【笔记】Python3|使用 PyVis 完成神经网络数据集的可视化
文章目录
版本:
pyvis 0.2.1
应用实例:
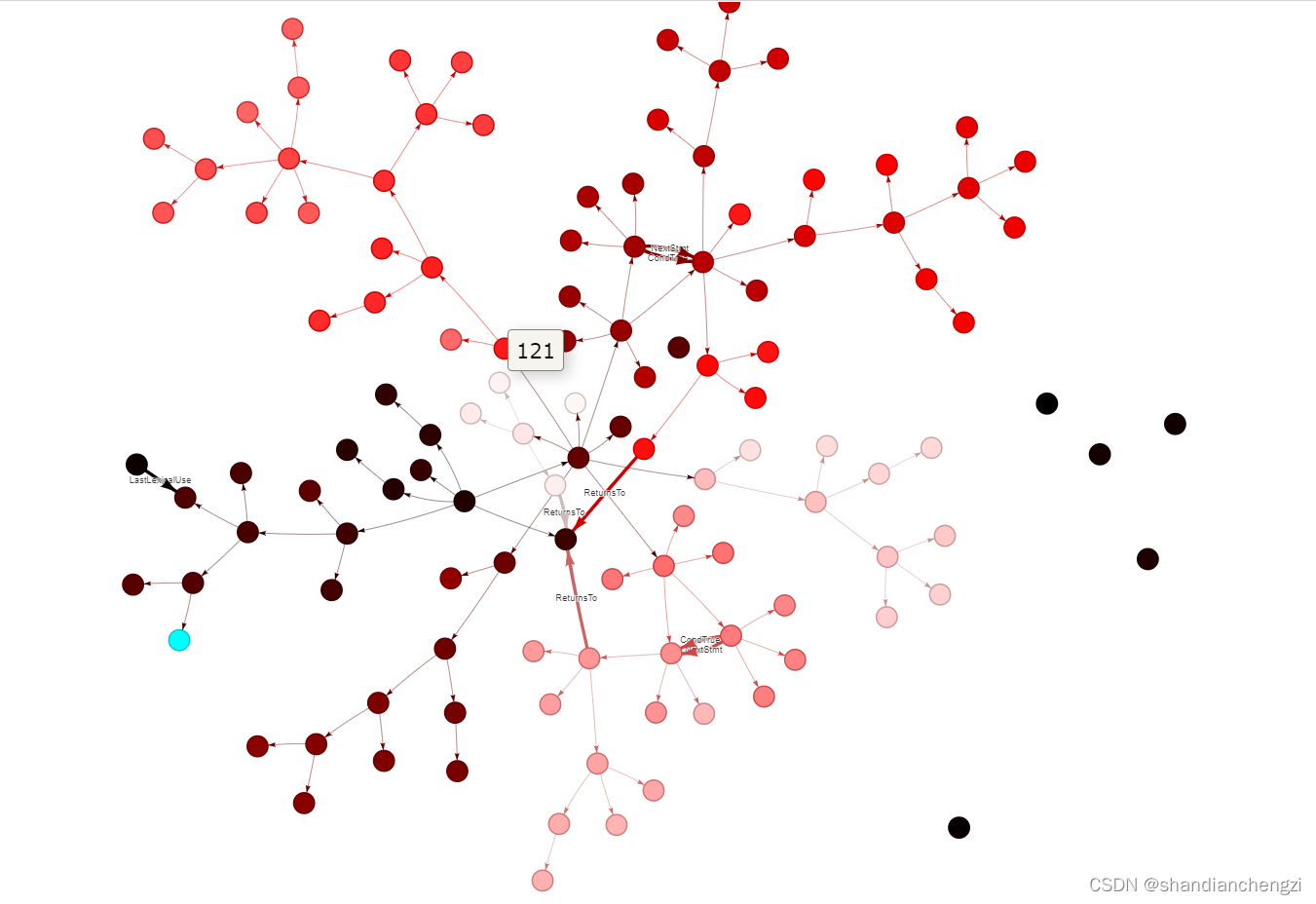
1 神经网络可视化
我自己的仓库:https://github.com/shandianchengzi/tree_sitter_DataExtractor。根目录的test1.html就是测试结果,show_data.py是本篇博客主要涉及的代码。
可视化结果:
2 别人的示例和代码
自定义 Pyvis 交互式网络图。有文字有图片有代码,讲得不错。
PyVis的应用:
零、官方教程
https://pyvis.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorial.html。
一、初始化画布Network
默认设置的初始化方式(长宽500px、无向图):
>>> from pyvis.network import Network
>>> net = Network()
其中Network()里可以加自定义参数,如长宽1000px、有向图:
net = Network('1000px', '1000px', directed=True)
可以修改的参数有:
| 参数名 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| height | 500px | 画布高度 |
| width | 500px | 画布宽度 |
| directed | False | 是否是有向图 |
| notebook | False | True if using jupyter notebook. |
| bgcolor | #ffffff | 画布背景颜色 |
| font_color | False | The color of the node labels text |
| layout | None | Use hierarchical layout if this is set |
授人以鱼不如授人以渔,这些参数、默认值以及说明全部都可以直接在pyvis的源代码中看到:https://github.com/WestHealth/pyvis/blob/master/pyvis/network.py。
二、添加结点
添加单个结点add_node:
>>> net.add_node(1, label="Node 1") # node id = 1 and label = Node 1
>>> net.add_node(2) # node id and label = 2
支持的参数:
n_id: 唯一标识(str or int)
label: 结点标签。
以上必须,以下可选。
· borderWidth: The width of the border of the node.
