神经网络第三部分:网络Neural Networks, Part 3: The Network
NEURAL NETWORKS, PART 3: THE NETWORK
We have learned about individual neurons in the previous section, now it’s time to put them together to form an actual neural network.
The idea is quite simple – we line multiple neurons up to form a layer, and connect the output of the first layer to the input of the next layer. Here is an illustration:
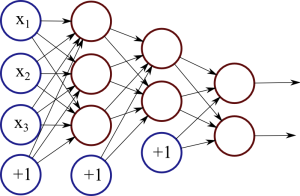 Figure 1: Neural network with two hidden layers.
Figure 1: Neural network with two hidden layers.
Each red circle in the diagram represents a neuron, and the blue circles represent fixed values. From left to right, there are four columns: the input layer, two hidden layers, and an output layer. The output from neurons in the previous layer is directed into the input of each of the neurons in the next layer.
We have 3 features (vector space dimensions) in the input layer that we use for learning: x1, x2 and x3. The first hidden layer has 3 neurons, the second one has 2 neurons, and the output layer has 2 output values. The size of these layers is up to you – on complex real-world problems we would use hundreds or thousands of neurons in each layer.
The number of neurons in the output layer depends on the task. For example, if we have a binary classification task (something is true or false), we would only have one neuron. But if we have a large number of possible classes to choose from, our network can have a separate output neuron for each class.
The network in Figure 1 is a deep neural network, meaning that it has two or more hidden layers, allowing the network to learn more complicated patterns. Each neuron in the first hidden layer receives the input signals and learns some pattern or regularity. The second hidden layer, in turn, receives input from these patterns from the first layer, allowing it to learn “patterns of patterns” and higher-level regularities. However, the cost of adding more layers is increased complexity and possibly lower generalisation capability, so finding the right network structure is important.
Implementation
I have implemented a very simple neural network for demonstration. You can find the code here: SimpleNeuralNetwork.java
The first important method is initialiseNetwork(), which sets up the necessary structures:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public void initialiseNetwork(){ input = new double[1 + M]; // 1 is for the bias hidden = new double[1 + H]; weights1 = new double[1 + M][H]; weights2 = new double[1 + H]; input[0] = 1.0; // Setting the bias hidden[0] = 1.0;} |
M is the number of features in the feature vectors, H is the number of neurons in the hidden layer. We add 1 to these, since we also use the bias constants.
We represent the input and hidden layer as arrays of doubles. For example, hidden[i] stores the current output value of the i-th neuron in the hidden layer.
The first set of weights, between the input and hidden layer, are stored as a matrix. Each of the (1+M) neurons in the input layer connects toH neurons in the hidden layer, leading to a total of (1+M)×Hweights. We only have one output neuron, so the second set of weights between hidden and output layers is technically a (1+H)×1 matrix, but we can just represent that as a vector.
The second important function is forwardPass(), which takes an input vector and performs the computation to reach an output value.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public void forwardPass(){ for(int j = 1; j < hidden.length; j++){ hidden[j] = 0.0; for(int i = 0; i < input.length; i++){ hidden[j] += input[i] * weights1[i][j-1]; } hidden[j] = sigmoid(hidden[j]); } output = 0.0; for(int i = 0; i < hidden.length; i++){ output += hidden[i] * weights2[i]; } output = sigmoid(output);} |
The first for-loop calculates the values in the hidden layer, by multiplying the input vector with the weight vector and applying the sigmoid function. The last part calculates the output value by multiplying the hidden values with the second set of weights, and also applying the sigmoid.
Evaluation
To test out this network, I have created a sample dataset using the database at quandl.com. This dataset contains sociodemographic statistics for 141 countries:
- Population density (per suqare km)
- Population growth rate (%)
- Urban population (%)
- Life expectancy at birth (years)
- Fertility rate (births per woman)
- Infant mortality (deaths per 1000 births)
- Enrolment in tertiary education (%)
- Unemployment (%)
- Estimated control of corruption (score)
- Estimated government effectiveness (score)
- Internet users (per 100)
Based on this information, we want to train a neural network that can predict whether the GDP per capita is more than average for that country (label 1 if it is, 0 if it’s not).
I’ve separated the dataset for training (121 countries) and testing (40 countries). The values have been normalised, by subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation, using a script from a previous article. I’ve also pre-trained a model that we can load into this network and evaluate. You can download these from here: original data,training data, test data, pretrained model.
You can then execute the neural network (remember to compile and link the binaries):
|
1
|
java neuralnet.SimpleNeuralNetwork data/model.txt data/countries-classify-gdp-normalised.test.txt |
The output should be something like this:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
Label: 0 Prediction: 0.01Label: 0 Prediction: 0.00Label: 1 Prediction: 0.99Label: 0 Prediction: 0.00...Label: 0 Prediction: 0.20Label: 0 Prediction: 0.01Label: 1 Prediction: 0.99Label: 0 Prediction: 0.00Accuracy: 0.9 |
The network is in verbose mode, so it prints out the labels and predictions for each test item. At the end, it also prints out the overall accuracy. The test data contains 14 positive and 26 negative examples; a random system would have had accuracy 50%, whereas a biased system would have accuracy 65%. Our network managed 90%, which means it has learned some useful patterns in the data.
