A Beginner’s Guide to the OUTPUT Clause in SQL Server
原文 A Beginner’s Guide to the OUTPUT Clause in SQL Server
T-SQL supports the OUTPUT clause after the inception of SQL server 2005 and later editions. We can use the OUTPUT clause with DML statements (INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE) to return information from modified rows.
We primarily use the OUTPUT clause for auditing and archiving modified rows. In this tutorial, we will walk through the use of the OUTPUT clause with different DML statements and examples. First, we will create a table, dbo.Songs, and populate it with some data.
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.Songs') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.Songs
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.Songs
(
Id int CONSTRAINT PK_Songs_Id PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
Singer varchar(50) NOT NULL
)
GO
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer)
VALUES (1, 'I hate everything about you', 'Adam Gontier');
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer) VALUES (2, 'Dil se', 'A. R. Rahman');
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer) VALUES
(3, 'My heart will go On', 'Celine Dion');
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer) VALUES (4, 'Maeri', 'Euphoria');
GO
SELECT * from dbo.Songs
GO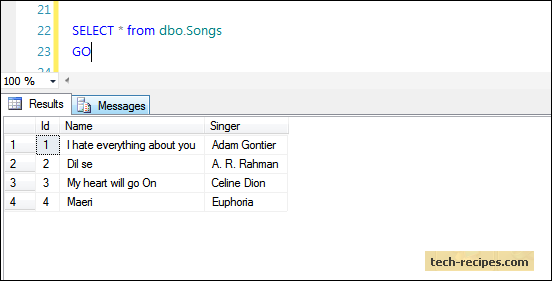
Inserted and Deleted Tables in an OUTPUT Clause
Inserted and Deleted tables are two memory-resident tables that reside within SQL server and are used with the OUTPUT clause.
Whenever any DML (INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE) statement is executed, these tables are populated.
The results of the INSERT statement are stored in the Inserted table, and the results of the Delete statement are stored in the Deleted table. Also, with an UPDATE statement, the deleted rows are stored in the Deleted table. The new inserted rows in the Inserted table as UPDATE are nothing but delete and insert operations combined together.
Note: You cannot directly query Inserted and Deleted tables to see what data they are currently holding, but you can use them with the OUTPUT clause as well as with Triggers.
The OUTPUT Clause with an Insert statement
When we do an Insert operation on a table, we get a message which reads, “(n row(s) affected),” but if we want to see what data rows were inserted into a table, we can use an OUTPUT clause and a memory resident inserted table to return the results back to the screen in the same way that a select statement does.
Let us insert a record, and use an OUTPUT clause to print the results on the screen.
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer)
OUTPUT INSERTED.ID, INSERTED.name, INSERTED.Singer
VALUES (5, 'AINT no grave', 'Johnny Cash');
GOCheck the dbo.Songs table. A new row is inserted with id=5.
select * from dbo.Songs;
GO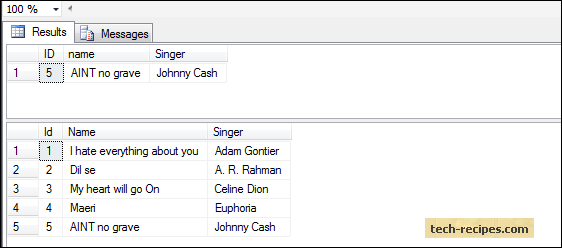
The OUTPUT Clause with a Delete Statement
The same goes with a delete operation. It shows only (n rows(s) affected). We can use an OUTPUT clause and a deleted table to see which rows were actually deleted from the table.
DELETE from dbo.Songs
OUTPUT DELETED.id, DELETED.name, DELETED.singer
WHERE ID=5;
GOQuery the dbo.Songs table row with id = 5 has been deleted.
select * from dbo.Songs;
GO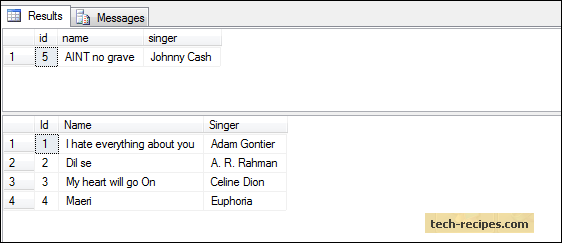
The OUTPUT Clause with an Update Statement
An Update statement does nothing but delete old data and insert new data, so with an Update statement, both memory resident tables are affected and are deleted as well as inserted.
