Stacks And Queues
栈和队列
大型填坑现场,第一部分的还没写,以上。
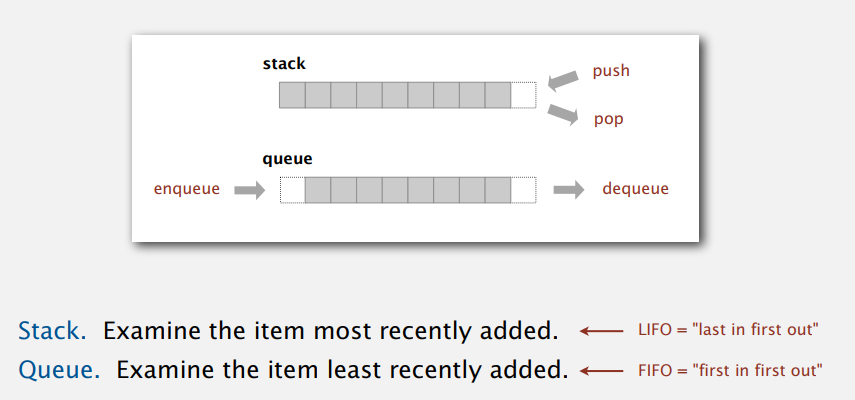
栈和队列是很基础的数据结构,前者后进先出,后者先进先出,如下图:
下面开始将客户端和具体实现分开,这样有两个好处:一是客户端不知道实现的细节,但同时也会有很多不同实现来选择;二是实现方面也不知道客户端需求的细节,但同时很多客户端可以也重用一样的实现。接口就像把二者连接起来的桥梁。

stacks
栈的操作主要是出栈入栈,热身来一个放字符串的栈。
stack API

栈的测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
StackOfStrings stack = new StackOfString();
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String s = StdIn.readString();
if (s.equals("-")) StdOut.print(stack.pop());
else stack.push(s);
}
}
stack linked-list
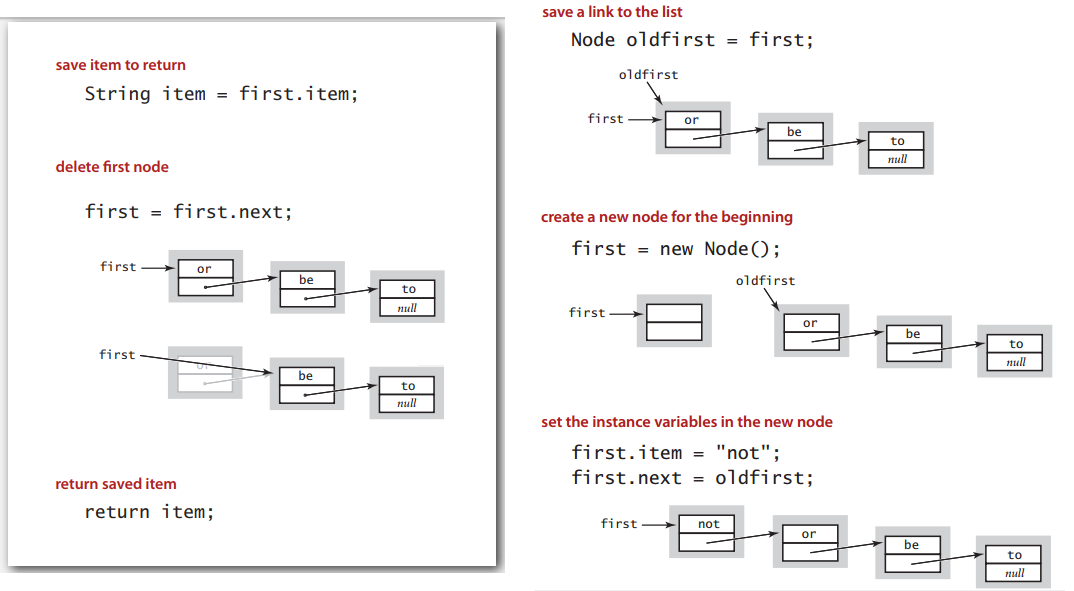
用链表来实现栈,出栈入栈示意:
代码:
public class LinkedStackOfStrings {
private Node first = null;
private class Node {
String item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
public void push(String item) {
Node oldfirst = first;
first = new Node();
first.item = item;
first.next = oldfirst;
}
public String pop() {
String item = first.item;
first = first.next;
return item;
}
}
链表实现出入栈都只要常数的时间,一直都很快,相对的会需要较多额外的空间。参考 Analysis of Algorithms 最后的内存部分。
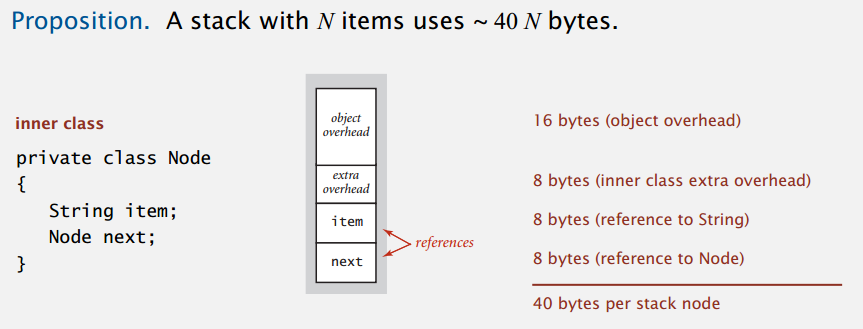
上面算的是每个栈节点需要的空间,不包括其中的字符串,字符串开销算在客户端上。
stack array
很常见的,能用链表实现,一般还有用数组实现的版本。

详细代码在下节的变长数组里,这里说下数组游离(loitering)问题。
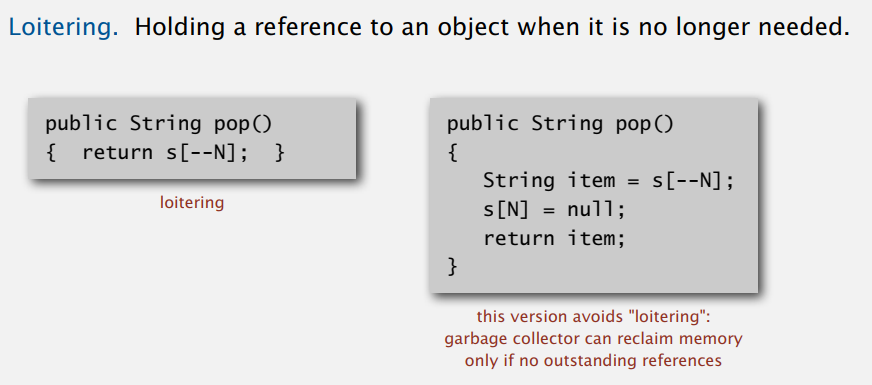
出栈时把不要的元素置空,垃圾回收机制才能回收不用的内存。
resizing arrays
用数组来实现栈,在栈满的时候需要自动扩大数组容量,这样才符合前面设计的 API。具体即栈满时再创建一个容量更大的数组,然后把栈里原有的元素复制过去。
要是每次创建个容量加一的数组,往栈里加入前 N 个元素,光是每次复制元素就会是平方级别(1 + 2 + ... + N ~ \(N^{2}/2\))。于是栈满的时候,我们直接把数组容量扩大两倍,这时往栈里加入前 N 个元素复制成本 2 + 4 + 8 + ... + N 和 N 成正比。
