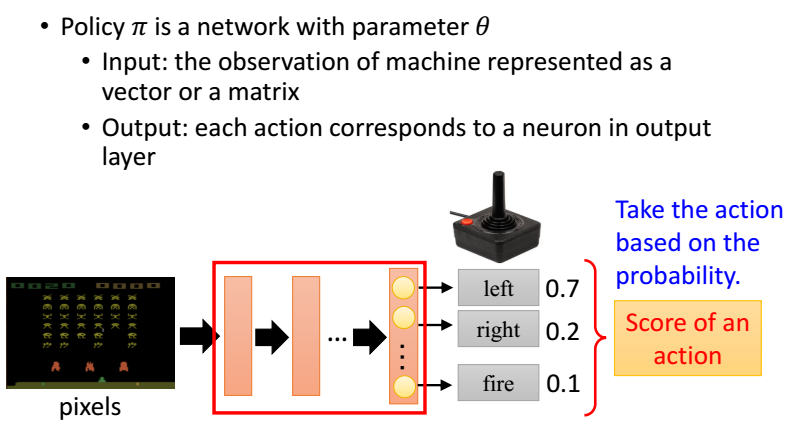
强化学习--Policy Gradient
Policy Gradient综述:
Policy Gradient,通过学习当前环境,直接给出要输出的动作的概率值。
Policy Gradient 不是单步更新,只能等玩完一个epoch,再更新参数,采取动作与动作评价是同一个函数,所以是一个on-policy
Policy Gradient 需要计算每一个state的期望reward,这个期望reward通过整个epoch的reward_list计算。所以只能等玩完1个epoch才能更新。
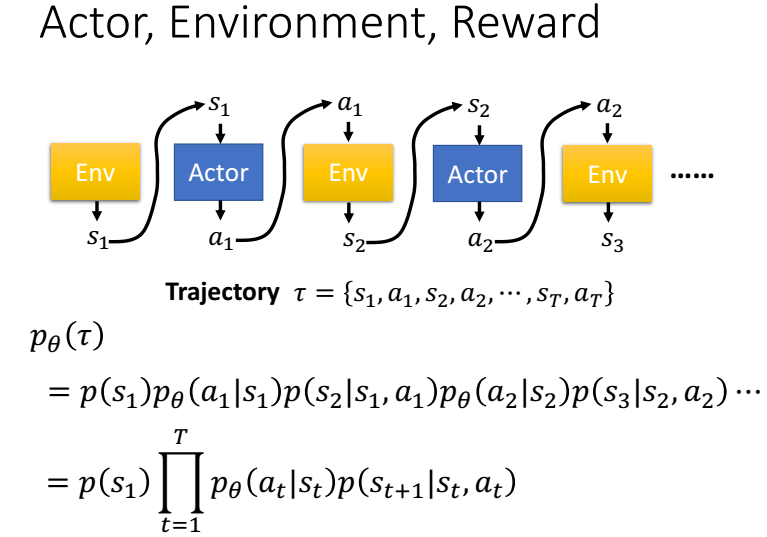
数学推导
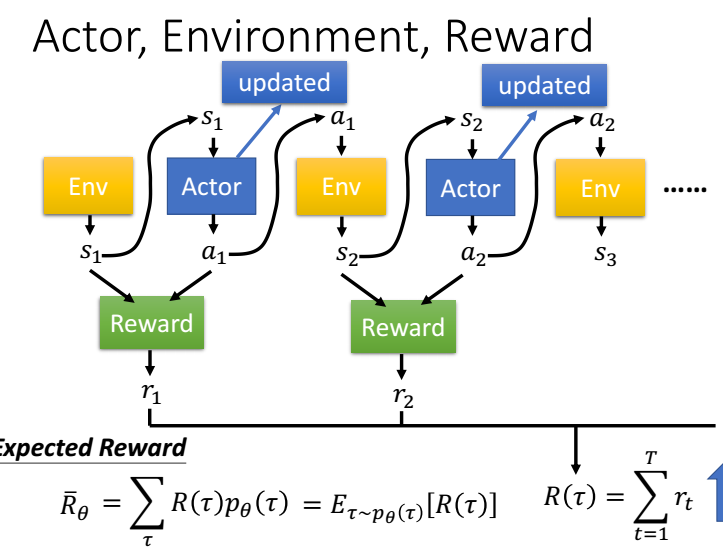
最大化R,,用梯度下降,需要求R的梯度。
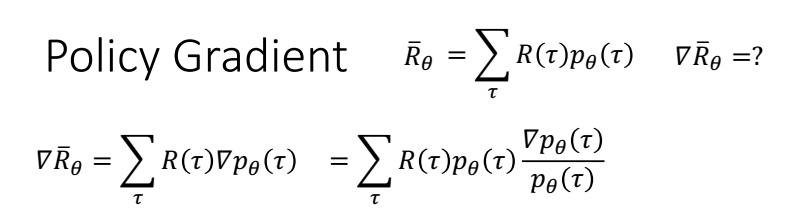
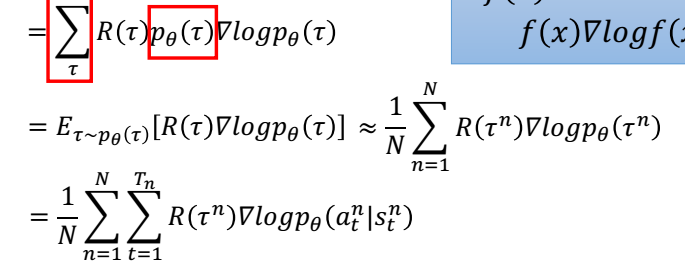
vt的计算
Policy Gradient 不是单步更新,只能等玩完一个epoch,得到每个epoch的observation_list \ action\_list reward_list
