k8s源码Client-go中Reflector解析
摘要:通过本文,可以了解Reflector通过ListWatcher从Kubernetes API中获取对象的流程,以及存储到store中,后续会对DeltaFIFO进行源码研读,通过结合informer,来加深对整个informer的理解。
本文分享自华为云社区《Client-go源码分析之Reflector》,作者: kaliarch 。
一 背景
Reflector 是保证 Informer 可靠性的核心组件,在丢失事件,收到异常事件,处理事件失败等多种异常情况下需要考虑的细节很多。单独的listwatcher缺少重新连接和重新同步机制,有可能出现数据不一致问题。其对事件响应是同步的,如果执行复杂的操作会引起阻塞,需要引入队列。
二 Reflector
Reflector可以成为反射器,将etcd中的数据反射到存储(DeltaFIFO)中。Reflector通过其内部的List操作获取所有资源对象数据,保存到本地存储,之后Watch监视资源变化,触发对应事件处理,例如Add、Update、Delete等。
Reflector 结构体的定义位于 staging/src/http://k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go 下面:
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
type Reflector struct {
// name 标识这个反射器的名称,默认为 文件:行数(比如reflector.go:125)
// 默认名字通过 k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/naming/from_stack.go 下面的 GetNameFromCallsite 函数生成
name string
// 期望放到 Store 中的类型名称,如果提供,则是 expectedGVK 的字符串形式
// 否则就是 expectedType 的字符串,它仅仅用于显示,不用于解析或者比较。
expectedTypeName string
// An example object of the type we expect to place in the store.
// Only the type needs to be right, except that when that is
// `unstructured.Unstructured` the object's `"apiVersion"` and
// `"kind"` must also be right.
// 放到 Store 中的对象类型
expectedType reflect.Type
// 如果是非结构化的,期望放在 Sotre 中的对象的 GVK
expectedGVK *schema.GroupVersionKind
// 与 watch 源同步的目标 Store
store Store
// 用来执行 lists 和 watches 操作的 listerWatcher 接口(最重要的)
listerWatcher ListerWatcher
// backoff manages backoff of ListWatch
backoffManager wait.BackoffManager
resyncPeriod time.Duration
// ShouldResync 会周期性的被调用,当返回 true 的时候,就会调用 Store 的 Resync 操作
ShouldResync func() bool
// clock allows tests to manipulate time
clock clock.Clock
// paginatedResult defines whether pagination should be forced for list calls.
// It is set based on the result of the initial list call.
paginatedResult bool
// Kubernetes 资源在 APIServer 中都是有版本的,对象的任何修改(添加、删除、更新)都会造成资源版本更新,lastSyncResourceVersion 就是指的这个版本
lastSyncResourceVersion string
// 如果之前的 list 或 watch 带有 lastSyncResourceVersion 的请求中是一个 HTTP 410(Gone)的失败请求,则 isLastSyncResourceVersionGone 为 true
isLastSyncResourceVersionGone bool
// lastSyncResourceVersionMutex 用于保证对 lastSyncResourceVersion 的读/写访问。
lastSyncResourceVersionMutex sync.RWMutex
// WatchListPageSize is the requested chunk size of initial and resync watch lists.
// If unset, for consistent reads (RV="") or reads that opt-into arbitrarily old data
// (RV="0") it will default to pager.PageSize, for the rest (RV != "" && RV != "0")
// it will turn off pagination to allow serving them from watch cache.
// NOTE: It should be used carefully as paginated lists are always served directly from
// etcd, which is significantly less efficient and may lead to serious performance and
// scalability problems.
