netty如何实现零拷贝
根据 Wiki 对 Zero-copy 的定义:
"Zero-copy" describes computer operations in which the CPU does not perform the task of copying data from one memory area to another. This is frequently used to save CPU cycles and memory bandwidth when transmitting a file over a network.
即所谓的 Zero-copy, 就是在操作数据时, 不需要将数据 buffer 从一个内存区域拷贝到另一个内存区域. 因为少了一次内存的拷贝, 因此 CPU 的效率就得到的提升.
在 OS 层面上的 Zero-copy通常指避免在 用户态(User-space)与 内核态(Kernel-space)之间来回拷贝数据. 例如 Linux 提供的 mmap系统调用, 它可以将一段用户空间内存映射到内核空间, 当映射成功后, 用户对这段内存区域的修改可以直接反映到内核空间; 同样地, 内核空间对这段区域的修改也直接反映用户空间. 正因为有这样的映射关系, 我们就不需要在 用户态(User-space)与 内核态(Kernel-space)之间拷贝数据, 提高了数据传输的效率.
而需要注意的是, Netty 中的 Zero-copy与上面我们所提到到 OS 层面上的 Zero-copy不太一样, Netty的 Zero-coyp完全是在用户态(Java 层面)的, 它的 Zero-copy的更多的是偏向于 优化数据操作这样的概念.
Netty 的 Zero-copy体现在如下几个个方面:
- Netty 提供了
CompositeByteBuf类, 它可以将多个 ByteBuf 合并为一个逻辑上的 ByteBuf, 避免了各个 ByteBuf 之间的拷贝. - 通过 wrap 操作, 我们可以将 byte[] 数组、ByteBuf、ByteBuffer等包装成一个 Netty ByteBuf 对象, 进而避免了拷贝操作.
- ByteBuf 支持 slice 操作, 因此可以将 ByteBuf 分解为多个共享同一个存储区域的 ByteBuf, 避免了内存的拷贝.
- 通过
FileRegion包装的FileChannel.tranferTo实现文件传输, 可以直接将文件缓冲区的数据发送到目标Channel, 避免了传统通过循环 write 方式导致的内存拷贝问题.
下面我们就来简单了解一下这几种常见的零拷贝操作.
通过 CompositeByteBuf 实现零拷贝
假设我们有一份协议数据, 它由头部和消息体组成, 而头部和消息体是分别存放在两个 ByteBuf 中的, 即:
ByteBuf header = ...
ByteBuf body = ...
我们在代码处理中, 通常希望将 header 和 body 合并为一个 ByteBuf, 方便处理, 那么通常的做法是:
ByteBuf allBuf = Unpooled.buffer(header.readableBytes() + body.readableBytes());
allBuf.writeBytes(header);
allBuf.writeBytes(body);
可以看到, 我们将 header 和 body 都拷贝到了新的 allBuf 中了, 这无形中增加了两次额外的数据拷贝操作了.
那么有没有更加高效优雅的方式实现相同的目的呢? 我们来看一下 CompositeByteBuf是如何实现这样的需求的吧.
ByteBuf header = ...
ByteBuf body = ... CompositeByteBuf compositeByteBuf = Unpooled.compositeBuffer();
compositeByteBuf.addComponents(true, header, body);
上面代码中, 我们定义了一个 CompositeByteBuf对象, 然后调用
public CompositeByteBuf addComponents(boolean increaseWriterIndex, ByteBuf... buffers) {
...
}
方法将 header与 body合并为一个逻辑上的 ByteBuf, 即:
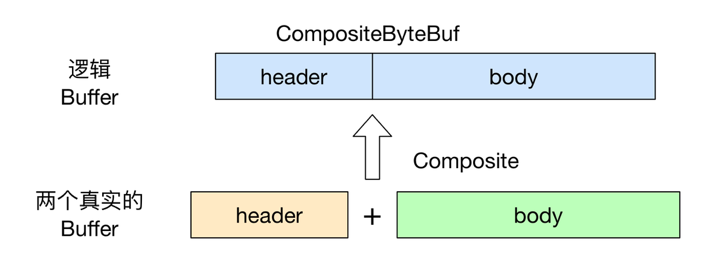
不过需要注意的是, 虽然看起来 CompositeByteBuf 是由两个 ByteBuf 组合而成的, 不过在 CompositeByteBuf 内部, 这两个 ByteBuf 都是单独存在的, CompositeByteBuf 只是逻辑上是一个整体.
