JavaScript数据结构——链表的实现与应用
链表用来存储有序的元素集合,与数组不同,链表中的元素并非保存在连续的存储空间内,每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的指针构成。当要移动或删除元素时,只需要修改相应元素上的指针就可以了。对链表元素的操作要比对数组元素的操作效率更高。下面是链表数据结构的示意图:
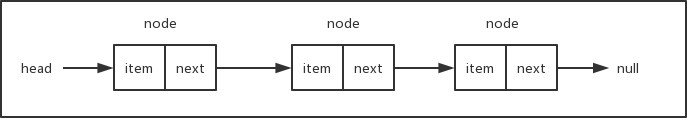
要实现链表数据结构,关键在于保存head元素(即链表的头元素)以及每一个元素的next指针,有这两部分我们就可以很方便地遍历链表从而操作所有的元素。可以把链表想象成一条锁链,锁链中的每一个节点都是相互连接的,我们只要找到锁链的头,整条锁链就都可以找到了。让我们来看一下具体的实现方式。
首先我们需要一个辅助类,用来描述链表中的节点。这个类很简单,只需要两个属性,一个用来保存节点的值,一个用来保存指向下一个节点的指针。
let Node = function (element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
};
下面是我们链表类的基本骨架:
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.length = 0;
this.head = null;
}
append (element) {} // 向链表中添加节点
insert (position, element) {} // 在链表的指定位置插入节点
removeAt (position) {} // 删除链表中指定位置的元素,并返回这个元素的值
remove (element) {} // 删除链表中对应的元素
indexOf (element) {} // 在链表中查找给定元素的索引
getElementAt (position) {} // 返回链表中索引所对应的元素
isEmpty () {} // 判断链表是否为空
size () {} // 返回链表的长度
getHead () {} // 返回链表的头元素
clear () {} // 清空链表
toString () {} // 辅助方法,按指定格式输出链表中的所有元素,方便测试验证结果
}
让我们从查找链表元素的方法getElementAt()开始,因为后面我们会多次用到它。
getElementAt (position) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < position; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
首先判断参数position的边界值,如果值超出了索引的范围(小于0或者大于length - 1),则返回null。我们从链表的head开始,遍历整个链表直到找到对应索引位置的节点,然后返回这个节点。是不是很简单?和所有有序数据集合一样,链表的索引默认从0开始,只要找到了链表的头(所以我们必须在LinkedList类中保存head值),然后就可以遍历找到索引所在位置的元素。
有了getElementAt()方法,接下来我们就可以很方便地实现append()方法,用来在链表的尾部添加新节点。
append (element) {
let node = new Node(element);
// 如果当前链表为空,则将head指向node
if (this.head === null) this.head = node;
else {
// 否则,找到链表尾部的元素,然后添加新元素
let current = this.getElementAt(this.length - 1);
current.next = node;
}
this.length++;
}
如果链表的head为null(这种情况表示链表为空),则直接将head指向新添加的元素。否则,通过getElementAt()方法找到链表的最后一个节点,将该节点的next指针指向新添加的元素。新添加的元素的next指针默认为null,链表最后一个元素的next值为null。将节点挂到链表上之后,不要忘记将链表的长度加1,我们需要通过length属性来记录链表的长度。
接下来我们要实现insert()方法,可以在链表的任意位置添加节点。
insert (position, element) {
// position不能超出边界值
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
let node = new Node(element);
if (position === 0) {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
else {
let previous = this.getElementAt(position - 1);
node.next = previous.next;
previous.next = node;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
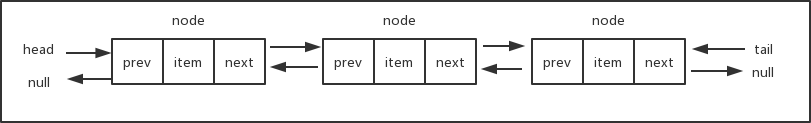
首先也是要判断参数position的边界值,不能越界。当position的值为0时,表示要在链表的头部插入新节点,对应的操作如下图所示。将新插入节点的next指针指向现在的head,然后更新head的值为新插入的节点。
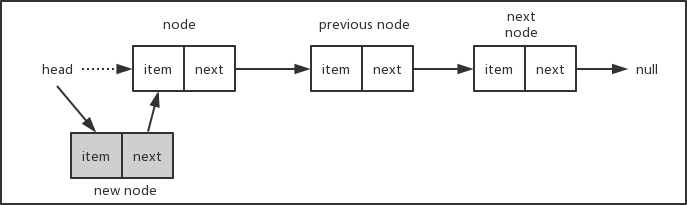
如果要插入的节点在链表的中间或者尾部,对应的操作如下图。假设链表长度为3,要在位置2插入新节点,我们首先找到位置2的前一个节点previous node,将新节点new node的next指针指向previous node的next所对应的节点,然后再将previous node的next指针指向new node,这样就把新节点挂到链表中了。考虑一下,当插入的节点在链表的尾部,这种情况也是适用的。而如果链表为空,即链表的head为null,则参数position会超出边界条件,从而insert()方法会直接返回false。

最后,别忘了更新length属性的值,将链表的长度加1。
按照相同的方式,我们可以很容易地写出removeAt()方法,用来删除链表中指定位置的节点。
removeAt (position) {
// position不能超出边界值
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
let current = this.head;
