day 7 __new___
1 __new__方法 创建对象
实质是:调用父类的__new__方法创建的对象
class Dog(object):
def __init__(self):
print("---init方法") def __str__(self):
print("---str方法") def __del__(self):
print("---init方法") def __new__(cls):
print("---new方法") dog1 = Dog()
---new方法 #只是创建了类对象,没有初始化,没有实例化对象
2)版本2: cls此时是Dog指向的那个类对象
class Dog(object):
def __init__(self):
print("---init方法") def __str__(self):
print("---str方法") def __del__(self):
print("---init方法") def __new__(cls):
print("---new方法")
print(id(cls)) print(id(Dog))
dog1 = Dog()
38097176
---new方法
38097176
3)版本3:调用 被重写的方法__new__ 创建对象
class Dog(object):
def __init__(self):
print("---init方法") def __str__(self):
print("---str方法") def __del__(self):
print("---del方法") def __new__(cls):
print("---new方法") #对父类的方法重写
# print(id(cls))
object.__new__(cls) #继续调用 被重写的方法 创建对象 #print(id(Dog))
dog1 = Dog()
---new方法
---del方法 #没有执行初始化
4)版本4 __init__ 只负责初始化
class Dog(object):
def __init__(self):
print("---init方法") def __str__(self):
print("---str方法") def __del__(self):
print("---del方法") def __new__(cls): #cls此时是Dog指向的那个类对象
print("---new方法")
# print(id(cls))
return object.__new__(cls) #print(id(Dog))
dog1 = Dog()
---new方法
---init方法
---del方法
5)版本5:优化版
class Dog(object):
#初始化 对象一创建开始执行
def __init__(self):
print("---init方法") def __str__(self):
print("---str方法")
return "返回对象的描述信息" #对象内存销毁时执行
def __del__(self):
print("---del方法") #通过父类的__new__方法创建对象
def __new__(cls): #cls此时是Dog指向的那个类对象
print("---new方法")
# print(id(cls))
return object.__new__(cls) #print(id(Dog))
dog1 = Dog()
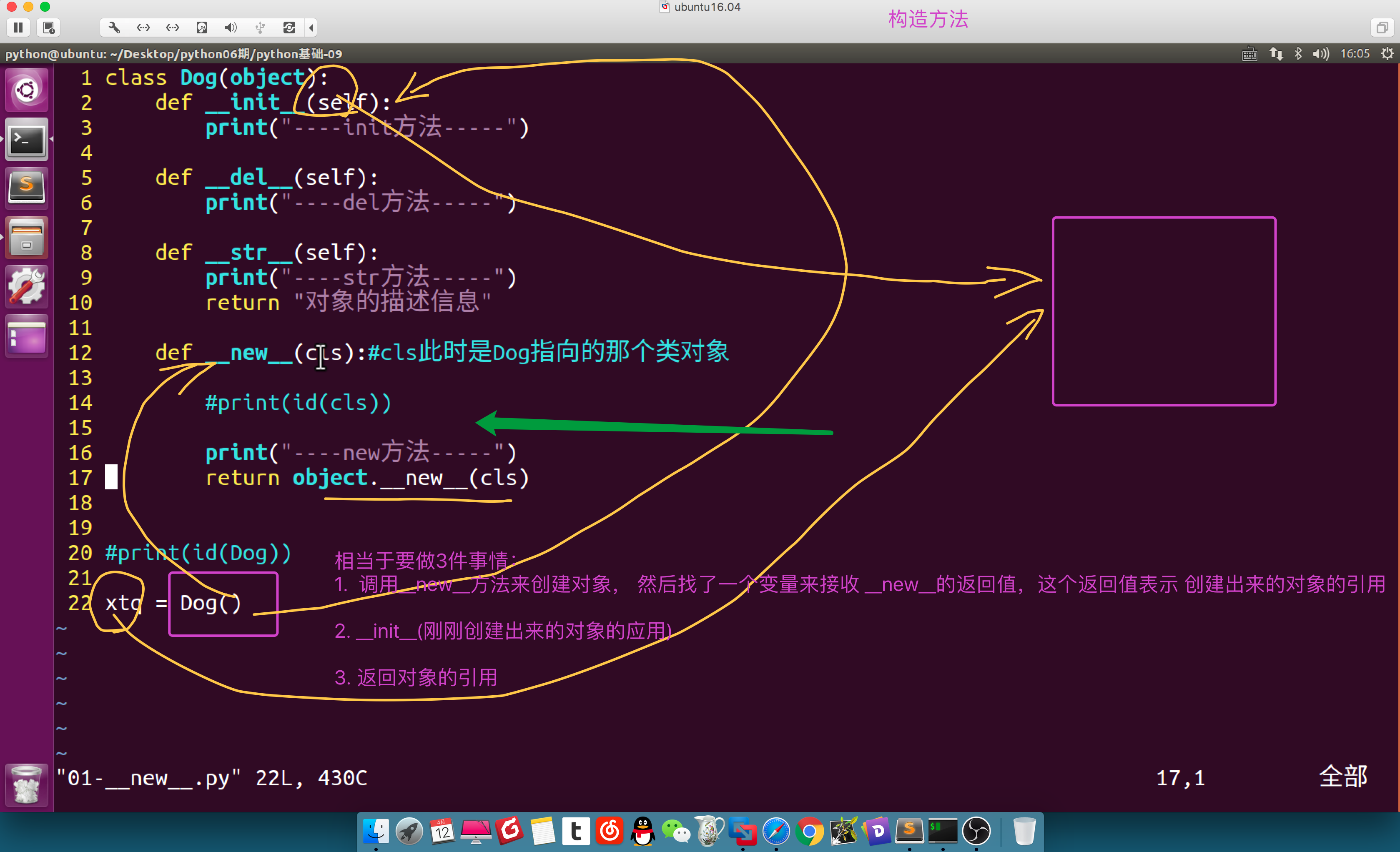
相当于做了3件事情 1.调用__new__方法来创建对象,然后找了一个变量来接受__new__的返回值,这个返回值表示创建出来的对象的引用 2. __init__(刚刚创建出来的对象的引用) 3. 返回对象的引用
构造方法
__new__只负责创建
__init__ 只负责初始化 __new__ 和 __init__相当于C语言的构造方法
2. 创建单例对象
1)什么是单例

class Dog(object):
pass dog1 = Dog()
dog2 = Dog()
print(id(dog1))
print(id(dog2))
139888234067784 #不是同一块内存 不是同一个对象
139888234068008
2)版本2:
class Dog(object):
