Python爬虫(四)——豆瓣数据模型训练与检测
前文参考:
Python爬虫(三)——对豆瓣图书各模块评论数与评分图形化分析
数据的构建
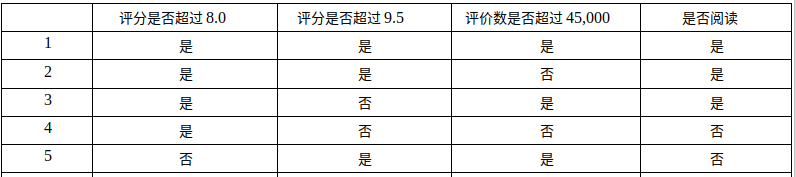
在这张表中我们可以发现这里有5个数据,这里有三个特征(评分是否超过8.0,评分是否超过9.5,评价数是否超过45,000)来划分这5本书是否选择阅读。
现在我们要做的就是是要根据第一个特征,第二个特征还是第三个特征来划分数据,进行分类。
def createDataSet():
dataSet = [[1,1,1,'yes'],
[1,1,0,'yes'],
[1,0,1,'yes'],
[1,0,0,'no'],
[0,1,1,'no']] # 我们定义了一个list来表示我们的数据集,这里的数据对应的是上表中的数据 labels = ['no surfacing','flippers'] return dataSet, labels
计算给定数据的信息熵
根据信息论的方法找到最合适的特征来划分数据集。在这里,我们首先要计算所有类别的所有可能值的香农熵,根据香农熵来我们按照取最大信息增益的方法划分数据集。
以信息增益度量属性选择,选择分裂后信息增益最大的属性进行分裂。信息熵是用来衡量一个随机变量出现的期望值。如果信息的不确定性越大,熵的值也就越大,出现的各种情况也就越多。
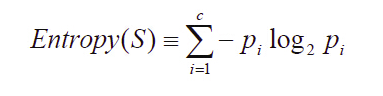
其中,S为所有事件集合,p为发生概率,c为特征总数。注意:熵是以2进制位的个数来度量编码长度的,因此熵的最大值是log2C。
信息增益(information gain)是指信息划分前后的熵的变化,也就是说由于使用这个属性分割样例而导致的期望熵降低。也就是说,信息增益就是原有信息熵与属性划分后信息熵(需要对划分后的信息熵取期望值)的差值,具体计算法如下:

代码实现:
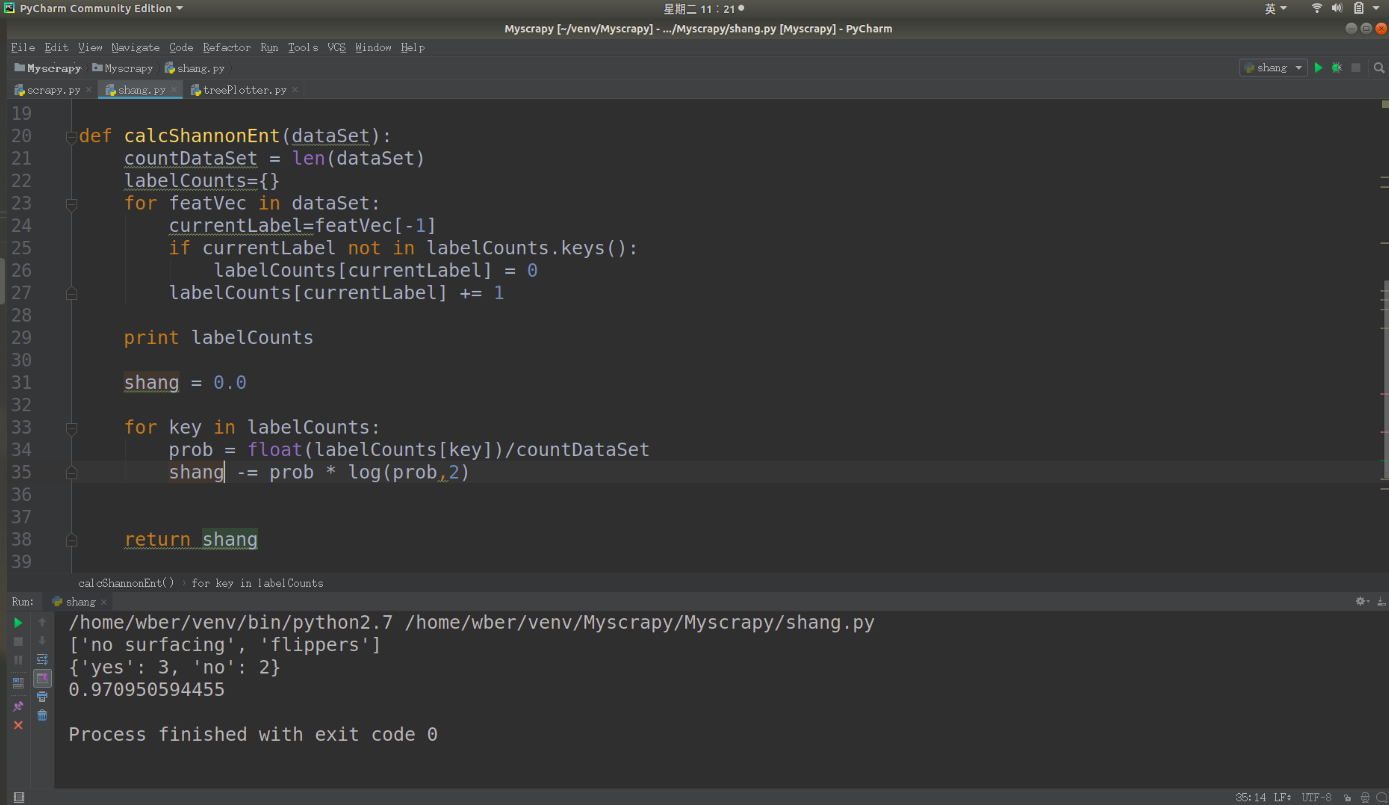
from math import log def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):#传入数据集
# 在这里dataSet是一个链表形式的的数据集
countDataSet = len(dataSet)
labelCounts={} # 构建字典,用键值对的关系我们表示出 我们数据集中的类别还有对应的关系
for featVec in dataSet: 通过for循环,我们每次取出一个数据集,如featVec=[1,1,'yes']
currentLabel=featVec[-1] # 取出最后一列 也就是类别的那一类,比如说‘yes’或者是‘no’
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 print labelCounts shang = 0.0 for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/countDataSet
shang -= prob * log(prob,2)