if (position === 0) this.head = current.next;
else {
let previous = this.getElementAt(position - 1);
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
下面两张示意图说明了从链表头部和其它位置删除节点的情况。
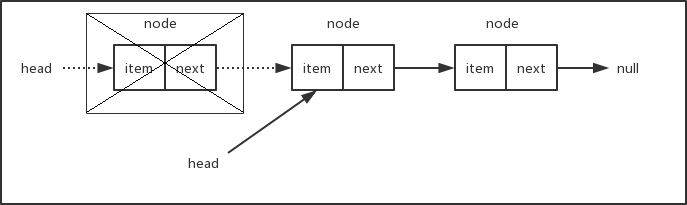
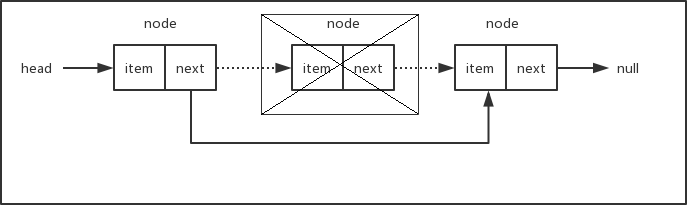
如果要删除的节点为链表的头部,只需要将head移到下一个节点即可。如果当前链表只有一个节点,那么下一个节点为null,此时将head指向下一个节点等同于将head设置成null,删除之后链表为空。如果要删除的节点在链表的中间部分,我们需要找出position所在位置的前一个节点,将它的next指针指向position所在位置的下一个节点。总之,删除节点只需要修改相应节点的指针,使断开位置左右相邻的节点重新连接上。被删除的节点由于再也没有其它部分的引用而被丢弃在内存中,等待垃圾回收器来清除。有关JavaScript垃圾回收器的工作原理,可以查看这里。
最后,别忘了将链表的长度减1。
下面我们来看看indexOf()方法,该方法返回给定元素在链表中的索引位置。
indexOf (element) {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (current.element === element) return i;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
我们从链表的头部开始遍历,直到找到和给定元素相同的元素,然后返回对应的索引号。如果没有找到对应的元素,则返回-1。
链表类中的其它方法都比较简单,就不再分部讲解了,下面是完整的链表类的代码:
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.length = 0;
this.head = null;
}
append (element) {
let node = new Node(element);
// 如果当前链表为空,则将head指向node
if (this.head === null) this.head = node;
else {
// 否则,找到链表尾部的元素,然后添加新元素
let current = this.getElementAt(this.length - 1);
current.next = node;
}
this.length++;
}
insert (position, element) {
// position不能超出边界值
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
let node = new Node(element);
if (position === 0) {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
else {
let previous = this.getElementAt(position - 1);
node.next = previous.next;
previous.next = node;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
removeAt (position) {
// position不能超出边界值
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
let current = this.head;
if (position === 0) this.head = current.next;
else {
let previous = this.getElementAt(position - 1);
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
remove (element) {
let index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
indexOf (element) {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (current.element === element) return i;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
getElementAt (position) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < position; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
isEmpty () {
// return this.head === null;
return this.length === 0;
}
size () {
return this.length;
}
getHead () {
return this.head;
}
clear () {
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
toString () {
let current = this.head;
let s = '';
while (current) {
let next = current.next;
next = next ? next.element : 'null';
s += `[element: ${current.element}, next: ${next}] `;
current = current.next;
}
return s;
}
}
LinkedList
在isEmpty()方法中,我们可以根据length是否为0来判断链表是否为空,当然也可以根据head是否为null来进行判断,前提是所有涉及到链表节点添加和移除的方法都要正确地更新length和head。toString()方法只是为了方便测试而编写的,我们来看看几个测试用例:
let linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.append(10);
linkedList.append(15);
linkedList.append(20); console.log(linkedList.toString()); linkedList.insert(0, 9);
