基于spark logicplan的表血缘关系解析实现
随着公司平台用户数量与表数量的不断增多,各种表之间的数据流向也变得更加复杂,特别是某个任务中会对源表读取并进行一系列复杂的变换后又生成新的数据表,因此需要一套表血缘关系解析机制能清晰地解析出每个任务所形成的表血缘关系链。
实现思路:
spark对sql的操作会形成一个dataframe,dataframe中的logicplan包含了sql的语法树,通过对logicplan的语法树解析可以获取当前stage所操作的输入表和输出表,将整套表关系链连接起来,再去除中间表即可获取当前作业的输入表和输出表信息。
核心代码:
def resolveLogicPlan(plan: LogicalPlan, currentDB:String): (util.Set[DcTable], util.Set[DcTable]) ={
val inputTables = new util.HashSet[DcTable]()
val outputTables = new util.HashSet[DcTable]()
resolveLogic(plan, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
Tuple2(inputTables, outputTables)
}
def resolveLogic(plan: LogicalPlan, currentDB:String, inputTables:util.Set[DcTable], outputTables:util.Set[DcTable]): Unit ={
plan match {
case plan: Project =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Project]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: Union =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Union]
for(child <- project.children){
resolveLogic(child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
}
case plan: Join =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Join]
resolveLogic(project.left, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
resolveLogic(project.right, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: Aggregate =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Aggregate]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: Filter =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Filter]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: Generate =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Generate]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: RepartitionByExpression =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[RepartitionByExpression]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: SerializeFromObject =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[SerializeFromObject]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: MapPartitions =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[MapPartitions]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: DeserializeToObject =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[DeserializeToObject]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: Repartition =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Repartition]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: Deduplicate =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Deduplicate]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: Window =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Window]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: MapElements =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[MapElements]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: TypedFilter =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[TypedFilter]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: Distinct =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[Distinct]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: SubqueryAlias =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[SubqueryAlias]
val childInputTables = new util.HashSet[DcTable]()
val childOutputTables = new util.HashSet[DcTable]()
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, childInputTables, childOutputTables)
if(childInputTables.size()>){
for(table <- childInputTables) inputTables.add(table)
}else{
inputTables.add(DcTable(currentDB, project.alias))
}
case plan: CatalogRelation =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[CatalogRelation]
val identifier = project.tableMeta.identifier
val dcTable = DcTable(identifier.database.getOrElse(currentDB), identifier.table)
inputTables.add(dcTable)