上面 CompositeByteBuf代码还以一个地方值得注意的是, 我们调用 addComponents(boolean increaseWriterIndex, ByteBuf... buffers)来添加两个 ByteBuf, 其中第一个参数是 true, 表示当添加新的 ByteBuf 时, 自动递增 CompositeByteBuf 的 writeIndex.
如果我们调用的是
compositeByteBuf.addComponents(header, body);
那么其实 compositeByteBuf的 writeIndex仍然是0, 因此此时我们就不可能从 compositeByteBuf中读取到数据, 这一点希望大家要特别注意.
除了上面直接使用 CompositeByteBuf类外, 我们还可以使用 Unpooled.wrappedBuffer方法, 它底层封装了 CompositeByteBuf操作, 因此使用起来更加方便:
ByteBuf header = ...
ByteBuf body = ... ByteBuf allByteBuf = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(header, body);
通过 wrap 操作实现零拷贝
例如我们有一个 byte 数组, 我们希望将它转换为一个 ByteBuf 对象, 以便于后续的操作, 那么传统的做法是将此 byte 数组拷贝到 ByteBuf 中, 即:
byte[] bytes = ...
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.buffer();
byteBuf.writeBytes(bytes);
显然这样的方式也是有一个额外的拷贝操作的, 我们可以使用 Unpooled 的相关方法, 包装这个 byte 数组, 生成一个新的 ByteBuf 实例, 而不需要进行拷贝操作. 上面的代码可以改为:
byte[] bytes = ...
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.buffer();
byteBuf.writeBytes(bytes);
可以看到, 我们通过 Unpooled.wrappedBuffer方法来将 bytes 包装成为一个 UnpooledHeapByteBuf 对象, 而在包装的过程中, 是不会有拷贝操作的. 即最后我们生成的生成的 ByteBuf 对象是和 bytes 数组共用了同一个存储空间, 对 bytes 的修改也会反映到 ByteBuf 对象中.
Unpooled 工具类还提供了很多重载的 wrappedBuffer 方法:
public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(byte[] array)
public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(byte[] array, int offset, int length) public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(ByteBuffer buffer)
public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(ByteBuf buffer) public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(byte[]... arrays)
public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(ByteBuf... buffers)
public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(ByteBuffer... buffers) public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(int maxNumComponents, byte[]... arrays)
public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(int maxNumComponents, ByteBuf... buffers)
public static ByteBuf wrappedBuffer(int maxNumComponents, ByteBuffer... buffers)
这些方法可以将一个或多个 buffer 包装为一个 ByteBuf 对象, 从而避免了拷贝操作.
通过 slice 操作实现零拷贝
slice 操作和 wrap 操作刚好相反, Unpooled.wrappedBuffer可以将多个 ByteBuf 合并为一个, 而 slice 操作可以将一个 ByteBuf 切片为多个共享一个存储区域的 ByteBuf 对象.
ByteBuf 提供了两个 slice 操作方法:
public ByteBuf slice();
public ByteBuf slice(int index, int length);
不带参数的 slice方法等同于 buf.slice(buf.readerIndex(), buf.readableBytes())调用, 即返回 buf 中可读部分的切片. 而 slice(int index, int length)方法相对就比较灵活了, 我们可以设置不同的参数来获取到 buf 的不同区域的切片.
下面的例子展示了 ByteBuf.slice方法的简单用法:
ByteBuf byteBuf = ...
ByteBuf header = byteBuf.slice(0, 5);
ByteBuf body = byteBuf.slice(5, 10);
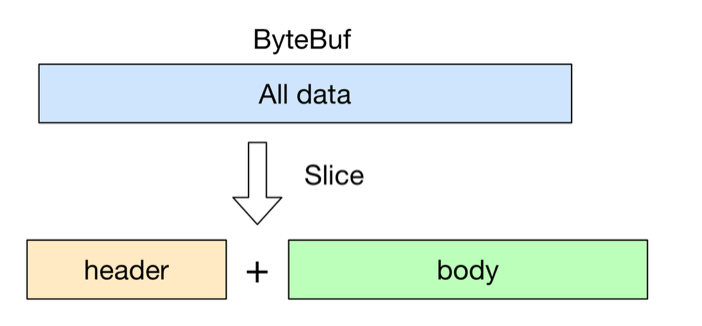
用 slice方法产生 header 和 body 的过程是没有拷贝操作的, header 和 body 对象在内部其实是共享了 byteBuf 存储空间的不同部分而已. 即:
通过 FileRegion 实现零拷贝
Netty 中使用 FileRegion 实现文件传输的零拷贝, 不过在底层 FileRegion 是依赖于 Java NIO FileChannel.transfer的零拷贝功能.