linkedList.insert(2, 11);
linkedList.insert(5, 25);
console.log(linkedList.toString()); console.log(linkedList.removeAt(0));
console.log(linkedList.removeAt(1));
console.log(linkedList.removeAt(3));
console.log(linkedList.toString()); console.log(linkedList.indexOf(20)); linkedList.remove(20); console.log(linkedList.toString()); linkedList.clear();
console.log(linkedList.size());
下面是执行结果:
双向链表
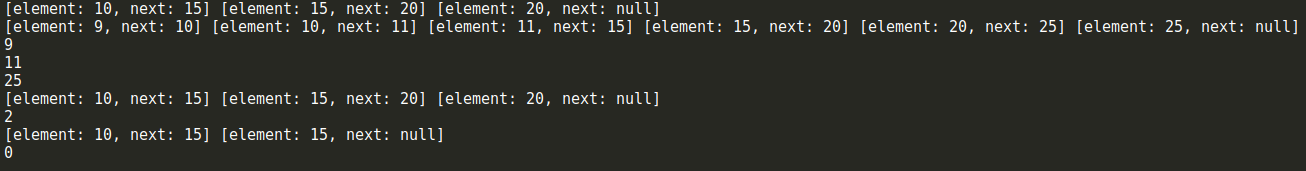
上面链表中每一个元素只有一个next指针,用来指向下一个节点,这样的链表称之为单向链表,我们只能从链表的头部开始遍历整个链表,任何一个节点只能找到它的下一个节点,而不能找到它的上一个节点。双向链表中的每一个元素拥有两个指针,一个用来指向下一个节点,一个用来指向上一个节点。在双向链表中,除了可以像单向链表一样从头部开始遍历之外,还可以从尾部进行遍历。下面是双向链表的数据结构示意图:
由于双向链表具有单向链表的所有特性,因此我们的双向链表类可以继承自前面的单向链表类,不过辅助类Node需要添加一个prev属性,用来指向前一个节点。
let Node = function (element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
};
下面是继承自LinkedList类的双向链表类的基本骨架:
class DoubleLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this.tail = null;
}
}
先来看看append()方法的实现。当链表为空时,除了要将head指向当前添加的节点外,还要将tail也指向当前要添加的节点。当链表不为空时,直接将tail的next指向当前要添加的节点node,然后修改node的prev指向旧的tail,最后修改tail为新添加的节点。我们不需要从头开始遍历整个链表,而通过tail可以直接找到链表的尾部,这一点比单向链表的操作要更方便。最后将length的值加1,修改链表的长度。
append (element) {
let node = new Node(element);
// 如果链表为空,则将head和tail都指向当前添加的节点
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}
else {
// 否则,将当前节点添加到链表的尾部
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++;
}
由于双向链表可以从链表的尾部往前遍历,所以我们修改了getElementAt()方法,对基类中单向链表的方法进行了改写。当要查找的元素的索引号大于链表长度的一半时,从链表的尾部开始遍历。
getElementAt (position) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
// 从后往前遍历
if (position > Math.floor(this.length / 2)) {
let current = this.tail;
for (let i = this.length - 1; i > position; i--) {
current = current.prev;
}
return current;
}
// 从前往后遍历
else {
return super.getElementAt(position);
}
}
有两种遍历方式,从前往后遍历调用的是基类单向链表里的方法,从后往前遍历需要用到节点的prev指针,用来查找前一个节点。
我们同时还需要修改insert()和removeAt()这两个方法。记住,与单向链表唯一的区别就是要同时维护head和tail,以及每一个节点上的next和prev指针。
insert (position, element) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 插入到尾部
if (position === this.length) this.append(element);
else {
let node = new Node(element);
// 插入到头部
if (position === 0) {
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}
else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
}
// 插入到中间位置
else {
let current = this.getElementAt(position);
let previous = current.prev;
node.next = current;
node.prev = previous;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
}
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
removeAt (position) {
// position不能超出边界值
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
let current = this.head;
let previous;
// 移除头部元素
if (position === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
this.head.prev = null;
if (this.length === 1) this.tail = null;
}
// 移除尾部元素
else if (position === this.length - 1) {
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
}
// 移除中间元素
else {
current = this.getElementAt(position);
previous = current.prev;
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
