Netty(五)Netty 高性能之道
4.背景介绍
4.1.1 Netty 惊人的性能数据
4.1.2 传统 RPC 调用性能差的三宗罪
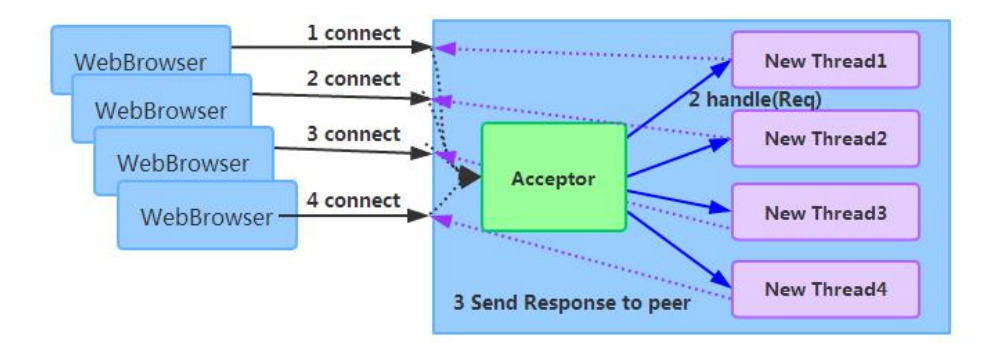
4.2 Netty 高性能之道
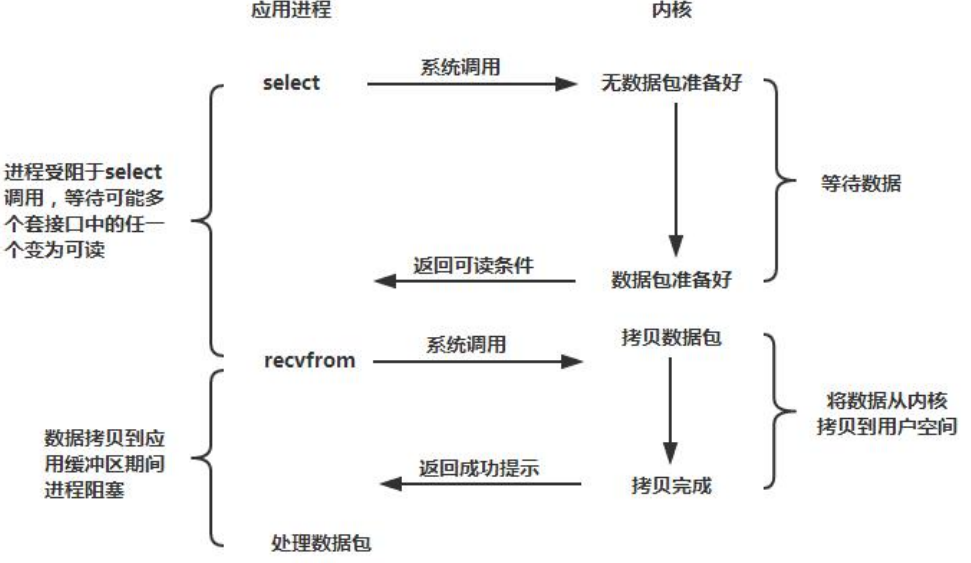
与 Socket 类和 ServerSocket 类相对应,NIO 也提供了 SocketChannel 和 ServerSocketChannel 两种不同的套接字通
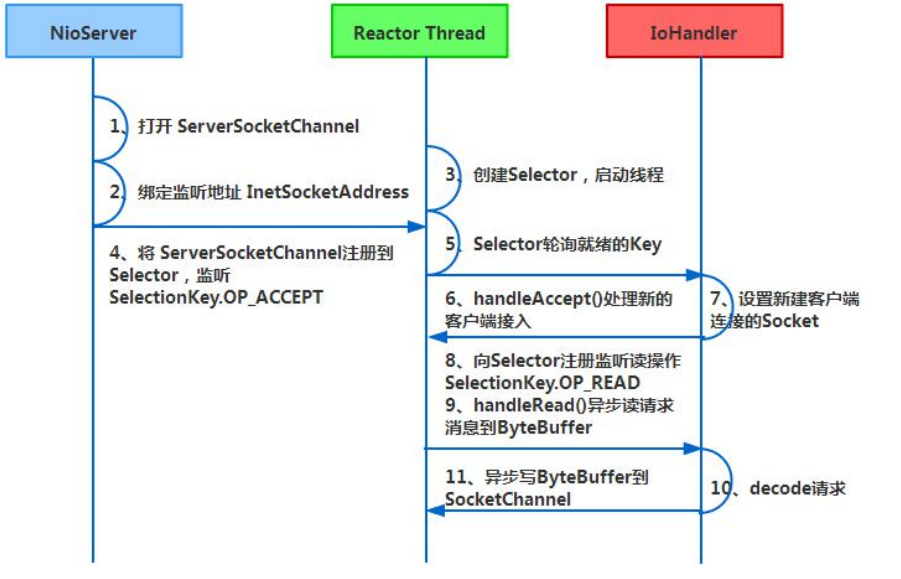
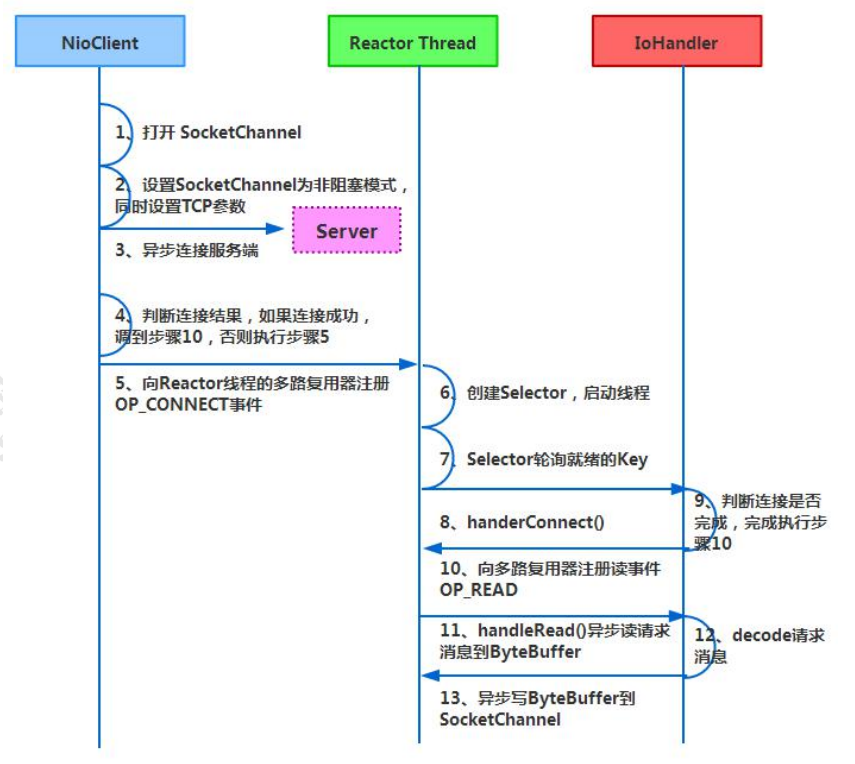
客户端通信序列图如下:
public final void read() {
ChannelConfig config = AbstractNioByteChannel.this.config();
ChannelPipeline pipeline = AbstractNioByteChannel.this.pipeline();
ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
Handle allocHandle = this.recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(AbstractNioByteChannel.this.doReadBytes(byteBuf));
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);
AbstractNioByteChannel.this.readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
byteBuf = null;
} while(allocHandle.continueReading());
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (close) {
this.closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable var11) {
this.handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, var11, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
if (!AbstractNioByteChannel.this.readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
this.removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
public ByteBuf allocate(ByteBufAllocator alloc) {