WatchListPageSize int64
}
// NewReflector 创建一个新的反射器对象,将使给定的 Store 保持与服务器中指定的资源对象的内容同步。
// 反射器只把具有 expectedType 类型的对象放到 Store 中,除非 expectedType 是 nil。
// 如果 resyncPeriod 是非0,那么反射器会周期性地检查 ShouldResync 函数来决定是否调用 Store 的 Resync 操作
// `ShouldResync==nil` 意味着总是要执行 Resync 操作。
// 这使得你可以使用反射器周期性地处理所有的全量和增量的对象。
func NewReflector(lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {
// 默认的反射器名称为 file:line
return NewNamedReflector(naming.GetNameFromCallsite(internalPackages...), lw, expectedType, store, resyncPeriod)
}
// NewNamedReflector 与 NewReflector 一样,只是指定了一个 name 用于日志记录
func NewNamedReflector(name string, lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {
realClock := &clock.RealClock{}
r := &Reflector{
name: name,
listerWatcher: lw,
store: store,
backoffManager: wait.NewExponentialBackoffManager(800*time.Millisecond, 30*time.Second, 2*time.Minute, 2.0, 1.0, realClock),
resyncPeriod: resyncPeriod,
clock: realClock,
}
r.setExpectedType(expectedType)
return r
}
三 流程
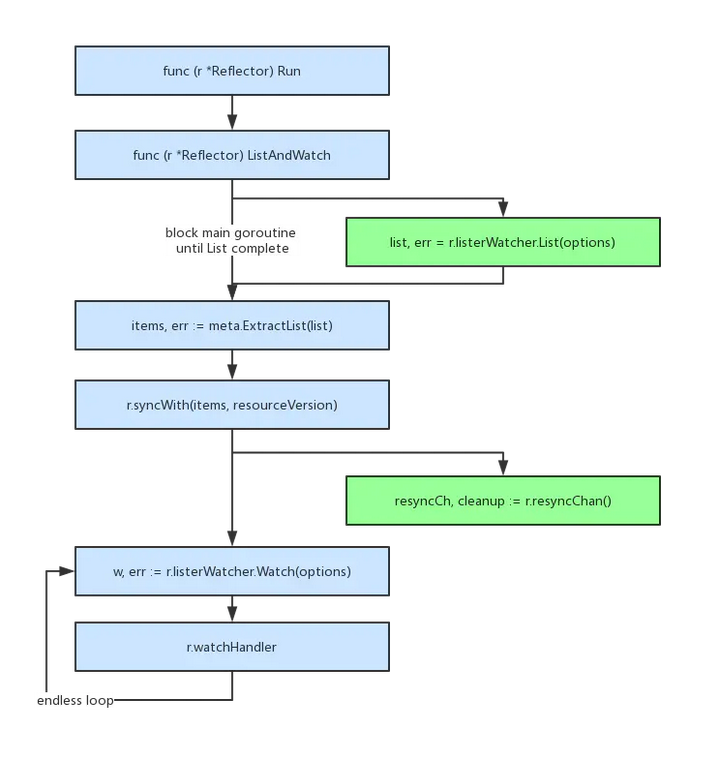
- Reflector.Run()调用ListAndWatch(), 启动一个子协程(goroutine)执行List,主协程阻塞等待List执行完成。
- Meta.ExtractList(list)把List结果转化成runtime.Object数组。
- r.syncWith(items, resourceVersion)写入DeltaFIFO,全量同步到Indexer。
- r.resyncChan()也是在一个子协程里执行。
- 循环执行r.ListerWatcher.Watch(optiopns)。
- r.WatchHandler增量同步runtime.Object到indexer。
- List只做一次全量同步,watch持续做增量同步。
四 Reflector关键方法
4.1 构造方法
// NewReflector 创建一个新的反射器对象,将使给定的 Store 保持与服务器中指定的资源对象的内容同步。
// 反射器只把具有 expectedType 类型的对象放到 Store 中,除非 expectedType 是 nil。
// 如果 resyncPeriod 是非0,那么反射器会周期性地检查 ShouldResync 函数来决定是否调用 Store 的 Resync 操作
// `ShouldResync==nil` 意味着总是要执行 Resync 操作。
// 这使得你可以使用反射器周期性地处理所有的全量和增量的对象。
func NewReflector(lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {
// 默认的反射器名称为 file:line
return NewNamedReflector(naming.GetNameFromCallsite(internalPackages...), lw, expectedType, store, resyncPeriod)
} // NewNamedReflector 与 NewReflector 一样,只是指定了一个 name 用于日志记录
func NewNamedReflector(name string, lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {
realClock := &clock.RealClock{}
r := &Reflector{
name: name,
listerWatcher: lw,
store: store,
backoffManager: wait.NewExponentialBackoffManager(800*time.Millisecond, 30*time.Second, 2*time.Minute, 2.0, 1.0, realClock),
resyncPeriod: resyncPeriod,
clock: realClock,
}
r.setExpectedType(expectedType)
return r
} //新建Indexer和reflector
func NewNamespaceKeyedIndexerAndReflector(lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, resyncPeriod time.Duration) (indexer Indexer, reflector *Reflector) {
indexer = NewIndexer(MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, Indexers{NamespaceIndex: MetaNamespaceIndexFunc})
reflector = NewReflector(lw, expectedType, indexer, resyncPeriod)
return indexer, reflector
}
4.2 Run方法
// Run 重复使用反射器的 ListAndWatch 来获取所有对象和后续增量。当 stopCh 关闭时,运行将退出
func (r *Reflector) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
klog.V(2).Infof("Starting reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
wait.BackoffUntil(func() {
if err := r.ListAndWatch(stopCh); err != nil {
r.watchErrorHandler(r, err)
}
}, r.backoffManager, true, stopCh)
klog.V(2).Infof("Stopping reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
}
4.3 ListWatch
- List部分逻辑:设置分页参数;执行list方法;将list结果同步进DeltaFIFO队列中,其实是调用store中的Replace方法。