操作过程中需要判断一些特殊情况,例如链表的头和尾,以及当前链表是否为空等等,否则程序可能会在某些特殊情况下导致越界和报错。下面是一个完整的双向链表类的代码:
class DoubleLinkedList extends LinkedList.LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this.tail = null;
}
append (element) {
let node = new Node(element);
// 如果链表为空,则将head和tail都指向当前添加的节点
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}
else {
// 否则,将当前节点添加到链表的尾部
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++;
}
getElementAt (position) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
// 从后往前遍历
if (position > Math.floor(this.length / 2)) {
let current = this.tail;
for (let i = this.length - 1; i > position; i--) {
current = current.prev;
}
return current;
}
// 从前往后遍历
else {
return super.getElementAt(position);
}
}
insert (position, element) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 插入到尾部
if (position === this.length) this.append(element);
else {
let node = new Node(element);
// 插入到头部
if (position === 0) {
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}
else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
}
// 插入到中间位置
else {
let current = this.getElementAt(position);
let previous = current.prev;
node.next = current;
node.prev = previous;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
}
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
removeAt (position) {
// position不能超出边界值
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
let current = this.head;
let previous;
// 移除头部元素
if (position === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
this.head.prev = null;
if (this.length === 1) this.tail = null;
}
// 移除尾部元素
else if (position === this.length - 1) {
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
}
// 移除中间元素
else {
current = this.getElementAt(position);
previous = current.prev;
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
getTail () {
return this.tail;
}
clear () {
super.clear();
this.tail = null;
}
toString () {
let current = this.head;
let s = '';
while (current) {
let next = current.next;
let previous = current.prev;
next = next ? next.element : 'null';
previous = previous ? previous.element : 'null';
s += `[element: ${current.element}, prev: ${previous}, next: ${next}] `;
current = current.next;
}
return s;
}
}
DoubleLinkedList
我们重写了toString()方法以方便更加清楚地查看测试结果。下面是一些测试用例:
let doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList();
doubleLinkedList.append(10);
doubleLinkedList.append(15);
doubleLinkedList.append(20);
doubleLinkedList.append(25);
doubleLinkedList.append(30);
console.log(doubleLinkedList.toString());
console.log(doubleLinkedList.getElementAt(1).element);
console.log(doubleLinkedList.getElementAt(2).element);
console.log(doubleLinkedList.getElementAt(3).element); doubleLinkedList.insert(0, 9);
doubleLinkedList.insert(4, 24);
doubleLinkedList.insert(7, 35);
console.log(doubleLinkedList.toString()); console.log(doubleLinkedList.removeAt(0));
console.log(doubleLinkedList.removeAt(1));