return alloc.ioBuffer(guess());
}
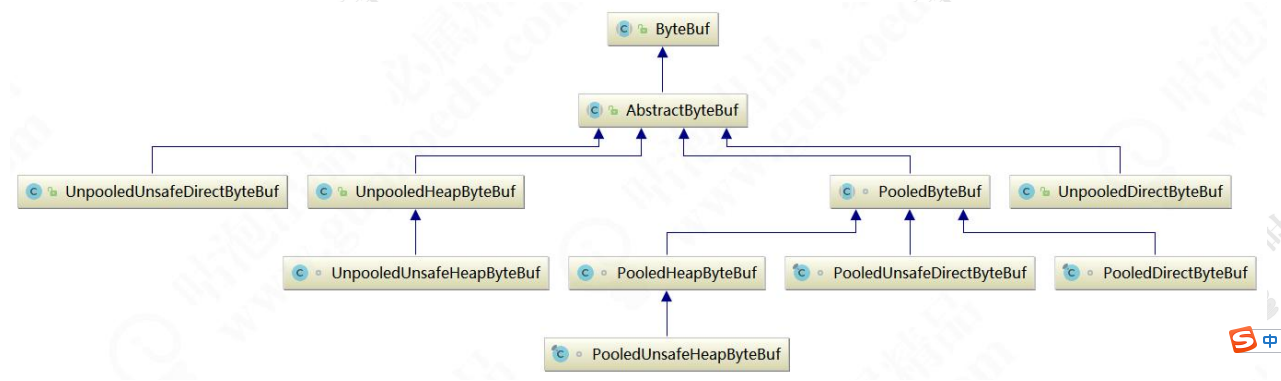
public abstract class ByteBuf implements ReferenceCounted, Comparable<ByteBuf> { ... }

通过继承关系我们可以看出 CompositeByteBuf 实际就是个 ByteBuf 的包装器,它将多个 ByteBuf 组合成一个集合,然
private static final ByteBuffer EMPTY_NIO_BUFFER = Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER.nioBuffer();
private static final Iterator<ByteBuf> EMPTY_ITERATOR = Collections.<ByteBuf>emptyList().iterator();
private final ByteBufAllocator alloc;
private final boolean direct;
private final List<Component> components; private final int maxNumComponents;
private boolean freed;
private int addComponents0(boolean increaseWriterIndex, int cIndex, ByteBuf[] buffers, int offset, int len) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(buffers, "buffers");
int i = offset;
boolean var16 = false;
int var20;
try {
var16 = true;
this.checkComponentIndex(cIndex);
while(true) {
if (i < len) {
ByteBuf b = buffers[i++];
if (b != null) {
cIndex = this.addComponent0(increaseWriterIndex, cIndex, b) + 1;
int size = this.components.size();
if (cIndex > size) {
cIndex = size;
}
continue;
}
}
var20 = cIndex;
var16 = false;
break;
}
} finally {
if (var16) {
while(true) {
if (i >= len) {
;
} else {
ByteBuf b = buffers[i];
if (b != null) {
try {
b.release();
} catch (Throwable var17) {
;
}
}
++i;
}
}
}
}
for(; i < len; ++i) {
ByteBuf b = buffers[i];
if (b != null) {
try {
b.release();
} catch (Throwable var18) {
;
}
}
}
return var20;
}
public long transferTo(WritableByteChannel target, long position) throws IOException {
long count = this.count - position;
if (count >= 0L && position >= 0L) {
if (count == 0L) {
return 0L;
} else if (this.refCnt() == 0) {
throw new IllegalReferenceCountException(0);
} else {
this.open();
long written = this.file.transferTo(this.position + position, count, target);
if (written > 0L) {
this.transferred += written;
}
return written;
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("position out of range: " + position + " (expected: 0 - " + (this.count - 1L) + ')');
}
}
/**
* Transfers bytes from this channel's file to the given writable byte
* channel.
*
* <p> An attempt is made to read up to <tt>count</tt> bytes starting at
* the given <tt>position</tt> in this channel's file and write them to the
* target channel. An invocation of this method may or may not transfer
* all of the requested bytes; whether or not it does so depends upon the
* natures and states of the channels. Fewer than the requested number of
* bytes are transferred if this channel's file contains fewer than
* <tt>count</tt> bytes starting at the given <tt>position</tt>, or if the
* target channel is non-blocking and it has fewer than <tt>count</tt>
* bytes free in its output buffer.