return shang
划分数据集
在度量数据集的无序程度的时候,分类算法除了需要测量信息熵,还需要划分数据集,度量花费数据集的熵,以便判断当前是否正确的划分了数据集。
我们将对每个特征数据集划分的结果计算一次信息熵,然后判断按照那个特征划分数据集是最好的划分方式。
也就是说,我们依次选取我们数据集当中的所有特征作为我们划定的特征,然后计算选取该特征时的信息增益,当信息增益最大时我们就选取对应信息增益最大的特征作为我们分类的最佳特征。

dataSet = [[1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 'no']]
在这个数据集当中有三个特征,就是每个样本的第一列,第二列和第三列,最后一列是它们所属的分类。
我们划分数据集是为了计算根据那个特征我们可以得到最大的信息增益,那么根据这个特征来划分数据就是最好的分类方法。
因此我们需要遍历每一个特征,然后计算按照这种划分方式得出的信息增益。信息增益是指数据集在划分数据前后信息的变化量。
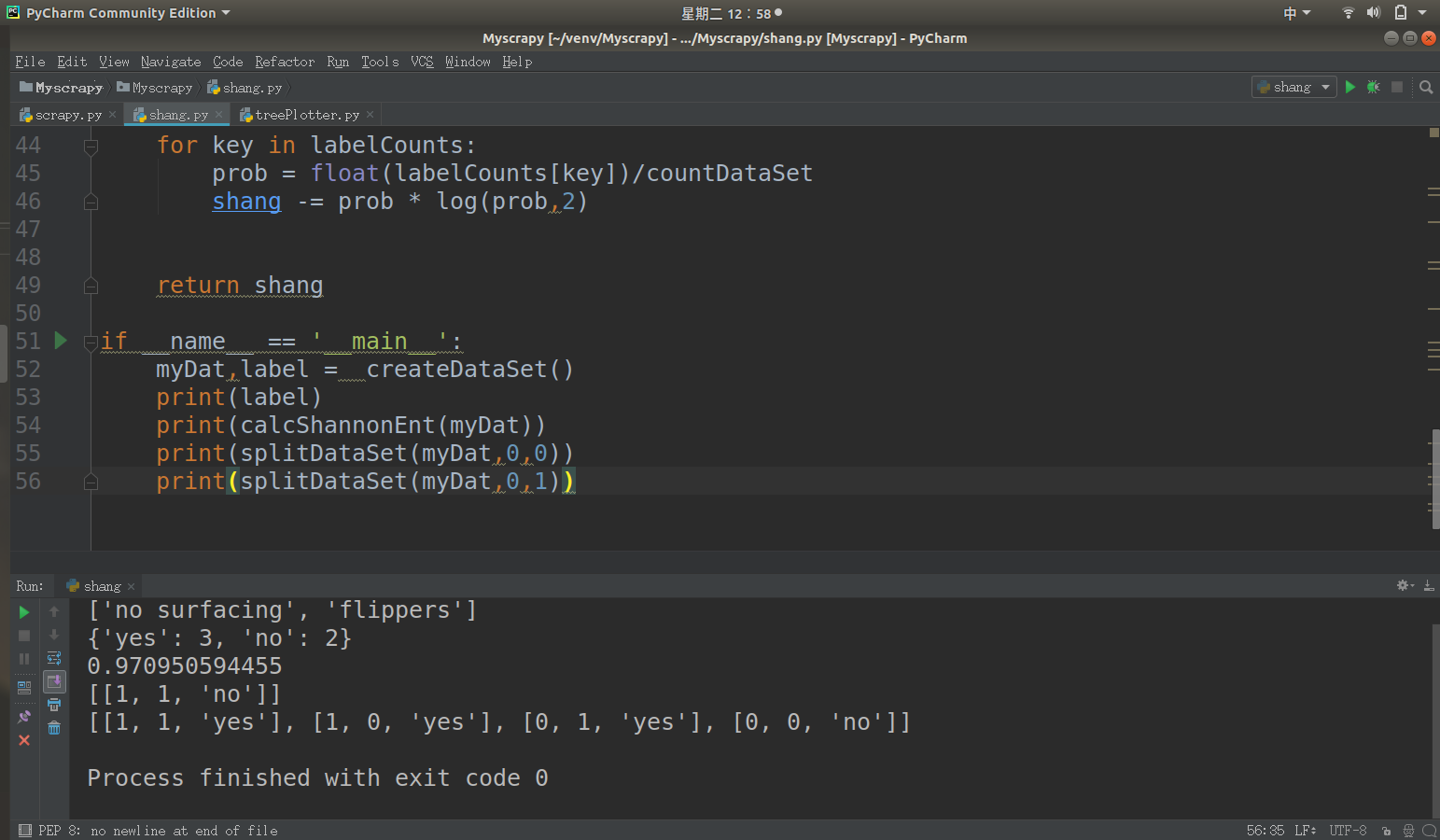
def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value):
retDataSet = [] for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
reduceFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reduceFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reduceFeatVec) return retDataSet
计算信息增益
依次遍历每一个特征,在这里我们的特征只有三个,就是评分是否超过8.0,评分是否超过9.5,评价数是否超过45,000。然后计算出根据每一个特征划分产生的数据集的熵,和初始的数据集的熵比较,我们找出和初始数据集差距最大的。那么这个特征就是我们划分时最合适的分类特征。
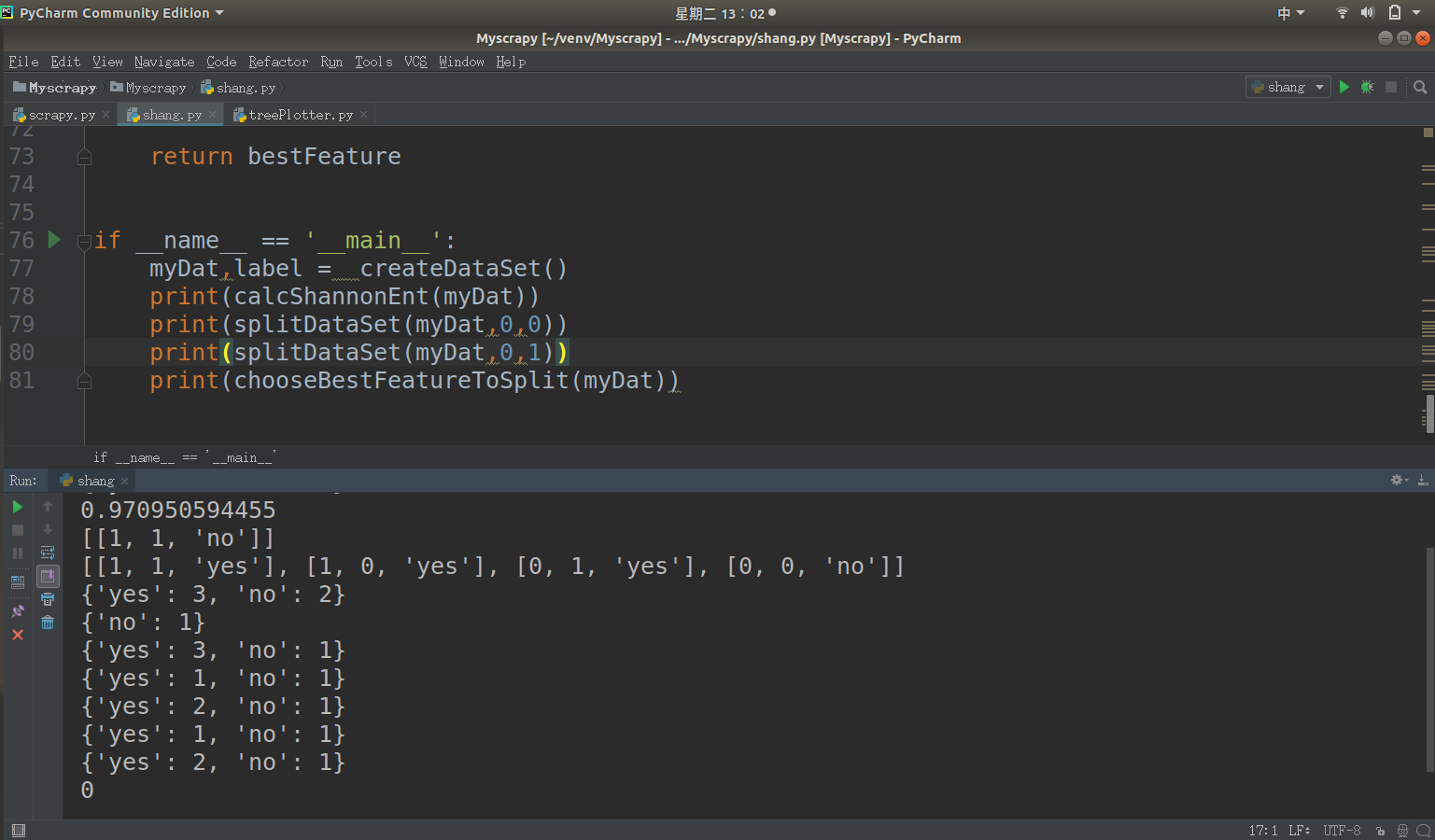
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0])-1
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain =0.0
bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures):
featList = [sample[i] for sample in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList)
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
if(infoGain > bestInfoGain):
bestInfoGain = infoGain