console.log(doubleLinkedList.removeAt(5));
console.log(doubleLinkedList.toString());
对应的结果如下:
[element: , prev: null, next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: null] [element: , prev: null, next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: null] [element: , prev: null, next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: ] [element: , prev: , next: null]
循环链表
顾名思义,循环链表的尾部指向它自己的头部。循环链表可以有单向循环链表,也可以有双向循环链表。下面是单向循环链表和双向循环链表的数据结构示意图:
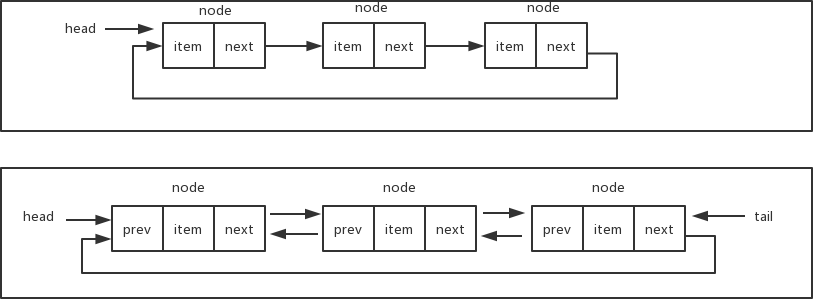
在实现循环链表时,需要确保最后一个元素的next指针指向head。下面是单向循环链表的完整代码:
class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList.LinkedList {
constructor () {
super();
}
append (element) {
let node = new LinkedList.Node(element);
if (this.head === null) this.head = node;
else {
let current = this.getElementAt(this.length - 1);
current.next = node;
}
node.next = this.head; // 将新添加的元素的next指向head
this.length++;
}
insert (position, element) {
// position不能超出边界值
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
let node = new LinkedList.Node(element);
if (position === 0) {
node.next = this.head;
let current = this.getElementAt(this.length - 1);
current.next = node;
this.head = node;
}
else {
let previous = this.getElementAt(position - 1);
node.next = previous.next;
previous.next = node;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
removeAt (position) {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
let current = this.head;
if (position === 0) this.head = current.next;
else {
let previous = this.getElementAt(position - 1);
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.length--;
if (this.length > 1) {
let last = this.getElementAt(this.length - 1);
last.next = this.head;
}
return current.element;
}
toString () {
let current = this.head;
let s = '';
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
let next = current.next;
next = next ? next.element : 'null';
s += `[element: ${current.element}, next: ${next}] `;
current = current.next;
}
return s;
}
}
CircularLinkedList
单向循环链表的测试用例:
let circularLinkedList = new CircularLinkedList();
circularLinkedList.append(10);
circularLinkedList.append(15);
circularLinkedList.append(20); console.log(circularLinkedList.toString()); circularLinkedList.insert(0, 9);
circularLinkedList.insert(3, 25);
console.log(circularLinkedList.toString()); console.log(circularLinkedList.removeAt(0));
console.log(circularLinkedList.toString());
对应的测试结果:

下一章我们将介绍如何用JavaScript来实现集合这种数据结构。
JavaScript数据结构——链表的实现与应用的更多相关文章
- JavaScript数据结构——链表
链表:存储有序的元素集合,但不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中不是连续放置的.每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(也称指针或链接)组成. 好处:可以添加或移除任意项,它会按需扩容 ...
- JavaScript数据结构——链表的实现
前面楼主分别讨论了数据结构栈与队列的实现,当时所用的数据结构都是用的数组来进行实现,但是数组有的时候并不是最佳的数据结构,比如在数组中新增删除元素的时候需要将其他元素进行移动,而在javascript ...
- javascript数据结构-链表
gihtub博客地址 链表 是一种物理存储单元上非连续.非顺序的存储结构,它既可以表示线性结构,也可以用于表示非线性结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的.链表由一系列结点(链表中每 ...