public ResizingArrayStackOfStrings() {
s = new String[1];
}
public void push(String item) {
if (N == s.length) {
resize(2 * s.length);
}
s[N++] = item;
}
private void resize(int capacity) {
String[] copy = new String[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
copy[i] = s[i];
}
s = copy;
}
当栈里元素数目小于数组容量时,缩减数组长度可以节省空间,缩减操作是有必要的。一样的,每次缩减一格的代价太大,但是当栈里只剩一半元素时缩减到一半也会有问题。因为前面是栈满就扩大到两倍,如果在阈值处频繁地出入栈,就会频繁地扩大缩减还有复制来复制去。于是这里等栈里只剩四分之一的时候再缩减到一半,所以数组会一直处在 25% 到 100% 满之间。
public String pop() {
String item = s[--N];
s[N] = null;
if (N > 0 && N == s.length / 4) {
resize(s.length / 2);
}
return item;
}
数组实现的栈,在时间性能方面,因为可能有数组的扩大缩减,不能保证每次都很快,但是平摊下来,出入栈操作也能在常数时间内完成。在空间方面,会比用链表实现的栈好点:
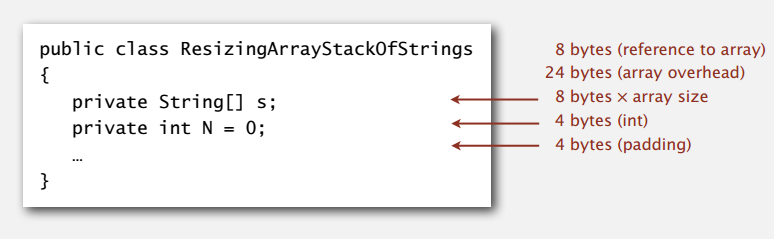
栈里有 N 个元素时,使用空间介于 ~8N 和 ~32N 比特(栈 25%~100% 满),同样的没有算上存在客户端上字符串本身。参考 Analysis of Algorithms 最后的内存部分。
综合来看,链表实现的栈保证每个操作都很快,相对的需要多一点空间;数组实现的需要的空间少点,平摊下来出入栈也算是能在常数时间内完成。所以选择哪个实现,要看具体的应用需求,比如对操作时间要求很严格就选链表,等下关键时刻碰上数组扩大缩减;要是不需要保证每次都很快,那选数组会省空间。
queues
仍然,以一个放字符串的队列为例。
queue API

queue linked-list
链表实现的队列,出入队示意:
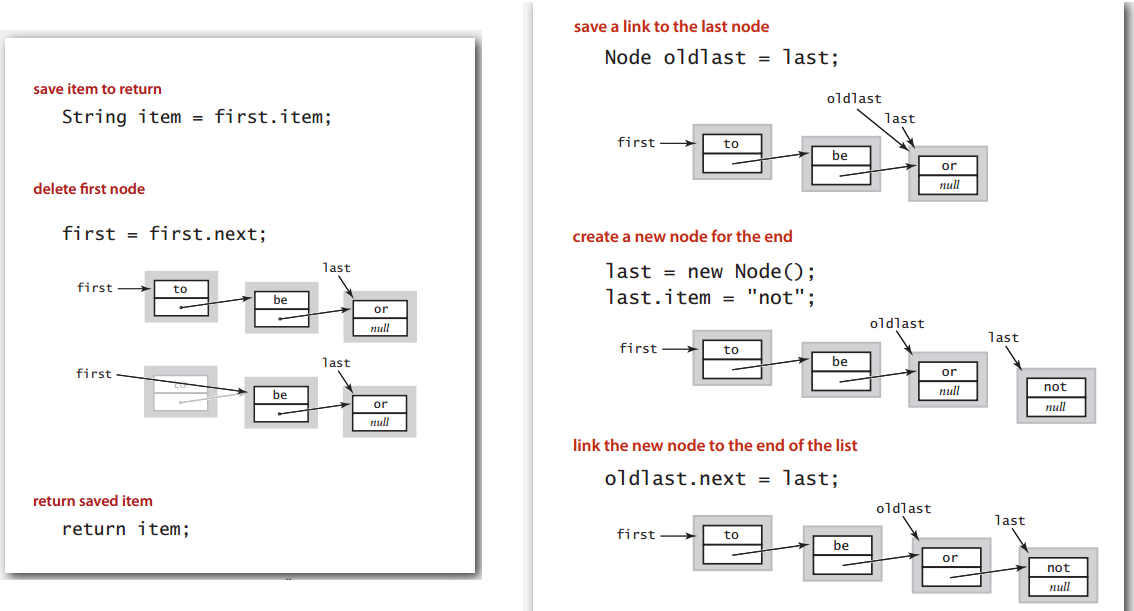
代码:
public class LinkedQueueOfStrings {
private Node first, last;
private class Node {
String item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
public void enqueue(String item) {
Node oldlast = last;
last = new Node();
last.item = item;
last.next = null;
if (isEmpty()) first = last;
else oldlast.next = last;
}
public String dequeue() {
String item = first.item;
first = first.next;
if (isEmpty()) last = null;
