Spark MLlib基本算法【相关性分析、卡方检验、总结器】
一.相关性分析
1.简介
计算两个系列数据之间的相关性是统计中的常见操作。在spark.ml中提供了很多算法用来计算两两的相关性。目前支持的相关性算法是Pearson和Spearman。Correlation使用指定的方法计算输入数据集的相关矩阵。输出是一个DataFrame,其中包含向量列的相关矩阵。
2.代码实现
package ml
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.{Matrix, Vectors}
import org.apache.spark.ml.stat.Correlation
import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2019/11/28.
*/
object CorrelationDemo {
Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.WARN)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName(s"${this.getClass.getSimpleName}").master("local[2]").getOrCreate()
import spark.implicits._ // 导入,否则无法使用toDF算子
val data = Seq(
Vectors.sparse(4, Seq((0, 1.0), (3, -2.0))),
Vectors.dense(4.0, 5.0, 0.0, 3.0),
Vectors.dense(6.0, 7.0, 0.0, 8.0),
Vectors.sparse(4, Seq((0, 9.0), (3, 1.0)))
)
val df = data.map(Tuple1.apply).toDF("features")
val Row(coeff : Matrix) = Correlation.corr(df, "features").head
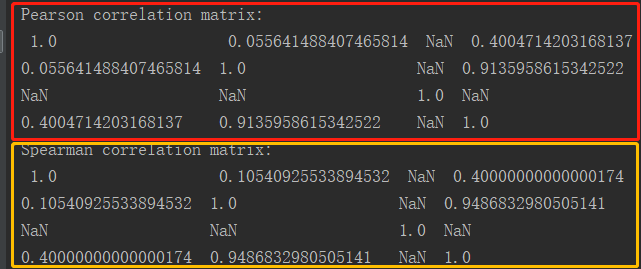
println(s"Pearson correlation matrix:\n $coeff")
df.cache()
val Row(coeff2 : Matrix) = Correlation.corr(df, "features", "spearman").head
println(s"Spearman correlation matrix:\n $coeff2")
}
}
3.源码分析
package org.apache.spark.ml.stat
import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
import org.apache.spark.annotation.{Experimental, Since}
import org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.{SQLDataTypes, Vector}
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.{Vectors => OldVectors}
import org.apache.spark.mllib.stat.{Statistics => OldStatistics}
import org.apache.spark.sql.{DataFrame, Dataset, Row}
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.{StructField, StructType}
/**
* API for correlation functions in MLlib, compatible with DataFrames and Datasets.
*
* The functions in this package generalize the functions in [[org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset#stat]]
* to spark.ml's Vector types.
*/
@Since("2.2.0")
@Experimental
object Correlation {
/**
* :: Experimental ::
* Compute the correlation matrix for the input Dataset of Vectors using the specified method.
* Methods currently supported: `pearson` (default), `spearman`.
*
* @param dataset A dataset or a dataframe
* @param column The name of the column of vectors for which the correlation coefficient needs
* to be computed. This must be a column of the dataset, and it must contain
* Vector objects.
* @param method String specifying the method to use for computing correlation.
* Supported: `pearson` (default), `spearman`
* @return A dataframe that contains the correlation matrix of the column of vectors. This
* dataframe contains a single row and a single column of name
* '$METHODNAME($COLUMN)'.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the column is not a valid column in the dataset, or if
* the content of this column is not of type Vector.
*
* Here is how to access the correlation coefficient:
* {{{
* val data: Dataset[Vector] = ...
* val Row(coeff: Matrix) = Correlation.corr(data, "value").head
* // coeff now contains the Pearson correlation matrix.
* }}}
*
* @note For Spearman, a rank correlation, we need to create an RDD[Double] for each column
* and sort it in order to retrieve the ranks and then join the columns back into an RDD[Vector],
* which is fairly costly. Cache the input Dataset before calling corr with `method = "spearman"`
* to avoid recomputing the common lineage.
*/
@Since("2.2.0")
def corr(dataset: Dataset[_], column: String, method: String): DataFrame = {
val rdd = dataset.select(column).rdd.map {
case Row(v: Vector) => OldVectors.fromML(v)
}
val oldM = OldStatistics.corr(rdd, method)
val name = s"$method($column)"
val schema = StructType(Array(StructField(name, SQLDataTypes.MatrixType, nullable = false)))
dataset.sparkSession.createDataFrame(Seq(Row(oldM.asML)).asJava, schema)
}
/**
* Compute the Pearson correlation matrix for the input Dataset of Vectors.
