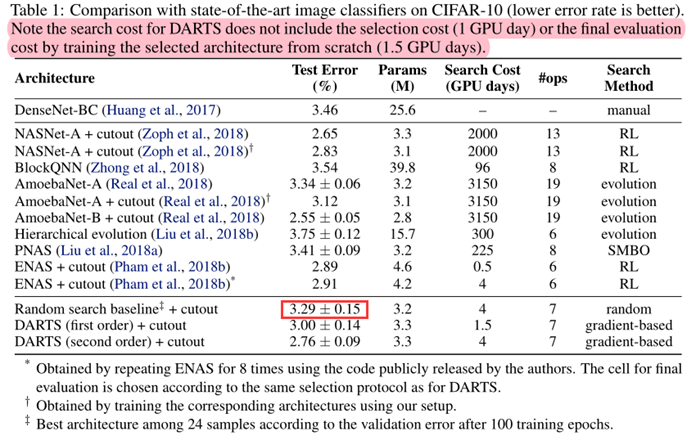
- DARTS achieved comparable results with the state of the art while using three orders of magnitude less computation resources.
- (i.e. 1.5 or 4 GPU days vs 2000 GPU days for NASNet and 3150 GPU days for AmoebaNet)
- The longer search time is due to the fact that we have repeated the search process four times for cell selection. This practice is less important for convolutional cells however, because the performance of discovered architectures does not strongly depend on initialization (Fig. 3).
- It is also interesting to note that random search is competitive for both convolutional and recurrent models, which reflects the importance of the search space design.
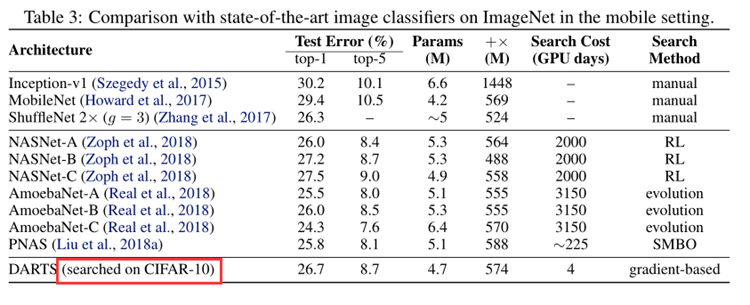
Results in Table 3 show that the cell learned on CIFAR-10 is indeed transferable to ImageNet.
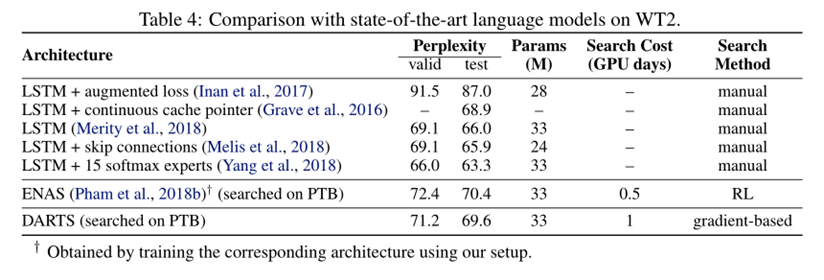
The weaker transferability between PTB and WT2 (as compared to that between CIFAR-10 and ImageNet) could be explained by the relatively small size of the source dataset (PTB) for architecture search.
The issue of transferability could potentially be circumvented by directly optimizing the architecture on the task of interest.
Conclusion
- We presented DARTS, a simple yet efficient NAS algorithm for both CNN and RNN.
- SOTA
- efficiency improvement by several orders of magnitude.
Improve
- discrepancies between the continuous architecture encoding and the derived discrete architecture. (softmax…)
- It would also be interesting to investigate performance-aware architecture derivation schemes based on the shared parameters learned during the search process.
Appendix
2019-ICLR-DARTS: Differentiable Architecture Search-论文阅读的更多相关文章
- 论文笔记:DARTS: Differentiable Architecture Search
DARTS: Differentiable Architecture Search 2019-03-19 10:04:26accepted by ICLR 2019 Paper:https://arx ...
- 论文笔记系列-DARTS: Differentiable Architecture Search
Summary 我的理解就是原本节点和节点之间操作是离散的,因为就是从若干个操作中选择某一个,而作者试图使用softmax和relaxation(松弛化)将操作连续化,所以模型结构搜索的任务就转变成了 ...
- 论文笔记:Progressive Differentiable Architecture Search:Bridging the Depth Gap between Search and Evaluation
Progressive Differentiable Architecture Search:Bridging the Depth Gap between Search and Evaluation ...