bestFeature = i return bestFeature
数据检测
sklearn实现交叉验证十折交叉验证流程
将数据集随机地切分为S个互不相交的大小相同的子集
然后挑选其中S-1个子集作为训练集,训练模型,用剩下的一个子集作测试集,获得测试误差或者评测指标
将上面过程对所有可能的S种选择重复进行,即每次都是用不同的测试集
最后对S次实验所得的数据(测试误差或者评测指标)取均值。
代码如下:
X = np.array(myDat)
y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
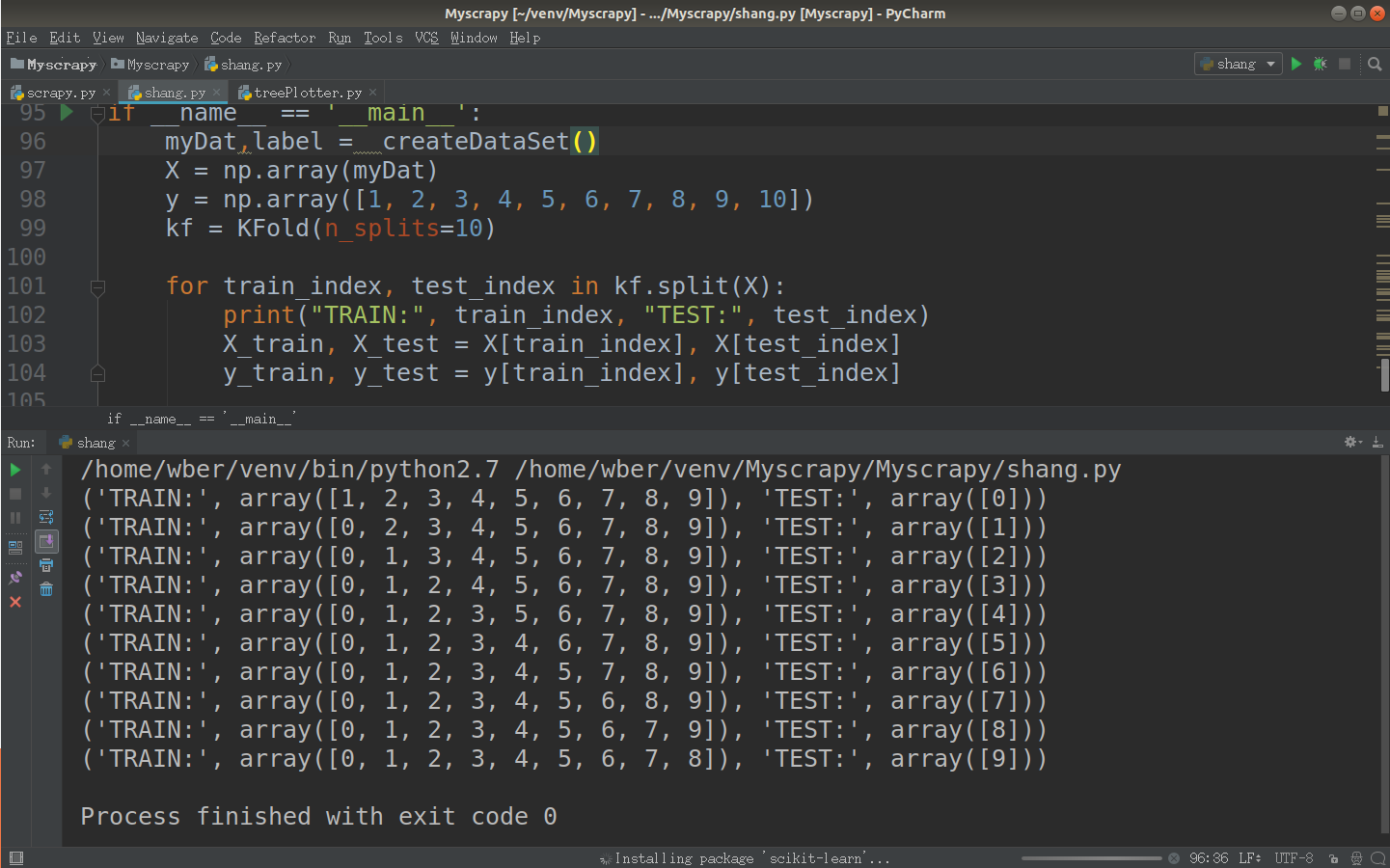
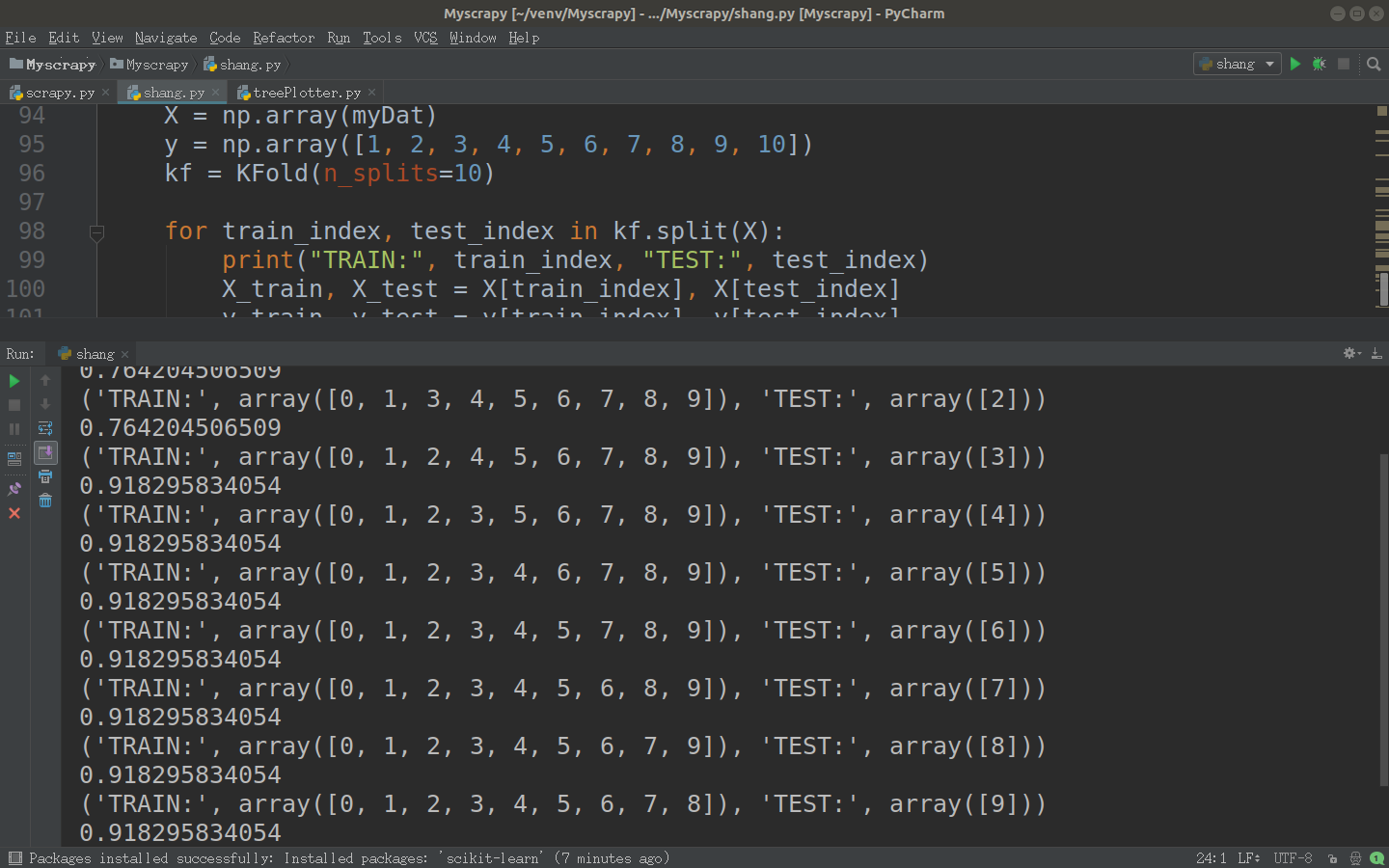
kf = KFold(n_splits=10) for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
print("TRAIN:", train_index, "TEST:", test_index)
X_train, X_test = X[train_index], X[test_index]
y_train, y_test = y[train_index], y[test_index]测试:
完整代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import csv from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
import mycsv
import sys reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf-8') # 请求头设置
header = {
'Accept': '*/*;',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9',
'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate, br',
'Host': 'book.douban.com',
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/67.0.3396.87 Safari/537.36'
} # 初始化csv文件
def info(name):
csvinfo = open(name + '.mycsv', 'ab')
begcsv = csv.writer(csvinfo)
begcsv.writerow(['titles', 'authors', 'nums', 'peoples'])
csvinfo.close() # 爬取指定name模块的url,并存储至name.csv文件
def web(url, name):
db_data = requests.get(url, headers=header)
soup = BeautifulSoup(db_data.text, 'lxml')