学习的时候,根据这三个list更新参数,其中下图公式中的vt 根据reward_list算出来。
vt的计算
Policy Gradient 不是单步更新,只能等玩完一个epoch,得到每个epoch的observation_list \ action\_list reward_list
学习的时候,根据这三个list更新参数,其中下图公式中的vt 根据reward_list算出来。
实现方式
神经网络分类模型,但是在算loss 的时候,logloss需要乘一个系数vt,这个系数与奖励Reward相关,如果采用当前动作,
在接下来的游戏中获得的Reward越大,那么在更新梯度的时候加大当前梯度下降的速度。
算法步骤
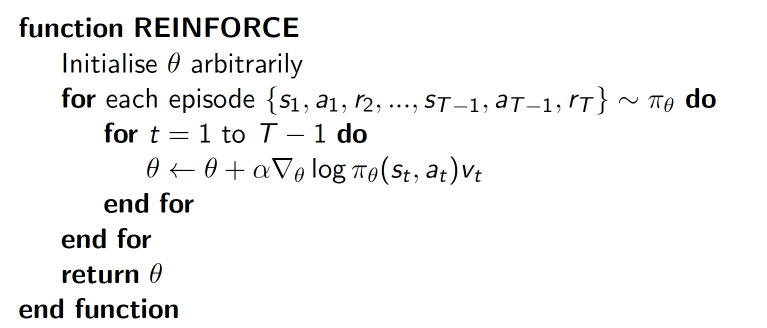
vt的计算
Policy Gradient 不是单步更新,只能等玩完一个epoch,得到每个epoch的observation_list \ action\_list reward_list
学习的时候,根据这三个list更新参数,其中下图公式中的vt 根据reward_list算出来。
代码
"""
This part of code is the reinforcement learning brain, which is a brain of the agent.