- 定时同步:定时同步以协程的方式运行,使用定时器实现定期同步,Store中的Resync操作。
- Watch部分逻辑:在for循环里;执行watch函数获取resultchan;监听resultchan中数据并处理;
// ListAndWatch 函数首先列出所有的对象,并在调用的时候获得资源版本,然后使用该资源版本来进行 watch 操作。
// 如果 ListAndWatch 没有初始化 watch 成功就会返回错误。
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
klog.V(3).Infof("Listing and watching %v from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.name)
var resourceVersion string options := metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()} // 1.List部分逻辑:设置分页参数;执行list方法;将list结果同步进DeltaFIFO队列中;
if err := func() error {
initTrace := trace.New("Reflector ListAndWatch", trace.Field{"name", r.name})
defer initTrace.LogIfLong(10 * time.Second)
var list runtime.Object
var paginatedResult bool
var err error
listCh := make(chan struct{}, 1)
panicCh := make(chan interface{}, 1)
go func() {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
panicCh <- r
}
}()
// Attempt to gather list in chunks, if supported by listerWatcher, if not, the first
// list request will return the full response.
pager := pager.New(pager.SimplePageFunc(func(opts metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.listerWatcher.List(opts)
}))
switch {
case r.WatchListPageSize != 0:
pager.PageSize = r.WatchListPageSize
case r.paginatedResult:
// We got a paginated result initially. Assume this resource and server honor
// paging requests (i.e. watch cache is probably disabled) and leave the default
// pager size set.
case options.ResourceVersion != "" && options.ResourceVersion != "0":
// User didn't explicitly request pagination.
//
// With ResourceVersion != "", we have a possibility to list from watch cache,
// but we do that (for ResourceVersion != "0") only if Limit is unset.
// To avoid thundering herd on etcd (e.g. on master upgrades), we explicitly
// switch off pagination to force listing from watch cache (if enabled).
// With the existing semantic of RV (result is at least as fresh as provided RV),
// this is correct and doesn't lead to going back in time.
//
// We also don't turn off pagination for ResourceVersion="0", since watch cache
// is ignoring Limit in that case anyway, and if watch cache is not enabled
// we don't introduce regression.
pager.PageSize = 0
} list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), options)
if isExpiredError(err) || isTooLargeResourceVersionError(err) {
r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(true)
// Retry immediately if the resource version used to list is unavailable.
// The pager already falls back to full list if paginated list calls fail due to an "Expired" error on
// continuation pages, but the pager might not be enabled, the full list might fail because the
// resource version it is listing at is expired or the cache may not yet be synced to the provided
// resource version. So we need to fallback to resourceVersion="" in all to recover and ensure
// the reflector makes forward progress.
list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()})
}
close(listCh)
}()
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
case r := <-panicCh:
panic(r)
case <-listCh:
}
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to list %v: %v", r.expectedTypeName, err)
} // We check if the list was paginated and if so set the paginatedResult based on that.