return item;
}
}
首尾两个节点在队列为空时要注意下。
queue array
数组实现不详述。

generics
上面我们实现了放字符串的栈和队列,要是现在需要放整数的呢,复制代码改下类型未免有点让人不太满意,泛型(generic)可以很好地解决这个问题。
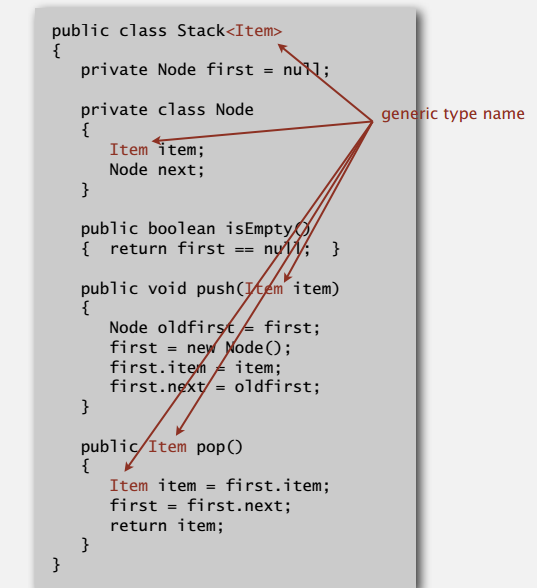
把链表实现的栈改成上面那样,客户端就可以用这个栈存放任意类型的元素,只要你在声明时指定类型(Item)。另外,原始数据类型(short, int, long, float, double,, byte, boolean)需要借助对应的包装类,例如放整型的栈:Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();。
但是有一个问题,Java 不允许创建泛型数组,所以数组实现的栈里面:
s = new Item[capacity]; // can't
s = (Item[]) new Object[capacity]; // ok
下面那行可行但编译时还是会有警告,不过也没什么关系。
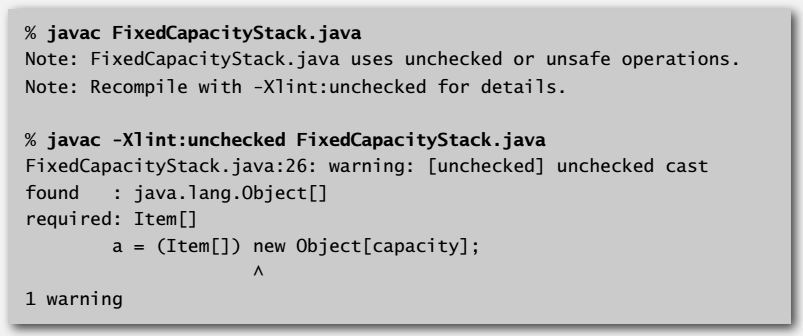
关于 Java 不允许创建泛型数组,可以看看链接 1 和链接 2 的说明。其实我不是很懂,总觉得可以用泛型数组的话,也不会写成会有问题的例子那样。
iterators
对可迭代的(iterable)对象,Java 支持更优雅的 foreach 遍历。可迭代的对象含有一个返回迭代器(iterator)的方法,迭代器里又含有方法 hasNext() 和 next()(还有 remove(),课程不建议使用)。上面的栈变成下面这样,就可以用 foreach 来遍历。
linkes-list
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Stack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
...
public Iterator<item> iterator() {
return new ListIterator();
}
private class ListIterator implements Iterator<Item> {
private Node current = first;
public boolean hasNext() {
return current != null;
}
public void remove() {
/* not supported */
}
public Item next() {
Item item = current.item;
current = current.next;
return item;
}
}
}
array
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Stack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
...
public Iterator<item> iterator() {
return new ReverseArrayIterator();
}
private class ReverseArrayIterator implements Iterator<Item> {