*
* <p> This method does not modify this channel's position. If the given
* position is greater than the file's current size then no bytes are
* transferred. If the target channel has a position then bytes are
* written starting at that position and then the position is incremented
* by the number of bytes written.
*
* <p> This method is potentially much more efficient than a simple loop
* that reads from this channel and writes to the target channel. Many
* operating systems can transfer bytes directly from the filesystem cache
* to the target channel without actually copying them. </p>
*
public abstract long transferTo(long position, long count,
WritableByteChannel target)
throws IOException;
Netty 提供了多种内存管理策略,通过在启动辅助类中配置相关参数,可以实现差异化的定制。
package com.lf.io.nio; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.PooledByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; public class BufTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
directBuf();
}
public static void directBuf() {
final byte[] CONTENT = new byte[1024];
int loop = 1800000;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ByteBuf poolBuffer = null;
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
poolBuffer = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.directBuffer(1024);
poolBuffer.writeBytes(CONTENT);
poolBuffer.release();
} long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("内存池分配缓冲区耗时" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms."); long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
ByteBuf buffer = null;
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
buffer = Unpooled.directBuffer(1024);
buffer.writeBytes(CONTENT);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("非内存池分配缓冲区耗时" + (endTime - startTime2) + "ms.");
} }
public ByteBuf directBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0 && maxCapacity == 0) {
return this.emptyBuf;
} else {
validate(initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
return this.newDirectBuffer(initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
}
代码跳转到 PooledByteBufAllocator 的 newDirectBuffer 方法,从 Cache 中获取内存区域 PoolArena,调用它的 allocate
protected ByteBuf newDirectBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
PoolThreadCache cache = (PoolThreadCache)this.threadCache.get();
PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena = cache.directArena;
Object buf;
if (directArena != null) {
buf = directArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
} else if (PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe()) {
buf = UnsafeByteBufUtil.newUnsafeDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
} else {
buf = new UnpooledDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
return toLeakAwareBuffer((ByteBuf)buf);
}
PooledByteBuf<T> allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, int reqCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
PooledByteBuf<T> buf = this.newByteBuf(maxCapacity);
this.allocate(cache, buf, reqCapacity);
return buf;