*/
@Since("2.2.0")
def corr(dataset: Dataset[_], column: String): DataFrame = {
corr(dataset, column, "pearson")
}
}
4.执行结果
二.卡方检验
1.简介
ChiSquareTest针对标签上的每个功能进行Pearson独立性检验。对于每个特征,将(特征,标签)对转换为列矩阵,针对该列矩阵计算卡方统计量。所有标签和特征必须是分类数据。
2.代码实现
package ml
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.Vectors
import org.apache.spark.ml.stat.ChiSquareTest
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2019/11/28.
*/
object ChiSquare {
Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.WARN)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName(s"${this.getClass.getSimpleName}").master("local[2]").getOrCreate()
import spark.implicits._// 导入,否则无法使用toDF算子
val data = Seq(
(0.0, Vectors.dense(0.5, 10.0)),
(0.0, Vectors.dense(1.5, 20.0)),
(1.0, Vectors.dense(1.5, 30.0)),
(0.0, Vectors.dense(3.5, 30.0)),
(0.0, Vectors.dense(3.5, 40.0)),
(1.0, Vectors.dense(3.5, 40.0))
)
val df = data.toDF("label", "features")
val chi = ChiSquareTest.test(df, "features", "label") // 卡方检验
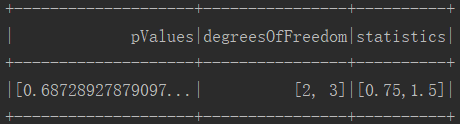
chi.show()
}
}
3.源码分析
package org.apache.spark.ml.stat
import org.apache.spark.annotation.{Experimental, Since}
import org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.{Vector, Vectors, VectorUDT}
import org.apache.spark.ml.util.SchemaUtils
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.{Vectors => OldVectors}
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.{LabeledPoint => OldLabeledPoint}
import org.apache.spark.mllib.stat.{Statistics => OldStatistics}
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import org.apache.spark.sql.functions.col
/**
* :: Experimental ::
*
* Chi-square hypothesis testing for categorical data.
*
* See <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chi-squared_test">Wikipedia</a> for more information
* on the Chi-squared test.
*/
@Experimental
@Since("2.2.0")
object ChiSquareTest {
/** Used to construct output schema of tests */
private case class ChiSquareResult(
pValues: Vector,
degreesOfFreedom: Array[Int],
statistics: Vector)
/**
* Conduct Pearson's independence test for every feature against the label. For each feature, the
* (feature, label) pairs are converted into a contingency matrix for which the Chi-squared
* statistic is computed. All label and feature values must be categorical.
*
* The null hypothesis is that the occurrence of the outcomes is statistically independent.
*
* @param dataset DataFrame of categorical labels and categorical features.
* Real-valued features will be treated as categorical for each distinct value.
* @param featuresCol Name of features column in dataset, of type `Vector` (`VectorUDT`)
* @param labelCol Name of label column in dataset, of any numerical type
* @return DataFrame containing the test result for every feature against the label.
* This DataFrame will contain a single Row with the following fields:
* - `pValues: Vector`
* - `degreesOfFreedom: Array[Int]`
* - `statistics: Vector`
* Each of these fields has one value per feature.
*/
@Since("2.2.0")
def test(dataset: DataFrame, featuresCol: String, labelCol: String): DataFrame = {
val spark = dataset.sparkSession
import spark.implicits._
SchemaUtils.checkColumnType(dataset.schema, featuresCol, new VectorUDT)
SchemaUtils.checkNumericType(dataset.schema, labelCol)
val rdd = dataset.select(col(labelCol).cast("double"), col(featuresCol)).as[(Double, Vector)]
.rdd.map { case (label, features) => OldLabeledPoint(label, OldVectors.fromML(features)) }
val testResults = OldStatistics.chiSqTest(rdd)
val pValues: Vector = Vectors.dense(testResults.map(_.pValue))
val degreesOfFreedom: Array[Int] = testResults.map(_.degreesOfFreedom)
val statistics: Vector = Vectors.dense(testResults.map(_.statistic))
spark.createDataFrame(Seq(ChiSquareResult(pValues, degreesOfFreedom, statistics)))
}
}
4.执行结果
三.总结器
1.简介
其提供矢量列汇总统计DataFrame的Summarizer。可以度量按列的最大值、最小值、平均值、方差和非零个数,以及总数。
2.代码实现
package ml
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.Vectors
import org.apache.spark.ml.stat.Summarizer._ // 导入总结器
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
import org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.Vector
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2019/11/28.