All decisions are made in here. Policy Gradient, Reinforcement Learning. View more on my tutorial page: https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/ Using:
Tensorflow: 1.0
gym: 0.8.0
""" import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf # reproducible
np.random.seed(1)
tf.set_random_seed(1) class PolicyGradient:
def __init__(
self,
n_actions,
n_features,
learning_rate=0.01,
reward_decay=0.95,
output_graph=False,
):
self.n_actions = n_actions
self.n_features = n_features
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay #每个epoch的observation \ action\ reward
self.ep_obs, self.ep_as, self.ep_rs = [], [], [] self._build_net() self.sess = tf.Session() if output_graph:
# $ tensorboard --logdir=logs
# http://0.0.0.0:6006/
# tf.train.SummaryWriter soon be deprecated, use following
tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", self.sess.graph) self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) def _build_net(self):
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
self.tf_obs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name="observations")
self.tf_acts = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, ], name="actions_num")
self.tf_vt = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, ], name="actions_value")
# fc1
layer = tf.layers.dense(
inputs=self.tf_obs,
units=10,
activation=tf.nn.tanh, # tanh activation
kernel_initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0, stddev=0.3),
bias_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1),
name='fc1'
)
# fc2
all_act = tf.layers.dense(
inputs=layer,
units=self.n_actions,
activation=None,
kernel_initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0, stddev=0.3),
bias_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1),
name='fc2'
) self.all_act_prob = tf.nn.softmax(all_act, name='act_prob') # use softmax to convert to probability with tf.name_scope('loss'):
# to maximize total reward (log_p * R) is to minimize -(log_p * R), and the tf only have minimize(loss)
neg_log_prob = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=all_act, labels=self.tf_acts) # this is negative log of chosen action
# or in this way:
# neg_log_prob = tf.reduce_sum(-tf.log(self.all_act_prob)*tf.one_hot(self.tf_acts, self.n_actions), axis=1)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(neg_log_prob * self.tf_vt) # reward guided loss with tf.name_scope('train'):
self.train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(self.lr).minimize(loss) def choose_action(self, observation):
prob_weights = self.sess.run(self.all_act_prob, feed_dict={self.tf_obs: observation[np.newaxis, :]})
action = np.random.choice(range(prob_weights.shape[1]), p=prob_weights.ravel()) # select action w.r.t the actions prob
return action def store_transition(self, s, a, r):
self.ep_obs.append(s)
self.ep_as.append(a)
self.ep_rs.append(r) def learn(self):
# discount and normalize episode reward
discounted_ep_rs_norm = self._discount_and_norm_rewards() # train on episode
self.sess.run(self.train_op, feed_dict={
self.tf_obs: np.vstack(self.ep_obs), # shape=[None, n_obs]
self.tf_acts: np.array(self.ep_as), # shape=[None, ]
self.tf_vt: discounted_ep_rs_norm, # shape=[None, ]
}) self.ep_obs, self.ep_as, self.ep_rs = [], [], [] # empty episode data
return discounted_ep_rs_norm def _discount_and_norm_rewards(self):
# discount episode rewards
discounted_ep_rs = np.zeros_like(self.ep_rs)
running_add = 0
for t in reversed(range(0, len(self.ep_rs))):
running_add = running_add * self.gamma + self.ep_rs[t]
discounted_ep_rs[t] = running_add # normalize episode rewards
discounted_ep_rs -= np.mean(discounted_ep_rs)
discounted_ep_rs /= np.std(discounted_ep_rs)
return discounted_ep_rs
强化学习--Policy Gradient的更多相关文章
- 深度增强学习--Policy Gradient
前面都是value based的方法,现在看一种直接预测动作的方法 Policy Based Policy Gradient 一个介绍 karpathy的博客 一个推导 下面的例子实现的REINFOR ...
- 强化学习(十三) 策略梯度(Policy Gradient)
在前面讲到的DQN系列强化学习算法中,我们主要对价值函数进行了近似表示,基于价值来学习.这种Value Based强化学习方法在很多领域都得到比较好的应用,但是Value Based强化学习方法也有很 ...