}
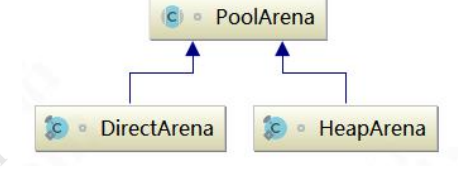
因此重点分析 DirectArena 的实现:如果没有开启使用 sun 的 unsafe,则
protected PooledByteBuf<ByteBuffer> newByteBuf(int maxCapacity) {
return (PooledByteBuf)(HAS_UNSAFE ? PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf.newInstance(maxCapacity) : PooledDirectByteBuf.newInstance(maxCapacity));
}
static PooledDirectByteBuf newInstance(int maxCapacity) {
PooledDirectByteBuf buf = (PooledDirectByteBuf)RECYCLER.get();
buf.reuse(maxCapacity);
return buf;
}
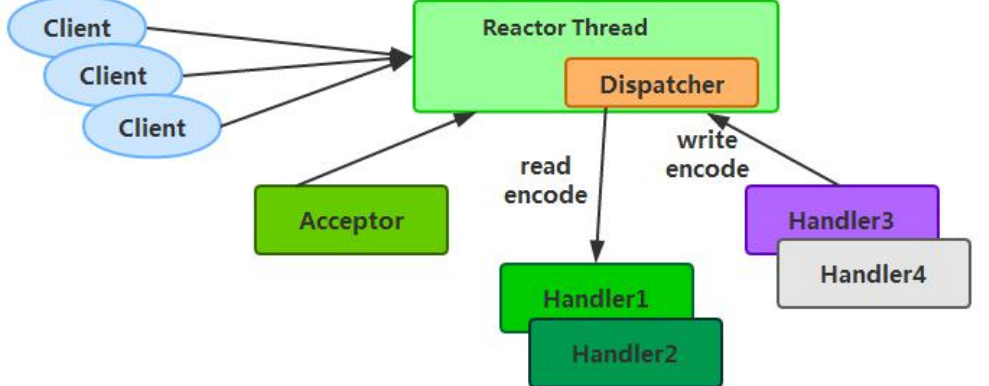
由于 Reactor 模式使用的是异步非阻塞 IO,所有的 IO 操作都不会导致阻塞,理论上一个线程可以独立处理所有 IO 相
2) 当 NIO 线程负载过重之后,处理速度将变慢,这会导致大量客户端连接超时,超时之后往往会进行重发,这更加重
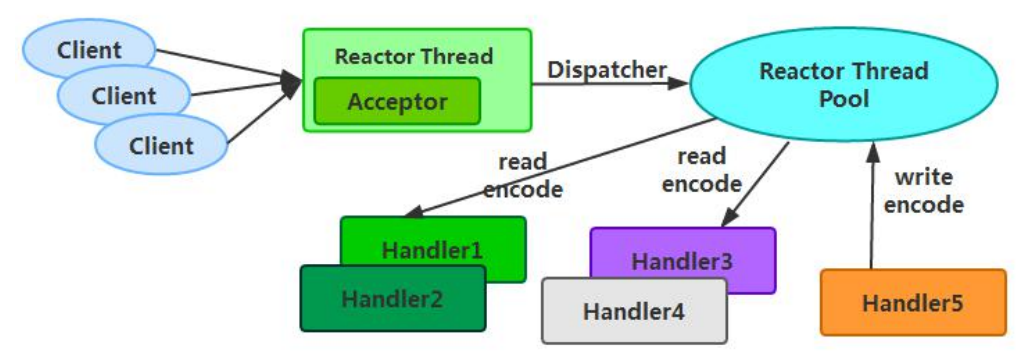
Reactor 多线程模型的特点:
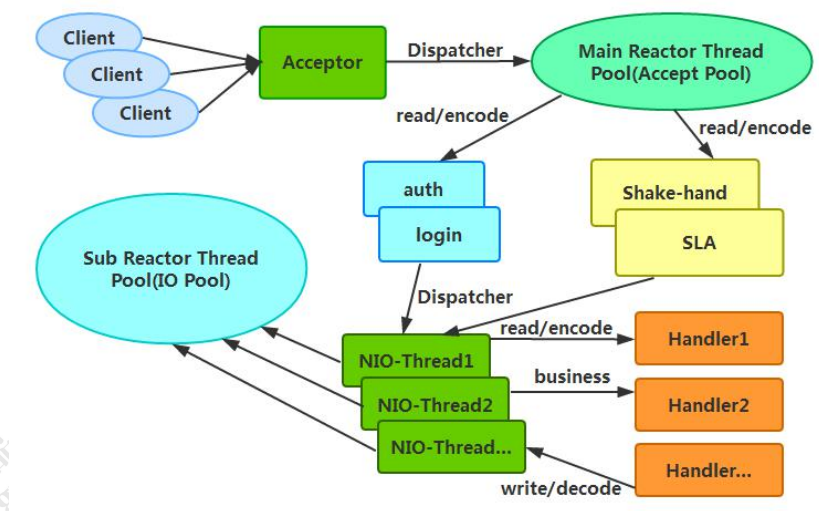
利用主从 NIO 线程模型,可以解决 1 个服务端监听线程无法有效处理所有客户端连接的性能不足问题。因此,在 Netty
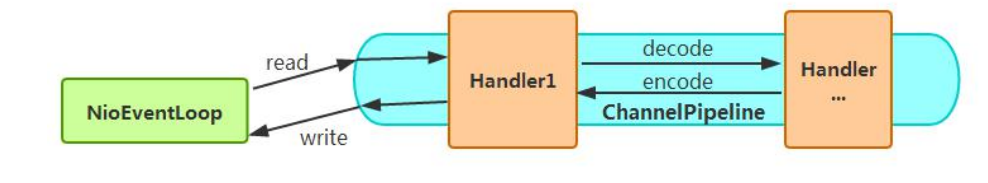
Netty 的 NioEventLoop 读取到消息之后,直接调用 ChannelPipeline 的 fireChannelRead(Object msg),只要用户不主
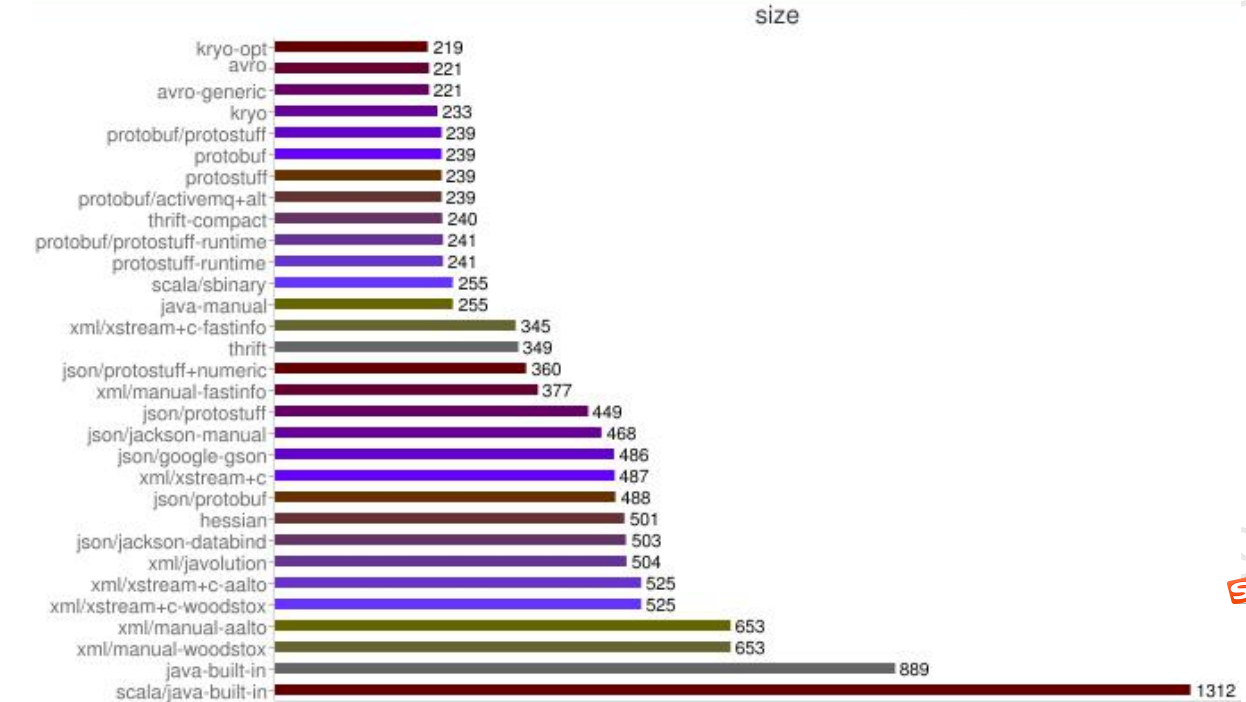
从上图可以看出,Protobuf 序列化后的码流只有 Java 序列化的 1/4 左右。正是由于 Java 原生序列化性能表现太差,


Netty(五)Netty 高性能之道的更多相关文章
- Netty(RPC高性能之道)原理剖析
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/zhiguozhu/article/details/50517551 1,Netty简述 Netty 是一个基于 JAVA NIO 类库的异步通信框架, ...
- Netty 系列之 Netty 高性能之道
1. 背景 1.1. 惊人的性能数据 最近一个圈内朋友通过私信告诉我,通过使用 Netty4 + Thrift 压缩二进制编解码技术,他们实现了 10 W TPS(1 K 的复杂 POJO 对象)的跨 ...
- Netty系列之Netty高性能之道
转载自http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/netty-high-performance 1. 背景 1.1. 惊人的性能数据 最近一个圈内朋友通过私信告诉我,通过使用Ne ...