titles = soup.select('#subject_list > ul > li > div.info > h2 > a')
authors = soup.select('#subject_list > ul > li > div.info > div.pub')
nums = soup.select('#subject_list > ul > li > div.info > div.star.clearfix > span.rating_nums')
peoples = soup.select('#subject_list > ul > li > div.info > div.star.clearfix > span.pl')
print(titles[0])
for title, author, num, people in zip(titles, authors, nums, peoples):
data = [
(
title.get('title'),
author.get_text().replace(' ', '').replace("\n", ""),
num.get_text().replace(' ', '').replace("\n", ""),
people.get_text().replace(' ', '').replace("\n", "")
)
]
csvfile = open(name + '.mycsv', 'ab')
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
print(data)
writer.writerows(data)
csvfile.close() # name模块标签分页 指定为前50页
def setCsv(name):
url = 'https://book.douban.com/tag/' + name
urls = [('https://book.douban.com/tag/' + name + '?start={}&type=T').format(str(i)) for i in range(20, 980, 20)]
info(name=name)
web(url, name)
for single_url in urls:
print(single_url)
web(single_url, name=name) if __name__ == '__main__':
setCsv(str) #str为标签名# coding=utf-8
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt decisionNode = dict(boxstyle='sawtooth', fc='')
leafNode = dict(boxstyle='round4',fc='0.8')
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle='<-') def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',\