*/
object Summary {
Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.WARN)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName(s"${this.getClass.getSimpleName}").master("local[2]").getOrCreate()
import spark.implicits._// 导入,否则无法使用toDF算子
/**
* features数据个数不一致时报错:
* Dimensions mismatch when merging with another summarizer. Expecting 3 but got 2.
*/
val data = Seq(
(Vectors.dense(2.0, 3.0, 5.0), 1.0),
(Vectors.dense(4.0, 6.0, 8.0), 2.0)
)
val df = data.toDF("features", "weight")
/**
* 计算均值时考虑权重
* [(2.0*1+4.0*2)/3,(3.0*1+6.0*2)/3,(5.0*1+8.0*2)/3) = [3.333333333333333,5.0,7.0]
* 方差的计算不考虑权重
*/
val (meanVal, varianceVal) = df.select(metrics("mean", "variance").summary($"features", $"weight").as("summary"))
.select("summary.mean", "summary.variance")
.as[(Vector, Vector)].first()
println(s"with weight:mean = ${meanVal},variance = ${varianceVal}")
/**
* 计算均值,无权重
* [(2.0+4.0)/2,(3.0+6.0)/2,(5.0+8.0)/2) = [3.0,4.5,6.5]
*/
val (meanVal2, varianceVal2) = df.select(mean($"features"), variance($"features"))
.as[(Vector, Vector)].first()
println(s"with weight:mean = ${meanVal2}, variance = ${varianceVal2}")
}
}
3.源码分析
/**
* Tools for vectorized statistics on MLlib Vectors.
*
* The methods in this package provide various statistics for Vectors contained inside DataFrames.
*
* This class lets users pick the statistics they would like to extract for a given column. Here is
* an example in Scala:
* {{{
* import org.apache.spark.ml.linalg._
* import org.apache.spark.sql.Row
* val dataframe = ... // Some dataframe containing a feature column and a weight column
* val multiStatsDF = dataframe.select(
* Summarizer.metrics("min", "max", "count").summary($"features", $"weight")
* val Row(Row(minVec, maxVec, count)) = multiStatsDF.first()
* }}}
*
* If one wants to get a single metric, shortcuts are also available:
* {{{
* val meanDF = dataframe.select(Summarizer.mean($"features"))
* val Row(meanVec) = meanDF.first()
* }}}
*
* Note: Currently, the performance of this interface is about 2x~3x slower than using the RDD
* interface.
*/
@Experimental
@Since("2.3.0")
object Summarizer extends Logging { import SummaryBuilderImpl._ /**
* Given a list of metrics, provides a builder that it turns computes metrics from a column.
*
* See the documentation of [[Summarizer]] for an example.
*
* The following metrics are accepted (case sensitive):
* - mean: a vector that contains the coefficient-wise mean.
* - variance: a vector tha contains the coefficient-wise variance.
* - count: the count of all vectors seen.
* - numNonzeros: a vector with the number of non-zeros for each coefficients
* - max: the maximum for each coefficient.
* - min: the minimum for each coefficient.
* - normL2: the Euclidean norm for each coefficient.
* - normL1: the L1 norm of each coefficient (sum of the absolute values).
* @param metrics metrics that can be provided.
* @return a builder.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the metric names is not understood.
*
* Note: Currently, the performance of this interface is about 2x~3x slower then using the RDD
* interface.
*/
@Since("2.3.0")
@scala.annotation.varargs
def metrics(metrics: String*): SummaryBuilder = {
require(metrics.size >= 1, "Should include at least one metric")
val (typedMetrics, computeMetrics) = getRelevantMetrics(metrics)
new SummaryBuilderImpl(typedMetrics, computeMetrics)
} @Since("2.3.0")
def mean(col: Column, weightCol: Column): Column = {
getSingleMetric(col, weightCol, "mean")
} @Since("2.3.0")
def mean(col: Column): Column = mean(col, lit(1.0)) @Since("2.3.0")
def variance(col: Column, weightCol: Column): Column = {
getSingleMetric(col, weightCol, "variance")
} @Since("2.3.0")
def variance(col: Column): Column = variance(col, lit(1.0))
...
4.执行结果

Spark MLlib基本算法【相关性分析、卡方检验、总结器】的更多相关文章
- Spark MLlib回归算法------线性回归、逻辑回归、SVM和ALS
Spark MLlib回归算法------线性回归.逻辑回归.SVM和ALS 1.线性回归: (1)模型的建立: 回归正则化方法(Lasso,Ridge和ElasticNet)在高维和数据集变量之间多 ...