首先我们从最基础的 Java IO 开始吧. 假设我们希望实现一个文件拷贝的功能, 那么使用传统的方式, 我们有如下实现:
public static void copyFile(String srcFile, String destFile) throws Exception {
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
int length;
while ((length = in.read(temp)) != -1) {
out.write(temp, 0, length);
}
in.close();
out.close();
}
上面是一个典型的读写二进制文件的代码实现了. 不用我说, 大家肯定都知道, 上面的代码中不断中源文件中读取定长数据到 temp 数组中, 然后再将 temp 中的内容写入目的文件, 这样的拷贝操作对于小文件倒是没有太大的影响, 但是如果我们需要拷贝大文件时, 频繁的内存拷贝操作就消耗大量的系统资源了.
下面我们来看一下使用 Java NIO 的 FileChannel是如何实现零拷贝的:
public static void copyFileWithFileChannel(String srcFileName, String destFileName) throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile srcFile = new RandomAccessFile(srcFileName, "r");
FileChannel srcFileChannel = srcFile.getChannel();
RandomAccessFile destFile = new RandomAccessFile(destFileName, "rw");
FileChannel destFileChannel = destFile.getChannel();
long position = 0;
long count = srcFileChannel.size();
srcFileChannel.transferTo(position, count, destFileChannel);
}
可以看到, 使用了 FileChannel后, 我们就可以直接将源文件的内容直接拷贝(transferTo) 到目的文件中, 而不需要额外借助一个临时 buffer, 避免了不必要的内存操作.
有了上面的一些理论知识, 我们来看一下在 Netty 中是怎么使用 FileRegion来实现零拷贝传输一个文件的:
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile raf = null;
long length = -1;
try {
// 1. 通过 RandomAccessFile 打开一个文件.
raf = new RandomAccessFile(msg, "r");
length = raf.length();
} catch (Exception e) {
ctx.writeAndFlush("ERR: " + e.getClass().getSimpleName() + ": " + e.getMessage() + '\n');
return;
} finally {
if (length < 0 && raf != null) {
raf.close();
}
} ctx.write("OK: " + raf.length() + '\n');
if (ctx.pipeline().get(SslHandler.class) == null) {
// SSL not enabled - can use zero-copy file transfer.
// 2. 调用 raf.getChannel() 获取一个 FileChannel.
// 3. 将 FileChannel 封装成一个 DefaultFileRegion
ctx.write(new DefaultFileRegion(raf.getChannel(), 0, length));
} else {
// SSL enabled - cannot use zero-copy file transfer.
ctx.write(new ChunkedFile(raf));
}
ctx.writeAndFlush("\n");
}
上面的代码是 Netty 的一个例子, 其源码在 netty/example/src/main/java/io/netty/example/file/FileServerHandler.java
可以看到, 第一步是通过 RandomAccessFile打开一个文件, 然后 Netty 使用了 DefaultFileRegion来封装一个 FileChannel即:
new DefaultFileRegion(raf.getChannel(), 0, length)
当有了 FileRegion 后, 我们就可以直接通过它将文件的内容直接写入 Channel 中, 而不需要像传统的做法: 拷贝文件内容到临时 buffer, 然后再将 buffer 写入 Channel. 通过这样的零拷贝操作, 无疑对传输大文件很有帮助.
转自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/1d1fa2fe1ed9
欢迎加群交流,QQ群:66728073,197321069,398808948 还可以扫描博客左上角二维码,关注游戏技术网公众号
netty如何实现零拷贝的更多相关文章
- 理解Netty中的零拷贝(Zero-Copy)机制【转】
理解零拷贝 零拷贝是Netty的重要特性之一,而究竟什么是零拷贝呢? WIKI中对其有如下定义: “Zero-copy” describes computer operations in which ...
- 对于 Netty ByteBuf 的零拷贝(Zero Copy) 的理解
此文章已同步发布在我的 segmentfault 专栏. 根据 Wiki 对 Zero-copy 的定义: "Zero-copy" describes computer opera ...