xytext=centerPt,textcoords='axes fraction',\
va='center', ha='center',bbox=nodeType,arrowprops\
=arrow_args) def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict:
if(type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict'):
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict:
if(type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict'):
thisDepth = 1+getTreeDepth((secondDict[key]))
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth def retrieveTree(i):
#预先设置树的信息
listOfTree = [{'no surfacing':{0:'no',1:{'flipper':{0:'no',1:'yes'}}}},
{'no surfacing':{0:'no',1:{'flipper':{0:{'head':{0:'no',1:'yes'}},1:'no'}}}},
{'Comment score greater than 8.0':{0:{'Comment score greater than 9.5':{0:'Yes',1:{'More than 45,000 people commented': {
0: 'Yes',1: 'No'}}}},1:'No'}}]
return listOfTree[i] def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1,facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks = [], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111,frameon = False,**axprops)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW;plotTree.yOff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree,(0.5,1.0), '')
plt.title('Douban reading Decision Tree\n')
plt.show() def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt,txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString) def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff+(1.0+float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW,\
plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt,parentPt,nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr,cntrPt,parentPt,decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict:
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key],(plotTree.xOff,plotTree.yOff),\
cntrPt,leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff,plotTree.yOff),cntrPt,str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD if __name__ == '__main__':
myTree = retrieveTree(2)
createPlot(myTree)# coding=utf-8
import random
from math import log
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
import numpy as np def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value):
retDataSet = [] for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
reduceFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reduceFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reduceFeatVec) return retDataSet def createDataSet():
dataSet = [[1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 'no'] ] labels = ['no surfacing','flippers'] return dataSet, labels def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
countDataSet = len(dataSet)
labelCounts={}
for featVec in dataSet:
currentLabel=featVec[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1
shang = 0.0 for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/countDataSet
shang -= prob * log(prob,2) return shang def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0])-1
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain =0.0
bestFeature = -1 for i in range(numFeatures):
featList = [sample[i] for sample in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList)
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy if(infoGain > bestInfoGain):
bestInfoGain = infoGain
bestFeature = i return bestFeature def SplitData(dataSet, k, seed):
testSet = []
trainSet = []
random.seed(seed)
for user, item in dataSet:
if random.randint(0,10) == k:
testSet.append([user,item])
else:
trainSet.append([user,item])
return testSet, trainSet if __name__ == '__main__':
myDat,label = createDataSet()
X = np.array(myDat)
y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
kf = KFold(n_splits=10) for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
print("TRAIN:", train_index, "TEST:", test_index)
X_train, X_test = X[train_index], X[test_index]
y_train, y_test = y[train_index], y[test_index]
print(calcShannonEnt(X[train_index]))
Python爬虫(四)——豆瓣数据模型训练与检测的更多相关文章
- Python爬虫(四)——开封市58同城数据模型训练与检测
前文参考: Python爬虫(一)——开封市58同城租房信息 Python爬虫(二)——对开封市58同城出租房数据进行分析 Python爬虫(三)——对豆瓣图书各模块评论数与评分图形化分析 数据的构建 ...