case plan: UnresolvedRelation =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[UnresolvedRelation]
val dcTable = DcTable(project.tableIdentifier.database.getOrElse(currentDB), project.tableIdentifier.table)
inputTables.add(dcTable)
case plan: InsertIntoTable =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[InsertIntoTable]
resolveLogic(project.table, currentDB, outputTables, inputTables)
resolveLogic(project.query, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: CreateTable =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[CreateTable]
if(project.query.isDefined){
resolveLogic(project.query.get, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
}
val tableIdentifier = project.tableDesc.identifier
val dcTable = DcTable(tableIdentifier.database.getOrElse(currentDB), tableIdentifier.table)
outputTables.add(dcTable)
case plan: GlobalLimit =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[GlobalLimit]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case plan: LocalLimit =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[LocalLimit]
resolveLogic(project.child, currentDB, inputTables, outputTables)
case `plan` => logger.info("******child plan******:\n"+plan)
}
}
上述代码是对logicplan做递归解析的,当logicplan为LocalLimit、GlobalLimit、Window等类型时,继续解析其子类型;当logicplan为CataLogRelation、UnresolvedRelation时,解析出的表名作为输入表;当logicplan为CreateTable、InsertIntoTable时,解析出的表名为输出表。
这里需要考虑一种特殊情况,某些源表是通过spark.read加载得到的,这样logicplan解析出来的类型为LogicRDD,不能直接获取到表名,以下面的python代码为例:
schema = StructType([StructField('id', IntegerType(), True), StructField('name', StringType(), True), StructField('age', IntegerType(), True)])
rdd = sparkSession.sparkContext.textFile('/user/hive/warehouse/bigdata.db/tdl_spark_test/testdata.txt').map(lambda r:r.split(',')).map(lambda p: Row(int(p[]), p[], int(p[])))
df = sparkSession.createDataFrame(rdd, schema)
df.createOrReplaceTempView('tdl_spark_test')
sparkSession.sql('create table tdl_file_test as select * from tdl_spark_test')
上述代码首先通过textFile读取文件得到rdd,再对rdd进行变换,最后将rdd注册成dataframe,这里对df的logicplan进行解析会得到LogicRDD,对于这种情况的解决思路是在调用textFile时记录产生的rdd,解析df的logicplan时获取其rdd,判断之前产生的rdd是否为当前rdd的祖先,如果是,则将之前rdd对应的表名计入。
判断rdd依赖关系的逻辑为:
def checkRddRelationShip(rdd1:RDD[_], rdd2:RDD[_]): Boolean ={
if (rdd1.id == rdd2.id) return true
dfsSearch(rdd1, rdd2.dependencies)
}
def dfsSearch(rdd1:RDD[_], dependencies:Seq[Dependency[_]]): Boolean ={
for(dependency <- dependencies){
if(dependency.rdd.id==rdd1.id) return true
if(dfsSearch(rdd1, dependency.rdd.dependencies)) return true
}
false
}
对LogicRDD的解析为:
case plan: LogicalRDD =>
val project = plan.asInstanceOf[LogicalRDD]
try{
for(rdd <- rddTableMap.keySet()){
if(checkRddRelationShip(rdd, project.rdd)){
val tableName = rddTableMap.get(rdd)
val db = StringUtils.substringBefore(tableName, ".")
val table = StringUtils.substringAfter(tableName, ".")
inputTables.add(DcTable(db, table))
}
}
}catch {
case e:Throwable => logger.error("resolve LogicalRDD error:", e)
}
在spark中会生成dataframe的代码段中通过aspect进行拦截,并且解析dataframe得到表的关系链,此时的关系链是一张有向无环图,图中可能包含中间表,去除掉中间表节点,则得到最终的数据流向图。
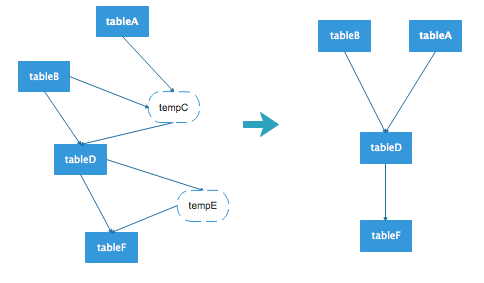
例如上图的左边是一张原始的表数据流向,其中tempC和tempE为临时表,去除这个图中的临时表节点,得到右图的数据流向图。对于前面给出的python代码,执行过后获取的数据流向为:
[bigdata.tdl_spark_test]--->bigdata.tdl_file_test
当然这种解析方式也存在一些缺点,比如首先通过spark.read读取数据注册一张临时表,再将临时表中的某些字段值拉到本地缓存,然后创建一个空的datadrame,将缓存的字段值直接插入到该df中,由于当前创建的df与之前创建的df已经没有依赖关系,因此这种情况将无法解析出准确的数据流向。
基于spark logicplan的表血缘关系解析实现的更多相关文章
- 基于Spark GraphX计算二度关系
关系计算问题描述 二度关系是指用户与用户通过关注者为桥梁发现到的关注者之间的关系.目前微博通过二度关系实现了潜在用户的推荐.用户的一度关系包含了关注.好友两种类型,二度关系则得到关注的关注.关注的好友 ...
- 苏宁基于Spark Streaming的实时日志分析系统实践 Spark Streaming 在数据平台日志解析功能的应用
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/KPTM02-ICt72_7ZdRZIHBA 苏宁基于Spark Streaming的实时日志分析系统实践 原创: AI+落地实践 AI前线 20 ...