Here we are updating the name of a singer, who has sung ‘Dil se’ song, with ID equal to two.
UPDATE dbo.Songs
SET Singer = 'Rahman'
OUTPUT DELETED.Singer, INSERTED.Singer
WHERE ID = 2;
GOYou can see the old singer’s name along with the new singer’s name.
select * from dbo.Songs;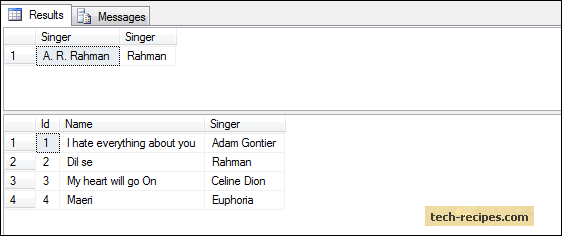
The three examples above show how to use an OUTPUT clause for auditing purposes. Now, we will see how to use it for archiving.
Before, we were just printing the results of a DML statement on the screen, which was temporary, but with the OUTPUT clause, you can store the results of a DML statement in a table, too.
Store Results of an OUTPUT Clause into a Table
Inserting the data return from an OUTPUT clause into a table can be done using an OUTPUT INTO clause. Keep in mind that you first need to create the target table which must have the same number of columns and data types that match the source table.
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.Songs_Inserted') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.Songs_Inserted
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.Songs_Inserted
(
Id int CONSTRAINT PK_Songs__Inserted_Id PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
Singer varchar(50) NOT NULL
)
GO
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer)
OUTPUT Inserted.* INTO dbo.Songs_Inserted
VALUES (5, 'Duniya', 'Piyush Mishra');
GO
-- Result of Songs_Inserted table and base table.
select * from dbo.Songs_Inserted;
select * from dbo.Songs;
GO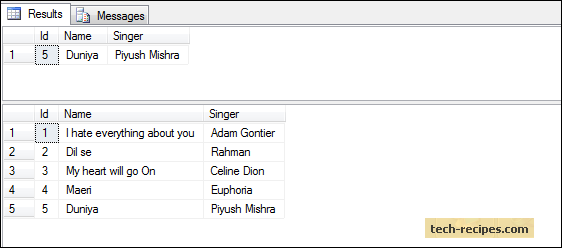
As the results above show, data is inserted into both the tables.
Store Results of an OUTPUT Clause into a Temporary Table
The same goes with a temporary table. Create a temporary table first, and then using an OUTPUT INTO clause, insert the data returned by the OUTPUT clause into a temporary table.
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#Songs_Deleted') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.#Songs_Deleted
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.#Songs_Deleted
(
Id int,
Name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
Singer varchar(50) NOT NULL
)
GO
DELETE from dbo.Songs
OUTPUT deleted.* INTO dbo.#Songs_Deleted
WHERE ID IN (4,5);
GO
-- Result of temporary table and base table.
SELECT * from dbo.#Songs_Deleted;
Select * from dbo.Songs;
Store Results of an OUTPUT Clause into a Table Variable
Nothing changes for table variables as well. Declare a table variable structure the same as a source table. Do not forget to run the entire script at once so that you can see the output inserted into a table variable.
Declare @Songs_Deleted TABLE
(
Id int,
Name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
Singer varchar(50) NOT NULL
)
DELETE from dbo.Songs
OUTPUT deleted.* INTO @Songs_Deleted
WHERE ID IN (1,2);
-- Result of table variable
SELECT * from @Songs_Deleted;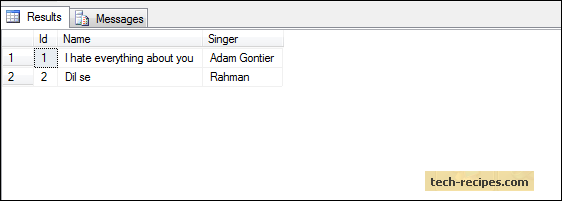
Browse through our SQL server archive articles for more useful information.