- 用Python爬虫对豆瓣《敦刻尔克》影评进行词云展示
最近很想看的一个电影,去知乎上看一下评论,刚好在学Python爬虫,就做个小实例. 代码基于第三方修改 原文链接 http://python.jobbole.com/88325/#comment-9 ...
- Python爬虫之豆瓣-新书速递-图书解析
1- 问题描述 抓取豆瓣“新书速递”[1]页面下图书信息(包括书名,作者,简介,url),将结果重定向到txt文本文件下. 2- 思路分析[2] Step1 读取HTML Step2 Xpath遍历元 ...
- Python爬虫(一)——豆瓣下图书信息
爬虫目的: 随着近年互联网的发展,网络上的信息飞速数量增长.在庞大的数据面前想要获得期望的信息往往如同大海捞针.通过合理的筛选,在百万甚至数亿计的数据中找到所需信息,无疑有着非常大的意义. 在豆瓣网下 ...
- python爬虫(四)_urllib2库的基本使用
本篇我们将开始学习如何进行网页抓取,更多内容请参考:python学习指南 urllib2库的基本使用 所谓网页抓取,就是把URL地址中指定的网络资源从网络流中读取出来,保存到本地.在Python中有很 ...
- Python 爬虫四 基础案例-自动登陆github
GET&POST请求一般格式 爬取Github数据 GET&POST请求一般格式 很久之前在讲web框架的时候,曾经提到过一句话,在网络编程中“万物皆socket”.任何的网络通信归根 ...
- python爬虫之一---------豆瓣妹子图
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = "carry" import urllib import urllib2 from bs4 import Be ...
- Python爬虫——爬豆瓣登录页面
直接上代码 import urllib.request import http.cookiejar from lxml import etree # from spiderImg import get ...
- Python爬虫(二)——豆瓣图书决策树构建
前文参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/LexMoon/p/douban1.html Matplotlib绘制决策树代码: # coding=utf-8 import matpl ...
随机推荐
- 怎么用js编写1——100的质数?
这里来自csdn问答的一个问题,怎么用js编写1——100的质数? http://ask.csdn.net/questions/214429 质数也就是素数,即只能被1和自身整除的数,因此可以构造循环 ...
- php 执行 命令行命令
PHP提供共了3个专门的执行外部命令的函数:system(),exec(),passthru().参考:http://www.jb51.net/article/19618.htm 区别: system ...
- centos7邮件服务器SSL配置
在上篇文章centos7搭建postfix邮件服务器的搭建中我们没有配置SSL,接下来我们在这篇文章中讲讲centos7邮件服务器SSL配置. 1. 创建SSL证书 [root@www ~]# cd ...
- What do cryptic Github comments mean?
LGTM — looks good to me ACK — acknowledgement, i.e. agreed/accepted change NACK/NAK — negative a ...
- ArcGIS AddIN开发之 设置当前工具为Edit Tool
在GIS数据处理中,经常需要选择要素,再进行操作.所以,为了处理的方便,可以将当前工具处理结束后,将当前工具设置为Edit Tool,以方便下一次的选择处理. 相关资料: 1.ArcMap Name ...
- loadrunner笔记(二):飞机订票系统--客户信息注册
(一) 几个重要概念说明 集合点:同步虚拟用户,以便同一时间执行任务. 事务:事务是指服务器响应用户请求所用的时间,当然它可以衡量某个操作,如登录所需要的时间,也可以衡量一系列的操作所用的时间,如从 ...
- mui 卡片视图 遮罩蒙版
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name ...
- jQuery 中的 39 个技巧【申明:来源于网络】
jQuery 中的 39 个技巧[申明:来源于网络] 地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zhongqi2513/article/details/53704812?ref=myread
- RMQPOJ3264
Balanced Lineup POJ-3264 DP分析 设A[i]是要求区间最值的数列,F[i, j]表示从第i个数起连续2^j个数中的最大值.(DP的状态) 初状态是F[i,0]=A[i] 状态 ...
- [daily] 比端口转发更高级的ssh device tunnel转发
没有什么能够阻挡,你对自由的向往. 场景: 我有一台设备Server100,在某一个f复杂的内网里,需要多次ssh跳转可以访问到.但是它不能直接访问internet. 我现在需要在我的ssh路径上,搭 ...