// However, we want to do that only for the initial list (which is the only case
// when we set ResourceVersion="0"). The reasoning behind it is that later, in some
// situations we may force listing directly from etcd (by setting ResourceVersion="")
// which will return paginated result, even if watch cache is enabled. However, in
// that case, we still want to prefer sending requests to watch cache if possible.
//
// Paginated result returned for request with ResourceVersion="0" mean that watch
// cache is disabled and there are a lot of objects of a given type. In such case,
// there is no need to prefer listing from watch cache.
if options.ResourceVersion == "0" && paginatedResult {
r.paginatedResult = true
} r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(false) // list was successful
initTrace.Step("Objects listed")
//
listMetaInterface, err := meta.ListAccessor(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v: %v", list, err)
}
// 获取资源版本号
resourceVersion = listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion()
initTrace.Step("Resource version extracted")
// 将资源对象转换为资源列表,讲runtime.Object 对象转换为[]runtime.Object对象
items, err := meta.ExtractList(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v (%v)", list, err)
}
initTrace.Step("Objects extracted")
// 将资源对象列表中的资源和版本号存储在store中
if err := r.syncWith(items, resourceVersion); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to sync list result: %v", err)
}
initTrace.Step("SyncWith done")
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
initTrace.Step("Resource version updated")
return nil
}(); err != nil {
return err
} // 2.定时同步:定时同步以协程的方式运行,使用定时器实现定期同步
resyncerrc := make(chan error, 1)
cancelCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(cancelCh)
go func() {
resyncCh, cleanup := r.resyncChan()
defer func() {
cleanup() // Call the last one written into cleanup
}()
for {
select {
case <-resyncCh:
case <-stopCh:
return
case <-cancelCh:
return
}
// 如果ShouldResync 为nil或者调用返回true,则执行Store中的Resync操作
if r.ShouldResync == nil || r.ShouldResync() {
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: forcing resync", r.name)
// 将indexer的数据和deltafifo进行同步
if err := r.store.Resync(); err != nil {
resyncerrc <- err
return
}
}
cleanup()
resyncCh, cleanup = r.resyncChan()
}
}() // 3.在for循环里;执行watch函数获取resultchan;监听resultchan中数据并处理;
for {
// give the stopCh a chance to stop the loop, even in case of continue statements further down on errors
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
default:
} timeoutSeconds := int64(minWatchTimeout.Seconds() * (rand.Float64() + 1.0))
options = metav1.ListOptions{
ResourceVersion: resourceVersion,
// We want to avoid situations of hanging watchers. Stop any wachers that do not
// receive any events within the timeout window.
TimeoutSeconds: &timeoutSeconds,
// To reduce load on kube-apiserver on watch restarts, you may enable watch bookmarks.
// Reflector doesn't assume bookmarks are returned at all (if the server do not support
// watch bookmarks, it will ignore this field).
AllowWatchBookmarks: true,
} // start the clock before sending the request, since some proxies won't flush headers until after the first watch event is sent
start := r.clock.Now()
w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
if err != nil {
// If this is "connection refused" error, it means that most likely apiserver is not responsive.
// It doesn't make sense to re-list all objects because most likely we will be able to restart
// watch where we ended.
// If that's the case begin exponentially backing off and resend watch request.
if utilnet.IsConnectionRefused(err) {
<-r.initConnBackoffManager.Backoff().C()
continue
}
return err
} if err := r.watchHandler(start, w, &resourceVersion, resyncerrc, stopCh); err != nil {
if err != errorStopRequested {
switch {
case isExpiredError(err):
// Don't set LastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable - LIST call with ResourceVersion=RV already
// has a semantic that it returns data at least as fresh as provided RV.
// So first try to LIST with setting RV to resource version of last observed object.