- 2019-ICCV-PDARTS-Progressive Differentiable Architecture Search Bridging the Depth Gap Between Search and Evaluation-论文阅读
P-DARTS 2019-ICCV-Progressive Differentiable Architecture Search Bridging the Depth Gap Between Sear ...
- 论文笔记系列-Auto-DeepLab:Hierarchical Neural Architecture Search for Semantic Image Segmentation
Pytorch实现代码:https://github.com/MenghaoGuo/AutoDeeplab 创新点 cell-level and network-level search 以往的NAS ...
- Research Guide for Neural Architecture Search
Research Guide for Neural Architecture Search 2019-09-19 09:29:04 This blog is from: https://heartbe ...
- 小米造最强超分辨率算法 | Fast, Accurate and Lightweight Super-Resolution with Neural Architecture Search
本篇是基于 NAS 的图像超分辨率的文章,知名学术性自媒体 Paperweekly 在该文公布后迅速跟进,发表分析称「属于目前很火的 AutoML / Neural Architecture Sear ...
- 论文笔记系列-Neural Architecture Search With Reinforcement Learning
摘要 神经网络在多个领域都取得了不错的成绩,但是神经网络的合理设计却是比较困难的.在本篇论文中,作者使用 递归网络去省城神经网络的模型描述,并且使用 增强学习训练RNN,以使得生成得到的模型在验证集上 ...
- 论文笔记:Auto-DeepLab: Hierarchical Neural Architecture Search for Semantic Image Segmentation
Auto-DeepLab: Hierarchical Neural Architecture Search for Semantic Image Segmentation2019-03-18 14:4 ...
随机推荐
- Java中的动态定义数组
1.一维矩阵的动态定义(代码注释) 1.1方法一 package dongtai; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList; publ ...
- tp5中使用ueditor编辑器保存文本到数据库后回显后显示html标签问题解决办法
在编辑器ueditor中获取文本,保存到到数据库后为 当在数据库中提取出来,在显示回ueditor编辑器时候,出了问题, html标签都显示出来了 百度了下别人的解决办法是,使用官方提供的api 可是 ...
- Spring官网阅读(四)BeanDefinition(上)
前面几篇文章已经学习了官网中的1.2,1.3,1.4三小结,主要是容器,Bean的实例化及Bean之间的依赖关系等.这篇文章,我们继续官网的学习,主要是BeanDefinition的相关知识,这是Sp ...
- 使用Hystrix的插件机制,解决在使用线程隔离时,threadlocal的传递问题
背景 在我们的项目中,比较广泛地使用了ThreadLocal,比如,在filter层,根据token,取到用户信息后,就会放到一个ThreadLocal变量中:在后续的业务处理中,就会直接从当前线程, ...
- 04_CSS入门和高级技巧(2)
上节课复习 HTML表格,table.tr.td(th):thead.tbody:caption. 一定要会根据图形,来写表格: <table border="1"> ...
- 【Elasticsearch学习】文档搜索全过程
在ES执行分布式搜索时,分布式搜索操作需要分散到所有相关分片,若一个索引有3个主分片,每个主分片有一个副本分片,那么搜索请求会在这6个分片中随机选择3个分片,这3个分片有可能是主分片也可能是副本分片, ...
- 假如用王者荣耀的方式学习webpack
英雄介绍 崴博.派克诞生于遥远西方的勇士之地,拥有着高超的机械技艺,善于运用各种工具来实现一些看似不可能完成的事.游历王者大陆时机缘巧合遇到了年轻的墨子,与之成为好友.后协助大宗师墨子建造了大陆第一雄 ...
- 「从零单排HBase 10」HBase集群多租户实践
在HBase1.1.0发布之前,HBase同一集群上的用户.表都是平等的,大家平等共用集群资源.容易碰到两个问题: 一是某些业务较其他业务重要,需要在资源有限的情况下优先保证核心重要业务的正常运行 二 ...
- 生产者消费者问题中的同步机制JAVA设计和实现
目录 问题描述 问题分析 利用记录型信号量解决 运行环境 实现思路 代码实现 运行截图 过程中出现的问题和注意点 利用AND信号集解决 运行环境 实现思路 代码实现 运行截图 问题描述 若干进程通过有 ...
- JDBC10 Blob二进制对象
//将图片输入到数据库中 // String sql="insert into t_user2 (username,headImg) values (?,?)"; // ps=co ...