- 基于MaxCompute InformationSchema进行血缘关系分析
一.需求场景分析 在实际的数据平台运营管理过程中,数据表的规模往往随着更多业务数据的接入以及数据应用的建设而逐渐增长到非常大的规模,数据管理人员往往希望能够利用元数据的分析来更好地掌握不同数据表的血缘 ...
- 基于Extjs的web表单设计器 第七节——取数公式设计之取数公式的使用
基于Extjs的web表单设计器 基于Extjs的web表单设计器 第一节 基于Extjs的web表单设计器 第二节——表单控件设计 基于Extjs的web表单设计器 第三节——控件拖放 基于Extj ...
- 基于 Spark 的文本情感分析
转载自:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/cognitive/library/cc-1606-spark-seniment-analysis/index.ht ...
- 京东基于Spark的风控系统架构实践和技术细节
京东基于Spark的风控系统架构实践和技术细节 时间 2016-06-02 09:36:32 炼数成金 原文 http://www.dataguru.cn/article-9419-1.html ...
- 血缘关系分析工具SQLFLOW--实践指南
SQLFlow 是用于追溯数据血缘关系的工具,它自诞生以来以帮助成千上万的工程师即用户解决了困扰许久的数据血缘梳理工作. 数据库中视图(View)的数据来自表(Table)或其他视图,视图中字段(Co ...
- Django 一对多,多对多关系解析
[转]Django 一对多,多对多关系解析 Django 的 ORM 有多种关系:一对一,多对一,多对多. 各自定义的方式为 : 一对一: OneToOneField ...
- mybatis整合spring 之 基于接口映射的多对一关系
转载自:http://my.oschina.net/huangcongmin12/blog/83731 mybatis整合spring 之 基于接口映射的多对一关系. 项目用到俩个表,即studen ...
随机推荐
- ModelForm的简单使用-注册用modelform编写
1.前端的ajax代码不用改动 2.modelform,在原来基础上稍作改动 from django import forms from app01.models import UserInfo fr ...
- python链接oracle数据库以及数据库的增删改查实例
初次使用python链接oracle,所以想记录下我遇到的问题,便于向我这样初次尝试的朋友能够快速的配置好环境进入开发环节. 1.首先,python链接oracle数据库需要配置好环境. 我的相关环境 ...
- [学习笔记]约数&欧拉函数
约数 一.概念 约数,又称因数.整数a除以整数b(b≠0) 除得的商正好是整数而没有余数,我们就说a能被b整除,或b能整除a.a称为b的倍数,b称为a的约数. 二.性质 1.整数唯一分解 1)定义 对 ...
- Apache Solr Velocity模板远程代码执行
更多内容,欢迎关注微信公众号:信Yang安全,期待与您相遇. 这里用的docker环境 很简单的 在这里不再介绍 本地搭建好环境然后访问8983端口 网页如下: 查下节点名称 同样名字可以访问http ...
- 执行DTS包将excel导入数据库
利用ssms生成dtsx文件,必须以32bit执行,到路径执行C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server\110\DTS\Binn > dtexec ...
- learning java AWT 剪贴板 传递文本
import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.datatransfer.Clipboard; import java.awt.dat ...
- 2019.11.29 Mysql的数据操作
为名为name的表增加数据(插入所有字段) insert into name values(1,‘张三’,‘男’,20); 为名为name的表增加数据(插入部分字段) insert into name ...
- matlab 万能实用的非线性曲线拟合方法
——转载网络 在科学计算和工程应用中,经常会遇到需要拟合一系列的离散数据,最近找了很多相关的文章方法,在这里进行总结一下其中最完整.几乎能解决所有离散参数非线性拟合的方法 第一步:得到散点数据 根据你 ...
- StringSequences
题意: 给出两个长度不超过\(50\)的字符串\(S, T\),每次可以在\(S\)中插入一个字符,把每次操作后的\(S\)写成一个序列,问有多少种不同的序列. 注意到我们可以把\(S\)拆分成一段一 ...
- 【概率论】5-8:Beta分布(The Beta Distributions)
title: [概率论]5-8:Beta分布(The Beta Distributions) categories: - Mathematic - Probability keywords: - Th ...