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v closed with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
default:
klog.Warningf("%s: watch of %v ended with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
}
}
return nil
}
}
}
4.4 LastSyncResourceVersion
获取上一次同步的资源版本
func (r *Reflector) LastSyncResourceVersion() string {
r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.RLock()
defer r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.RUnlock()
return r.lastSyncResourceVersion
}
4.5 resyncChan
返回一个定时通道和清理函数,清理函数就是停止计时器。这边的定时重新同步是使用定时器实现的。
func (r *Reflector) resyncChan() (<-chan time.Time, func() bool) {
if r.resyncPeriod == 0 {
return neverExitWatch, func() bool { return false }
}
// The cleanup function is required: imagine the scenario where watches
// always fail so we end up listing frequently. Then, if we don't
// manually stop the timer, we could end up with many timers active
// concurrently.
t := r.clock.NewTimer(r.resyncPeriod)
return t.C(), t.Stop
}
4.6 syncWith
将从apiserver list的资源对象结果同步进DeltaFIFO队列中,调用队列的Replace方法实现。
func (r *Reflector) syncWith(items []runtime.Object, resourceVersion string) error {
found := make([]interface{}, 0, len(items))
for _, item := range items {
found = append(found, item)
}
return r.store.Replace(found, resourceVersion)
}
4.7 watchHandler
watch的处理:接收watch的接口作为参数,watch接口对外方法是Stop和Resultchan,前者关闭结果通道,后者获取通道。
func (r *Reflector) watchHandler(start time.Time, w watch.Interface, resourceVersion *string, errc chan error, stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
eventCount := 0
// Stopping the watcher should be idempotent and if we return from this function there's no way
// we're coming back in with the same watch interface.
defer w.Stop()
loop:
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
return errorStopRequested
case err := <-errc:
return err
case event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():
if !ok {
break loop
}
if event.Type == watch.Error {
return apierrors.FromObject(event.Object)
}
if r.expectedType != nil {
if e, a := r.expectedType, reflect.TypeOf(event.Object); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected type %v, but watch event object had type %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
// 判断期待的类型和监听到的事件类型是否一致
if r.expectedGVK != nil {
if e, a := *r.expectedGVK, event.Object.GetObjectKind().GroupVersionKind(); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected gvk %v, but watch event object had gvk %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
// 获取事件对象
meta, err := meta.Accessor(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
continue
}
newResourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()
// 对事件类型进行判断,并进行对应操作
switch event.Type {
case watch.Added:
err := r.store.Add(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Modified:
err := r.store.Update(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to update watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Deleted:
// TODO: Will any consumers need access to the "last known
// state", which is passed in event.Object? If so, may need
// to change this.
err := r.store.Delete(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to delete watch event object (%#v) from store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Bookmark:
// 表示监听已在此处同步,只需更新
// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersion
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
}
*resourceVersion = newResourceVersion
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)
