What's the difference between @Component, @Repository & @Service annotations in Spring?
@Component is equivalent to
<bean>@Service, @Controller , @Repository = {@Component + some more special functionality}
That mean Service,Controller and Repository are functionally the same.
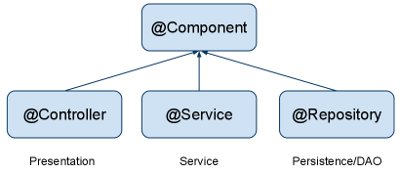
The three annotations are used to separate "Layers" in your application,
- Controllers just do stuff like dispatching, forwarding, calling service methods etc.
- Service Hold business Logic, Calculations etc.
- Repository are the DAOs(Data Access Objects), they access the database directly.
Now you may ask why separate them:(I assume you know AOP-Aspect Oriented Programming)
Lets say you want to Monitors the Activity of the DAO Layer only. You will write an Aspect(A class) class that does some logging before and after every method of your DAO is invoked, you are able to do that using AOP as you have three distinct Layers and are not mixed.
So you can do logging of DAO "around", "before" or "after" the DAO methods. You could do that because you had a DAO in the first place. What you just achieved is Separation of concerns or tasks.
Imagine if there were only one annotation @Controller, then this component will have dispatching, business logic and accessing database all mixed, so dirty code!
Above mentioned is one very common scenario, there are many more use cases of why to use three annotations.
In Spring @Component, @Service, and @Controller. @Component are Stereotype annotations which is used for:
@Controller: where your request mapping from presentation page done i.e. Presentation layer won't go to any other file it goes directly to @Controller class and check for requested path in @RequestMapping annotation which written before method calls if necessary.
@Service: All business logic is here i.e. Data related calculations and all.This annotation of business layer in which our user not directly call persistence method so it will call this methods using this annotation. It will request @Repository as per user request
@Repository:This is Persistence layer(Data Access Layer) of application which used to get data from database. i.e. all the Database related operations are done by repository.
@Component - Annotate your other components (for example REST resource classes) with component stereotype.
From Spring Documentation:
In Spring 2.0 and later, the @Repository annotation is a marker for any class that fulfills the role or stereotype (also known as Data Access Object or DAO) of a repository. Among the uses of this marker is the automatic translation of exceptions.
Spring 2.5 introduces further stereotype annotations: @Component, @Service, and @Controller. @Component is a generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component. @Repository, @Service, and @Controller are specializations of @Component for more specific use cases, for example, in the persistence, service, and presentation layers, respectively.
Therefore, you can annotate your component classes with @Component, but by annotating them with @Repository, @Service, or @Controller instead, your classes are more properly suited for processing by tools or associating with aspects. For example, these stereotype annotations make ideal targets for pointcuts.
Thus, if you are choosing between using @Component or @Service for your service layer, @Service is clearly the better choice. Similarly, as stated above, @Repository is already supported as a marker for automatic exception translation in your persistence layer.
| Annotation | Meaning |
+------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| @Component | generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component |
| @Repository| stereotype for persistence layer |
| @Service | stereotype for service layer |
| @Controller| stereotype for presentation layer (spring-mvc) |Spring 2.5 introduces further stereotype annotations: @Component, @Service and @Controller. @Component serves as a generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component; whereas, @Repository, @Service, and @Controller serve as specializations of @Component for more specific use cases (e.g., in the persistence, service, and presentation layers, respectively). What this means is that you can annotate your component classes with @Component, but by annotating them with @Repository, @Service, or @Controller instead, your classes are more properly suited for processing by tools or associating with aspects. For example, these stereotype annotations make ideal targets for pointcuts. Of course, it is also possible that @Repository, @Service, and @Controller may carry additional semantics in future releases of the Spring Framework. Thus, if you are making a decision between using @Component or @Service for your service layer, @Service is clearly the better choice. Similarly, as stated above, @Repository is already supported as a marker for automatic exception translation in your persistence layer.
@Component – Indicates a auto scan component.
@Repository – Indicates DAO component in the persistence layer.
@Service – Indicates a Service component in the business layer.
@Controller – Indicates a controller component in the presentation layer.
reference :- http://static.springsource.org/spring/docs/3.0.0.M3/reference/html/ch04s12.html
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/25633477/security-configuration-with-spring-boot?rq=1
What's the difference between @Component, @Repository & @Service annotations in Spring?的更多相关文章
- [转]what’s the difference between @Component ,@Repository & @Service annotations in Spring
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/6070314.html @Component is equivalent to <bean> @Servi ...