· borderWidthSelected: The width of the border of the node when it is selected. When undefined, the borderWidth * 2 is used.
· brokenImage: 图片结点(shape=image或circularImage)加载不出来时,显示的URL或文字说明。
· group: 如果未定义,则节点将属于已经定义的组。该组的样式信息将应用于此节点。特定于节点的样式会覆盖组样式。
· hidden: When true, the node will not be shown. It will still be part of the physics simulation though!
· image: When the shape is set to image or circularImage, this option should be the URL to an image. If the image cannot be found, the brokenImage option can be used.
· labelHighlightBold: Determines whether or not the label becomes bold when the node is selected.
· level: When using the hierarchical layout, the level determines where the node is going to be positioned.
· mass: The barnesHut physics model (which is enabled by default) is based on an inverted gravity model. By increasing the mass of a node, you increase it's repulsion. Values lower than 1 are not recommended.
· physics: When false, the node is not part of the physics simulation. It will not move except for from manual dragging.
· shape: 定义了节点的外观。节点有两种类型。一种是标签在内部,另一种是标签在下方。标签在内部的类型有:椭圆ellipse、圆形circle、数据库database、方框box、文本text 。标签在外面的类型有:图像image、圆形图像circularImage、菱形diamond、点dot、星形star、三角形triangle、下三角triangleDown、正方形square和图标icon。
· size: The size is used to determine the size of node shapes that do not have the label inside of them. These shapes are: image, circularImage, diamond, dot, star, triangle, triangleDown, square and icon.
· title: 鼠标移到结点上方时,会显示的内容。hover-text。
· value: When a value is set, the nodes will be scaled using the options in the scaling object defined above.
· x: This gives a node an initial x position. When using the hierarchical layout, either the x or y position is set by the layout engine depending on the type of view. The other value remains untouched. When using stabilization, the stabilized position may be different from the initial one. To lock the node to that position use the physics or fixed options.
· y: This gives a node an initial y position. When using the hierarchical layout,either the x or y position is set by the layout engine depending on the type of view. The other value remains untouched. When using stabilization, the stabilized position may be different from the initial one. To lock the node to that position use the physics or fixed options.
更详细的参数赋值说明直接看源代码:https://github.com/WestHealth/pyvis/blob/58a3b673832670240c8f025d9e76168370214c84/pyvis/network.py#L128。
添加一系列结点add_nodes:
可选参数变少了,只支持参数["size", "value", "title", "x", "y", "label", "color", "shape"]。
应用样例如下:
net.add_nodes(range(node_nums),
title=[str(x) for x in range(node_nums)],
label=[name[str(x)] for x in range(node_nums)],
color=color
)
三、添加边
添加一条边add_edge:
>>> net.add_node(0, label='a')
>>> net.add_node(1, label='b')
>>> net.add_edge(0, 1)
支持的参数:
· arrowStrikethrough: When false, the edge stops at the arrow. This can be useful if you have thick lines and you want the arrow to end in a point. Middle arrows are not affected by this.
· from: Edges are between two nodes, one to and one from. This is where you define the from node. You have to supply the corresponding node ID. This naturally only applies to individual edges.
· hidden: When true, the edge is not drawn. It is part still part of the physics simulation however!
· physics: When true, the edge is part of the physics simulation. When false, it will not act as a spring.
· title: The title is shown in a pop-up when the mouse moves over the edge.