if rvu, ok := r.store.(ResourceVersionUpdater); ok {
rvu.UpdateResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)
}
eventCount++
}
}
watchDuration := r.clock.Since(start)
if watchDuration < 1*time.Second && eventCount == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("very short watch: %s: Unexpected watch close - watch lasted less than a second and no items received", r.name)
}
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: Watch close - %v total %v items received", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, eventCount)
return nil
}
4.8 relistResourceVersion
relistResourceVersion 函数获得反射器 relist 的资源版本,如果资源版本非 0,则表示根据资源版本号继续获取,当传输过程中遇到网络故障或者其他原因导致中断,下次再连接时,会根据资源版本号继续传输未完成的部分。可以使本地缓存中的数据与Etcd集群中的数据保持一致,该函数实现如下所示:
// 如果最后一次relist的结果是HTTP 410(Gone)状态码,则返回"",这样relist将通过quorum读取etcd中可用的最新资源版本。
// 返回使用 lastSyncResourceVersion,这样反射器就不会使用在relist结果或watch事件中watch到的资源版本更老的资源版本进行relist了
func (r *Reflector) relistResourceVersion() string {
r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.RLock()
defer r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.RUnlock() if r.isLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable {
// 因为反射器会进行分页List请求,如果 lastSyncResourceVersion 过期了,所有的分页列表请求就都会跳过 watch 缓存
// 所以设置 ResourceVersion="",然后再次 List,重新建立反射器到最新的可用资源版本,从 etcd 中读取,保持一致性。
return ""
}
if r.lastSyncResourceVersion == "" {
// 反射器执行的初始 List 操作的时候使用0作为资源版本。
return "0"
}
return r.lastSyncResourceVersion
}
五 整体流程
// k8s.io/client-go/informers/apps/v1/deployment.go // NewFilteredDeploymentInformer 为 Deployment 构造一个新的 Informer。
// 总是倾向于使用一个 informer 工厂来获取一个 shared informer,而不是获取一个独立的 informer,这样可以减少内存占用和服务器的连接数。
func NewFilteredDeploymentInformer(client kubernetes.Interface, namespace string, resyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers cache.Indexers, tweakListOptions internalinterfaces.TweakListOptionsFunc) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.AppsV1().Deployments(namespace).List(context.TODO(), options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.AppsV1().Deployments(namespace).Watch(context.TODO(), options)
},
},
&appsv1.Deployment{},
resyncPeriod,
indexers,
)
}
从上面代码我们就可以看出来当我们去调用一个资源对象的 Informer() 的时候,就会去调用上面的 NewFilteredDeploymentInformer 函数进行初始化,而在初始化的使用就传入了 cache.ListWatch 对象,其中就有 List 和 Watch 的实现操作,也就是说前面反射器在 ListAndWatch 里面调用的 ListWatcher 的 List 操作是在一个具体的资源对象的 Informer 中实现的,比如我们这里就是通过的 ClientSet 客户端与 APIServer 交互获取到 Deployment 的资源列表数据的,通过在 ListFunc 中的 client.AppsV1().Deployments(namespace).List(context.TODO(), options) 实现的。
- 获取到了全量的 List 数据过后,通过 listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion() 来获取资源的版本号,ResourceVersion(资源版本号)非常重要,Kubernetes 中所有的资源都拥有该字段,它标识当前资源对象的版本号,每次修改(CUD)当前资源对象时,Kubernetes API Server 都会更改 ResourceVersion,这样 client-go 执行 Watch 操作时可以根据ResourceVersion 来确定当前资源对象是否发生了变化。
- 然后通过 meta.ExtractList 函数将资源数据转换成资源对象列表,将 runtime.Object 对象转换成 []runtime.Object 对象,因为全量获取的是一个资源列表。
- 接下来是通过反射器的 syncWith 函数将资源对象列表中的资源对象和资源版本号存储在 Store 中,这个会在后面的章节中详细说明。
- 最后处理完成后通过 r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion) 操作来设置最新的资源版本号,其他的就是启动一个 goroutine 去定期检查是否需要执行 Resync 操作,调用存储中的 r.store.Resync() 来执行。
- 紧接着就是 Watch 操作了,Watch 操作通过 HTTP 协议与 APIServer 建立长连接,接收Kubernetes API Server 发来的资源变更事件,和 List 操作一样,Watch 的真正实现也是具体的 Informer 初始化的时候传入的,比如上面的 Deployment Informer 中初始化的时候传入的 WatchFunc,底层也是通过 ClientSet 客户端对 Deployment 执行 Watch 操作 client.AppsV1().Deployments(namespace).Watch(context.TODO(), options) 实现的。
- 获得 watch 的资源数据后,通过调用 r.watchHandler 来处理资源的变更事件,当触发Add 事件、Update 事件、Delete 事件时,将对应的资源对象更新到本地缓存(DeltaFIFO)中并更新 ResourceVersion 资源版本号。