- JavaScript数据结构——字典和散列表的实现
在前一篇文章中,我们介绍了如何在JavaScript中实现集合.字典和集合的主要区别就在于,集合中数据是以[值,值]的形式保存的,我们只关心值本身:而在字典和散列表中数据是以[键,值]的形式保存的,键 ...
- JavaScript数据结构——树的实现
在计算机科学中,树是一种十分重要的数据结构.树被描述为一种分层数据抽象模型,常用来描述数据间的层级关系和组织结构.树也是一种非顺序的数据结构.下图展示了树的定义: 在介绍如何用JavaScript实现 ...
- 学习javascript数据结构(二)——链表
前言 人生总是直向前行走,从不留下什么. 原文地址:学习javascript数据结构(二)--链表 博主博客地址:Damonare的个人博客 正文 链表简介 上一篇博客-学习javascript数据结 ...
- 为什么我要放弃javaScript数据结构与算法(第五章)—— 链表
这一章你将会学会如何实现和使用链表这种动态的数据结构,这意味着我们可以从中任意添加或移除项,它会按需进行扩张. 本章内容 链表数据结构 向链表添加元素 从链表移除元素 使用 LinkedList 类 ...
- JavaScript数据结构与算法-链表练习
链表的实现 一. 单向链表 // Node类 function Node (element) { this.element = element; this.next = null; } // Link ...
- 重读《学习JavaScript数据结构与算法-第三版》- 第6章 链表(一)
定场诗 伤情最是晚凉天,憔悴厮人不堪言: 邀酒摧肠三杯醉.寻香惊梦五更寒. 钗头凤斜卿有泪,荼蘼花了我无缘: 小楼寂寞新雨月.也难如钩也难圆. 前言 本章为重读<学习JavaScript数据结构 ...
随机推荐
- Python将pyc转为py
安装pip install uncompyle2, 使用uncompyle2 xxx.pyc > xxx.py
- Python笔记【1】_字符串学习
#!/usr/bin/env/python #-*-coding:utf-8-*- #Author:LingChongShi #查看源码Ctrl+左键 #字符串:通常有单引号“'”.双引号“" ...
- json数据转为对象,一般在前台把数据传回后端中使用 转https://www.cnblogs.com/zxtceq/p/6610214.html
public static JArray GetData2JArray(string url, string key) { string jsonData = HttpHelper.HttpGet(u ...
- 每天学点node系列-http
任何可以使用JavaScript来编写的应用,最终会由JavaScript编写.--Atwood's Law http模块概览 http模块主要用于创建http server服务,并且 支持更多特性 ...
- Ubuntu系统 apt-get update失败解决办法
使用apt-get的时候发现ubuntu和阿里云均已经不提供该版本的源,所以需要找到其他的替代源. 使用的ubuntu版本是14.10,属于非LTS(长期支持版本),因此前一段时间还可以使用apt-g ...
- 9.22考试 crf的数数 题解
这道题当时第一反应是线段树,但没有继续想,因为当时打完第一题打算这道题和第二道题并列做,打完第二道题状压后时间还有两个小时多,先打完暴力再说,打完之后又接着去想,然后想了5分多钟吧,扑街. 然后就发现 ...
- [译]Vulkan教程(33)多重采样
[译]Vulkan教程(33)多重采样 Multisampling 多重采样 Introduction 入门 Our program can now load multiple levels of d ...
- 工作经验之石氏thinking
经常听到N多人说工作经验这个名词:也时常听到人说工作多少年就是多少年工作经验.我听着总觉得有点别扭,感觉他们把这个名词说的太简单了,而且觉得不是工作N年就一定有所谓的工作经验.我觉得归根结底还是在于工 ...
- 用Python玩数据-笔记整理-第一章
第一个程序:print >>>print("Hallo World!") >>>Hallo World! mystring = "Ha ...
- ASP.NET CORE 入门教程(附源码)
ASP.NET CORE 入门教程 第一课 基本概念 基本概念 Asp.Net Core Mvc是.NET Core平台下的一种Web应用开发框架 符合Web应用特点 .NET Core跨平台解决方案 ...