· to: Edges are between two nodes, one to and one from. This is where you define the to node. You have to supply the corresponding node ID. This naturally only applies to individual edges.
· value: When a value is set, the edges' width will be scaled using the options in the scaling object defined above.
· width: The width of the edge. If value is set, this is not used.
添加多条边add_edges:
>>> edges = [[0,1],[1,2,2],[2,3]]
>>> net.add_edges(edges)
只支持width参数,它的实现是这样的,相当鸡肋,感觉可能是作者懒得写了:
def add_edges(self, edges):
for edge in edges:
# if incoming tuple contains a weight
if len(edge) == 3:
self.add_edge(edge[0], edge[1], width=edge[2])
else:
self.add_edge(edge[0], edge[1])
四、为结点添加漂亮的颜色(从而表明结点顺序)
color = ['#00ffff'] # 为第一个结点赋予特殊颜色
for x in range(node_nums - 1):
current_of_color = int(x / node_nums * 255 * 2)
if current_of_color > 255:
color.append('#%02x%02x%02x' % (255, current_of_color - 255, current_of_color - 255))
else:
color.append('#%02x%02x%02x' % (current_of_color, 0, 0))
参考:《如何实现从一种颜色的渐变效果(如从深红-红-浅红),RGB()不好用,但又没有SHL()这个函数。》-CSDN-帖子
完整代码(仅供参考):
from pyvis.network import Network
import gzip
import json
def load_graph(path):
with gzip.open(path, 'r') as f:
content = f.read().decode('utf-8')
context_graph = []
items = content.split('\n')
for item in items:
try:
context_graph.append(json.loads(item))
except:
print(item)
return context_graph
# input:path:数据集路径;index:数据集条目索引;labels:需要显示的额外边的名称
# 将数据集的某条数据可视化
def show_graph(path, index, *labels):
# 1. 载入数据
graph = load_graph(path)
one_data = graph[index]
child_edges = one_data['ContextGraph']['Edges']['Child']
node_nums = len(one_data['ContextGraph']['NodeLabels'])
# 2. 为结点按顺序选取不同的颜色(从深色冷色调到浅色暖色调,并为首个结点赋予特殊颜色,这种方法在结点超过255*2后相邻结点颜色可能重复)
color = ['#00ffff'] # 为第一个结点赋予特殊颜色
for x in range(node_nums - 1):
current_of_color = int(x / node_nums * 255 * 2)
if current_of_color > 255:
color.append('#%02x%02x%02x' % (255, current_of_color - 255, current_of_color - 255))
else:
color.append('#%02x%02x%02x' % (current_of_color, 0, 0))
# 3. 初始化画布,并添加结点和Child边
nt = Network('1000px', '1000px', directed=True)
nt.add_nodes(range(node_nums),
title=[str(x) for x in range(node_nums)],
label=[one_data['ContextGraph']['NodeLabels'][str(x)] for x in range(node_nums)],
color=color
)
nt.add_edges(child_edges)
# 4. 依次添加其他需要额外显示的边
for idx, (label) in enumerate(labels):
try:
to_show_edges = one_data['ContextGraph']['Edges'][label]
for edge in to_show_edges:
nt.add_edge(edge[0], edge[1],
value=4,
label=label)
except:
print('no ' + label + ' edges')
return
# 5. 显示图
nt.show(path.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0] + str(index) + '.html')
本账号所有文章均为原创,欢迎转载,请注明文章出处:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_46106285/article/details/125638283。百度和各类采集站皆不可信,搜索请谨慎鉴别。技术类文章一般都有时效性,本人习惯不定期对自己的博文进行修正和更新,因此请访问出处以查看本文的最新版本。
【笔记】Python3|使用 PyVis 完成神经网络数据集的可视化的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow笔记-05-反向传播,搭建神经网络的八股
TensorFlow笔记-05-反向传播,搭建神经网络的八股 反向传播 反向传播: 训练模型参数,在所有参数上用梯度下降,使用神经网络模型在训练数据上的损失函数最小 损失函数:(loss) 计算得到的 ...
- UFLDL深度学习笔记 (六)卷积神经网络
UFLDL深度学习笔记 (六)卷积神经网络 1. 主要思路 "UFLDL 卷积神经网络"主要讲解了对大尺寸图像应用前面所讨论神经网络学习的方法,其中的变化有两条,第一,对大尺寸图像 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(四)之神经网络
Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(四)之神经网络 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请指明转载地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/fydeblog/p/7365730.html 前言 ...