- 深度学习课程笔记(十三)深度强化学习 --- 策略梯度方法(Policy Gradient Methods)
深度学习课程笔记(十三)深度强化学习 --- 策略梯度方法(Policy Gradient Methods) 2018-07-17 16:50:12 Reference:https://www.you ...
- 强化学习读书笔记 - 13 - 策略梯度方法(Policy Gradient Methods)
强化学习读书笔记 - 13 - 策略梯度方法(Policy Gradient Methods) 学习笔记: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, Richa ...
- Deep Learning专栏--强化学习之从 Policy Gradient 到 A3C(3)
在之前的强化学习文章里,我们讲到了经典的MDP模型来描述强化学习,其解法包括value iteration和policy iteration,这类经典解法基于已知的转移概率矩阵P,而在实际应用中,我们 ...
- 深度学习-深度强化学习(DRL)-Policy Gradient与PPO笔记
Policy Gradient 初始学习李宏毅讲的强化学习,听台湾的口音真是费了九牛二虎之力,后来看到有热心博客整理的很细致,于是转载来看,当作笔记留待复习用,原文链接在文末.看完笔记再去听一听李宏毅 ...
- 强化学习七 - Policy Gradient Methods
一.前言 之前我们讨论的所有问题都是先学习action value,再根据action value 来选择action(无论是根据greedy policy选择使得action value 最大的ac ...
- 深度学习课程笔记(十四)深度强化学习 --- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)
深度学习课程笔记(十四)深度强化学习 --- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) 2018-07-17 16:54:51 Reference: https://b ...
- DRL之:策略梯度方法 (Policy Gradient Methods)
DRL 教材 Chpater 11 --- 策略梯度方法(Policy Gradient Methods) 前面介绍了很多关于 state or state-action pairs 方面的知识,为了 ...
随机推荐
- Maven项目Update Project后JRE System Library自动变回1.5解决办法
最近在搭建Spring Boot项目<一步步搭建 Spring Boot maven 框架的工程>的时候,虽然设置JRE System Library为1.8,但是,当我 用 Maven ...
- php获取数据库结构
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- Vue的双向数据绑定原理是什么?
vue.js是采用数据劫持结合发布者-订阅者模式的方式,通过Object.defineProperty()来劫持各个属性的setter,getter,在数据变动时发布消息给订阅者,触发相应的监听回调. ...
- EC2(elastic compute cloud,弹性计算云,又称EC2实例)
(一)定义:EC2和实例EC2(elastic compute cloud,弹性计算云),即云中的虚拟服务器. 是用于在云中创建和运行虚拟机的 Amazon Web 服务.简言之,EC2就是一部具有无 ...
- Vue main.js 文件中全局组件注册部分
在 \src\components\index.js 文件中export组件 import HeaderList from './HeaderList' import HeaderMenu from ...
- linux dmesg 查看系统故障信息
dmesg 可以查看linux 内核信息 dmesg’命令设备故障的诊断是非常重要的.在‘dmesg’命令的帮助下进行硬件的连接或断开连接操作时,我们可以看到硬件的检测或者断开连接的信息.‘dmesg ...
- MySQL 多源复制(Mulit-Source Replication)
MySQL多源复制方案 看复制源Master_1的同步状态:SHOW SLAVE STATUS FOR CHANNEL 'Master_1'\G 查看复制源Master_2的同步状态:S ...
- Nginx的基础配置管理
Nginx的基本功能 1.静态资源的web服务器 2.http协议反向代理服务器 3.tcp/udp协议的请求转发 安装nginx yum install epel-release yum insta ...
- 在IIS6中FLV不能播放
故障:Flv文件在本地能播放,上传到服务器上不能播放. 原因:WIN2003加强了IIS6的MIME验证,一切未注册扩展文件格式统统显示404错误. 解决办法:在IIS服务器上添加对.FLV文件的支持 ...
- drf频率组件
1.简介 控制访问频率的组件 2.使用 手写一个自定义频率组件 import time #频率限制 #自定义频率组件,return True则可以访问,return False则不能访问 class ...