In this case we simply loaded a pre-trained model. In the next section, I will describe how to learn this model from some training data.
from: http://www.marekrei.com/blog/neural-networks-part-3-network/
神经网络第三部分:网络Neural Networks, Part 3: The Network的更多相关文章
- NEURAL NETWORKS, PART 3: THE NETWORK
NEURAL NETWORKS, PART 3: THE NETWORK We have learned about individual neurons in the previous sectio ...
- 深度学习笔记(三 )Constitutional Neural Networks
一. 预备知识 包括 Linear Regression, Logistic Regression和 Multi-Layer Neural Network.参考 http://ufldl.stanfo ...
- 深度学习笔记 (一) 卷积神经网络基础 (Foundation of Convolutional Neural Networks)
一.卷积 卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Networks)是一种在空间上共享参数的神经网络.使用数层卷积,而不是数层的矩阵相乘.在图像的处理过程中,每一张图片都可以看成一张“ ...
- 递归神经网络(RNN,Recurrent Neural Networks)和反向传播的指南 A guide to recurrent neural networks and backpropagation(转载)
摘要 这篇文章提供了一个关于递归神经网络中某些概念的指南.与前馈网络不同,RNN可能非常敏感,并且适合于过去的输入(be adapted to past inputs).反向传播学习(backprop ...
- 卷积神经网络用语句子分类---Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification 学习笔记
读了一篇文章,用到卷积神经网络的方法来进行文本分类,故写下一点自己的学习笔记: 本文在事先进行单词向量的学习的基础上,利用卷积神经网络(CNN)进行句子分类,然后通过微调学习任务特定的向量,提高性能. ...
- [C4W1] Convolutional Neural Networks - Foundations of Convolutional Neural Networks
第一周 卷积神经网络(Foundations of Convolutional Neural Networks) 计算机视觉(Computer vision) 计算机视觉是一个飞速发展的一个领域,这多 ...
- Neural Networks for Machine Learning by Geoffrey Hinton (1~2)
机器学习能良好解决的问题 识别模式 识别异常 预測 大脑工作模式 人类有个神经元,每一个包括个权重,带宽要远好于工作站. 神经元的不同类型 Linear (线性)神经元 Binary thresho ...
- [C3] Andrew Ng - Neural Networks and Deep Learning
About this Course If you want to break into cutting-edge AI, this course will help you do so. Deep l ...
- 吴恩达《深度学习》-课后测验-第一门课 (Neural Networks and Deep Learning)-Week 3 - Shallow Neural Networks(第三周测验 - 浅层神 经网络)
Week 3 Quiz - Shallow Neural Networks(第三周测验 - 浅层神经网络) \1. Which of the following are true? (Check al ...
随机推荐
- [JAVA][RCP]Clean project之后报错:java.lang.RuntimeException: No application id has been found.
Clean了一下Project,然后就报了如下错误 !ENTRY com.release.nattable.well_analysis 2 0 2015-11-20 17:04:44.609 !MES ...
- 使用WinSetupFromUSB来U盘安装WINDOWS2003
今天用UltraISO制作WINDOWS2003的U盘的安装启动,在安装系统的时候发现错误提示“INF file txtsetup.sif is corrupt or missing .status ...
- LoadRunner 学习笔记(2)VuGen运行时设置Run-Time Setting
定义:在Vugen中Run-Time Setting是用来设置脚本运行时所需要的相关选项
- windows 2008 怎么对外开放端口
服务器已经运行了程序,但是android客户端连接不上, 网上提示说用: start /min telnet 192.168.3.42 2121 查看,但是我的提示tenlet找不到命令,估计是端口的 ...
- Jquery.linq 使用示例
http://linqjs.codeplex.com/ /*Linq JS*/ //range var aa = Enumerable.range(1, 10).toArray(); var kk = ...
- linux常用命令详解
Linux提供了大量的命令,利用它可以有效地完成大量的工作,如磁盘操作.文件存取.目录操作.进程管理.文件权限设定等.所以,在Linux系统上工作离不开使用系统提供的命令.要想真正理解Linux系统, ...
- 【BZOJ】【1529】 【POI2005】ska Piggy banks
本来以为是tarjan缩点……但是64MB的空间根本不足以存下原图和缩点后的新图.所以呢……并查集= = orz hzwer MLE的tarjan: /************************ ...
- 无法从 ajax.googleapis.com 下载问题
除FQ外的解决办法: 打开目录 C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc,修改 hosts 文件,添加一行 : 127.0.0.1 ajax.googleapis.com 打开I ...
- window dos 设置网络
->netsh ->pushd interface ip ->set address "本地连接" static 192.168.1.2 255.255.255. ...
- 【Entity Framework】 Entity Framework资料汇总
Fluent API : http://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Search/zh-CN?query=Fluent%20API&Refinement=95& ...