- python聚类算法实战详细笔记 (python3.6+(win10、Linux))
python聚类算法实战详细笔记 (python3.6+(win10.Linux)) 一.基本概念: 1.计算TF-DIF TF-IDF是一种统计方法,用以评估一字词对于一个文件集或一个语料库 ...
- CNN笔记:通俗理解卷积神经网络
CNN笔记:通俗理解卷积神经网络 2016年07月02日 22:14:50 v_JULY_v 阅读数 250368更多 分类专栏: 30.Machine L & Deep Learning 机 ...
- 使用 Visual Studio 2015 + Python3.6 + tensorflow 构建神经网络时报错:'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xcc in position 78: invalid continuation byte
使用 Visual Studio 2015 + Python3.6 + tensorflow 构建神经网络时报错:'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xcc in pos ...
- tensorflow笔记:模型的保存与训练过程可视化
tensorflow笔记系列: (一) tensorflow笔记:流程,概念和简单代码注释 (二) tensorflow笔记:多层CNN代码分析 (三) tensorflow笔记:多层LSTM代码分析 ...
- Seaborn(二)之数据集分布可视化
Seaborn(二)之数据集分布可视化 当处理一个数据集的时候,我们经常会想要先看看特征变量是如何分布的.这会让我们对数据特征有个很好的初始认识,同时也会影响后续数据分析以及特征工程的方法.本篇将会介 ...
- TensorFlow学习笔记——LeNet-5(训练自己的数据集)
在之前的TensorFlow学习笔记——图像识别与卷积神经网络(链接:请点击我)中了解了一下经典的卷积神经网络模型LeNet模型.那其实之前学习了别人的代码实现了LeNet网络对MNIST数据集的训练 ...
- 【pytorch】学习笔记(四)-搭建神经网络进行关系拟合
[pytorch学习笔记]-搭建神经网络进行关系拟合 学习自莫烦python 目标 1.创建一些围绕y=x^2+噪声这个函数的散点 2.用神经网络模型来建立一个可以代表他们关系的线条 建立数据集 im ...
随机推荐
- flutter ios 深色模式下状态栏文字是白色的,白色背景下看不见
flutter ios 深色模式下状态栏文字是白色的,白色背景下看不见 theme: ThemeData( appBarTheme: const AppBarTheme( systemOverlayS ...
- 删除binlog日志
手动删除 在备库检查正在使用的binlog SHOW REPLICA STATUS 在主库获取binlog列表 SHOW BINARY LOGS 删除备库使用前或主库正在写入前的binlog 不要将正 ...
- 【译】HTTP 文件更新了请求变量
许多用户都要求在 Visual Studio 的 HTTP 文件中添加对请求变量的支持.使用请求变量,您可以发送 HTTP 请求,然后在从 HTTP 文件发送的任何后续请求中使用响应或请求中的数据.我 ...
- 【忍者算法】从入环点到相遇点:深入理解环形链表 II|LeetCode第142题 环形链表 II
[忍者算法]从入环点到相遇点:深入理解环形链表 II|LeetCode第142题 问题升级:不止要找环,还要找入环点 在上一题中,我们讨论了如何判断链表是否有环.现在让我们更进一步:如果确定链表中有环 ...
- PERT 图表教程
(翻译自: PERT Chart Tutorial) PERT 图表 是(程序评估和审查技术)的首字母缩写.PERT 图是一种项目管理工具,用于在项目中安排.组织和协调任务.它基本上是一种分析完成给定 ...
- Flink学习(十) Sink到Redis
添加依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.bahir</groupId> <artifactId>flink-conn ...
- CF2018C Tree Pruning
分析 好像官方题解是反向求解的,这里提供一个正向求解的思路,即直接求出最后所有叶节点到根的距离相同为 \(x\) 时需要删除的结点数 \(ans_x\) . 如果我们最后到根的相同距离为 \(x\), ...
- event.stopPropagation
先记录一下坑: var btn = test.getElementsByTagName('label'); btn[0].active = 'active'; ...
- 【vscode】vscode配置python
[vscode]vscode配置python 前言 每次配环境的经历,其实都值得写一篇博客记录一下,以便于自己以后查阅. 笔者环境: win10 过程 step1:python解释器下 ...
- 基于OpenSSL的密码管理系统-应用密码学课程报告
第1章 概要设计 1.1 设计目的 本研究旨在设计并实现一个基于OpenSSL的密码管理系统,该系统具备密钥对的生成.密钥上传.密钥的核对.身份认证.文件与邮件的加密和解密.数字签名及数字证书管理等常 ...