- Netty:Netty中的零拷贝(Zero Copy)
零复制概念: " 零复制"描述了计算机操作,其中CPU不执行将数据从一个存储区复制到另一个存储区的任务.通过网络传输文件时,通常用于节省CPU周期和内存带宽. WIKI的定义中,我 ...
- NIO学习笔记,从Linux IO演化模型到Netty—— Java NIO零拷贝
同样只是大致上的认识. 其中,当使用transferFrom,transferTo的时候用的sendfile(). 如果系统内核不支持 sendfile,进一步执行 transferToTrusted ...
- 感悟优化——Netty对JDK缓冲区的内存池零拷贝改造
NIO中缓冲区是数据传输的基础,JDK通过ByteBuffer实现,Netty框架中并未采用JDK原生的ByteBuffer,而是构造了ByteBuf. ByteBuf对ByteBuffer做了大量的 ...
- NIO学习笔记,从Linux IO演化模型到Netty—— Netty零拷贝
Netty的中零拷贝与上述零拷贝是不一样的,它并不是系统层面上的零拷贝,只是相对于ByteBuf而言的,更多的是偏向于数据操作优化这样的概念. Netty中的零拷贝: 1.CompositeByteB ...
- Netty源码解析 -- 零拷贝机制与ByteBuf
本文来分享Netty中的零拷贝机制以及内存缓冲区ByteBuf的实现. 源码分析基于Netty 4.1.52 Netty中的零拷贝 Netty中零拷贝机制主要有以下几种 1.文件传输类DefaultF ...
- Linux、JDK、Netty中的NIO与零拷贝
一.先理解内核空间与用户空间 Linux 按照特权等级,把进程的运行空间分为内核空间和用户空间,分别对应着下图中, CPU 特权等级分为4个,Linux 使用 Ring 0 和 Ring 3. 内核空 ...
- 深入剖析Linux IO原理和几种零拷贝机制的实现
深入剖析Linux IO原理和几种零拷贝机制的实现 来源 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/83398714 零壹技术栈 公众号[零壹技术栈] 前言 零拷贝(Zero ...
随机推荐
- Failed to execute 'write' on 'Document'动态载入的js不能执行write
统计代码一般都是直接一个标签,插入js,标签放在哪里,统计图表就放在哪里! 我现在是稍微改了一下,我自己加了一点js,在页面所有元素都加载完成之后我再动态的把统计js插入到我需要的地方. 统计代码的s ...
- (转)x264的一些参数设置对编码效率的影响
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/wainiwann/p/5647521.html i_luma_deadzone[0]和i_luma_deadzone[1]分别对应inter和in ...
- 本人SW知识体系导航 - Programming menu
将感悟心得记于此,重启程序员模式. js, py, c++, java, php 融汇之全栈系列 [Full-stack] 快速上手开发 - React [Full-stack] 状态管理技巧 - R ...
- windows 10 更新补丁包
http://www.catalog.update.microsoft.com/Search.aspx?q=windows%2010%20prohttp://www.catalog.update.mi ...
- 自己动手实现RPC
一.需求:用户管理系统(UMS),仓库管理系统(WMS),订单管理系统(OMS) 现在OMS有一张订单表:[订单id,用户id,商品id,订单状态,订单时间],需要在客户端展示此订单对应的用户详情和商 ...
- RuntimeException: Type "nmethodBucket*", referenced in VMStructs::localHotSpotVMStructs in the remot
问题:使用jmap命令查看某个进程的堆情况时(jmap -heap 198376),抛异常如下: Attaching to process ID 198376, please wait...Excep ...
- JavaScript 运行机制详解
一.为什么JavaScript是单线程? JavaScript语言的一大特点就是单线程,也就是说,同一个时间只能做一件事.那么,为什么JavaScript不能有多个线程呢?这样能提高效率啊. Java ...
- ZOJ 4067 - Books - [贪心][2018 ACM-ICPC Asia Qingdao Regional Problem J]
题目链接:http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=4067 题意: 给出 $n$ 本书(编号 $1 \sim n$), ...
- Java图片合并
/** * 纵向合并图片,ossObject.getObjectContent()返回InputStream对象 */ private BufferedImage mergeImage(List< ...
- windos上安装jenkins部署springboot的jar包(未运行,只是在打包并上传linux成功了)
流程: 从linux上的svn拉取代码,到本地(windos)jenkins的工作区间的workspace,然后通过构建,打包,部署到linux上 环境: windos上安装:maven jdk je ...