- 【转载】@Component, @Repository, @Service的区别
@Component, @Repository, @Service的区别 官网引用 引用spring的官方文档中的一段描述: 在Spring2.0之前的版本中,@Repository注解可以标记在任何 ...
- SpringAnnotation注解之@Component,@Repository,@Service,@Controller
@Component:组件,表示此写上了此注解的bean,作为一个组件存在于容器中.这样的话别的地方就可以使用@Resource这个注解来把这个组件作为一个资源来使用了.初始化bean的名字为类名首字 ...
- @Component @Repository @Service @Controller
Spring 2.5 中除了提供 @Component 注释外,还定义了几个拥有特殊语义的注释,它们分别是:@Repository.@Service 和 @Controller.在目前的 Spring ...
- @Component, @Repository, @Service的区别
注解 含义 @Component 最普通的组件,可以被注入到spring容器进行管理 @Repository 作用于持久层 @Service 作用于业务逻辑层 @Controller 作用于表现层(s ...
- @Component, @Repository, @Service,@Controller的区别
@Component, @Service, @Controller, @Repository是spring注解,注解后可以被spring框架所扫描并注入到spring容器来进行管理 @Componen ...
- 从头认识Spring-2.7 自己主动检測Bean(1)-@Component @Repository @Service @Controller
这一章节我们来讨论一下自己主动检測Bean. 1.domain 厨师类: package com.raylee.my_new_spring.my_new_spring.ch02.topic_1_19; ...
- @Component @Controller @Service @Repository@Resourse
@Component @Controller @Service @Repository@Resourse这些全部是Spring提供的注解. 其中@Component用来表示把一个类纳入spring容器 ...
- Spring注解详解@Repository、@Component、@Service 和 @Constroller
概述 注释配置相对于 XML 配置具有很多的优势: 它可以充分利用 Java 的反射机制获取类结构信息,这些信息可以有效减少配置的工作.如使用 JPA 注释配置 ORM 映射时,我们就不需要指定 PO ...
随机推荐
- [SinGuLaRiTy] 高级搜索算法
[SinGuLaRiTy-1039] Copyright (c) SinGuLaRiTy 2017. All Rights Reserved. 迭代加深搜索(ID) 迭代加深搜索,实质上就是限定下界的 ...
- vs更改项目文件夹名称
改完之后会提示找不到.csproj,用文档工具打开.sln文件,把里面找.csproj的路径修改一下就好了
- MySQL学习笔记(一):查询
查询实例: 1.创建数据库并使用: create database school; use school; 2.创建表并插入内容: create table student( Sno char(9) ...
- MATLAB版本(2012b 64bit),在尝试调用svmtrain函数时报错
问题:MATLAB版本(2012b 64bit),在尝试调用svmtrain函数时报错: 解决方案:参照https://blog.csdn.net/TIME_LEAF/article/details/ ...
- Mac的Parallels在启动Win的时候让它独立全屏窗口
这里备忘一下,由于经常需要***,Win方法比较多少,所以使用Parallels在Win下***还是很有必要的,为了使用使用方便,一般让Parallels启动系统之后自动生成一个独立的全窗口,方便来回 ...
- JS 为任意元素添加任意事件的兼容代码
为元素绑定事件(DOM):有两种 addEventListener 和 attachEvent: 相同点: 都可以为元素绑定事件 不同点: 1.方法名不一样 2.参数个数不一样addEventLi ...
- 5A - Matrix
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int n, m, q; struct node { int v; // 节点权值 int r; // 右 ...
- Android 线程+Handler的使用
1.介绍 2.线程的使用 (1)启动 (2)执行 3.xml布局 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> &l ...
- tornado 05 模块继承
tornado 05 模块继承 一.模板继承 #问题:在浏览网页的时候,很多页面上很多部分其实是重复的,那这些部分在每个页面都去写一次吗? #不是,这只不过是通过继承实现的 #模板继承 #在字模板中写 ...
- python的下划线
首先是单下划线开头,这个被常用于模块中,在一个模块中以单下划线开头的变量和函数被默认当作内部函数,如果使用 from a_module import * 导入时,这部分变量和函数不会被导入.不过值得注 ...