private int i = N;
public boolean hasNext() {
return i > 0;
}
public remove() {
/* not supported */
}
public Item next() {
return s[--i];
}
}
}
applications
课程建议我们在课程中不要使用 Java 里实现的栈和队列,除非你真的理解它们到底做了什么,因为商业实现的代码功能丰富,API 比较臃肿,未必像你想的那么有效率。
然后列了很多栈的应用,像网页回退,Word 中的撤销,编译器中的函数调用等等,特别介绍了算术表达式计算的双栈法。
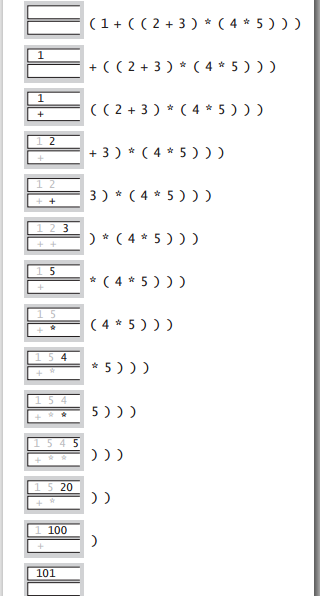
- 操作数:压入操作数栈。
- 操作符:压入操作符栈。
- 左括号:忽略。
- 右括号:弹出两个操作数和一个操作符进行运算,结果再压入操作数栈。
代码:
public class Evaluate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> ops = new Stack<String>();
Stack<Double> vals = new Stack<Double>();
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String s = StdIn.readString();
if (s.equals("(")) ;
else if (s.equals("+")) ops.push(s);
else if (s.equals("-")) ops.push(s);
else if (s.equals(")")) {
String op = ops.pop();
if (op.equals("+")) vals.push(vals.pop() + vals.pop());
else if (op.equals("*")) vals.push(vals.pop() * vals.pop());
}
else vals.push(Double.parseDouble(s));
}
StdOut.println(vals.pop());
}
}
这又是 Dijkstra 发明的方法,一步步从里到外把括号里的运算换成运算结果,最后即是整个算术表达式的结果。在此基础上,可以拓展到更多的其它运算,上面的例子只有加法和乘法,操作数可以交换,要是减法和除法的话,得把先 pop() 出的减(除)数储下来,再 pop() 出被减(除)数来减(除)去前者,不能像上面那么写。更有建立优先级矩阵,可以处理不带括号的表达式等。
另外,把上面表达式的操作符放操作数后面,变成 (1 ((2 3 +) (4 5 +)*)+),Dijkstra 的双栈法也会算出同样的结果,而且这时式中的括号是冗余的,去掉也会得到正确的答案。原始的表达式操作符在操作数中间,称为中缀表达式,这里是它的后缀表达式或者叫逆波兰表示。
Stacks And Queues的更多相关文章
- Cracking the Coding Interview(Stacks and Queues)
Cracking the Coding Interview(Stacks and Queues) 1.Describe how you could use a single array to impl ...