这就是 Reflector 反射器中最核心的 ListAndWatch 实现,从上面的实现我们可以看出获取到的数据最终都流向了本地的 Store,也就是 DeltaFIFO,所以接下来我们需要来分析 DeltaFIFO 的实现。
六 小试牛刀
package main import (
"fmt"
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/fields"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/wait"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
"k8s.io/client-go/util/homedir"
"path/filepath"
"time"
) func Must(e interface{}) {
if e != nil {
panic(e)
}
} func InitClientSet() (*kubernetes.Clientset, error) {
kubeconfig := filepath.Join(homedir.HomeDir(), ".kube", "config")
restConfig, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", kubeconfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return kubernetes.NewForConfig(restConfig)
} // 生成listwatcher
func InitListerWatcher(clientSet *kubernetes.Clientset, resource, namespace string, fieldSelector fields.Selector) cache.ListerWatcher {
restClient := clientSet.CoreV1().RESTClient()
return cache.NewListWatchFromClient(restClient, resource, namespace, fieldSelector)
} // 生成pods reflector
func InitPodsReflector(clientSet *kubernetes.Clientset, store cache.Store) *cache.Reflector {
resource := "pods"
namespace := "default"
resyncPeriod := 0 * time.Second
expectedType := &corev1.Pod{}
lw := InitListerWatcher(clientSet, resource, namespace, fields.Everything()) return cache.NewReflector(lw, expectedType, store, resyncPeriod)
} // 生成 DeltaFIFO
func InitDeltaQueue(store cache.Store) cache.Queue {
return cache.NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(cache.DeltaFIFOOptions{
// store 实现了 KeyListerGetter
KnownObjects: store,
// EmitDeltaTypeReplaced 表示队列消费者理解 Replaced DeltaType。
// 在添加 `Replaced` 事件类型之前,对 Replace() 的调用的处理方式与 Sync() 相同。
// 出于向后兼容的目的,默认情况下为 false。
// 当为 true 时,将为传递给 Replace() 调用的项目发送“替换”事件。当为 false 时,将发送 `Sync` 事件。
EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,
}) }
func InitStore() cache.Store {
return cache.NewStore(cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc)
} func main() {
clientSet, err := InitClientSet()
Must(err)
// 用于在processfunc中获取
store := InitStore()
// queue
DeleteFIFOQueue := InitDeltaQueue(store)
// 生成podReflector
podReflector := InitPodsReflector(clientSet, DeleteFIFOQueue) stopCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(stopCh)
go podReflector.Run(stopCh)
//启动
ProcessFunc := func(obj interface{}) error {
// 最先收到的事件会被最先处理
for _, d := range obj.(cache.Deltas) {
switch d.Type {
case cache.Sync, cache.Replaced, cache.Added, cache.Updated:
if _, exists, err := store.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {
if err := store.Update(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
} else {
if err := store.Add(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
}
case cache.Deleted:
if err := store.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
}
pods, ok := d.Object.(*corev1.Pod)
if !ok {
return fmt.Errorf("not config: %T", d.Object)
} fmt.Printf("Type:%s: Name:%s\n", d.Type, pods.Name)
}
return nil
} fmt.Println("Start syncing...") wait.Until(func() {
for {
_, err := DeleteFIFOQueue.Pop(ProcessFunc)
Must(err)
}
}, time.Second, stopCh)
}
七 总结
通过本文,可以了解Reflector通过ListWatcher从Kubernetes API中获取对象的流程,以及存储到store中,后续会对DeltaFIFO进行源码研读,通过结合informer,来加深对整个informer的理解。
参考链接
k8s源码Client-go中Reflector解析的更多相关文章
- Spring源码情操陶冶#task:scheduled-tasks解析器
承接前文Spring源码情操陶冶#task:executor解析器,在前文基础上解析我们常用的spring中的定时任务的节点配置.备注:此文建立在spring的4.2.3.RELEASE版本 附例 S ...
- 100 - k8s源码分析-准备工作
今天我们开始讲kubernetes的源码! 之前的其他开源项目还没有说完,后续会陆陆续续更新,我们把主线先放到k8s的源码上. 之前我想详细讲解每一行k8s源码,但是越看越发现一个大型开源项目如果拘泥 ...