- Spark MLlib之线性回归源代码分析
1.理论基础 线性回归(Linear Regression)问题属于监督学习(Supervised Learning)范畴,又称分类(Classification)或归纳学习(Inductive Le ...
- Spark MLlib回归算法LinearRegression
算法说明 线性回归是利用称为线性回归方程的函数对一个或多个自变量和因变量之间关系进行建模的一种回归分析方法,只有一个自变量的情况称为简单回归,大于一个自变量情况的叫做多元回归,在实际情况中大多数都是多 ...
- spark mllib k-means算法实现
package iie.udps.example.spark.mllib; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import org.apache.spark.SparkC ...
- Spark MLlib架构解析(含分类算法、回归算法、聚类算法和协同过滤)
Spark MLlib架构解析 MLlib的底层基础解析 MLlib的算法库分析 分类算法 回归算法 聚类算法 协同过滤 MLlib的实用程序分析 从架构图可以看出MLlib主要包含三个部分: 底层基 ...
- Spark入门实战系列--8.Spark MLlib(上)--机器学习及SparkMLlib简介
[注]该系列文章以及使用到安装包/测试数据 可以在<倾情大奉送--Spark入门实战系列>获取 .机器学习概念 1.1 机器学习的定义 在维基百科上对机器学习提出以下几种定义: l“机器学 ...
- Spark 实践——基于 Spark MLlib 和 YFCC 100M 数据集的景点推荐系统
1.前言 上接 YFCC 100M数据集分析笔记 和 使用百度地图api可视化聚类结果, 在对 YFCC 100M 聚类出的景点信息的基础上,使用 Spark MLlib 提供的 ALS 算法构建推荐 ...
- Spark MLlib介绍
Spark MLlib介绍 Spark之所以在机器学习方面具有得天独厚的优势,有以下几点原因: (1)机器学习算法一般都有很多个步骤迭代计算的过程,机器学习的计算需要在多次迭代后获得足够小的误差或者足 ...
- FP-Growth in Spark MLLib
并行FP-Growth算法思路 上图的单线程形成的FP-Tree. 分布式算法事实上是对FP-Tree进行分割,分而治之 首先,假设我们只关心...|c这个conditional transactio ...
随机推荐
- JavaMap常用操作
判断key值是否存在 map.containsKey("youkey") 根据key修改value值 map.put("youkey","you ne ...
- SysML——CSE 599W: Systems for ML
CSE 599W: Systems for ML Assignments Materials Projects Schedule Schedule The schedule is tentative ...
- LG5200 「USACO2019JAN」Sleepy Cow Sorting 树状数组
\(\mathrm{Sleepy Cow Sorting}\) 问题描述 LG5200 题解 树状数组. 设\(c[i]\)代表\([1,i]\)中归位数. 显然最终的目的是将整个序列排序为一个上升序 ...
- Gym101667 H. Rock Paper Scissors
将第二个字符串改成能赢对方时对方的字符并倒序后,字符串匹配就是卷积的过程. 那么就枚举字符做三次卷积即可. #include <bits/stdc++.h> struct Complex ...
- pyenv python 多版本管理工具
pyenv fork 自rbenv 以及ruby-build ,然后修改为转为python 使用 venv 以及virtualenv 解决了版本选择的问题,pyenv 同时为我们解决 了python ...
- 数据结构——顺序栈(sequence stack)
/* sequenceStack.c */ /* 栈 先进后出(First In Last Out,FILO)*/ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdl ...
- BBS 03day
目录 BBS_03 day: 自定义标签 过滤器: 文章的点赞,点彩功能: 文章的评论功能 transaction用法: 自定义 标签代码展示: BBS_03 day: 自定义标签 过滤器: --&g ...
- 第01组 Beta冲刺(3/5)
队名:007 组长博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/Linrrui/p/12008397.html 作业博客: https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fz ...
- oracle--DBWN
一,DBWN功能 将脏数据写盘 二,什么情况下会触发DBWN的进程呢? 1) check pointer:有检查点, 2) 脏数据达到阀值:达到buffer内存的10%即要将脏数据写到磁盘: 这就是造 ...
- c# 在DataTable的第一列(指定列)的前面添加一列
c# 在DataTable的第一列(指定列)的前面添加一列 dt.Columns.Add("ID").SetOrdinal(0)