- Netty高性能之道
1. 背景 1.1. 惊人的性能数据 最近一个圈内朋友告诉我,通过使用Netty4 + Thrift压缩二进制编解码技术,他们实现了10W TPS(1K的复杂POJO对象)的跨节点远程服务调用.相比于 ...
- 转:Netty系列之Netty高性能之道
1. 背景 1.1. 惊人的性能数据 最近一个圈内朋友通过私信告诉我,通过使用Netty4 + Thrift压缩二进制编解码技术,他们实现了10W TPS(1K的复杂POJO对象)的跨节点远程服务调用 ...
- Netty(RPC高性能之道)原理剖析
1,Netty简述 Netty 是一个基于 JAVA NIO 类库的异步通信框架,用于创建异步非阻塞.基于事件驱动.高性能.高可靠性和高可定制性的网络客户端和服务器端 RPC高性能分析,请参考文章“[ ...
- 【读后感】Netty 系列之 Netty 高性能之道 - 相比 Mina 怎样 ?
[读后感]Netty 系列之 Netty 高性能之道 - 相比 Mina 怎样 ? 太阳火神的漂亮人生 (http://blog.csdn.net/opengl_es) 本文遵循"署名-非商 ...
- Netty 系列之 Netty 高性能之道 高性能的三个主题 Netty使得开发者能够轻松地接受大量打开的套接字 Java 序列化
Netty系列之Netty高性能之道 https://www.infoq.cn/article/netty-high-performance 李林锋 2014 年 5 月 29 日 话题:性能调优语言 ...
- 谈谈如何使用Netty开发实现高性能的RPC服务器
RPC(Remote Procedure Call Protocol)远程过程调用协议,它是一种通过网络,从远程计算机程序上请求服务,而不必了解底层网络技术的协议.说的再直白一点,就是客户端在不必知道 ...
随机推荐
- 爬虫学习(二)requests模块的使用
一.requests的概述 requests模块是用于发送网络请求,返回响应数据.底层实现是urllib,而且简单易用,在python2.python3中通用,能够自动帮助我们解压(gzip压缩的等) ...
- JavaScript中eval的替代方法
引自:https://www.cnblogs.com/lxg0/p/7805266.html 通常我们在使用ajax获取到后台返回的json数据时,需要使用 eval 这个方法将json字符串转换成对 ...
- 网络编程 — Windows TCP服务端和客户端
1. 服务端 #include <iostream> #include <signal.h> #include <forward_list> #include &l ...
- 【UNIAPP】接入导航系统完整版
// 查询附近/搜索关键词 <template> <view> <!--地图容器--> <map id="myMap" :markers= ...
- 你真的了解Android系统启动流程吗?Android高级工程师必看系列,已开源
前言 从毕业到现在面试也就那么几家公司,单前几次都比较顺利,在面到第三家时都给到了我offer!前面两次找工作,没考虑到以后需要什么,自己的对未来的规划是什么,只要有份工作,工资符合自己的要求就行!所 ...
- LVS负载均衡IP隧道模式原理介绍以及配置实战
LVS 基本工作原理 当用户向负载均衡调度器(Director Server)发起请求,调度器将请求发往至内核空间 PREROUTING 链首先会接收到用户请求,判断目标 IP 确定是本机 IP,将数 ...
- Linux系统中的Page cache和Buffer cache
Linux系统中的Page cache和Buffer cache Linux中有两个很容易混淆的概念,pagecache和buffercache,首先简单将一些Linux系统下内存的分布,使用free ...
- CentOS 镜像下载地址
CentOS镜像地址:http://isoredirect.centos.org/altarch/7/isos/i386/
- 研发流程 接口定义&开发&前后端联调 线上日志观察 模型变动
阿里等大厂的研发流程,进去前先了解一下_我们一起进大厂 - SegmentFault 思否 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000021831640 接口定义 测试用例评 ...
- 使用Redis有序集合实现投票排行榜系统
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/GcPF8jte8Nzi4Ae0jojXuQ 先说最简单的排行榜.其实之前我们有个用于投票的系统,但是他没有用有序集合,他是这样做的:用redis ...