- 612.1.003 ALGS4 | Stacks and Queues
Algorithm | Coursera - by Robert Sedgewick Type the code one by one! 不要拜读--只写最有感触的!而不是仅仅做一个笔记摘录员,那样毫 ...
- CCI_chapter 3 Stacks and Queues
3.1Describe how you could use a single array to implement three stacks for stack 1, we will use [0, ...
- uva 120 stacks of flapjacks ——yhx
Stacks of Flapjacks Background Stacks and Queues are often considered the bread and butter of data ...
- UVa120 - Stacks of Flapjacks
Time limit: 3.000 seconds限时:3.000秒 Background背景 Stacks and Queues are often considered the bread and ...
- Uva 120 - Stacks of Flapjacks(构造法)
UVA - 120 Stacks of Flapjacks Time Limit: 3000MS Memory Limit: Unknown 64bit IO Format: %lld &a ...
- stacks and queues--codility
lesson 7: stacks and queues 1. Nesting 2. StoneWall 3. Brackets 4. Finsh lesson 7: stacks and queues ...
- Stacks of Flapjacks(栈)
Stacks of Flapjacks Background Stacks and Queues are often considered the bread and butter of data ...
- Stacks of Flapjacks
Stacks of Flapjacks Background Stacks and Queues are often considered the bread and butter of data s ...
随机推荐
- C#语法之泛型
前面两篇C#语法主要是回顾委托相关的.这篇主要回顾了泛型. 一.为什么要有泛型? 我们在写一些方法时可能会方法名相同,参数类型不同的方法,这种叫做重载.如果只是因为参数类型不同里面做的业务逻辑都是相同 ...
- 小白学习之Code First(四)
code first :约定大于配置(通过配置实体重写约定) 通过两种方式配置实体:DataAnnotations Fluent Api System.ComponentModel.Data ...
- [转]使用C#进行图像处理的几种方法
最近做监控图像由彩色变灰处理的时候发现图像处理过程中,很慢很慢代码如下: int Height = this.picInfo.Image.Height; int ...
- Myeclipse安装与破解
安装包+破解包 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1G4mYsTOMDixyr2UmdqqY5A 提取码:a2n8 红色框框内的是安装包,蓝色框框内的是破解包 安装过程中比较简单, ...
- Windows标准控件
学习目的 学习创建, 使用Windows标准控件(按钮, 滚动条, 静态控件, 列表框, 编辑框, 组合框); 学习使用子窗口控件操作函数(EnableWindow, MoveWindow, SetW ...
- 纠错帖:Zuul & Spring Cloud Gateway & Linkerd性能对比 (转载)
纠错帖:Zuul & Spring Cloud Gateway & Linkerd性能对比 Spring Cloud Spring Cloud Spring Cloud Gatew ...
- LeetCode CombinationSum
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int> > combinationSum(vector<int> &cand ...
- UOJ#410. 【IOI2018】会议
传送门 首先可以设 \(f[l][r]\) 表示 \([l,r]\) 的答案 设 \(x\) 为区间 \([l,r]\) 的最大值的位置,那么 \(f[l][r] = min(f[l][x-1]+h[ ...
- bootstrap前端框架使用总结分享
1.bootstrap 排版 全局样式style.css: 1.移除body的margin声明 2.设置body的背景色为白色 3.为排版设置了基本的字体.字号和行高 4.设置全局链接颜色,且当链接处 ...
- 【MUI框架】学习笔记整理 Day 2
参考整理自MUI官网 http://dev.dcloud.net.cn/mui/ui/ (1)numbox(数字输入框) mui提供了数字输入框控件,可直接输入数字,也可以点击“+”.“-”按钮变换当 ...