def __new__(cls):
if xxx :
return object.__new__(cls)
else:
return 上一次创建的对象的引用 dog1 = Dog()
dog2 = Dog()
3)版本3:flag标志
class Dog(object):
__flag = 0
def __new__(cls):
if flag == 0:
flag = 1
return object.__new__(cls)
else:
xxxxx dog1 = Dog()
dog2 = Dog()
4)版本4:类属性 实现
class Dog(object):
__flag = 0 #类属性 当做标志位 类属性是公有的
__instance = 0 #类属性 存储 上一次创建对象的引用
def __new__(cls): #这是一个类方法,cls指向类对象cls
if cls.__flag == 0:
cls.__flag = 1
cls.__instance = object.__new__(cls)
return cls.__instance
else:
return cls.__instance dog1 = Dog()
dog2 = Dog()
#类方法
@classmethod
def add_num(cls): #cls指向类对象
cls.num += 1
#实例方法
def __init__(self,new_name):
self.name = new_name #self.name 是实例属性 ,实例对象独有的
#对类属性 +1
Dog.num += 1
5)版本5:__instance = None
class Dog(object):
__instance = None
def __new__(cls):
if cls.__instance == None:
cls.__instance = object.__new__(cls)
return cls.__instance
else:
return cls.__instance dog1 = Dog()
dog2 = Dog()
6)版本6:查看对应的内存id
class Dog(object):
__instance = None
def __new__(cls):
if cls.__instance == None:
cls.__instance = object.__new__(cls)
return cls.__instance
else:
return cls.__instance dog1 = Dog()
dog2 = Dog()
print(dog1)
print(dog2)
python@ubuntu:~/pythonS6/python基础092$ python3 08-单例对象.py
<__main__.Dog object at 0x7f46d4584828>
<__main__.Dog object at 0x7f46d4584828>
7)版本7:只初始化一次对象
class Dog(object):
__instance = None
def __new__(cls,name):
if cls.__instance == None:
cls.__instance = object.__new__(cls)
return cls.__instance
else:
return cls.__instance def __init__(self,new_name):
self.name = new_name dog1 = Dog("tom") #单例对象 name='tom'
print(id(dog1))
print(dog1.name)
dog2 = Dog("jack") #同一对象 令name='jack'
print(id(dog2))
print(dog2.name)
140546425677920
tom
140546425677920
jack #如何让对象都是tom

8)版本8:添加flag
class Dog(object):
__instance = None
__flag = False
def __new__(cls,name):
if cls.__instance == None:
cls.__instance = object.__new__(cls)
return cls.__instance