A Beginner’s Guide to the OUTPUT Clause in SQL Server的更多相关文章
- Guide to Database Migration from Microsoft SQL Server using MySQL Workbench
http://mysqlworkbench.org/2012/07/migrating-from-ms-sql-server-to-mysql-using-workbench-migration-wi ...
- A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks(转)
A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks Introduction Convolutional neural ...
- (转)A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks Part 2
Adit Deshpande CS Undergrad at UCLA ('19) Blog About A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolution ...
- (转)A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks
Adit Deshpande CS Undergrad at UCLA ('19) Blog About A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolution ...
- A Beginner’s Guide to Eigenvectors, PCA, Covariance and Entropy
A Beginner’s Guide to Eigenvectors, PCA, Covariance and Entropy Content: Linear Transformations Prin ...
- A Beginner's Guide to Paxos
Google Drive: A Beginner's Guide to Paxos The code ideas of Paxos protocol: 1) Optimistic concurrenc ...
- Beginner's Guide to Python-新手指导
Refer English Version: http://wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide New to programming? Python is free ...
- 新手教程之:循环网络和LSTM指南 (A Beginner’s Guide to Recurrent Networks and LSTMs)
新手教程之:循环网络和LSTM指南 (A Beginner’s Guide to Recurrent Networks and LSTMs) 本文翻译自:http://deeplearning4j.o ...
- Photography theory: a beginner's guide(telegraph.co.uk)
By Diane Smyth, Tim Clark, Rachel Segal Hamilton and Lewis Bush 11:00AM BST 09 Jun 2014 Have you r ...
随机推荐
- springboot11 JPA
一.JPA 1. JPA 介绍 JPA是Java Persistence API的简称,中文名Java持久层API,是JDK 5.0注解或XML描述对象-关系表的映射关系,并将运行期的实体对象持久化到 ...
- 团队项目-第四次Scrum 会议
时间:10.26 时长:30分钟 地点:线上 工作情况 团队成员 已完成任务 待完成任务 解小锐 编写project和projectGenerator类 编写下一步的规格说明 陈鑫 采用creator ...
- iOS CGContextRef 画一条直线,仅仅是画一条直线
今天周末休息,想好好补补课,无奈,弄了一上午,全部都是半边拉块的demo,有一种深深的挫败感. 中午睡醒一觉后,又看了一集“奔跑吧兄弟”,然后一下午时间就过去了. 仔细一想,应该是我的补课方法不对:要 ...
- 微信公众号开发java框架:wx4j(入门篇)
导航 入门 http://www.cnblogs.com/2333/p/6617819.html WxServlet介绍 MaterialUtils 素材工具类使用说明 http://www.cnbl ...
- linux常见的编码转换
1.如何界定是utf-8编码还是其他如 ANSI 或者gb2312编码 以“浙”这个汉字为例,用16进制编码查看时,显示 D5 E3 为2个字节,则为 ansi或者gb2312编码 "苏&q ...
- SQLServer对视图或函数’XXX’的更新或插入失败,因其包含派生域或常量域解决
原因:视图view不允许修改. 解决:重新创建一个相同结构内容的表. 解释:因为所创建的视图对其属性值进行了计算的其他形式上的改变,而对视图的更改最终表现为对表的更改而表中不存在视图的某一属性,或属性 ...
- GIS专业分析方法(待更新)
遗传算法 核密度估计 http://blog.163.com/zhuandi_h/blog/static/1802702882012111092743556/ http://blog.csdn.net ...
- bzoj 2618 半平面交模板+学习笔记
题目大意 给你n个凸多边形,求多边形的交的面积 分析 题意\(=\)给你一堆边,让你求半平面交的面积 做法 半平面交模板 1.定义半平面为向量的左侧 2.将所有向量的起点放到一个中心,以中心参照进行逆 ...
- SQL触发器(AFTER和INSTEAD OF)
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/shepherldeng/archive/2010/06/23/1763766.html 何为触发器:触发器是数据库服务器中发生事件时自动执行的特种 ...
- hibernate用配置文件的方式实现orm
本文主要讲用配置文件的方式讲如何把一个对象和数据库中的表关联起来,其实用配置文件本质是和用注解的方式是一样的. 思路:1.写一个domain对象(如Person.java) 2.写这个domain对象 ...