- 2018-09-24 Java源码英翻中网页演示
在线演示地址: 源代码翻译 两部分如下. 独立的Java代码翻译库 续前文代码翻译尝试-使用Roaster解析和生成Java源码 源码库: program-in-chinese/java_code_t ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(8)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(util命名空间)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(9)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context命名空间上)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- # 曹工说Spring Boot源码(10)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:annotation-config 解析)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(12)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:component-scan完整解析)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- Hadoop3.1.1源码Client详解 : 入队前数据写入
该系列总览: Hadoop3.1.1架构体系——设计原理阐述与Client源码图文详解 : 总览 紧接着上一篇: Hadoop3.1.1源码Client详解 : 写入准备-RPC调用与流的建立 先给出 ...
- Hadoop3.1.1源码Client详解 : Packet入队后消息系统运作之DataStreamer(Packet发送) : 主干
该系列总览: Hadoop3.1.1架构体系——设计原理阐述与Client源码图文详解 : 总览 在上一章(Hadoop3.1.1源码Client详解 : 写入准备-RPC调用与流的建立) 我们提到, ...
- Hadoop3.1.1源码Client详解 : Packet入队后消息系统运作之ResponseProcessor(ACK接收)
该系列总览: Hadoop3.1.1架构体系——设计原理阐述与Client源码图文详解 : 总览 紧接着上一篇文章: Hadoop3.1.1源码Client详解 : Packet入队后消息系统运作之D ...
随机推荐
- 对 List 列表中的数据按指定字段进行排序
/** * 对列表中的数据按指定字段进行排序.要求类必须有相关的方法返回字符串.整型.日期等值以进行比较. * * @param list 集合 * @param sortName 需要排序的字段,目 ...
- 一篇适合躺收藏夹的 Nexus3 搭建 NuGet&Docker 私有库的安装使用总结
前言 Nexus 是支持 Nuget.Docker.Npm 等多种包的仓库管理器,可用做私有包的存储分发,缓存官方包.本篇将手把手教学使用 Nexus 搭建自己的 NuGe t& Docker ...
- zookeeper源码(04)leader选举流程
在"zookeeper源码(03)集群启动流程"中介绍了leader选举的入口,本文将详细分析leader选举组件和流程. leader选举流程(重要) quorumPeer的st ...
- 栈与队列应用:逆波兰计算器(逆波兰表达式;后缀表达式)把运算符放到运算量后边 && 中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式
1 //1.实现对逆波兰输入的表达式进行计算如(2-1)*(2+3)= 5 就输入2 1 - 2 3 + * //先把2 1 压栈 遇到-弹栈 再把2 3压进去 遇到+弹栈 最后遇到*弹栈 2 //2 ...
- python之递归(斐波那契数列)与迭代
对于较大的计算来说,迭代不如递归计算速度快,并且可以说非常慢 但是迭代对于较小的运算又比递归巧妙 # 迭代方法 def slowsnail(x): am = [1, 1] if x < 0: p ...
- Codeforces Round #691 (Div. 2) D - Glass Half Spilled(DP)
题目 补下因实验漏掉的CF(还以为是晚上,没想到是下午开始).前三题过的很顺利,到D题时想了会发现数据很小爆搜貌似能过,就以为是道水题,交了一发T了,胡乱加了点剪枝还是T.逐渐意识到事情的严重性.考虑 ...
- [ARC122D] XOR Game
Problem Statement There are $2N$ integers written on a blackboard. The $i$-th integer is $A_i$. Alic ...
- 一招MAX降低10倍,现在它是我的了
一.背景 性能优化是一场永无止境的旅程. 到家门店系统,作为到家核心基础服务之一,门店C端接口有着调用量高,性能要求高的特点. C端服务经过演进,核心接口先查询本地缓存,如果本地缓存没有命中,再查询R ...
- npm 发布流程
登录npm 查看本地是否登录 # 全局配置源 npm who am i # 官方源 npm who am i --registry https://registry.npmjs.org 注: npm源 ...
- 数字孪生与VR设备的融合为旅游行业带来革新
数字时代的推动下,旅游行业正迎来一场革命性的变革.数字孪生系统与虚拟现实(VR)的融合为旅游体验带来了全新的可能性.通过数字孪生技术的实时模拟和VR设备的沉浸式体验,旅游行业迎来了全新的变革时代. 数 ...