else:
return cls.__instance def __init__(self,new_name):
if Dog.__flag == False:
self.name = new_name
Dog.__flag = True dog1 = Dog("tom")
print(id(dog1))
print(dog1.name) #对象里面name = “tom”
dog2 = Dog("jack")
print(id(dog2))
print(dog2.name)
139813073586272
tom
139813073586272
tom #只初始化了一次对象
day 7 __new___的更多相关文章
- 面向对象的封装、继承和多态特性_python
一.面向对象的几个特点 面向对象也称为类,拥有下面几个特点 1.封装特性:利用类的__init__(self)构造方法封装对象 构造方法:__init__(self):在生成对象的时候会自动调用 例子 ...
随机推荐
- python process,queue
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*- from multiprocessing import Process,Queue import os,time,random def write(q): ...
- 深入理解 iOS Rendering Process
本文将从 OpenGL 的角度结合 Apple 官方给出的部分资料,介绍 iOS Rendering Process 的概念及其整个底层渲染管道的各个流程. 相信在理解了 iOS Rendering ...
- yii2.0 联表查询数据库报错:undefined index order_id
1.在查询时加了->select();如下,要加上order_id,即关联的字段(比如:order_id)比如要在select中,否则会报错:undefined index order_id / ...
- canvas二三事之签名板与视频绘制
今天,不知道怎么的就点开了语雀,然后就看到了<HTML5 Canvas 教程>,开始了canvas的研究(学习)之旅. 首先,想到的第一个东西就是签名板,上代码: <canvas i ...
- 基于物理文件的HBase备份还原
前提说明: 1.HBase数据分表,所以备份的粒度是表. 2.备份的内容为Azure的Blob存储. HBase Blob备份 备份时,需要先将表disable,以保持数据一致性. 备份的工具可以用A ...
- PHP面试系列 之Linux(六)---- 面试题整理
1.shell命令 top:查看有哪些系统进程正在运行.该命令提供了实时对系统处理器状态的监控,它能够实时显示系统中各个进程的资源占用情况.该命令可以按照对CPU.内存使用和执行时间对系统任务进程进行 ...
- Luogu_3239 [HNOI2015]亚瑟王
Luogu_3239 [HNOI2015]亚瑟王 vim-markdown 真好用 这个题难了我一下午 第一道概率正而八经\(DP\),还是通过qbxt讲解才会做的. 发现Sengxian真是个dal ...
- 前端基础-HTML的的标签详解
阅读目录 一.head内常用标签 二. HTML语义化 三. 字符实体 四. h系列标签 五. p标签 六. img标签 七. a标签 八. 列表标签 九. table标签 十. form标签 一. ...
- ORA-10485: Real-Time Query cannot be enabled while applying migration redo
情景:利用Dataguard滚动方式升级数据库后,备库应用redo报错:ORA-10485 MRP0: Background Media Recovery terminated with error ...
- 记一次 oracle 12.2 RAC : Transaction recovery: lock conflict caught and ignored
节点一 alert日志: PDB(17):Transaction recovery: lock conflict caught and ignored PDB(17):Transaction reco ...
